Professional Documents
Culture Documents
H Bifasica (Tema 5)
Uploaded by
Bettina HerreraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
H Bifasica (Tema 5)
Uploaded by
Bettina HerreraCopyright:
Available Formats
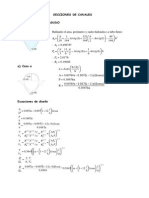
UNIVERSIDAD DE CARABOBO FACULTAD DE INGENIERA ESCUELA DE INGENIERA QUMICA CTEDRA DE FENMENOS DE TRANSPORTE II Prof: Jon Ander Aguinaco *Material
tomado de resumen hecho por el prof.: Juan Bruce ESTIMACIN DE COEFICIENTES PARA CONVECCIN BIFSICA Condensacin. Por gotas.
o o Si 22 C <T SAT <100 C kW h 2 =51,104+2,044T SAT m K Si T SAT >100 C
o Placa inclinada Dhir y Lienhard (1971) Mostraron que el modelo
mejorado por Roheson se puede usar para placas inclinadas si g se reemplaza por gcos , donde es el ngulo respecto a la vertical.
4 h PI =h PV cos
o Dentro o fuera de un cilindro vertical Se puede usar el modelo mejorado de Rohsenon R o Cilindro horizontal Re D 3600 Dhir y Lienhard (1971) h=0,729
h
De pelcula.
kW =255,51 2 m K
o Esfera Popiel y Boguslawski (1975) h=0,815 g f f g k 3f h fg 0,68 Cp f T SAT T w
Rgimen laminar (Re<1800) o Placa vertical Nusselt (1916)
Do f T SAT T w o Interna en tubos horizontales Re vapor 35000 Chato(1962) 3 g f ( f g ) k h fg + Cp f ( T SAT T w ) 8 h=0,555 Di f ( T SAT T w )
3 f
[ [
g f ( f g ) k 3f ( h fg+0,68 C pf ( T SAT T w ) ) D0 f ( T SAT T w )
] ]
1 4
1 4
1 4
( x) =
4 k f f ( T SAT T w ) x g f ( f g) h f g
1 4
3 g f ( f g ) k 3f h fg + Cp f (T SAT T w ) k 8 h ( x) = L ( x ) 4 f (T SAT Tw) x
]
1 4
1 4
1 h= h( x ) dx L0 3 g f ( f g ) k 3f h fg + C p f (T SAT Tw) 8 h=0,943 L f ( T SAT T w )
Rgimen turbulento (Re D >1800) Colburn (1933) 1 g 2 3 0,52 f h=0,056 Re k f Pr f 2f
( )
(
Re=
4m b f
placas: ancho de la placa b : cilindros: vertical:b=L horizontal: b= Do esferas: b = dimetro
Rohsenon (1956) Recomend sustituir
3 por 0,68 8
Columna de tubos horizontales Chen (1961)
Pr>0,5
Y se cumple cuando:
C pf (T SAT Tw)<1 h fg
Cp f h T SAT T w N t 1 hor 1 h fg N t4 Cp f ( T SAT T w ] si se cumple que: ( N t 1 )>2 h fg = 10,02 h
o Banco de tubos de un equipo de tubo y coraza Tubos verticales (condensacin externa) h=1,47
NtD 0 fg 4 mcond v 2f
1 3
kf
Tubos horizontales
h=1,5 k f
h=1,5 k f
[ [
g LN f 4 mcond 2f g LN f 8 mcond 2f
2 3 t
2 3 t
] ]
1 3
(condensacin externa)
1 3
(condensacin interna) K 1= f g f g Acalentador
Ebullicin. De estanque Nuclear Rohsenon (1952)
g [ f g Cp f T w T SAT Q = f h fg n A f C sf h fg Pr f
Punto de Leidenfrost (Zber, Berenson)
f g ( f g ) Q MN =0,09 h fg g 2 A ( f + g)
Pelicular o Cilindro horizontal Bromley (1950)
1 4
h=0,62
g g ( f g ) k 3 ( h fg +0,8 Cp g ( T w T SAT ) ) g D 0 g ( T w T SAT )
1 4
o Esfera Lienhard y Dhir (1973) h=0,67
(1962)
g g ( f g ) k 3 ( h fg +0,8 Cp g ( T w T SAT ) ) g D0 g ( T w T SAT )
1 4
o Placa horizontal o tubos de gran dimetro Westwater y Breen n : 1 : agua 1,7 : otros fluidos
Punto de quemado Kutateladze (1948)
h= 0,590,69 D
g g f g k 3 h fg 0,68 Cp g T w T SAT g g T w T SAT =2
1 4
Q MAX f g f g f g =C cr h fg g A f 2 g
1 4
o Si los efectos radiantes son significativos 4 4 1 T 4 T 4 SAT 3 3 3 h rad = w h comb=h conv +h rad hcomb T w T SAT
f g ( f g )
You might also like
- ExamenDocument15 pagesExamen3cesNo ratings yet
- Correlaciones y Tablas - TCDocument24 pagesCorrelaciones y Tablas - TCSonia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Condensador HorizontalDocument15 pagesCondensador HorizontaleselcosacNo ratings yet
- Vaciado de Tanque EsfericoDocument11 pagesVaciado de Tanque EsfericoSara CristinaNo ratings yet
- Capa Límite PDFDocument12 pagesCapa Límite PDFJulio ChavarriNo ratings yet
- Grupos adimensionales y correlaciones de convecciónDocument20 pagesGrupos adimensionales y correlaciones de convecciónviolet HumeNo ratings yet
- Tiempo de vaciado de tanque con orificio de 75mmDocument3 pagesTiempo de vaciado de tanque con orificio de 75mmMoyse Alejandro Vigil100% (1)
- Algoritmo de Diseño de Intercambiadores de Calor de Carcasa y TubosDocument15 pagesAlgoritmo de Diseño de Intercambiadores de Calor de Carcasa y TubosFlyxs0% (1)
- Informe MetalicasDocument19 pagesInforme MetalicasjhasmanyNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 WuilberDocument6 pagesTarea 1 Wuilberwuilber joseNo ratings yet
- Solucion Parcial 1Document2 pagesSolucion Parcial 1Johny Quintero SabogalNo ratings yet
- Transferencia de calor por convección en superficies extendidasDocument29 pagesTransferencia de calor por convección en superficies extendidasSantiagoGonzálezNo ratings yet
- VISCOSIDAD DE LÍQUIDOS Y FLUIDOSDocument40 pagesVISCOSIDAD DE LÍQUIDOS Y FLUIDOSCa SoPreNo ratings yet
- Diseño Del Intercambiador de Calor Tubo CorazaDocument30 pagesDiseño Del Intercambiador de Calor Tubo CorazaOrlando Poma100% (1)
- Cálculo coeficiente fricción placa laminar turbulentaDocument7 pagesCálculo coeficiente fricción placa laminar turbulentapedroantoni22No ratings yet
- Proyecto 1 MI-3Document5 pagesProyecto 1 MI-3Kevin RoqueNo ratings yet
- Transferencia de calor por conducción y convecciónDocument12 pagesTransferencia de calor por conducción y convecciónMaca Abdenur AraosNo ratings yet
- Cap VIR2Document13 pagesCap VIR2Adri Moral RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de Tuberías en SerieDocument8 pagesSistemas de Tuberías en SerieBRANNY RONALDO RODRIGUEZ AGUILARNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Una MarmitaDocument8 pagesDiseño de Una MarmitaChristian Andrew Aguilar MamaniNo ratings yet
- Coeficientes de transferencia de calorDocument8 pagesCoeficientes de transferencia de calorLuis PerezNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Ivanova TapiaDocument83 pagesTrabajo Ivanova TapiaIvanova TapiaNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Descarga TDocument19 pagesProyecto Descarga TGominola3010 GominolaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios TermodinamicaDocument63 pagesEjercicios TermodinamicaCarlos LevanoNo ratings yet
- Sistemas dinámicos de orden superiorDocument27 pagesSistemas dinámicos de orden superiormkrzoNo ratings yet
- Estática de Fluidos Ej ResueltosDocument26 pagesEstática de Fluidos Ej ResueltosJavier88% (16)
- Cuánto Tiempo Tarda El Agua en Salir Por El Agujero en El Fondo Del TanqueDocument8 pagesCuánto Tiempo Tarda El Agua en Salir Por El Agujero en El Fondo Del TanqueSebas VargasNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio #20Document5 pagesEjercicio #20Walter VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas Perdidas de CargaDocument3 pagesFórmulas Perdidas de CargarungekutasaNo ratings yet
- Problema Resueltos Primer ParcialDocument14 pagesProblema Resueltos Primer ParcialVictor Gimenez100% (2)
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales 2Document4 pagesEcuaciones Diferenciales 2santiago castelblancoNo ratings yet
- Modelo Matemático para Un Evaporador de Placa PlanaDocument6 pagesModelo Matemático para Un Evaporador de Placa PlanaSergio Andres Peña ParralesNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 Valvula Globo y CompuertaxlsxDocument27 pagesEjercicio 1 Valvula Globo y CompuertaxlsxKendy SahibNo ratings yet
- Ingenieria AntisismicaDocument20 pagesIngenieria AntisismicaEsteban Jose Goodman JustoNo ratings yet
- Infor 2calorDocument55 pagesInfor 2calorcbaracatt1No ratings yet
- Fisica 4Document11 pagesFisica 4Ronald vidalesNo ratings yet
- Actividad 8.1Document10 pagesActividad 8.1BernardoNo ratings yet
- Practica #5. FriccionDocument22 pagesPractica #5. FriccionALVARADO GATICA JOSÉ CARLOSNo ratings yet
- Calculo de Cimentaciones en Redes Secundarias en Baja TensionDocument1 pageCalculo de Cimentaciones en Redes Secundarias en Baja TensionJohny Lamas VenturaNo ratings yet
- Curso de Diseño y Construcción de Tanques de Acero - API 650Document43 pagesCurso de Diseño y Construcción de Tanques de Acero - API 650Brajhan ChorresNo ratings yet
- Deber 4Document21 pagesDeber 4Jilson SandovalNo ratings yet
- Sistemas dinámicos de primer orden: procesos térmicos y de fluidosDocument20 pagesSistemas dinámicos de primer orden: procesos térmicos y de fluidosFelipe MonteroNo ratings yet
- Formulario MejoradoDocument56 pagesFormulario MejoradoGus Zalles ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Secciones Finalisimo Imprimir Del Ultimo Dela AntepenultimoDocument67 pagesTrabajo de Secciones Finalisimo Imprimir Del Ultimo Dela AntepenultimoRuler Altamirano AtaoNo ratings yet
- Vaciado de Tanques PDFDocument33 pagesVaciado de Tanques PDFavatarlan0% (1)
- Proyecto 1 HidráulicaDocument15 pagesProyecto 1 HidráulicaLiz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Capitulo 4 CorripioDocument35 pagesEjercicios Capitulo 4 CorripioMark Antony100% (2)
- Ejemplo 13 - 1 FoglerDocument10 pagesEjemplo 13 - 1 FoglerPauu CalderonNo ratings yet
- Tanques de Almacenamiento Ejemplo de CalculoDocument15 pagesTanques de Almacenamiento Ejemplo de CalculoJosueValderramaNo ratings yet
- Ingeniería química. Soluciones a los problemas del tomo IFrom EverandIngeniería química. Soluciones a los problemas del tomo INo ratings yet
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesFrom EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Modelado fenomenológico del proceso de combustión por difusión diéselFrom EverandModelado fenomenológico del proceso de combustión por difusión diéselNo ratings yet
- Guía de cálculo y diseño de conductos para ventilación y climatizaciónFrom EverandGuía de cálculo y diseño de conductos para ventilación y climatizaciónRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesFrom EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesNo ratings yet
- 100 MontaditosDocument3 pages100 MontaditosjosemanuelNo ratings yet
- Valvula Ahorro de AguaDocument17 pagesValvula Ahorro de AguaSergio Fabian Bayona ReyNo ratings yet
- 11 0906 07 277395 1 1 - DB - 20111030180116Document57 pages11 0906 07 277395 1 1 - DB - 20111030180116Will J CGNo ratings yet
- Ensayo Hardware y SoftwareDocument3 pagesEnsayo Hardware y SoftwareBrench de la ParraNo ratings yet
- Manometros Compuertas CapquiqueDocument25 pagesManometros Compuertas CapquiqueAle MachacaNo ratings yet
- Laboratorios Fisica 1 2020 PDFDocument47 pagesLaboratorios Fisica 1 2020 PDFMauricio AcostaNo ratings yet
- Anexo 2Document3 pagesAnexo 2luisNo ratings yet
- Memoria Descriptiva (Caminos I)Document20 pagesMemoria Descriptiva (Caminos I)Andy Greey Mera VásquezNo ratings yet
- Funciones del dinero: medio de pago, unidad de cuenta y depósito de valorDocument1 pageFunciones del dinero: medio de pago, unidad de cuenta y depósito de valorCARLOS XAVIEL PEREZ PUJOLSNo ratings yet
- Instrucciones Nivel Optico Leica Serie Na700Document36 pagesInstrucciones Nivel Optico Leica Serie Na700Jose Rodriguez RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario 17Document4 pagesCuestionario 174722 - HANNAH SIOMARA GALVAN CÁRDENASNo ratings yet
- Transesterificación ExpoDocument20 pagesTransesterificación ExpoJesus Santiago AlejandroNo ratings yet
- MODULO 2 Evaluadores de ClínicasDocument37 pagesMODULO 2 Evaluadores de ClínicasDANIELGAXIOLAQNo ratings yet
- Regimen DisciplinarioDocument11 pagesRegimen DisciplinarioNaomi Kiara Lazo CampanaNo ratings yet
- A. C. N°06 Autorización Registros de FirmasDocument2 pagesA. C. N°06 Autorización Registros de Firmasjoly villena quispeNo ratings yet
- Taller MineriaDocument17 pagesTaller MineriaEmily Anchicoque Riera100% (1)
- Red estrella extendidaDocument3 pagesRed estrella extendidaAbraham Reyes0% (1)
- Desarrollo Sustentable - Unidad 3Document5 pagesDesarrollo Sustentable - Unidad 3Angel RuedaNo ratings yet
- Mapama PDFDocument4 pagesMapama PDFmagyNo ratings yet
- Logística: Conceptos básicos, funciones y objetivosDocument66 pagesLogística: Conceptos básicos, funciones y objetivosShirley Maguiña anduhagaNo ratings yet
- Monografia BBLDocument2 pagesMonografia BBLEDUARDO ELISEO FLORES ESPINOZANo ratings yet
- Cadena de Suministros IGE 2009Document10 pagesCadena de Suministros IGE 2009Antonio Mendoza RamirezNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Matematica FinancieraDocument10 pagesTaller 1 Matematica FinancieraWadith Antonio Rojas Cruz100% (3)
- Atencion Telefonica 03:19Document140 pagesAtencion Telefonica 03:19Dani WhiteNo ratings yet
- Ley 28793-mDocument3 pagesLey 28793-mEstefani Reyes MamaniNo ratings yet
- Celdas SM6 ScheneiderDocument26 pagesCeldas SM6 ScheneiderChristianEnrique17No ratings yet
- DiapositivasDocument9 pagesDiapositivasChimmy AdribNo ratings yet
- Derechos y Obligaciones Contractuales Del SeguroDocument7 pagesDerechos y Obligaciones Contractuales Del SeguroRomina MarcilloNo ratings yet
- Taller - Parcial Corte 2 - 2021Document3 pagesTaller - Parcial Corte 2 - 2021Daniel MontiillaNo ratings yet
- Elaboración de Galletas Enriquecidas Con SoyaDocument11 pagesElaboración de Galletas Enriquecidas Con SoyaYersy BravoNo ratings yet