Professional Documents
Culture Documents
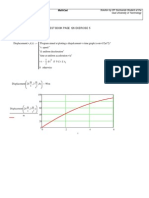
Mathcad - 3D
Uploaded by
Desejo SozinandoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathcad - 3D
Uploaded by
Desejo SozinandoCopyright:
Available Formats
Coefficient of Unit Vectors
3D Vectors
Explanation by DF Sozinando Vaal University of Technology
Coefficient of Unit Vectors (3D vectors)
If the externally applied force is not the direction of one of principal axes, then the components of the force in the x-, y- and z-directions must be calculated. To simplify these calculations an coefficient of unit vectors is introduced.
Any vector
of magnitude
can be written as:
(1)
Respective coefficients of unit vectors in equation (1) are called direction coefficients and determine the inclination/direction of respective vectors. These coefficients can also be calculated using the position vector and spatial coordinates as indicated in equation (2)
(2)
Coefficient of Unit Vectors
3D Vectors
Explanation by DF Sozinando Vaal University of Technology
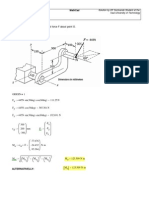
Example: * A force of 7KN is applied at point A in figure and its line of action passes trough point E
Let the Force direction or Cosine of the angle be:
Force_direction =
"axes direction" "distance between points A and E"
Cos =
"adjacent" "hypoteneuse"
Force_direction =
2
x x +y +z
2 2
Force direction at x axes or
cosx =
x x +y +z
2 2 2
Force_direction =
2
y x +y +z
2 2
Force direction at y axes or
cosy =
y x +y +z
2 2 2
Force_direction =
2
z x +y +z
2 2
Force direction at z axes or
cosz =
z x +y +z
2 2 2
Coefficient of Unit Vectors
3D Vectors
Explanation by DF Sozinando Vaal University of Technology
Let the component of Force in each direction be:
"The component of Force in the each direction" = "Force_direction x Applied Force" there for: NB: Respect the sign in each axes direction and the point zero or the reference is where the cartesian plane is placed. Fx = x x +y +z
2 2 2
Fx :=
5 5 +2 +7
2 2 2
7 kN
Fx = 3.963 kN
Fy =
y x +y +z
2 2 2
Fy :=
-2 5 +2 +7
2 2 2
7 kN
Fy = -1.585 kN
Fz =
y x +y +z
2 2 2
Fz :=
-7 5 +2 +7
2 2 2
7 kN
Fz = -5.548 kN
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Mathcad - Extra33Document1 pageMathcad - Extra33Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- Mathcad - ProgrammDocument1 pageMathcad - ProgrammDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra32Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra32Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra43Document1 pageMathcad - Extra43Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Proramming Spot2Document2 pagesMathcad - Proramming Spot2Desejo Sozinando100% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra34Document1 pageMathcad - Extra34Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra37Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra37Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra30Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra30Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- Mathcad - Extra28Document3 pagesMathcad - Extra28Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra44Document1 pageMathcad - Extra44Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra35Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra35Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra41Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra41Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra23Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra23Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra42Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra42Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Test 2Document2 pagesMathcad - Test 2Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra40Document1 pageMathcad - Extra40Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra24Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra24Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines IIIDocument73 pagesHydraulic Machines IIIDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra39Document1 pageMathcad - Extra39Desejo Sozinando100% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra27Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra27Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Beam ProgrammingDocument1 pageMathcad - Beam ProgrammingDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra31Document1 pageMathcad - Extra31Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra26Document1 pageMathcad - Extra26Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Spot Questions1Document5 pagesMathcad - Spot Questions1Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra38Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra38Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra36Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra36Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra25Document1 pageMathcad - Extra25Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Test 1Document3 pagesMathcad - Test 1Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Gyrops 22 08 2016Document7 pagesGyrops 22 08 2016Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra29Document1 pageMathcad - Extra29Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet