Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrinology
Uploaded by
AliehsEiram18Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrinology
Uploaded by
AliehsEiram18Copyright:
Available Formats
Endocrinology - Scientific study of function & pathology of the endocrine glands Endocrine System - Release their secretions (hormones)
directly into the circulatory system o Endocrine glands o Chromaffin system o Neurosecretory system Hormone - Produced by ductless internal glands that are directly discharged into the bloodstream in response to a stimulus - 10-7 to 10-12 mol/L - Exert specific regulatory effects on selected target cells (hormone receptors) Exocrine glands - Discharge their secretions via ducts Autocrine - Mode of hormone action - Hormone binds to receptors on or in the cell type that produced it affects the function of that cell Paracrine - Type of hormone function - Hormone synthesized in and released from one type of cell binds to the hormone receptor in nearby cells of a different type and affects their function Classification of Hormones 1. Polypeptide or Protein - Pancreas & pituitary gland Insulin Parathyroid Hormone Adrenocorticotropin - Water-solube & circulate freely in plasma - Half-life: 10-30 minutes or less - Bind to cell membrane receptors or intracellular effects mediated by second messenger system to initiate their response
2. Steroid (structurally related to cholesterol) - Sex glands & adrenal cortex Cortisol Aldosterone & Estradiol Progesterone Testosterone - Hyrdrophobic & insoluble in water - Circulates reversibly bound to transport proteins - Half-life: 30-90 minutes - Enters cell by passive diffusion & binds to intracellular receptors 3. Amino Acid (Tyrosine) Derivatives - Adrenal medulla & thyroid gland Catecholamines Thyroxine - Water-soluble but circulate in plasma either free (catecholamines) or bound to proteins (thyroxine) - Half-life of thyroxine: 7-10 days - Half-life of free catecholamines (epinephrine): 1 minute or less - Interacts with membrane-associated receptors & uses a second messenger system Action of Hormones: 1. Growth & Development - Gonadotropins (Luteinizing Hormone & Follicle-stimulating Hormone) o regulate the development, growth, & function of the ovary & testis o regulate pubertal growth o development & maintenance of secondary sex characteristics o growth, development, & maintenance of the skeletons & muscles o distribution of body fat - Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) o regulates the growth of the adrenal glands & secretion of adrenal hormones - Thyrois-stimulating Hormone (TSH) o regulates the growth of the thyroid glands o regulates the iodination of amino acids to produce thyroid hormones: triiodothyronine & thyroxine ** NOTE: Production & release are controlled by the hypothalamic hormones of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system.
2. Homeostatic Control of Metabolic Pathways - Regulation of blood glucose o Insulin Regulates the dispersal of glucose into cells (fat, muscle, liver, brain) o Counter-regulatory hormones: Glucagon Corticosteroids Catecholamines (Epinephrine / Norepinephrine) Growth Hormone HORMONE Insulin Glucagon Catecholamines Growth Hormone Corticosteroids GLYCOGEN Synthesis Breakdown Breakdown Breakdown Synthesis GLUCONEOGENESIS Decrease Increase Increase (indirect by Insulin Inhibition) Increase GLUCOSE UPTAKE Stimulates No Effect Decrease (indirect by GH Insulin Inhibition) Decrease Decrease GLUCOSE Decrease Increase Transient Increase Increase Increase
Homeostasis of calcium o Calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) On the parathyroid gland Recognizes the ambient concentration of ionized calcium Regulates synthesis and secretion of parathyroid hormone Regulation of water, and electrolyte metabolism o Regulated by: Aldosterone adrenal gland Rennin kidneys Vasopressin (Anti-diuretic Hormone, ADH) posterior pituitary gland
3. Regulation of Energy Production & Storage - Neuro-endocrine hormones participates actively in the integrative metabolic process that affects most organs in the body The Pituitary Gland - spit mucus - Master gland - Hypophysis undergrowth unique position under the hypothalamus - 3 Parts: o Anterior pituitary or Adenohypophysis o Intermediate Lobe or Pars Intermedialis o Posterior pituitary or Neurohypophysis
Functions: o Feedback loops o Pulsatile secretions o Diurnal rhythms o Environmental or external modification of its performance Pituitary function can be detected between the seventh & ninth weeks of gestation Hormones produced by Anterior Pituitary: o Go - Growth Hormone - Bones & Tissues o Look - Luteinizing Hormone - Ovaries & Testes o For - Follicle-stimulating Hormone - Ovaries & Testes o The - Thyroid-stimulating Hormone - Thyroid Gland o Adenoma - Adrenocorticotropic Hormone - Adrenal Cortex o Please - Prolactin - Mammary Glands Hormones produced by Anterior Pituitary: o Oxytocin - Mammary Glands o Vasopressin / Anti-diuretic Hormone - Kidney Tubules
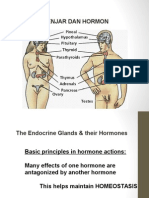
Hormones Produced by Glands: - Pineal Glands (Epiphysis) o Melatonin - Thyroid Gland o Free T4 o Free T3 o Calcitonin - Adrenal Glands o Cortisol o Aldosterone o DHEA-SO4 - Ovaries o Estradiol o Progesterone - Testes o Testosterone o Testosterone Free - Pancreas o Insulin o Glucagon - Parathyroid Gland o Parathyroid Hormone
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) o Growth Hormone o ACTH o TSH o FSH o LH o Prolactin o ADH
Control of Hormone Secretion: The Concept of Feedback Mechanisms a. Short Feedback Loop o Feedback of thyroxine at the level of the pituitary b. Long Feedback Loop o Feedback at the level of the hypothalamus c. Ultrashort Feedback Loop o Feedback between the pituitary & hypothalamus
HYPOTHALAMUS PITUITARY THYROID
You might also like
- Reiki Level 1 ManualDocument29 pagesReiki Level 1 ManualFabian DeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PhysiologyDocument20 pagesAnatomy PhysiologyAneez Malik100% (2)
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Module 5 Regulation of Internal EnvironmentDocument17 pagesModule 5 Regulation of Internal EnvironmentSakshi Jauhari100% (1)
- Neural and Hormonal Control of Human SystemsDocument19 pagesNeural and Hormonal Control of Human SystemsjessNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine SystemPeej Reyes100% (1)
- Endocrine Pathophysiology Nursing NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine Pathophysiology Nursing Notesgrad_nurse_2015100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 21 The Sensory SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 21 The Sensory SystemThanh Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- Control Our Bodies Homeostasis via Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesControl Our Bodies Homeostasis via Endocrine GlandsJohn Philip VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table ReviewDocument8 pagesParasitology Table ReviewAliehsEiram18No ratings yet
- Endocrinology NotesDocument24 pagesEndocrinology NotesEmily Dong100% (1)
- Endocrine Diseases and Hormone MechanismsDocument27 pagesEndocrine Diseases and Hormone MechanismsValerie Gonzaga-CarandangNo ratings yet
- Sex HormonesDocument58 pagesSex Hormonesbug4444not100% (1)
- Comparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcDocument36 pagesComparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcNarasimha Murthy100% (4)
- Comprehensive Nursing Board Exam Review 500 Page Test 111213225254 Phpapp02 PDFDocument546 pagesComprehensive Nursing Board Exam Review 500 Page Test 111213225254 Phpapp02 PDF698rickyNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument43 pagesHormonesDontu Maria0% (1)
- Hormone and Nervous System BioloveDocument28 pagesHormone and Nervous System BioloveOrkid FazzNo ratings yet
- November 2008Document84 pagesNovember 2008giansulakisosuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument50 pagesEndocrine DrugsJohney DoeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocument35 pagesThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesShe JocelynNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument86 pagesLecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyAlexandru Ionut Popistaș100% (1)
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocument23 pagesExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- Endocrine RegulationDocument18 pagesEndocrine RegulationAdela RomeroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument3 pagesEndocrine DisordersIrish OrleansNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Endocrine Guided NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Endocrine Guided NotesJeanette IrambonaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and its Major HormonesDocument34 pagesThe Endocrine System and its Major Hormonesdianpn27No ratings yet
- Hormonal Regulation of MetabolismDocument80 pagesHormonal Regulation of MetabolismVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineDocument36 pages1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - The Endocrine System - ReviewDocument11 pagesChapter 17 - The Endocrine System - ReviewAnonymous xTR2A3TfdhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Endocrine System NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 13 Endocrine System NotesJane XuNo ratings yet
- NEUROENDOCRINE SYSTEMDocument43 pagesNEUROENDOCRINE SYSTEMMeldy Muzada ElfaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Metabolic & Endocrine DiseasesDocument280 pagesMetabolic & Endocrine DiseasesHussenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Noteshannah pelonia100% (1)
- HormonesDocument55 pagesHormonesAvinashNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15 Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15Document33 pagesEndocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15 Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15Omed Zarifi100% (1)
- Endocrine Test 8 NotesDocument9 pagesEndocrine Test 8 NotesHayden ShulerNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Sistem EndokrinDocument42 pagesAnatomi Sistem Endokrinnisya rafikoh100% (1)
- Overview of The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Endocrine SystemTAGUIAM, Danica A.No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Dr. Dedi Ardinata, M.Kes Physiology Department Medical School of University Sumatera UtaraDocument94 pagesEndocrine System: Dr. Dedi Ardinata, M.Kes Physiology Department Medical School of University Sumatera UtaraAdryansyah ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Hormonal Control Nervous ControlDocument5 pagesHormones: Hormonal Control Nervous Controlvaibhav trivediNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: EndocrinologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: EndocrinologyAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Biology 112: Chapter 11: The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesBiology 112: Chapter 11: The Endocrine SystemLuisNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PPT Session 12-13Document35 pagesEndocrine System PPT Session 12-13LawrenceNo ratings yet
- 1 EndocrinologyDocument15 pages1 EndocrinologyJessa MayNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Responses To ExerciseDocument38 pagesHormonal Responses To ExercisesajjadNo ratings yet
- Biosintesis Dan Mekanisme Kerja Hormon Repro Wanita PDFDocument39 pagesBiosintesis Dan Mekanisme Kerja Hormon Repro Wanita PDFsallynorcelinaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction of EndocrineDocument35 pages1.introduction of EndocrineCabdiladif Ahmed McrfNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PPT Session 12-13Document35 pagesEndocrine System PPT Session 12-13Lawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument24 pagesEndocrine Systemfrowee23No ratings yet
- Endocrine Act SheetDocument3 pagesEndocrine Act SheetTrisha ArdedNo ratings yet
- Histology of Major Endocrine OrgansDocument64 pagesHistology of Major Endocrine OrgansAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Regulasi Endokrin 22 IntensifDocument25 pagesRegulasi Endokrin 22 IntensifWignes WarenNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument52 pagesHypothalamus and PituitaryMuhammad JameelNo ratings yet
- Secretion From The Pineal GlandDocument8 pagesSecretion From The Pineal GlandVince Laurence BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument5 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYMarina ArvanitopoulouNo ratings yet
- SISTEM ENDOKRIN DAN FUNGSI HORMONDocument49 pagesSISTEM ENDOKRIN DAN FUNGSI HORMONJessiee YeoNo ratings yet
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument32 pagesM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Chapter SummaryDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Chapter SummaryShiny ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document3 pagesChapter 10Zoe DorothyNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Hormones: Biochemistry Department Dr. Mutiara Indah Sari, MkesDocument37 pagesFemale Reproductive Hormones: Biochemistry Department Dr. Mutiara Indah Sari, MkesHabib Al KahfiNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversityDocument25 pagesThe Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversitypashaNo ratings yet
- Apollon Reviewer PDFDocument72 pagesApollon Reviewer PDFAliehsEiram18No ratings yet
- One Way AnovaDocument9 pagesOne Way Anovaginavasile2000No ratings yet
- Two Way AnovaDocument11 pagesTwo Way AnovaDolih GozaliNo ratings yet
- The Hypothalamus: Contouring Accuracy ProgramDocument13 pagesThe Hypothalamus: Contouring Accuracy ProgramAna Paula IoostNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10-ReviwerDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 10-ReviwerPhilline ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PointersDocument2 pagesEndocrine System PointersAlthea ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Live All Questions Final2020Document47 pagesLive All Questions Final2020Hab AnneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument27 pagesEndocrine SystemJhemDelfin100% (1)
- Endocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical MessengersDocument10 pagesEndocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical Messengersahmed100% (1)
- Endocrine System: Organs and Their FunctionDocument61 pagesEndocrine System: Organs and Their FunctionSherifaNo ratings yet
- Heal with self-love and acceptanceDocument2 pagesHeal with self-love and acceptanceKajalNo ratings yet
- EBOOK 978 0123750976 Handbook of Neuroendocrinology Download Full Chapter PDF KindleDocument61 pagesEBOOK 978 0123750976 Handbook of Neuroendocrinology Download Full Chapter PDF Kindlejuan.speight804100% (34)
- 2 - BIO-Explain The Effects of A Particular Hormone If It Is Not Properly RegulatedDocument3 pages2 - BIO-Explain The Effects of A Particular Hormone If It Is Not Properly RegulatedCarlo ThornappleNo ratings yet
- AsdfgDocument28 pagesAsdfgrerereNo ratings yet
- Group 4 DiencephalonDocument23 pagesGroup 4 Diencephalonkqnvhmwx9dNo ratings yet
- National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test NEET (UG), 2017: Booklet Code-D (APRA)Document21 pagesNational Eligibility Cum Entrance Test NEET (UG), 2017: Booklet Code-D (APRA)nabarunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ReviewDocument18 pagesEndocrine System ReviewJessa SuacitoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals GuideDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals Guidealexenneth canilaNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesThe Pituitary Glandshrabasti89No ratings yet
- The Physiological SelfDocument22 pagesThe Physiological SelfRussell AgoncilloNo ratings yet
- Lec 8-Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesLec 8-Endocrine SystemHarahap DarwisNo ratings yet
- Zoology Practical Syllabus For IV Semester BabaDocument23 pagesZoology Practical Syllabus For IV Semester BabaBolloju BabaNo ratings yet
- (Pediaii) 013 Pediatric Endocrine DisordersDocument29 pages(Pediaii) 013 Pediatric Endocrine DisordersdoktoraronaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJamesBatesypcmi100% (13)
- Yen Jaffes Reproductive Endocrinology E Book Physiology Pathophysiology and Clinical Management 7Th Full ChapterDocument38 pagesYen Jaffes Reproductive Endocrinology E Book Physiology Pathophysiology and Clinical Management 7Th Full Chapterjoseph.chavez825100% (27)