Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Tutorial
Uploaded by
luqmansulyman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesA semiconductor diode is a two-terminal device. The application of a voltage across its terminals leaves three possibilities: no bias (V = 0 V), forward bias (VD > 0 V) and reverse bias (V > 0 v) silicon versus Germanium RESISTANCE LEVELS: DC or Static Resistance AC or Dynamic Resistance: Average AC Resistance: e = emmsion coefficient or ideality factor 1= e = 2.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA semiconductor diode is a two-terminal device. The application of a voltage across its terminals leaves three possibilities: no bias (V = 0 V), forward bias (VD > 0 V) and reverse bias (V > 0 v) silicon versus Germanium RESISTANCE LEVELS: DC or Static Resistance AC or Dynamic Resistance: Average AC Resistance: e = emmsion coefficient or ideality factor 1= e = 2.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesChapter 1 Tutorial
Uploaded by
luqmansulymanA semiconductor diode is a two-terminal device. The application of a voltage across its terminals leaves three possibilities: no bias (V = 0 V), forward bias (VD > 0 V) and reverse bias (V > 0 v) silicon versus Germanium RESISTANCE LEVELS: DC or Static Resistance AC or Dynamic Resistance: Average AC Resistance: e = emmsion coefficient or ideality factor 1= e = 2.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
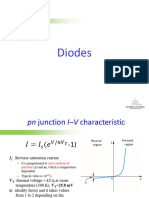
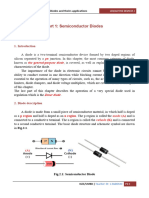
SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE SUMMARY Since the diode is a two-terminal device, the application of a voltage across its terminals leaves
three possibilities: no bias (VD = 0 V), forward bias (VD 0 V), and reverse bias (VD 0 V).
It can be demonstrated through the use of solid-state physics that the general characteristics of a semiconductor diode can be defined by the following equation for the forward- and reversebias regions:
= emmsion coefficient or ideality factor 1 2
Silicon versus Germanium
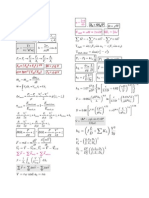
RESISTANCE LEVELS:
DC or Static Resistance
AC or Dynamic Resistance:
Average AC Resistance:
ZENER DIODES:
You might also like
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics LabDocument60 pagesBasic Electronics Labrahulsingle67% (3)
- Electron DeviceDocument112 pagesElectron DevicekrishnaNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 01 Characteristics of PN Junction Diode AimDocument4 pagesExperiment: 01 Characteristics of PN Junction Diode Aimaty27062004No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document23 pagesBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode-2Document45 pagesPN Junction Diode-2RAUNAK GARGNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 (Semiconductor Diodes) ReviseDocument30 pagesChapter1 (Semiconductor Diodes) Revisejohn456royNo ratings yet
- ECE 027 - Diode Resistance Levels and Equivalent CircuitsDocument80 pagesECE 027 - Diode Resistance Levels and Equivalent CircuitsMiyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodeDocument74 pagesSemiconductor DiodeOnie EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2Nasimul HasanNo ratings yet
- عملي دوائر اليوم2Document24 pagesعملي دوائر اليوم2معاً إلى الجنةNo ratings yet
- Exam RevisionDocument61 pagesExam RevisionRachul heenimNo ratings yet
- Ee6351 Basics of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument128 pagesEe6351 Basics of Electrical and Electronics Engineeringvishaalsi692004No ratings yet
- L4 - Diode 1Document29 pagesL4 - Diode 1amonNo ratings yet
- Lab Task Exp-1,2,3Document9 pagesLab Task Exp-1,2,3Ashish patelNo ratings yet
- Edc - 2 Marks With AnswerDocument0 pagesEdc - 2 Marks With AnswerJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- ED - Mid Lecture-2Document26 pagesED - Mid Lecture-2ahmedtanvir11387No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document8 pagesExperiment 1Qusai BakerNo ratings yet
- 2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01Document66 pages2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01peter brownNo ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument33 pagesDiode Applicationspransdom10No ratings yet
- AE EEE2039 Lecture4-DiodesDocument30 pagesAE EEE2039 Lecture4-DiodesArvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Document18 pagesBASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Mr SpamNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Diode Guide (Esaki DiodeDocument20 pagesTunnel Diode Guide (Esaki DiodeRAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document34 pagesModule 1deepakNo ratings yet
- Electronics Chapter 3Document34 pagesElectronics Chapter 3venkeekuNo ratings yet
- Diode Test and FamiliarizationDocument4 pagesDiode Test and Familiarizationcent carinoNo ratings yet
- Part I: Diode Characteristics ObjectiveDocument11 pagesPart I: Diode Characteristics ObjectivePhilip Arpia0% (1)
- EDCDocument51 pagesEDCprabhasvinnyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: TheoryDocument13 pagesExperiment No. 1: Aim: TheoryAyushiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - ELEC311 CH 2 Ch1 of Course PackDocument29 pagesWeek 2 - ELEC311 CH 2 Ch1 of Course PackDavid Mitry ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Diode Applications Part121Document34 pagesChapter2 Diode Applications Part121Joel PravinNo ratings yet
- Experiment-No 2Document5 pagesExperiment-No 2carloNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 - DiodesDocument7 pagesLab 11 - DiodesJuliánDavidMesaCárdenasNo ratings yet
- ECE111 - Analog Electronics: Sandeep Saini Gaurav ChatterjeeDocument27 pagesECE111 - Analog Electronics: Sandeep Saini Gaurav ChatterjeeAAYUSH SHUKLANo ratings yet
- ClaireDocument15 pagesClaireClaireNo ratings yet
- Intro To EE IITDDocument60 pagesIntro To EE IITDKush KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes-Mock ExamDocument8 pagesPractical Notes-Mock ExamannalisaNo ratings yet
- EE Lab Mannual EDCDocument10 pagesEE Lab Mannual EDCAzmat AmeenNo ratings yet
- JJJJJDocument148 pagesJJJJJTanXiNingNo ratings yet
- ED - Mid Lecture-2Document26 pagesED - Mid Lecture-2Anemesh BaruaNo ratings yet
- EEE206 Device Lab ManualDocument117 pagesEEE206 Device Lab ManualGiaa RahmanNo ratings yet
- EDCDocument232 pagesEDClakshmipo67% (3)
- CH 2Document41 pagesCH 2avishek aviNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ve Diode 1Document43 pagesBai Tap Ve Diode 1maithuong85100% (1)
- EXP-1Document8 pagesEXP-1Parthiv IjardarNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diodes and Theirs ApplicationsDocument9 pagesSemiconductor Diodes and Theirs Applicationsamerican dxb memesNo ratings yet
- CHAP 2 - Diode Applications-Clippers ClampersDocument33 pagesCHAP 2 - Diode Applications-Clippers Clampersksreddy2002No ratings yet
- What is Diode Approximation: Types & Models in 38 CharactersDocument5 pagesWhat is Diode Approximation: Types & Models in 38 CharactersTobi Uchiha0% (1)
- Diode CircuitsDocument102 pagesDiode Circuitswkibiwot10No ratings yet
- Title: Study On Clamper Circuits.: Experiment No. 04Document4 pagesTitle: Study On Clamper Circuits.: Experiment No. 04shuvon3344No ratings yet
- Tutorials of EDDocument30 pagesTutorials of EDSunil NamdevNo ratings yet
- PSG Unit3 Motor ProtectionDocument86 pagesPSG Unit3 Motor ProtectionRaja DesinguNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument8 pagesLab Manualbond 777No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document29 pagesChapter 2Shime EthiopianNo ratings yet
- AE Expt 1 - Clippers & ClampersDocument4 pagesAE Expt 1 - Clippers & ClampersPriNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply As Zener Regulator PDFDocument8 pagesDC Power Supply As Zener Regulator PDFzohaibNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply Using Zener RegulatorDocument8 pagesDC Power Supply Using Zener RegulatorzohaibNo ratings yet
- Diode IntroDocument34 pagesDiode IntroSachin AroraNo ratings yet
- Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitDocument13 pagesSirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitMohd Helmy Hakimie RozlanNo ratings yet
- Research of Infrared Thermal On-Line Detection Technology of Zero Resistance InsulatorDocument4 pagesResearch of Infrared Thermal On-Line Detection Technology of Zero Resistance InsulatorluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Research On Bead Image Recognition Algorithm For Determination of Insulator LeversDocument4 pagesResearch On Bead Image Recognition Algorithm For Determination of Insulator LeversluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Remote Online Monitoring System For Suspension Insulator StringsDocument5 pagesRemote Online Monitoring System For Suspension Insulator StringsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Sensor Network For Monitoring The State of Pollution of High-Voltage Insulators Via SatelliteDocument10 pagesSensor Network For Monitoring The State of Pollution of High-Voltage Insulators Via SatelliteluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Methods For Outdoor Polymeric InsulatorsDocument16 pagesDiagnostic Methods For Outdoor Polymeric InsulatorsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Leakage Current Wave Forms For Field-Aged and New Composite InsulatorsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Leakage Current Wave Forms For Field-Aged and New Composite InsulatorsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Two UV Imaging Parameters's in The Insulator Fault DiagnosisDocument4 pagesComparison of Two UV Imaging Parameters's in The Insulator Fault DiagnosisluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Correlation Among ESDD, NSDD and Leakage Current in Distribution InsulatorsDocument7 pagesCorrelation Among ESDD, NSDD and Leakage Current in Distribution InsulatorsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Identifying Faulty Insulator Strings by Detecting Insulator Corona Pulse CurrentDocument4 pagesIdentifying Faulty Insulator Strings by Detecting Insulator Corona Pulse CurrentluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic of Pre-Breakdown State of Polymeric Insulators by The Thermovision MethodDocument4 pagesDiagnostic of Pre-Breakdown State of Polymeric Insulators by The Thermovision MethodluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Application of UV-C Pulse Radiation Detection in Checking Faulty InsulatorsDocument4 pagesApplication of UV-C Pulse Radiation Detection in Checking Faulty InsulatorsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Contamination Condition of Insulator Based On PSO-SVMDocument5 pagesAssessment of Contamination Condition of Insulator Based On PSO-SVMluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Hydrophobicity Estimation of HV Polymeric Insulating Materials. Development of A Digital Image Processing MethodDocument10 pagesHydrophobicity Estimation of HV Polymeric Insulating Materials. Development of A Digital Image Processing MethodluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Formation and Characterization of Dry Bands in Clean Fog On Polluted InsulatorsDocument8 pagesFormation and Characterization of Dry Bands in Clean Fog On Polluted InsulatorsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Frequency Characteristics of Leakage Current Waveforms of A String of Suspension InsulatorsDocument7 pagesFrequency Characteristics of Leakage Current Waveforms of A String of Suspension InsulatorsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document36 pagesCH 04Rahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Characteristics of Leakage Current WaveformsDocument5 pagesFrequency Characteristics of Leakage Current WaveformsAdnan YavasNo ratings yet
- Nii Resi I Iieb Iii: E (5 I!5T I GF Lig?Document18 pagesNii Resi I Iieb Iii: E (5 I!5T I GF Lig?luqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- 2 4sDocument18 pages2 4sluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus GEEN 3311 101 Spring 12-13 DDocument4 pagesSyllabus GEEN 3311 101 Spring 12-13 DluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- 4-Bit Carry Look Ahead AdderDocument5 pages4-Bit Carry Look Ahead AdderluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Problem Formulation and Design of Combinational CircuitsDocument30 pagesProblem Formulation and Design of Combinational CircuitsOrange CloverNo ratings yet
- I It, II I GGDocument16 pagesI It, II I GGluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- ECE 438 Assignment 5 - CMOS Logic GatesDocument9 pagesECE 438 Assignment 5 - CMOS Logic GatesluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Digital Design LaboratoryDocument13 pagesDigital Design LaboratoryKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- EE541 Assignment 1: Computer Arithmetic ProblemsDocument1 pageEE541 Assignment 1: Computer Arithmetic ProblemsluqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- 11Document4 pages11luqmansulymanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of ESDD On High-Voltageinsulators Using ArtificialneuralnetworkDocument6 pagesAssessment of ESDD On High-Voltageinsulators Using ArtificialneuralnetworkluqmansulymanNo ratings yet