Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan Nephritis
Uploaded by
deric82%(17)82% found this document useful (17 votes)
16K views2 pagesA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Nephritis.
Original Title
NursingCrib.com Nursing Care Plan Nephritis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Nephritis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
82%(17)82% found this document useful (17 votes)
16K views2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephritis
Uploaded by
dericA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Nephritis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
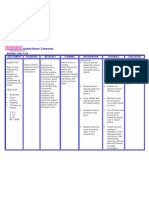
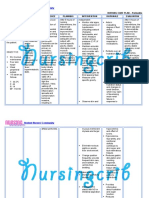
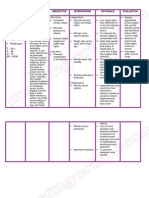
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBEJECTIVE INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM
Subjective: • Nephritis refers to Short term: Independent: • Display
inflammation of one • Increased • Record accurate • Low output (less appropriate
“Namamanas or both kidneys. It urinary output. intake and output than 400ml/24 hr) urinary output
ang binti ko” as can be caused by (I&O). is the first indicator with normal
infection, but is
verbalized by the • Minimize of acute renal specific gravity
most commonly
patient. presence of failure. and laboratory
caused by
autoimmune edema. • Monitor urine • To measure the status within
Objective: disorders that affect specific gravity. kidney’s ability to normal range.
• Oliguria. the major organs. • Achieve stable concentrate urine. • Absence of
For example, those weight and • Weigh daily at the • Daily body weight edema and
• Weight gain. with lupus are at a stable vital same time of the is best monitor of body weight
much higher risk for signs. day. fluid status. A returns to
T : 36.4 developing weight gain of normal.
P : 98 nephritis. In rare Long term: more than 0.5kg/ • Vital signs
cases nephritis can
R : 18
be genetically
• Prevents day suggest fluid within normal
BP: 130/80 complication retention. range.
inherited, though it
may not present in of the disease. • Monitor heart rate • Tachycardia and
childhood. As the and Bp. hypertension can
kidneys inflame, occur because of
they begin to failure of the
excrete needed kidney to excrete
protein from the urine.
body into the urine • Elevate edematous • To promote
stream. Nephritis body part. venous return.
also causes
additional problems
like water retention, Collaborative:
as the kidneys • Monitor serum • Hyponatremia may
cannot function sodium. result from fluid
properly to rid the overload or
body of water. kidney’s inability to
Water retention or conserve sodium.
edema, can further Hypernatremia
cause swelling of indicates total
the feet, ankles, body water
legs, and hands.
deficits.
• Monitor serum • Lack of renal
potassium. excretion and
selective retention
of potassium to
excrete excess
hydrogen ions lead
to hyperkalemia
requiring prompt
treatment.
• Administer diuretics. • To promote
adequate urine
volume.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Pedia TB MeningitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pedia TB Meningitisderic100% (10)
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis ADocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis APravesh Verma100% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageHyperthyroidism N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKatrene Lequigan100% (1)
- After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient was able to demonstrate behaviors and lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors and protect self from injuryDocument2 pagesAfter 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient was able to demonstrate behaviors and lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors and protect self from injuryTeresa JunioNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesAcute PancreatitisAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- NCP For CHDDocument2 pagesNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Monitor patient for signs of increased intracranial pressureDocument3 pagesMonitor patient for signs of increased intracranial pressurestar7707100% (1)
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- NCP Measles Case PresDocument1 pageNCP Measles Case PresFranz RolfNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCP 2013 ObDocument1 pageNCP 2013 ObSonny Dizon Pareñas100% (2)
- Anemia N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageAnemia N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEli Xma100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan DM Type 2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan DM Type 2Jay V. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaPuteri AzmanNo ratings yet
- Case Plan On Diarrhoea (Medical Surgical Nursing)Document15 pagesCase Plan On Diarrhoea (Medical Surgical Nursing)kamini ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP Arra AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP Arra AnemiaShin GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Cva NCP AnxietyDocument1 pageCva NCP AnxietyQueenElsaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusMarlon AnryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJamie Haravata0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument4 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP of Renal CalculiDocument3 pagesNCP of Renal Calculidextroid1289% (9)
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- 5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for HypertensionDocument7 pages5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for Hypertensionmelerine16No ratings yet
- Student Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageHydrocephalus N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP For MGDocument1 pageNCP For MGSandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM) 2Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus (DM) 2Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Nephrotic Syndromederic80% (45)
- Nursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeJames Pachejo100% (1)
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocument12 pagesMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- The Most Commonly Ordered (Chemistry) Laboratory InvestigationsDocument94 pagesThe Most Commonly Ordered (Chemistry) Laboratory InvestigationsZEESHAN YOUSUFNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToJen BallesterosNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Liver Cirrhosisderic100% (27)
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument11 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalancesDemiar Madlansacay QuintoNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument36 pagesFluids and Electrolytespuleng matshabaNo ratings yet
- Excretory System Bio 20 ApDocument39 pagesExcretory System Bio 20 Apapi-649067754No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nephritis SeminarDocument27 pagesNephritis Seminaryeon kookminNo ratings yet
- IVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts 2Document3,980 pagesIVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts 2Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Nephritis: Alport Syndrome, or Hereditary NephritisDocument3 pagesNephritis: Alport Syndrome, or Hereditary NephritisSuneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The KidneysDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The KidneysSanthu SuNo ratings yet
- Nephritis by Triveni SidhaDocument23 pagesNephritis by Triveni SidhaTriveni SidhaNo ratings yet
- Interstitial Nephritis: Inflammation of the Renal InterstitiumDocument2 pagesInterstitial Nephritis: Inflammation of the Renal InterstitiumYosi Dwi Saputro Part IINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- Understanding Lupus NephritisDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Lupus Nephritissaritha Oruganti100% (1)