Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motion Along A Straight Line
Uploaded by
Nik NorhafizaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motion Along A Straight Line
Uploaded by
Nik NorhafizaCopyright:
Available Formats
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 1. A particle moves in a straight line.
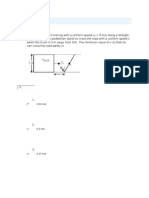
Its displacement, s m, from a fixed point O, t seconds after passing through O, is given by . Find a) the initial acceleration of the particle, b) the values of t when the particle comes instantaneously to rest, c) the displacement of the particle for each moment when the particle comes instantaneously to rest, d) the total distance travelled by the particle from the instant of t = 0 to the instant the particle comes instantaneously to rest for the second time. 2. A particle starts to move from a fixed point O along a straight line. Its velocity, v ms-1, is given by where t is the time in seconds after the particle has left O and m and n are constants. The acceleration of the particle at time t = 2 is 6 ms-1 and the particle is at 14m to the left of O after 1 second. a) Find i) the value of m and n, ii) the range of values of t when the particle decelerates. b) Sketch the velocity-time graph of the motion of the particle for 0 t 3. P Q
5.
The diagram shows the positions of two fixed points, A and B, on a straight line where AB = 4m. At an instant, particle P passes through point A with a velocity of vp= 2t+ 3 while particle Q passes through point B with a velocity of vq= 4 t, where t is the time in seconds after particle P and particle Q passes through points A and B respectively. Taking the direction from A to B as the positive direction, find a) the displacement of particle P and particle Q from point A after t seconds, b) the distance between particles P and Q at the instant particle Q is instantaneously at rest, c) the range of values of t when both particles move to the right, d) the time when both particles P and Q meet. 4. A particle moves along a straight line which passes through a fixed point , O, with a velocity of 18 ms-1. Its acceleration, a ms-2, t seconds after leaving O is given by a = 3 2t. The particle stops instantaneously at time n s. a) Find i) the maximum velocity of the particle, ii) the value of n. b) Sketch a velocity-time graph for 0 t n. Hence, or otherwise, calculate the total distance travelled during that period.
You might also like
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument3 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineKrit JimenezNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: Quiz/EnrichmentDocument2 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: Quiz/EnrichmentRadz AbdulNo ratings yet
- SPM AddMath Motion Along A Straight LineDocument8 pagesSPM AddMath Motion Along A Straight LineLeneNo ratings yet
- 9 Motion Along A Straight LineDocument3 pages9 Motion Along A Straight LineAidil-Nur ZainalNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument9 pagesMotion Along A Straight Lineahmednalla50% (2)
- Motion in The Straight Line SPM 2008-2011Document1 pageMotion in The Straight Line SPM 2008-2011maazioNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Lines Exercises PDFDocument2 pagesMotion Along A Straight Lines Exercises PDFMaria SabariNo ratings yet
- Module 19 Motion Along A Straight LineDocument13 pagesModule 19 Motion Along A Straight LineDon Amaru Sarma100% (1)
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument1 pageKinematics WorksheetMalcolmCoNo ratings yet
- Topical Test F5C8Document1 pageTopical Test F5C8cikgu ngNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line (Past-Year Questions) : 1. SPM 2003 P2 Q12Document2 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line (Past-Year Questions) : 1. SPM 2003 P2 Q12Muhammad Redzuan SaidiNo ratings yet
- Intregration PT 2Document4 pagesIntregration PT 2Augustin LouisNo ratings yet
- Seeds Instittute: Motion in One DimensionDocument1 pageSeeds Instittute: Motion in One DimensionAshwin JambhulkarNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line SPM 2003 - 2011Document4 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line SPM 2003 - 2011Ni'mazakirah Ab Rahman100% (1)
- Kinematics 1 FileDocument36 pagesKinematics 1 FileSRI ABHYASA HIGH SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- Topic 17 KinematicsDocument3 pagesTopic 17 Kinematicsmaths_w_mr_tehNo ratings yet
- G 12 M1Document4 pagesG 12 M1Hui ZhengNo ratings yet
- Exercise (S-1) : Definitions of Kinematics VariablesDocument5 pagesExercise (S-1) : Definitions of Kinematics VariablesAmit RoutNo ratings yet
- Assignment Motion in Straight LineDocument2 pagesAssignment Motion in Straight LinePrateek Kapoor100% (1)
- 66.0.0 Differentiation QDocument4 pages66.0.0 Differentiation QBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Mechanics Unit 9 TestDocument1 pageAS Maths Mechanics Unit 9 TestMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Session 5: Mechanics Post-Session HomeworkDocument9 pagesSession 5: Mechanics Post-Session Homeworkalexandra owNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument7 pagesKinema TicsJimmy HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - KinematicsDocument10 pagesChapter - 2 - KinematicsMd AftabNo ratings yet
- Revision On Motion: SI UnitsDocument6 pagesRevision On Motion: SI UnitsYoussef SalemNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument16 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineNorhapidah Mohd SaadNo ratings yet
- F - AMa Topic 1 Seminar Questions - CondensedDocument4 pagesF - AMa Topic 1 Seminar Questions - CondensedMartinLukNo ratings yet
- Variable AccelerationDocument3 pagesVariable AccelerationsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Exercises For KinematicsDocument2 pagesExercises For KinematicsMaria Laksmi SarestriNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document1 pagePhysics 1Hukum ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument130 pagesProjectile Motionrockingjoe100% (7)
- 31 Basic Mathematics and Vectors Home AssignmentDocument8 pages31 Basic Mathematics and Vectors Home AssignmentHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 AssignmentDocument1 pageUnit 2 AssignmentSagar YadavNo ratings yet
- Applied Mech. IIDocument38 pagesApplied Mech. IIJanaki RamanNo ratings yet
- SPT-1 Only QuestionsDocument4 pagesSPT-1 Only QuestionsAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Rectilinear MotionDocument33 pagesModule 2 - Rectilinear MotionRozel100% (2)
- Kinematics 1Document3 pagesKinematics 1Harish RaghavendarNo ratings yet
- Tiliner Motion - Jee Main AdvancedDocument69 pagesTiliner Motion - Jee Main AdvancedAnubhav KohliNo ratings yet
- XI P Notes Projectile MotionDocument33 pagesXI P Notes Projectile Motionsarawalem1No ratings yet
- Day 01 - Kinematics 1dDocument4 pagesDay 01 - Kinematics 1dLakshya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Sheet No 1 - Rectilinear MotionDocument2 pagesSheet No 1 - Rectilinear MotionSubNaderNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument6 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineSin YeeNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument28 pagesCircular MotionAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Dynamic SsssssDocument10 pagesDynamic SsssssSindy N. SagunNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Theory - EDocument24 pagesKinematics Theory - Ethinkiit100% (1)
- Soal Latihan Fisika Kelas 2 SmaDocument10 pagesSoal Latihan Fisika Kelas 2 SmaNisrina Azizah LubisNo ratings yet
- All Semester Activities PDFDocument19 pagesAll Semester Activities PDFIan Gerardo Memije NuñezNo ratings yet
- Set2 Kinematics Page12 Translated Oct2023Document2 pagesSet2 Kinematics Page12 Translated Oct2023yasminemohand4No ratings yet
- Abd El Rahman Ali Saad - Sheet PDFDocument49 pagesAbd El Rahman Ali Saad - Sheet PDFMahmoud samahaNo ratings yet
- DPP KinematicsDocument10 pagesDPP KinematicsMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ask IITiankineDocument2 pagesAsk IITiankineSethurathienam IyerNo ratings yet
- Problems in Physics I For IIT JEE Vol 1 IITJEE Main Advanced Standard 12 XII Shashi Bhusan Tiwari MC Graw Hill (PDFDrive) (3) - 24-52Document29 pagesProblems in Physics I For IIT JEE Vol 1 IITJEE Main Advanced Standard 12 XII Shashi Bhusan Tiwari MC Graw Hill (PDFDrive) (3) - 24-52Mehebub PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Q. 5. A Particle Is Moving Along Positive X DirectionDocument101 pagesKinematics: Q. 5. A Particle Is Moving Along Positive X DirectionDivyanshu PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 PDFAhmed AttallaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Subjective Questions: Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesKinematics Subjective Questions: Page 1 of 4Nilay LilawalaNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument8 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineSiti HasanahNo ratings yet
- SHMDocument3 pagesSHMkemigishapatience369No ratings yet
- Free Test01Document131 pagesFree Test01social servantNo ratings yet
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorFrom EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo ratings yet
- Mathematics, Form 4 2016 MRSM Tun Abdul RazakDocument6 pagesMathematics, Form 4 2016 MRSM Tun Abdul RazakNik NorhafizaNo ratings yet
- Set - IGCSE MathematicsDocument3 pagesSet - IGCSE MathematicsNik NorhafizaNo ratings yet
- No. Rules Number Number of Significant FiguresDocument2 pagesNo. Rules Number Number of Significant FiguresNik NorhafizaNo ratings yet
- Sudoku #119 (Easy) : STARTING TIME: - END TIMEDocument2 pagesSudoku #119 (Easy) : STARTING TIME: - END TIMENik NorhafizaNo ratings yet
- Limit and Tangent To A Curve: Component of Calculus C1Document3 pagesLimit and Tangent To A Curve: Component of Calculus C1Nik NorhafizaNo ratings yet