Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Keil Software
Uploaded by
sunnynnus100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views3 pagesKeil compiler is a software used where the machine language code is written and compiled. After compilation, the machine source code is converted into hex code which is to be dumped into the microcontroller for further processing.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKeil compiler is a software used where the machine language code is written and compiled. After compilation, the machine source code is converted into hex code which is to be dumped into the microcontroller for further processing.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views3 pagesKeil Software
Uploaded by
sunnynnusKeil compiler is a software used where the machine language code is written and compiled. After compilation, the machine source code is converted into hex code which is to be dumped into the microcontroller for further processing.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
KEIL SOFTWARE:
Keil compiler is a software used where the machine language code is written and
compiled. After compilation, the machine source code is converted into hex code which
is to be dumped into the microcontroller for further processing. Keil compiler also
supports C language code.
STEPS TO WRITE AN ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAM IN KEIL AND HOW TO COMPILE
IT:
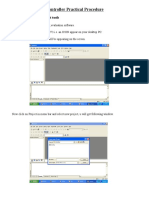
1. Install the Keil Software in the PC in any of the drives.
2. After installation, an icon will be created with the name “Keil uVision3”. Just
drag this icon onto the desktop so that it becomes easy whenever you try to write
programs in keil.
3. Double click on this icon to start the keil compiler.
4. A page opens with different options in it showing the project workspace at the
leftmost corner side, output window in the bottom and an ash coloured space for
the program to be written.
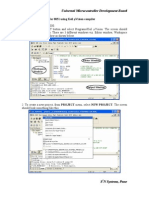
5. Now to start using the keil, click on the option “project”.
6. A small window opens showing the options like new project, import project, open
project etc. Click on “New project”.
7. A small window with the title bar “Create new project” opens. The window asks
the user to give the project name with which it should be created and the
destination location. The project can be created in any of the drives available. You
can create a new folder and then a new file or can create directly a new file.
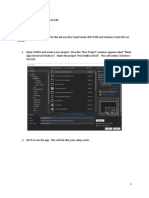
8. After the file is saved in the given destination location, a window opens where a
list of vendors will be displayed and you have to select the device for the target
you have created.
9. The most widely used vendor is Atmel. So click on Atmel and now the family of
microcontrollers manufactured by Atmel opens. You can select any one of the
microcontrollers according to the requirement.
10. When you click on any one of the microcontrollers, the features of that particular
microcontroller will be displayed on the right side of the page. The most
appropriate microcontroller with which most of the projects can be implemented
is the AT89C51. Click on this microcontroller and have a look at its features. Now
click on “OK” to select this microcontroller.
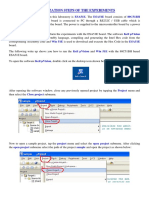
11. A small window opens asking whether to copy the startup code into the file you
have created just now. Just click on “No” to proceed further.
12. Now you can see the TARGET and SOURCE GROUP created in the project
workspace.
13. Now click on “File” and in that “New”. A new page opens and you can start
writing program in it.
14. After the program is completed, save it with any name but with the .asm
extension. Save the program in the file you have created earlier.
15. You can notice that after you save the program, the predefined keywords will be
highlighted in bold letters.
16. Now add this file to the target by giving a right click on the source group. A list of
options open and in that select “Add files to the source group”. Check for this file
where you have saved and add it.
17. Right click on the target and select the first option “Options for target”. A window
opens with different options like device, target, output etc. First click on “target”.
18. Since the set frequency of the microcontroller is 11.0592 MHz to interface with
the PC, just enter this frequency value in the Xtal (MHz) text area and put a tick
on the Use on-chip ROM. This is because the program what we write here in the
keil will later be dumped into the microcontroller and will be stored in the inbuilt
ROM in the microcontroller.
19. Now click the option “Output” and give any name to the hex file to be created in
the “Name of executable” text area and put a tick to the “Create HEX file” option
present in the same window. The hex file can be created in any of the drives. You
can change the folder by clicking on “Select folder for Objects”.
20. Now to check whether the program you have written is errorless or not, click on
the icon exactly below the “Open file” icon which is nothing but Build Target
icon. You can even use the shortcut key F7 to compile the program written.
21. To check for the output, there are several windows like serial window, memory
window, project window etc. Depending on the program you have written, select
the appropriate window to see the output by entering into debug mode.
22. The icon with the letter “d” indicates the debug mode.
23. Click on this icon and now click on the option “View” and select the appropriate
window to check for the output.
24. After this is done, click the icon “debug” again to come out of the debug mode.
25. The hex file created as shown earlier will be dumped into the microcontroller with
the help of another software called Proload.
You might also like
- Microcontroller Practical Procedure: Keil Software Development ToolsDocument5 pagesMicrocontroller Practical Procedure: Keil Software Development ToolsRicha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Creating HexDocument8 pagesCreating Hexkirwalegajanan1No ratings yet
- Keil Softwar1Document5 pagesKeil Softwar1Bhargavi BodigeNo ratings yet
- Study on KEIL μVISION5: EX NO: 01-b DateDocument2 pagesStudy on KEIL μVISION5: EX NO: 01-b DateThangaraj KNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2019Document15 pagesGetting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2019Zerihun BekeleNo ratings yet
- Mikroc Pro For Avr: Creating The First Project inDocument12 pagesMikroc Pro For Avr: Creating The First Project inadeelNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Keil Uvision CompilerDocument10 pagesGetting Started With Keil Uvision CompilerAshish PillaiNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemDocument165 pagesEmbedded SystemMuhammad Zeeshan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Mplab Xc8 Getting Started GuideDocument12 pagesMplab Xc8 Getting Started GuideTutorias CardonaNo ratings yet
- Using Pelles CDocument1 pageUsing Pelles CsunbeamNo ratings yet
- Creating A Console Project With Borland C++ CompilersDocument4 pagesCreating A Console Project With Borland C++ CompilersMike ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Proview TutorialDocument12 pagesProview TutorialManoel NascimentoNo ratings yet
- C++ With Visual BasicDocument10 pagesC++ With Visual BasicSovan PalNo ratings yet
- How To Work With Code Blocks - TutorialDocument17 pagesHow To Work With Code Blocks - TutorialSuraz Verma100% (1)
- Getting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2017Document17 pagesGetting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2017Zerihun BekeleNo ratings yet
- Kail StepsDocument12 pagesKail StepsVirenmsNo ratings yet
- 1st Project in MikrocDocument9 pages1st Project in Mikrocapi-195761152No ratings yet
- Getting Started With MASMDocument22 pagesGetting Started With MASMWilliam Smith100% (1)
- A Guide To Simulating and Programming PIC Microcontrollers Using The MPLAB IDE ProgramDocument7 pagesA Guide To Simulating and Programming PIC Microcontrollers Using The MPLAB IDE ProgramHarshal AmbatkarNo ratings yet
- Windows 10 UWP - Hands On Lab Lab 1Document10 pagesWindows 10 UWP - Hands On Lab Lab 1api-293252615No ratings yet
- Guide To Installation And Use Of Keil Μvision2 SoftwareDocument40 pagesGuide To Installation And Use Of Keil Μvision2 Softwareasma mushtaqNo ratings yet
- Micrcontroller Programming Using C With Keil IDEDocument2 pagesMicrcontroller Programming Using C With Keil IDERenganathan ThandavakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial WINCUPLDocument8 pagesTutorial WINCUPLAlex SandovalNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2012Document22 pagesGetting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2012jriver64No ratings yet
- Getting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2015Document29 pagesGetting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2015Hugo Betto Wilde Lunicer100% (1)
- Embedded CDocument60 pagesEmbedded CShamanthaka ManiNo ratings yet
- Create VB Net ProjectDocument23 pagesCreate VB Net ProjectAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- Le1 1Document12 pagesLe1 1Nivedita Acharyya 2035No ratings yet
- Opengl Using CodeblocksDocument9 pagesOpengl Using CodeblocksNomsa MwayengaNo ratings yet
- Initialization Steps of The Experiments: ESA51E ESA51E 80C51BHDocument12 pagesInitialization Steps of The Experiments: ESA51E ESA51E 80C51BHSaketh BoggavarapuNo ratings yet
- What You Need For This ProjectDocument14 pagesWhat You Need For This ProjectJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- Keil v5 FRDM KL25Z ProjectDocument16 pagesKeil v5 FRDM KL25Z ProjectDương Trương TấnNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Visual C++ 6.0 TutorialDocument26 pagesMicrosoft Visual C++ 6.0 Tutorialhalimsiddiq100% (1)
- EXPT-0-Introduction To KeilDocument4 pagesEXPT-0-Introduction To KeildharmaNo ratings yet
- CST2335 Lab1Document6 pagesCST2335 Lab1Nguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- Dev CDocument7 pagesDev CCody OrazNo ratings yet
- Borland Graphics ProjectDocument2 pagesBorland Graphics ProjectAnikethRameshNo ratings yet
- Keil User ManualDocument26 pagesKeil User ManualRohal SahuNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With WiFiMote ExamplesDocument9 pagesGetting Started With WiFiMote ExamplesDEEPAK PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Getting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2010Document22 pagesGetting Started With MASM and Visual Studio 2010jriver64No ratings yet
- Codeblock StepsDocument6 pagesCodeblock StepsDakshitaNo ratings yet
- 1st Project 8051 Basic v100Document12 pages1st Project 8051 Basic v100kywheat3306No ratings yet
- MPLab Tutorial v1Document45 pagesMPLab Tutorial v1ASIM RIAZNo ratings yet
- OpenVXML Without TearsDocument27 pagesOpenVXML Without TearsRashard Dyess-LaneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MFC ProgrammingDocument93 pagesIntroduction To MFC ProgrammingCremildo VascoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document9 pagesExperiment No 2Rohini BhadangeNo ratings yet
- 1st Project Pic Basic v101Document12 pages1st Project Pic Basic v101Geovanni ReyesNo ratings yet
- Installing SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinDocument9 pagesInstalling SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinOmotoyosi TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Installing SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinDocument9 pagesInstalling SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinOmotoyosi TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Masm ProceduresDocument9 pagesMasm ProceduressenthamilairmenNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals Lab 01 (Understanding and Installation of IDE)Document15 pagesProgramming Fundamentals Lab 01 (Understanding and Installation of IDE)Ahmad AbduhuNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic C++ 6Document17 pagesVisual Basic C++ 6Ashis Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Cloud Lab ManualDocument61 pagesCloud Lab ManualSathishk1982No ratings yet
- Project C Pro Pic v100Document12 pagesProject C Pro Pic v100adnene gharssallah100% (2)
- An Ultimate Guide to Kali Linux for BeginnersFrom EverandAn Ultimate Guide to Kali Linux for BeginnersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- C# For Beginners: An Introduction to C# Programming with Tutorials and Hands-On ExamplesFrom EverandC# For Beginners: An Introduction to C# Programming with Tutorials and Hands-On ExamplesNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic 6.0 Programming By Examples: 7 Windows Application ExamplesFrom EverandVisual Basic 6.0 Programming By Examples: 7 Windows Application ExamplesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CCC Exams PostponedDocument2 pagesCCC Exams PostponedsunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Defragmented File System DocumentationDocument63 pagesDefragmented File System DocumentationsunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Concepts and TechniquesDocument50 pagesData Mining: Concepts and TechniquessunnynnusNo ratings yet
- CseDocument95 pagesCseapi-3798998100% (2)
- Unit-1 Color Models in Image and VideoDocument58 pagesUnit-1 Color Models in Image and VideosunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Smart Vehicle Information Tracking System Introduction: Svits Is A MobileDocument2 pagesSmart Vehicle Information Tracking System Introduction: Svits Is A MobilesunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Concepts and TechniquesDocument70 pagesData Mining: Concepts and TechniquessunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques: Mining Association Rules in Large DatabasesDocument81 pagesData Mining: Concepts and Techniques: Mining Association Rules in Large DatabasessunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument10 pagesData MiningsunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Pro LoadDocument2 pagesPro Loadsunnynnus100% (2)
- 7 ClassificationDocument63 pages7 Classificationsunnynnus100% (1)
- CseDocument95 pagesCseapi-3798998100% (2)
- Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques: Cluster AnalysisDocument97 pagesData Mining: Concepts and Techniques: Cluster AnalysissunnynnusNo ratings yet
- LDR: LDRs or Light Dependent Resistors Are Very Useful EspeciallyDocument1 pageLDR: LDRs or Light Dependent Resistors Are Very Useful Especiallysunnynnus75% (4)
- AIM: 3. Create and Save AnXML Document at The Server, WhichDocument2 pagesAIM: 3. Create and Save AnXML Document at The Server, WhichsunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Port DescriptionDocument3 pagesPort DescriptionsunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Develop Static Pages (Using Only HTML) of An Online Book Store - The The Following PagesDocument9 pagesDevelop Static Pages (Using Only HTML) of An Online Book Store - The The Following PagessunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Aim: 6.implement The "Hello World!" Program Using JSP Struts Framework Procedure: Step 1Document5 pagesAim: 6.implement The "Hello World!" Program Using JSP Struts Framework Procedure: Step 1sunnynnusNo ratings yet
- Develop Static Pages (Using Only HTML) of An Online Book Store - The The Following PagesDocument8 pagesDevelop Static Pages (Using Only HTML) of An Online Book Store - The The Following PagessunnynnusNo ratings yet
- P 222Document16 pagesP 222sunnynnus100% (2)
- Redo The Previous Task Using JSP by Converting The Static Web Pages ofDocument18 pagesRedo The Previous Task Using JSP by Converting The Static Web Pages ofsunnynnus100% (2)
- P 222Document16 pagesP 222sunnynnus100% (2)
- P 44Document25 pagesP 44sunnynnus100% (2)
- CseDocument95 pagesCseapi-3798998100% (2)
- Chap03 3Document40 pagesChap03 3sunnynnus100% (2)
- CSCI 8150 Advanced Computer ArchitectureDocument46 pagesCSCI 8150 Advanced Computer Architecturesunnynnus100% (2)
- Btechcalender of II 2 IVDocument3 pagesBtechcalender of II 2 IVRambo IIINo ratings yet
- Btechcalender of II 2 IVDocument3 pagesBtechcalender of II 2 IVRambo IIINo ratings yet
- CSCI 8150 Advanced Computer ArchitectureDocument28 pagesCSCI 8150 Advanced Computer Architecturesunnynnus100% (2)
- Team Mate+AM+IT+Overview+12Document41 pagesTeam Mate+AM+IT+Overview+12epajueloNo ratings yet
- OD (In) Weight (PPF) I.D (In) Capacity (BPF)Document8 pagesOD (In) Weight (PPF) I.D (In) Capacity (BPF)Ebrahim SoleimaniNo ratings yet
- Table UCS-56-2 Postweld Heat Treatment Requirements For Carbon and Low Alloy Steels - P-No. 3Document7 pagesTable UCS-56-2 Postweld Heat Treatment Requirements For Carbon and Low Alloy Steels - P-No. 3MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Vladimir Lopez Stem Teacher ResumeDocument1 pageVladimir Lopez Stem Teacher Resumeapi-325782374No ratings yet
- Assignment On BTRC (Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission) Tools and Techniques.Document26 pagesAssignment On BTRC (Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission) Tools and Techniques.Mosabbir Ahmed0% (1)
- ModelsGuidelines v5Document37 pagesModelsGuidelines v5Martin NolanNo ratings yet
- Hse United Industrial Services Co Rev 02Document69 pagesHse United Industrial Services Co Rev 02Ahmad Zaid100% (1)
- Surdial Service Manual PDFDocument130 pagesSurdial Service Manual PDFHelpmedica IDI100% (1)
- A88JY ManualDocument6 pagesA88JY ManualionmocanuNo ratings yet
- Tabla 1-1 (W Shapes)Document17 pagesTabla 1-1 (W Shapes)Leonardo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Logic Families and Their Characteristics CharacteristicsDocument26 pagesLogic Families and Their Characteristics CharacteristicsanunilaNo ratings yet
- Execution Without ExcusesDocument16 pagesExecution Without ExcusesVishnu Menon100% (1)
- Novell Course 3076 SUSE Upgrading To Certified Linux Engineer 10Document362 pagesNovell Course 3076 SUSE Upgrading To Certified Linux Engineer 10Legioner LegionerovNo ratings yet
- McbcomDocument72 pagesMcbcomopenjavier5208No ratings yet
- BTICINO Catalog Matix PDFDocument80 pagesBTICINO Catalog Matix PDFsokolobanNo ratings yet
- 165 NebulizerDocument2 pages165 NebulizerLotfi BahriNo ratings yet
- 10 MIPS Floating Point ArithmeticDocument28 pages10 MIPS Floating Point ArithmeticHabibullah Khan MazariNo ratings yet
- 14 QuestionnaireDocument14 pages14 QuestionnaireEkta SinghNo ratings yet
- MotRadar System PrinciplesDocument26 pagesMotRadar System PrinciplesReadmotNo ratings yet
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Di Diesel Engine Fuelled With Camphor Oil-Diesel BlendsDocument4 pagesPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Di Diesel Engine Fuelled With Camphor Oil-Diesel BlendsRam KrishNo ratings yet
- HRTC RoutesDiverted Via KiratpurManali Four LaneDocument9 pagesHRTC RoutesDiverted Via KiratpurManali Four Lanepibope6477No ratings yet
- Pre-Disciplinary and Post-Disciplinary Perspectives: Bob Jessop & Ngai-Ling SumDocument13 pagesPre-Disciplinary and Post-Disciplinary Perspectives: Bob Jessop & Ngai-Ling SumMc_RivNo ratings yet
- Assessment PlanDocument2 pagesAssessment Planapi-282348214No ratings yet
- Technical Data - Fan Model ECE152SM: Location: Designation: Performance - Required ActualDocument2 pagesTechnical Data - Fan Model ECE152SM: Location: Designation: Performance - Required ActualJNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Management 120A Intermediate Accounting - Spring 2009Document6 pagesSyllabus For Management 120A Intermediate Accounting - Spring 2009John KimNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Applying Innovation Strategies in The Public SectorDocument21 pagesUnderstanding and Applying Innovation Strategies in The Public SectorEda Paje AdornadoNo ratings yet
- 04 Cuculic Celic PrencDocument8 pages04 Cuculic Celic PrencStanislava RokvicNo ratings yet
- Ion PropulsionDocument24 pagesIon PropulsionHarish TalluriNo ratings yet
- Dlms DocumentDocument71 pagesDlms DocumentSudarshan ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Exercises SolutionsDocument13 pagesA Exercises SolutionsuxNo ratings yet