Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAP Best Practise of Make-To-Order Production (Schaeffler)
Uploaded by
ASHOKA GOWDAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAP Best Practise of Make-To-Order Production (Schaeffler)
Uploaded by
ASHOKA GOWDACopyright:
Available Formats
SAP Best Practise of Make-to-Order Make to Order Production
Jun. 8th, 2009 | Version 0.2 Shanghai Jiang, Lai (George)
Table of Contents
Concept of Make-to-Order Production Make-to-Order Production Process Overview SAP Best Practise for Make-to-Order Production
Page 2
Concept of Make-to-Order Production
Make-to-Order (MTO) is a production approach where once a confirmed order for products is received, products are built. MTO is the most appropriate approach used for highly customized or low-volume products. products
Market Requireme nt
Stock Level
Correct and Appropriate Balance
Operationa l Stability
Scenario Engineer-to-Order (ETO)
P:D* D>>P
Characteristic The product is designed and built to customer specifications
Typical Usage Large construction projects and one-off products, such as Formula 1 cars High-end motor vehicles and aircraft Dell's approach to customizing its computers The grocery and retail sectors
Make-to-Order (MTO)
D>P
The product is based on a standard design, but component production and manufacture of the final product is linked to the order placed by the final customer's specifications The product is built to customer specifications from a stock of existing components. This assumes a modular product architecture that allows for the final product to be configured in this way The product is built against a sales forecast, and sold to the customer from finished goods stock
Assemble-to-Order Assemble to Order (ATO)
D<P
Make-to-Stock (MTS)
D=0
* P is defined as the production lead-time, i.e. how long it takes to manufacture a product, and D is the demand lead-time, i.e. how long customers are willing to wait for the order to be completed
Page 3
Make-to-Order Production Process Overview
Vendor
Purchase Requisition
Production Plant
Material Requirements Planning
Customer
Inquiry (optional)
Purchase Order Execution
Goods Receipt for Purchase Order
Create Production Order
Quotation (Optional)
Invoice
Goods Issue to Production Order
Release and Print Production Order
Sales Order Processing
Goods Receipt from Production Order
Confirm Production Order w/ or w/o Backflush
Delivery
Month-end Closing
Picking and Packing
Goods Issue against Delivery
Invoice
Page 4
SAP Best Practise for Make-to-Order Production
Market Requireme nt
Stock Level
Correct and Appropriate Balance
Operational Stability
Aggregation Aggregationbased Demand Planning on Product Level
Planning with Planning Material
Proactive P ti Demand Management
Pre-procurement of the Long Lead-time Common Parts
Component Supppy with Pull + KANBAN + JIT
Page 5
Thanks for your attention!
Page 6
You might also like
- Lorhan-Texpro Solution - V3.0Document41 pagesLorhan-Texpro Solution - V3.0sihalim17100% (1)
- E-To-Order (MTO) / Purchase-To-Order (PTO)Document4 pagesE-To-Order (MTO) / Purchase-To-Order (PTO)mjNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Consultant ProfileDocument3 pagesSAP MM Consultant ProfileBILLVARAJ GNo ratings yet
- Implementing Release Strategy in SAPDocument8 pagesImplementing Release Strategy in SAPDinesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 7.1.1 MM-J1ID-Excise Master DataDocument19 pages7.1.1 MM-J1ID-Excise Master DataPriyanka BarotNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Sap Overview PP PC IntegrationDocument84 pagesFdocuments - in Sap Overview PP PC IntegrationHimanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Sap Is Retail Sample Resume 2Document4 pagesSap Is Retail Sample Resume 2Deepak Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- 04 - Materials Management - Enterprise StructureDocument57 pages04 - Materials Management - Enterprise StructureLaura Sofia Mendoza PovedaNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Agreement Release DocuDocument3 pagesScheduling Agreement Release Docupandu MNo ratings yet
- INTERVIEWDocument8 pagesINTERVIEWSireesha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Material MasterDocument17 pagesMaterial Mastermic29100% (3)
- ERP - Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument38 pagesERP - Enterprise Resource Planningnehank17100% (2)
- Anubandh - SAP MM - 4.6 Yrs of ExperienceDocument5 pagesAnubandh - SAP MM - 4.6 Yrs of ExperienceMallu LoharNo ratings yet
- Procure To Pay Process Scenarios in SAPDocument92 pagesProcure To Pay Process Scenarios in SAPSyed AquibNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Consultant Role for Pune LocationDocument3 pagesSAP SD Consultant Role for Pune Locationpritam0993No ratings yet
- Sap MM Organization StructureDocument4 pagesSap MM Organization Structuredudhmogre23No ratings yet
- AID OTC Sale Order Processing 1Document25 pagesAID OTC Sale Order Processing 1SUBHOJIT BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Creation of Plant in SAPDocument31 pagesCreation of Plant in SAPnagibvbNo ratings yet
- Sap MM - Quick Guide Sap MM - OverviewDocument140 pagesSap MM - Quick Guide Sap MM - Overviewcvalent100% (1)
- Purchase Orders Search Master in SAP MMDocument30 pagesPurchase Orders Search Master in SAP MMJosé RoblesNo ratings yet
- Optimize SAP Vendor Master ProcessDocument69 pagesOptimize SAP Vendor Master ProcessPRATEEKNo ratings yet
- SBWP Release Purchase Requisition via WorkflowDocument12 pagesSBWP Release Purchase Requisition via WorkflowAnupam Samanta100% (1)
- Edi Orders TemplateDocument19 pagesEdi Orders TemplatesimplepunjabiNo ratings yet
- 18 Source DeterminationDocument18 pages18 Source DeterminationlymacsauokNo ratings yet
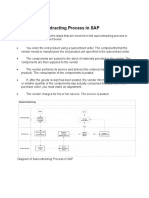
- Steps of Subcontracting Process in SAPDocument1 pageSteps of Subcontracting Process in SAPgyanaranjan_3No ratings yet
- KPMG Sample QuestionDocument1 pageKPMG Sample QuestionambroselinNo ratings yet
- MM PM 300 v3 PDFDocument123 pagesMM PM 300 v3 PDFsajjadNo ratings yet
- Material Type ConfigurationDocument24 pagesMaterial Type ConfigurationShailendra TiwariNo ratings yet
- SAP S4HANA DTS Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesSAP S4HANA DTS Practice QuestionsCédric SinclairNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Module for Material ManagementDocument15 pagesSAP MM Module for Material Managementraman_bhoomi2761No ratings yet
- SD OverviewDocument85 pagesSD OverviewSamatha GantaNo ratings yet
- Material Determination in SAPDocument13 pagesMaterial Determination in SAPJosé RoblesNo ratings yet
- The Integration Between FI, SD, MM, and SF: Prepared By: Mona IbrahimDocument6 pagesThe Integration Between FI, SD, MM, and SF: Prepared By: Mona IbrahimSUBHOJIT BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Functional Specification (Workflow)Document3 pagesFunctional Specification (Workflow)Prashant KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Batch Specific UoM and Active Ingredient ManagementDocument2 pages1 Batch Specific UoM and Active Ingredient ManagementpoojaNo ratings yet
- Concept of SAPDocument22 pagesConcept of SAPramesh B100% (1)
- Common Errors and Solutions in Sap MMDocument5 pagesCommon Errors and Solutions in Sap MMDISHIMUKH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Organisation StructureDocument22 pagesOrganisation StructureSubbu SuniNo ratings yet
- 4+ Years SAP MM / WM ConsultantDocument4 pages4+ Years SAP MM / WM ConsultantSurya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Customer Master DataDocument24 pagesCustomer Master DataAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- S4680 - EN - Col17 Cross-Application Processes in SAP S4HANA Sales and ProcurementDocument190 pagesS4680 - EN - Col17 Cross-Application Processes in SAP S4HANA Sales and ProcurementGerardo Sebastián Lavella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Tata SteelDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Tata SteelRishabh SethiNo ratings yet
- 006 Sales Order ProcessDocument119 pages006 Sales Order ProcessSalih SahinNo ratings yet
- Combined Production Order ProcessingDocument12 pagesCombined Production Order Processingsaps4hana ppNo ratings yet
- Using Two Planning Strategies For The Same MaterialDocument10 pagesUsing Two Planning Strategies For The Same MaterialVigneshNo ratings yet
- Pricing in SAP ECO PDFDocument11 pagesPricing in SAP ECO PDFbobNo ratings yet
- MM - Material - Master - User ManualDocument21 pagesMM - Material - Master - User ManualajayNo ratings yet
- BRF+ in SAP S4 HANADocument22 pagesBRF+ in SAP S4 HANAdamar100% (1)
- Define Product Hierarchies (SAP Library - Material Master)Document4 pagesDefine Product Hierarchies (SAP Library - Material Master)varunnuraNo ratings yet
- TDS Config in SAPDocument31 pagesTDS Config in SAPvaishaliak2008No ratings yet
- Primus - Abap FactoryDocument2 pagesPrimus - Abap FactorySambhajiNo ratings yet
- Intra Company Sto: Sap MMDocument5 pagesIntra Company Sto: Sap MMManoj reddyNo ratings yet
- Movilizer SAP DSD enDocument7 pagesMovilizer SAP DSD enParag PandyaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Sap SD ModuleDocument20 pagesBasics of Sap SD ModuleSourav DarukaNo ratings yet
- 12.RFQ Process in SAP S4 HANADocument16 pages12.RFQ Process in SAP S4 HANAAbhijeetLaturkarNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Procurement Allocation Table: SAP AG 2005Document19 pagesSeasonal Procurement Allocation Table: SAP AG 2005Pallavi RastogiNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire For ClientDocument7 pagesQuestionnaire For ClientAnonymous hjPz1PYlrNo ratings yet
- LSMW Data Migration MethodsDocument8 pagesLSMW Data Migration Methodssouvik karmakarNo ratings yet
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesFrom EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet SAP Uat Scheduel Script Sap Ecc 6.0v For MGDocument14 pagesWorksheet SAP Uat Scheduel Script Sap Ecc 6.0v For MGASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 3Document17 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 3ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 3Document17 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 3ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 3Document17 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 3ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- Sap Fico User Manual: Published by Team of SAP Consultants at SaptopjobsDocument6 pagesSap Fico User Manual: Published by Team of SAP Consultants at SaptopjobsASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 2Document4 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 2ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 3Document17 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 3ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 3Document17 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 3ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 1Document5 pagesSAP FSCM Sample Resume 1ASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- Fund - CreateDocument5 pagesFund - CreateASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- Case Study: AgendaDocument12 pagesCase Study: AgendaASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- BTE (How To)Document16 pagesBTE (How To)emc_cefre1735No ratings yet
- RentDocument56 pagesRentASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet
- ErpDocument40 pagesErpbhuppy007No ratings yet
- Different Testing in SapDocument3 pagesDifferent Testing in SapIshan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Complete Fico ManualDocument374 pagesComplete Fico ManualJigar Shah96% (23)
- Cash JournalDocument7 pagesCash JournalASHOKA GOWDANo ratings yet