Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment2ed PDF
Uploaded by
Iza HamdanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment2ed PDF
Uploaded by
Iza HamdanCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 3: KINEMATIC OF RIGID BODY 1. The telephone cable reel rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface.
If point A on the cable has a velocity vA = 0.8 m/s to the right, compute the velocity of the center O and the angular velocity of the reel. (Be careful not to make the mistake of assuming that the reel rolls to the left.) Ans: vo = 1.2 m/s, = 1.333 rad/s CW
2. The hydraulic cylinder D is causing the distance OA to increase at the rate of 50 mm/s. Calculate the velocity of the pin at C in its horizontal guide for the instant when = 50o. Ans: vc = 59.6 mm/s
3. At the instant represented the triangular plate ABD has a clockwise angular velocity of 3 rad/s. For this instant determine the angular velocity BC of link BC. Ans: BC = 3 rad/s CW
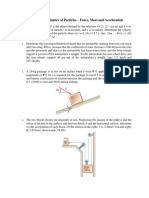
4(a). For the instant represented, Crank OB has a clockwise angular velocity = 0.8 rad/s and is passing the horizontal position. Determine the corresponding velocity of the guide roller A in the 20o slot and the velocity of point C midway between A and B. 4(b). Locate the instantaneous center of zero velocity and use it to find the velocity of the guide roller A in the 20o slot and the velocity of point C midway between A and B. Ans: vA = 226 mm/s, vc = 174.7 mm/s
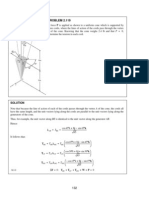
5. The mechanism for pushing small boxes from an assembly line onto a conveyor belt is shown with arm OD and crank CB in their vertical positions. For the configuration shown, crank CB has a constant clockwise angular velocity of rad/s. Determine the acceleration of E. Ans: E = 0.285 m/s2
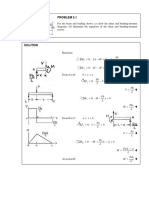
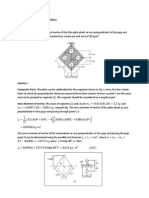
CHAPTER 4: KINETIC OF RIGID BODY 1. The uniform 8 kg slender bar is hinged about a horizontal axis through O and released from rest in the horizontal position. Determine the distance b from the mass center to O which will result in an initial angular acceleration of 16 rad/s 2, and find the force R on the bar at O just after release.
2. The uniform 24 m mast has a mass of 300 kg and is hinged at its lower end to a fixed support at O. If the winch C develops a starting torque of 1300 N.m, calculate the total force supported by the pin at O as the mast begins to lift off its support at B. Also, find the corresponding angular acceleration of the mast. The cable at A is horizontal and the mass of the pulleys and winch is negligible. Ans: = 0.0709 rad/s2 , O = 5260 N
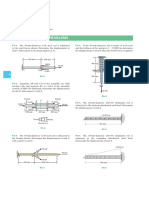
3. The figure shows the cross section AB of a garage door which is a rectangular 2.5 m by 5 m panel of uniform thickness with a mass of 200 kg. The door is supported by the struts of negligible mass and hinged at O. Two spring-and-cable assemblies, one on each side of the door, control the movement. When the door is in the horizontal open position, each spring is unextended. If the door is given a slight inbalance from the open position and allowed to fall, determine the value of the spring constant k for each spring which will limit the angular velocity of the door to 1.5 rad/s when edge B strikes the floor. Ans: k = 1.270 kN/m
4. The 10 kg double wheel with radius of gyration of 125 mm about O is connected to the spring of stiffness k = 600 N/m by a cordwhich is wrapped securely around the inner hub. If the wheel is released from rest on the incline with the spring stretched 225 mm, calculate the maximum velocity v of its center O during the ensuing motion. The wheel rolls without slipping. Ans: vmax = 1.325 m/s
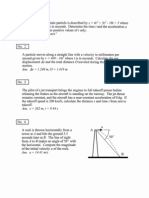
5. A couple M = 12 N.m is applied at C to the spring-toggle mechanism, which is released from rest in the position = 45o. In this position the spring, which has the stiffness of 140 N/m is stretched 150 mm. Bar AB has a mass of 3 kg and BC a mass of 6 kg. Calculate the angular velocity of BC as it crosses the position = 0. Motion is in the vertical plane, and friction is negligible. Ans: = 4.15 rad/s
You might also like
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Blast Pressure ExampleDocument14 pagesBlast Pressure ExamplekeshavnvaityNo ratings yet
- Problems in Unit - 1Document25 pagesProblems in Unit - 1Prakasini SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Speed, Time and DistanceDocument28 pagesSpeed, Time and Distancerehan23456789100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- Forced Vibrations Formula & NotesDocument4 pagesForced Vibrations Formula & NotesFahim AkmalNo ratings yet
- M Rades - Dynamics of Machinery 2Document243 pagesM Rades - Dynamics of Machinery 2Mircea Rades100% (9)
- Tutorial 9 Solutions PDFDocument20 pagesTutorial 9 Solutions PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- CEGR 202 Homework ProblemsDocument9 pagesCEGR 202 Homework ProblemsEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- CH 23Document25 pagesCH 23Shadan9250% (2)
- Graph of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesGraph of Motion WorksheetDhanBahadur100% (1)
- Solucionario Riley Dynamics PDFDocument253 pagesSolucionario Riley Dynamics PDFElsa Vasquez VargasNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Weeks 1 - 2Document22 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Weeks 1 - 2Maljan CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Solutions 10Document12 pagesSolutions 10JCLLNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Eccentric LoadDocument8 pagesCylinder Eccentric LoadKyle Mast100% (1)
- Tutorial 3Document19 pagesTutorial 3Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- Engineering MEchanics Part - BDocument38 pagesEngineering MEchanics Part - BPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- SHEAR AND BENDING DIAGRAMSDocument10 pagesSHEAR AND BENDING DIAGRAMSËmêrson SîntujNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ch1 ProblemDocument5 pagesTutorial Ch1 ProblemKiat HauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions Modern Physics 4th EditionDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Solutions Modern Physics 4th EditionDaniele CastroNo ratings yet
- 112 116Document10 pages112 116Monica Jones100% (1)
- 9A01504 Structural Analysis-IIDocument8 pages9A01504 Structural Analysis-IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Bead and Ring ProblemDocument4 pagesBead and Ring ProblemsayanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester-V Engineering ElectromagneticsDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester-V Engineering ElectromagneticsGECM85100% (1)
- ME 308 Machine Design II Problem Set #2 Gear Trains and DifferentialsDocument3 pagesME 308 Machine Design II Problem Set #2 Gear Trains and DifferentialsabdulwahabNo ratings yet
- G12 Constrained Motion of Connected ParticlesDocument14 pagesG12 Constrained Motion of Connected Particlesrahulnag10febNo ratings yet
- A5Q4Document8 pagesA5Q4chicaiza10No ratings yet
- Unit VDocument10 pagesUnit VAbinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Problem Set PDFDocument2 pagesZener Diode Problem Set PDFfree5050No ratings yet
- ENGN 37 HomeworkDocument25 pagesENGN 37 HomeworkLucia AntoniusNo ratings yet
- Measuring Beam Bending MomentsDocument1 pageMeasuring Beam Bending MomentsTarique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument101 pagesStrength of MaterialsLucksy Marcus PalloNo ratings yet
- Axial Load and Torsion ProblemsDocument3 pagesAxial Load and Torsion ProblemsG. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- Bs Experiment 1Document5 pagesBs Experiment 1Hui Zhi100% (2)
- Statically Indeterminate Systems 2Document16 pagesStatically Indeterminate Systems 2nageshNo ratings yet
- Ada 5 Condensadores PDFDocument2 pagesAda 5 Condensadores PDFTony Maldonado PinzonNo ratings yet
- Alciatore Mechatronics Solution Manual 5th EditionDocument16 pagesAlciatore Mechatronics Solution Manual 5th Editionsajal agarwalNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document46 pagesCH 04AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Tensions in Cables Supporting Machinery ProblemDocument10 pagesTensions in Cables Supporting Machinery ProblemGonçalo CruzeiroNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and Dielectrics: Answers To QuestionsDocument24 pagesCapacitance and Dielectrics: Answers To QuestionsAladdinSultanAlTamimiNo ratings yet
- Procedure BONDDocument1 pageProcedure BONDMorapedi D. KealebogaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Kinematics of Particles Sample ProblemsDocument82 pagesChapter 12 - Kinematics of Particles Sample ProblemsZizhen JiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rigid Bodies ProblemsDocument24 pagesKinematics of Rigid Bodies ProblemsMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- WS XI PH Rotational Motion RollingDocument11 pagesWS XI PH Rotational Motion Rollingkaushik247No ratings yet
- Dynamics Tutorial 11-Damped Vibrations-13p PDFDocument13 pagesDynamics Tutorial 11-Damped Vibrations-13p PDFmanfredm6435100% (1)
- Introduction To Elasticity Torsion of Triangular Cylinder - WikiversityDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Elasticity Torsion of Triangular Cylinder - WikiversityDavidThomasNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL+CHAPTER+4 SolutionDocument13 pagesTUTORIAL+CHAPTER+4 SolutionNoOna MieyraNo ratings yet
- Application of Numerical Methods To Truss Bridge Using Finite Element AnalysisDocument12 pagesApplication of Numerical Methods To Truss Bridge Using Finite Element AnalysisBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- FMDocument13 pagesFMSaurabh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Planar Kinematics of a Rigid BodyDocument47 pagesPlanar Kinematics of a Rigid Bodyrana abdul waasay0% (1)
- HW#2 Solutions ME363 Fall 2007 PDFDocument8 pagesHW#2 Solutions ME363 Fall 2007 PDFjessicaHannaNo ratings yet
- Static friction limits pole angleDocument30 pagesStatic friction limits pole angleAnonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- Strain: Strength of MaterialsDocument5 pagesStrain: Strength of MaterialsDon MatiasNo ratings yet
- NuMeths (Unit1)Document34 pagesNuMeths (Unit1)kathrin_jazz26No ratings yet
- Chap 23 64 Regular PhysicsDocument395 pagesChap 23 64 Regular Physicsmatthew_schreiber_2No ratings yet
- Module 4 Defects in SolidDocument38 pagesModule 4 Defects in SolidRalph Andrew Silverio67% (3)
- Speed of SoundDocument6 pagesSpeed of Soundmpho100% (2)
- Work Sheet On DynamicsDocument6 pagesWork Sheet On DynamicstorsrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 AE688Document7 pagesAssignment 03 AE688Mhmoud Al-TamimiNo ratings yet
- Opción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDocument11 pagesOpción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDiego Naspud UrgilesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial TwoDocument5 pagesTutorial TwoParas gurungNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3JeeveshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems Wk1-4Document4 pagesTutorial Problems Wk1-4Kano MolapisiNo ratings yet
- FE Review Dynamics Notes Z ExamplesDocument7 pagesFE Review Dynamics Notes Z ExamplesDan 's Gone100% (2)
- Applied Dynamics QuestionsDocument5 pagesApplied Dynamics QuestionsKritamMaharjanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 WEDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A Particle: Review QuestionDocument8 pagesKinematics of A Particle: Review QuestionIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document4 pagesExercise 2Iza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Particle Motion ProblemsDocument6 pagesKinematics Particle Motion Problemsstupidscribd41234123No ratings yet
- Week5 - Chap6 - Operators and ExpresssionDocument84 pagesWeek5 - Chap6 - Operators and ExpresssionIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Page SOLID MECHANICDocument2 pagesPage SOLID MECHANICIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document4 pagesExercise 2Iza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Particle Motion ProblemsDocument6 pagesKinematics Particle Motion Problemsstupidscribd41234123No ratings yet
- C++ Special Characters PDFDocument1 pageC++ Special Characters PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 1.1 Part2 - ContourLines, Level Curves and 3D Graphs) PDFDocument3 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 1.1 Part2 - ContourLines, Level Curves and 3D Graphs) PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 1.1 Part2 - ContourLines, Level Curves and 3D Graphs) PDFDocument3 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 1.1 Part2 - ContourLines, Level Curves and 3D Graphs) PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN AND RANGEDocument3 pagesDOMAIN AND RANGEIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN AND RANGEDocument3 pagesDOMAIN AND RANGEIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN AND RANGEDocument3 pagesDOMAIN AND RANGEIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Dynamics Unit Test ResultsDocument4 pagesGrade 11 Dynamics Unit Test ResultsFarhan HabibzaiNo ratings yet
- SC9 Q4W3Document8 pagesSC9 Q4W3Rocky Parinas DuqueNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis and Hydraulic SimilitudeDocument9 pagesDimensional Analysis and Hydraulic SimilitudeinsaneabhayNo ratings yet
- BT VLDC 3 CH29Document26 pagesBT VLDC 3 CH29caotrieu108No ratings yet
- 11.3b SoundDocument3 pages11.3b SoundWeteachNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - Fundamentals of Compressible FlowDocument1 pageAssignment - 1 - Fundamentals of Compressible FlowABHI THAKKARNo ratings yet
- Annex 5 - ElectromagnetismoDocument16 pagesAnnex 5 - ElectromagnetismocarlosNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions & Identities - SolutionsDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Functions & Identities - SolutionswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Basic Ultrasonic+Transducer TechnotesDocument9 pagesBasic Ultrasonic+Transducer Technoteslram70No ratings yet
- Matlab을이용한해양파도표면의해석Document7 pagesMatlab을이용한해양파도표면의해석윤현진No ratings yet
- Effects of Taper Ratio on Aircraft Wing Aerodynamic ParametersDocument7 pagesEffects of Taper Ratio on Aircraft Wing Aerodynamic ParametersTrần Phước TrungNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1Document13 pagesTarea 1Mario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Rotational MotionDocument29 pagesLesson 6 - Rotational MotionJonathan VillapanaNo ratings yet
- Bra Ket & Linear AlgebraDocument4 pagesBra Ket & Linear AlgebracrguntalilibNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines: Introduction to CamsDocument51 pagesMechanics of Machines: Introduction to CamsJustin IanNo ratings yet
- WECDocument50 pagesWECRyan SmithNo ratings yet
- Ae2301 LPDocument1 pageAe2301 LPRamaswamy SubbiahNo ratings yet
- Naming Angles: Name The Vertex and Sides of Each AngleDocument4 pagesNaming Angles: Name The Vertex and Sides of Each AngleTOBINo ratings yet
- Physics InterferenceDocument23 pagesPhysics InterferencechutiyaaaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4. Projectile MotionDocument6 pagesLesson 4. Projectile MotionJeffNo ratings yet
- Dynamics WorsksheetDocument3 pagesDynamics WorsksheetUmaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Science Physics NotesDocument46 pagesScience Physics Noteshenry bhoneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Problems PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 1 Problems PDFErwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic jack force-speed curvesDocument5 pagesHydraulic jack force-speed curvesAnas OdehNo ratings yet