Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Minor Disorders of Newborn and Its Management
Uploaded by
arun261988Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Minor Disorders of Newborn and Its Management
Uploaded by
arun261988Copyright:
Available Formats
MINOR DISORDERS OF NEWBORN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Molding The head may appear asymmetric in the newborn of a vertex
ewborn of a vertex birth. Caused by the overriding of the cranial bones during labor and birth. Dimnishes within few days after birth. Head moulding Cephalhematoma Collection of blood between the cranial bone and the periosteal membrane Unilateral or bilateral and do not cross suture lines Disappear with in 2 to 3 weeks Caput succedaneum Collection of fluid between the periosteum and the scalp Overrides suture line Present at birth Caput Forceps and Vacuum marks Reddened areas over the cheeks and jaws. Disappear with in 1 or 2 days. Vacuum extractor suction marks on the scalp. No treatment is necessary Telangiectati nevi Pale pink or red spots frequently found on the eyelids, nose, lower occipital bone and nape of the neck. More noticeable during the periods of crying. Fade by the second birthday. Telangiectati stork bite Stuffy nose It may lead to mouth breathing and excessive air swallowing which may lead to abdominal distention and vomiting. Management : The nostrils may be cleansed with cotton wool soaked with normal saline. Sticky eyes It may be due to a chemical irritant or bacterial conjunctivitis due to Staphylococcus. Erythromycin (0.5%) ointment every 6 hrs for 7-10 days. Subconjunctival hemorrhage Found on the sclera Caused by the changes in vascular tension or ocular pressure during birth
Remain for a few weeks Reassure the parents Oral Thrush 1% gentian violet solution or nystatin suspension, applied to each side of the mouth with a cotton swab 3-4 times a day. Oral thrush/ Epsteins pearls Milia Exposed sebaceous glands, appear as raised white spots on the face, especially across the nose. No treatment is necessary, because they clear up spontaneously with in the first month Erythema toxicum Perifollicular eruption of lesions that are firm, vary in size from 1 to 3mm and consist of white or pale yellow papule or pustule with an erythematous base. It is often called newborn rash or flea bite dermatitis. No treatment is necessary. Disappear in a few hours or days. Napkin rash More common in artificially fed babies. It can be prevented by frequent care and attention to the napkin area along with immediate changes of the napkins after each soiling. Perianal dermatitis It is situated around the anal opening. It is due to the alkalinity of the stool and also seen in artificially fed babies. Management: Use of lactose, instead of glucose. Congenital phymosis Pinpoint prepuce which makes the baby cry during the act of micturition. Management: dilatation by mosquito forceps. Pseudomenstruation Thick, whitish mucus vaginal discharge which is tinged with blood. Caused by the withdrawal of maternal hormones Smegma White cheese like substance is often present between the labia Physiological jaundice This is observed in 60% of term and 80% of preterm neonates. Occurs after the first 24 hours of life. Resolves with hydration and frequent feedings Constipation
It is commonly met in artificially fed babies. Management : Correction of the diet and extra water is usually effective. If it fails, milk of magnesia 4ml by mouth is effective. Mangolian spot Macular areas of bluish black or gray- blue pigmentation on the dorsal area and the buttocks. Fade during the first or second year of life. Nevus flammeus Port wine stain Red to purple area of dense capillaries Commonly appears on the face Cosmetic cream Nevus vasculosus Strawberry mark Raised, clearly declined, dark red, rough surfaced birth mark usually found in the head region It resolves spontaneously
You might also like
- STAGES OF LABOURDocument37 pagesSTAGES OF LABOURJude Martin100% (1)
- Elderly PrimiDocument7 pagesElderly PrimiAnnapurna Dangeti67% (3)
- First Stage of Labour ExplainedDocument5 pagesFirst Stage of Labour ExplainedSucharita PandaNo ratings yet
- Managing Obstetrical Emergencies & Its ChallengesDocument58 pagesManaging Obstetrical Emergencies & Its Challengessanthiyasandy100% (1)
- New High RiskDocument75 pagesNew High RiskNeha ThemystryNo ratings yet
- Prolong LabourDocument5 pagesProlong LabourNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Uterine MalformationsDocument6 pagesUterine MalformationssubashikNo ratings yet
- Management of Woman During First Stage of Labour Management of Woman During First Stage of LabourDocument21 pagesManagement of Woman During First Stage of Labour Management of Woman During First Stage of LabourKinjal Vasava67% (3)
- Puerperium and Its Management 1Document35 pagesPuerperium and Its Management 1Elvis100% (2)
- Iugr FinalDocument35 pagesIugr Finalsanthiyasandy100% (3)
- Birth Canal Injuries: Causes, Types, Prevention and ManagementDocument67 pagesBirth Canal Injuries: Causes, Types, Prevention and ManagementnamitaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument96 pagesAbnormal Uterine ActionN. Siva100% (2)
- Physiological Processes in Second Stage of LabourDocument32 pagesPhysiological Processes in Second Stage of Labournamita100% (1)
- Obstructed LabourDocument11 pagesObstructed Labourabhay jain100% (2)
- Cephalo Pelvic DispoportionDocument12 pagesCephalo Pelvic DispoportionN. Siva100% (1)
- Newborn Adaptation FinalDocument28 pagesNewborn Adaptation Finalsanthiyasandy91% (11)
- Definition of Contracted Pelvis and Factors Affecting LabourDocument19 pagesDefinition of Contracted Pelvis and Factors Affecting LabourAuri SururyNo ratings yet
- IUGRDocument11 pagesIUGRAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Complication of 3rd Stage PPHDocument13 pagesSeminar On Complication of 3rd Stage PPHjuhi labana0% (1)
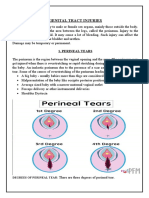
- Genital Tract InjuriesDocument19 pagesGenital Tract InjuriesMarvella Nongkhar100% (1)
- INDUCTION OF LABOUR: METHODS & PROTOCOLSDocument8 pagesINDUCTION OF LABOUR: METHODS & PROTOCOLSgeorgeloto12100% (1)
- Elderly Primigravida, Adolescent Pregnancy, Grand MultiparaDocument3 pagesElderly Primigravida, Adolescent Pregnancy, Grand MultiparamercyNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labour Seminar: Malpositions & MalpresentationsDocument40 pagesAbnormal Labour Seminar: Malpositions & MalpresentationsMonika Bagchi100% (4)
- Obg - 15.4.20 (Afternoon) Unit 10 - Birth InjuriesDocument102 pagesObg - 15.4.20 (Afternoon) Unit 10 - Birth InjuriesElakkiyaanu64 Elakkiyaanu64100% (3)
- Normal PuerperiumDocument3 pagesNormal PuerperiumarunshreerajendranNo ratings yet
- Breast Complications in PuerperiumDocument24 pagesBreast Complications in Puerperiumvincentsharon100% (9)
- PRO Post Natal AssessmentDocument9 pagesPRO Post Natal AssessmentMali KanuNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LabourDocument18 pagesMechanism of LabournamithaNo ratings yet
- Assessing High-Risk Newborns (AHRNDocument76 pagesAssessing High-Risk Newborns (AHRNEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- Management of LabourDocument16 pagesManagement of LabourAlbert MusinguziNo ratings yet
- Cervical DystociaDocument22 pagesCervical DystociaBaldau TiwariNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes of Pregancy. NEW VERSION-For BSC Nursing StudentsDocument107 pagesPhysiological Changes of Pregancy. NEW VERSION-For BSC Nursing StudentsKripa Susan100% (2)
- Abnormalities of Amniotic FluidDocument27 pagesAbnormalities of Amniotic FluidRukmini kakatikar0% (1)
- Birth InjuriesDocument13 pagesBirth InjuriesLekshmi Manu100% (1)
- Seminar On Various Child Birth Practice, PositionDocument26 pagesSeminar On Various Child Birth Practice, PositionPiyush Dutta100% (1)
- OccipitoposteriorDocument11 pagesOccipitoposteriorVijith.V.kumar100% (1)
- Cephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted PelvisDocument45 pagesCephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted Pelvisbinipsamuel250% (1)
- Planned ParenthoodDocument34 pagesPlanned Parenthoodvincentsharon80% (5)
- Prolonged Labour: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument24 pagesProlonged Labour: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Puerperal Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary EmbolismDocument14 pagesPuerperal Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary EmbolismSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiNo ratings yet
- The Role of Magnesium Sulphate in Obstetrics: by Sneha Sehrawat M. C Nursing I YearDocument18 pagesThe Role of Magnesium Sulphate in Obstetrics: by Sneha Sehrawat M. C Nursing I YearRajaNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical Complication in PregnancyDocument29 pagesMedical and Surgical Complication in PregnancyVictor-Gabriel Rugina0% (1)
- Antenatal CareDocument3 pagesAntenatal CareAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Obs Vaginal ExaminationDocument15 pagesObs Vaginal Examinationaparna shamaNo ratings yet
- PRECONCEPTION CARE & PLANNED PARENTHOODDocument7 pagesPRECONCEPTION CARE & PLANNED PARENTHOODDelphy Varghese86% (7)
- Thromboembolic DisordersDocument11 pagesThromboembolic Disordersannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Minor Disorders of PregnancyDocument28 pagesMinor Disorders of PregnancyAbdullahi Suleiman Maka100% (1)
- Manual Removal of PlacentaDocument10 pagesManual Removal of PlacentaSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Face Presentation: Diagnosis, Mechanism and ManagementDocument6 pagesFace Presentation: Diagnosis, Mechanism and ManagementNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Practical - 7 Antenatal ClinicDocument17 pagesPractical - 7 Antenatal ClinicSujatha J JayabalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Puerperium and LactationDocument34 pagesPhysiology of Puerperium and LactationKholoud Kholoud100% (3)
- Female PelvisDocument4 pagesFemale PelvisAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument44 pagesPhysiological Changes During PregnancyvrutipatelNo ratings yet
- Management of PuerperiumDocument22 pagesManagement of Puerperiumannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Appearance of A NewbornDocument33 pagesAppearance of A NewbornGeguirra, Michiko SarahNo ratings yet
- Minor Disorders of The NewbornDocument2 pagesMinor Disorders of The NewbornMandeep Kaur50% (2)
- Common Neonatal Problems - 085835Document39 pagesCommon Neonatal Problems - 085835Jack AdamNo ratings yet
- MCN NBDocument6 pagesMCN NBJudy BaguiwenNo ratings yet
- Labour and Material: Building ConstructionDocument2 pagesLabour and Material: Building Constructionarun261988No ratings yet
- Indian CultureDocument13 pagesIndian Culturearun261988No ratings yet
- Indian CultureDocument13 pagesIndian Culturearun261988No ratings yet
- Indian CultureDocument13 pagesIndian Culturearun261988No ratings yet
- Low BirthweightDocument7 pagesLow Birthweightarun261988No ratings yet
- Mukti Accounting bill for EPF digital signature chargesDocument1 pageMukti Accounting bill for EPF digital signature chargesarun261988No ratings yet
- Indian CultureDocument13 pagesIndian Culturearun261988No ratings yet
- Indian CultureDocument13 pagesIndian Culturearun261988No ratings yet
- Mukti Accounting bill for EPF digital signature chargesDocument1 pageMukti Accounting bill for EPF digital signature chargesarun261988No ratings yet
- Udavi SchoolDocument2 pagesUdavi Schoolarun261988No ratings yet
- Swami VivekanandaDocument6 pagesSwami Vivekanandaarun261988No ratings yet
- Tailors Time Chart-ProductionDocument11 pagesTailors Time Chart-Productionarun261988No ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument4 pagesProblemsarun261988No ratings yet
- Emerging Importance Social Marketing: AbstractDocument10 pagesEmerging Importance Social Marketing: Abstractarun261988No ratings yet
- AnanmalaiDocument3 pagesAnanmalaiarun261988No ratings yet
- HML AnalysisDocument2 pagesHML Analysisarun261988No ratings yet
- WCDocument5 pagesWCarun261988No ratings yet
- Indian Capital Market StructureDocument5 pagesIndian Capital Market Structurearun261988No ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Labor Relations Process 10th Edition HolleyDocument36 pagesTest Bank For The Labor Relations Process 10th Edition Holleyjakraging7odbt100% (43)
- Revista Latinoamericana de Psicología 1979 article on social behaviorismDocument39 pagesRevista Latinoamericana de Psicología 1979 article on social behaviorismMarco GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Radiographic InterpretationDocument104 pagesPrinciples of Radiographic InterpretationPraney SlathiaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating rational fears and bizarre delusions in paranoiaDocument7 pagesEvaluating rational fears and bizarre delusions in paranoiaSandraNo ratings yet
- De Leon v. MaunladDocument4 pagesDe Leon v. MaunladTibsNo ratings yet
- Virgin Media CaseDocument18 pagesVirgin Media CaseRiaz AttrashNo ratings yet
- Developmental Dysplasia of The HipDocument16 pagesDevelopmental Dysplasia of The Hipjonathan_alvaNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Health and Social Care PackDocument735 pagesLevel 3 Health and Social Care PackGeorgiana Deaconu100% (4)
- Management Principles ExampleDocument55 pagesManagement Principles ExampleAnonymous PcPkRpAKD5No ratings yet
- Boston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire BCTQDocument2 pagesBoston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire BCTQElsye Lalupanda75% (4)
- PHARMACEUTICAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY: Radiopharmaceuticals: December 2017Document7 pagesPHARMACEUTICAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY: Radiopharmaceuticals: December 2017pankaj dagurNo ratings yet
- ID Senyawa Goitrogenik Dalam Bahan MakananDocument4 pagesID Senyawa Goitrogenik Dalam Bahan MakananSindi MegaNo ratings yet
- Volume 1. No.1 Tahun 2019, e-ISSN:: ST STDocument10 pagesVolume 1. No.1 Tahun 2019, e-ISSN:: ST STDicky CaritoNo ratings yet
- Jaw RelationsDocument44 pagesJaw Relationsjquin3100% (1)
- Appendix II DNV-M-scatDocument1 pageAppendix II DNV-M-scatGökhan Ulukuz100% (1)
- HattttDocument15 pagesHattttFrences Ann VillamorNo ratings yet
- COPD and asthma global burden 1990-2015Document3 pagesCOPD and asthma global burden 1990-2015yumna yumenNo ratings yet
- Urban HydrologyDocument39 pagesUrban Hydrologyca rodriguez100% (1)
- Cold Laser: Dr. Amal Hassan MohammedDocument46 pagesCold Laser: Dr. Amal Hassan MohammedAmal IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1st Hrpta AgendaDocument3 pages1st Hrpta AgendaJomarNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintenance Manual R1600G Load Haul Dump PDFDocument196 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual R1600G Load Haul Dump PDFDavid Garcia100% (2)
- Rachael Lewkowiez Resume 7 14 17Document3 pagesRachael Lewkowiez Resume 7 14 17api-364212510No ratings yet
- Okamura 1999Document4 pagesOkamura 1999Araceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- Gait Abnormalities and Pediatric Orthopedic ConditionsDocument10 pagesGait Abnormalities and Pediatric Orthopedic ConditionsRajan PatelNo ratings yet
- Note 13 - Grievance & DisciplineDocument3 pagesNote 13 - Grievance & DisciplineVishesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Oral Pathology-Anil G. Ghom, S. Mhaske (2013)Document1,050 pagesTextbook of Oral Pathology-Anil G. Ghom, S. Mhaske (2013)Khánh Vũ100% (2)
- CBR Guidelines 1st Meeting ReportDocument26 pagesCBR Guidelines 1st Meeting ReportJeffery SamuelNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Article Parents' Receptiveness and Teachers' Readiness in Teaching Sexuality Education in Grade School.Document5 pagesA Review On The Article Parents' Receptiveness and Teachers' Readiness in Teaching Sexuality Education in Grade School.Diane KintaoNo ratings yet
- Soap For Follow On Hiv-Aids #7Document2 pagesSoap For Follow On Hiv-Aids #7carlos fernandezNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument6 pagesJournalkhaiz_142989No ratings yet