Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Notes 4
Uploaded by
api-234133814Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Notes 4
Uploaded by
api-234133814Copyright:
Available Formats
Study Notes 4
In Chemistry, gases and liquids are considered fluids. The molecules of fluids move freely past each other in random directions. The pressure of a fluid is felt equally in all directions because of this random motion of molecules. Pressure is defined as force per unit area. The force in fluids (liquids, gases) comes from collisions of atoms or molecules with the walls of a container the molecules collide with the walls of the container. For example, when a pot of water H2O is heated, the water molecules move faster and faster, and collide with the walls of the pot more often & with greater force. Air pressure is caused by the weight of the gas in the atmosphere striking surfaces. Gravity pulls air molecules (N2, O2, etc) towards the Earth, so there is greater air pressure at lower altitudes and lower air pressure at higher altitudes (this is why airplane cabins are pressurized). Pressure in water INCREASES with depth this explains why your ears hurt when you swim to the bottom of a swimming pool. You feel the pressure of all the water above you! Similarly, the air pressure is greater at sea level (where you are now) than it is at higher altitude. Since water is much denser than air, we feel the weight of the water molecules much more than the weight of air molecules. (Question: What would happen if you opened the window of an airplane at 30,000 feet elevation?) Force Pressure = --------Area
Units of Pressure
1 atmosphere (atm) = 760 Torr (T) = 14.7 lb./in.2 (psi) (760mm Hg)
Gases diffuse into each other to form homogenous mixtures that are evenly mixed. Air in our atmosphere (that we breathe) is an example of such a mixture of gases (nitrogen, oxygen, argon, etc) Heavier gases (denser) diffuse much slower than lighter gases. GAS LAWS P1V1 = P2V2 V1 ----T1 (P = pressure, V = volume, T = temperature in Kelvin) at constant Temperature, moles of gas is constant (Boyles Law) (Charles Law)
V2 = ----- at constant Pressure, moles of gas is constant T2 remember to use KELVIN scale!
Combining these two formulas, we have: P1V1 -----T1 P2V2 = ------T2 moles of gas is constant, note similarity to PV = nRT, Ideal Gas Eqn
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
Standard Temperature = 0C = 273K and Standard Pressure = 1ATM = 760T When comparing volumes of gases, temperature and pressure must be specified. *One liter of ideal gas has a volume = 22.4 Liters at STP
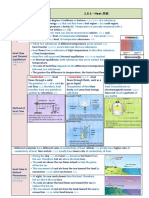
Temperature Scale Conversions (Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin)
Temperature may be expressed as C, F, or K. Most of the world uses C, though we use F in the USA. We can convert between these scales using the following info: 0C = 32F = 273K 1C = 1K 1C = 1.8F
remember this info and you dont need to memorize the equations below
These equations follow from the above info: F = 1.8 (C) + 32 K = 273 + (C) use to convert between F and C use to convert between C and K
Note the freezing point and boiling point of water in C, F, and K
Fahrenheit Celsius F C BPwater FPwater 212 32 100 0 -273
Kelvin K 373 273 0
Absolute -459.4 Zero
Why do we have the Kelvin scale? Absolute zero is the coldest theoretical temperature possible, all atoms and molecules would be absolutely motionless at 0K, though this temperature cant actually be reached.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chem3002-3-Stage and Continuous Gas Liquid Separation ProcessesDocument116 pagesChem3002-3-Stage and Continuous Gas Liquid Separation ProcessesJezreel CardinalesNo ratings yet
- Environment EconomicsDocument9 pagesEnvironment EconomicsUmar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Theories 1Document42 pagesAcid-Base Theories 1api-234133814No ratings yet
- Ps 5Document1 pagePs 5api-234133814No ratings yet
- Study Notes 6Document8 pagesStudy Notes 6api-234133814No ratings yet
- Study Notes 3Document6 pagesStudy Notes 3api-234133814No ratings yet
- Problem Set 5 StoichiometryDocument2 pagesProblem Set 5 Stoichiometryapi-234133814No ratings yet
- ps3 2013 14Document1 pageps3 2013 14api-234133814No ratings yet
- Study Notes 5Document5 pagesStudy Notes 5api-234133814No ratings yet
- Study Notes 2Document11 pagesStudy Notes 2api-234133814No ratings yet
- Study Notes 1Document5 pagesStudy Notes 1api-234133814No ratings yet
- Ps 2Document1 pagePs 2api-234133814No ratings yet
- Quick Sheets TAKS Review: Provided by G.I.S.D. Secondary ScienceDocument6 pagesQuick Sheets TAKS Review: Provided by G.I.S.D. Secondary ScienceuddinnadeemNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table W ElectronegativityDocument1 pagePeriodic Table W Electronegativityapi-234133814No ratings yet
- Brochure Stormaxx Solar Storage TanksDocument9 pagesBrochure Stormaxx Solar Storage Tankscherent alebelNo ratings yet
- GE T700 Gas Turbine Engine (Updated 7 - 22 - 2014)Document4 pagesGE T700 Gas Turbine Engine (Updated 7 - 22 - 2014)Habib ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 4 Way Reversing Valve Series SHF L Data PDFDocument3 pages4 Way Reversing Valve Series SHF L Data PDFDharani PathyNo ratings yet
- Cooling Coil - Refrigeration & Air Conditions - Stocker PDFDocument14 pagesCooling Coil - Refrigeration & Air Conditions - Stocker PDFAbed BaayounNo ratings yet
- Bimetallic Thermometer PDFDocument3 pagesBimetallic Thermometer PDFHesti Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Week 3: Assignment 3Document4 pagesUnit 4 - Week 3: Assignment 3Sankar SabarishNo ratings yet
- Past Present and Future Perspectives of Refrigerants in Air-Conditioning Refrigeration and Heat Pump ApplicationsDocument13 pagesPast Present and Future Perspectives of Refrigerants in Air-Conditioning Refrigeration and Heat Pump ApplicationsviclucNo ratings yet
- MECE2640 Chapter 3Document33 pagesMECE2640 Chapter 3colaarawrNo ratings yet
- Applied Systems: Pricelist 2018-2019Document73 pagesApplied Systems: Pricelist 2018-2019Aleksandar DutinaNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Applied Thermodynamics Course Code: 4051 Course Category: B Periods/Week: 5 Periods/Semester: 70 Credits: 5Document4 pagesCourse Title: Applied Thermodynamics Course Code: 4051 Course Category: B Periods/Week: 5 Periods/Semester: 70 Credits: 5VaisakVenugopalNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Optimization of Distillation Processes For Separating A Close-Boiling Mixture of N-Butanol and IsobutanolDocument6 pagesSimulation and Optimization of Distillation Processes For Separating A Close-Boiling Mixture of N-Butanol and IsobutanolZangNo ratings yet
- Gate Questions Bank ME HMTDocument4 pagesGate Questions Bank ME HMTTaanzNo ratings yet
- CalorimetryDocument55 pagesCalorimetryjaymart villartaNo ratings yet
- First Order de Problem Set 2010 Math 208Document3 pagesFirst Order de Problem Set 2010 Math 208Jen ChavezNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Flip CrystallizationDocument2 pagesProblem Set Flip CrystallizationSam Denielle TugaoenNo ratings yet
- ME 231 All Instructors Whharris 11-9-17SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesME 231 All Instructors Whharris 11-9-17SOLUTIONEstebanGiraldoNo ratings yet
- RAC SyllabusDocument2 pagesRAC SyllabusjaiNo ratings yet
- Tecumseh Guidelines For Utilization of R600A and R290.AshxDocument4 pagesTecumseh Guidelines For Utilization of R600A and R290.AshxVinod NairNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Freezing Faster Than ColdDocument10 pagesHot Water Freezing Faster Than ColdviiolettaNo ratings yet
- Apho2018 Theory Q3 Thermoelectricity Solution & Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesApho2018 Theory Q3 Thermoelectricity Solution & Marking SchemempecthNo ratings yet
- Gcesoln 7Document7 pagesGcesoln 7api-3734333No ratings yet
- Clausius-Clapeyron Equation: Liquid SolidDocument28 pagesClausius-Clapeyron Equation: Liquid SolidDiki AriNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT PHENOMENA ASSIGNMENT HEAT TRANSFER PROBLEMSDocument2 pagesTRANSPORT PHENOMENA ASSIGNMENT HEAT TRANSFER PROBLEMSNitish NehraNo ratings yet
- Indra: A - INST/K. Fujita 11-SEP-2018Document13 pagesIndra: A - INST/K. Fujita 11-SEP-2018med chabaneNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection & Air ConditioningDocument12 pagesFire Protection & Air ConditioningMUHAMMAD FARIS IQBAL BIN RIDUANNo ratings yet
- A Computational Model For The Prediction of Steel HardenabilityDocument12 pagesA Computational Model For The Prediction of Steel HardenabilityfdcarazoNo ratings yet
- Science - CM Chong: 2.9.1-HeatDocument2 pagesScience - CM Chong: 2.9.1-HeatChloe KhorNo ratings yet
- Turbo Expander FinalDocument25 pagesTurbo Expander Finalmohamed100% (2)