Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Set 1 (Unit 2)
Uploaded by
Tare Er KshitijOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Set 1 (Unit 2)
Uploaded by
Tare Er KshitijCopyright:
Available Formats
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.
P)
SET 1 OF 2 (UNIT 2) PROBLEM 1:- A rectangular bar of cross-sectional area 10000mm2 is subjected to an axial load of 20kN. Determine the normal and shear stresses on a section which is inclined at an angle of 300 with normal cross-section of the bar. (Answer: - n= 1.5N/mm2, =0.866N/mm2) PROBLEM 2:- A circular bar is subjected to an axial pull of 100kN. If the maximum intensity of shear stress on any oblique plane is not to exceed 60MN/m2, determine the diameter of the bar. (Answer: - 32.6mm) PROBLEM 3:- A short metallic column of 500mm2 cross-sectional area carries an axial compressive load of 100kN. For a plane inclined at 600 with the direction of load, calculate (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) Normal stress. Tangential stress. Resultant stress. Maximum shear stress. Obliquity of the resultant stress.
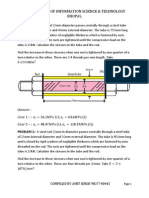
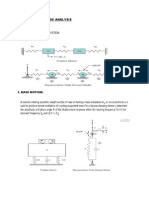
(Answer: - 150.1MN/m2 (c), 86.6MN/m2 (shear), 173.29MN/m2 (c), 100MN/m2, 300) PROBLEM 4:- Find the diameter of a circular bar which is subjected to an axial pull of 160kN, if the maximum allowable shear stress on any section is 65N/mm2. (Answer: - d=39.58mm) PROBLEM 5:- Two wooden pieces in cross-section are glued together along line AB as shown. What maximum axial force P can be applied if the allowable shearing stress along AB is 1.2N/mm2?
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 1
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
(Answer: - P=27.71kN) PROBLEM 6:- A rectangular bar of cross-sectional area of 11000mm2 is subjected to a tensile load P as shown. The permissible normal and shear stresses on the oblique plane BC are given as 7N/mm2 and 3.5N/mm2 respectively. Determine the safe value of P.
(Answer: - P=88.913kN) PROBLEM 7:- A prismatic bar carrying an axial tensile stress is cut by an oblique section LM as shown. If the normal and shear stresses on this section are 90MN/m2 and 30MN/m2 respectively. Find the value of and the angle defining the aspect of section LM.
(Answer: -
94.87MN/m2, =71033)
Page 2
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
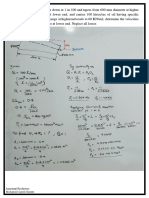
PROBLEM 8:- The principal stresses at a point across two perpendicular planes are 75MN/m2 (tensile) and 35MN/m2 (tensile). Find the normal, tangential stresses and the resultant stress and its obliquity on a plane at 200 with the major principal plane.
(Answer: ) PROBLEM 9:- The principal stresses in the wall of a container are 40MN/m2 and 80MN/m2. Determine the normal, shear and resultant stresses in magnitude and direction in a plane, the normal of which makes an angle of 300 with the direction of maximum principal stress. (Answer: PROBLEM 10:- The tensile stresses at a point across two mutually perpendicular planes are 120N/mm2 and 60N/mm2. Determine the normal tangential and resultant stresses on a plane inclined at 300 to the axis of minor stress. (Answer: - n = 105N/mm2, t = 25.98 N/mm2, R = 108.16 N/mm2) PROBLEM 11:- The stresses at a point in a bar are 200 N/mm2 (tensile) and 100 N/mm2 (compressive). Determine the resultant stress in magnitude and direction on a plane inclined at 600 to the axis of the major stress. Also determine the maximum intensity of shear stress in the material at the point. (Answer: - R =180.27 N/mm2, =4606, (t)max =150 N/mm2)
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com) Page 3
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
PROBLEM 12:- A point is subjected to perpendicular stresses of 50MN/m2 and 30MN/m2, both tensile. Calculate the normal, tangential stresses and the resultant stress and its obliquity on a plane making an angle of 300 with the axis of second stress. (Answer: )
PROBLEM 13:- Draw the Mohrs stress circle for direct stresses of 65MN/m2 (tensile) and 35MN/m2 (compressive) and estimate the magnitude and direction of the resultant stresses on planes making angles of 200 and 650 with the plane of the first principal stress. Find also the normal and tangential stresses on these planes. Answer: CASE 1 (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (t) (shear) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) CASE 2 (c) (shear)
PROBLEM 14:- At a point in a strained material the principal stresses are 100N/mm2 (tensile) and 60 N/mm2 (compressive). Determine the normal stress, shear stress and resultant stress on a plane inclined at 500 to the axis major principal stress. Also determine the maximum shear stress at the point. (Answer: - n = 33.89 N/mm2, t =78.78 N/mm2, R = 85.76 N/mm2, (t)max= 80 N/mm2) PROBLEM 15:- At a point in a strained material, the principal stresses are 100N/mm2 (tensile) and 40 N/mm2 (compressive). Determine the resultant stress in magnitude and direction on a plane inclined at 600 to the axis of the major
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 4
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
principal stress. What is the maximum intensity of shear stress in the material at the point? (Answer: - n = 65 N/mm2, t =60.62 N/mm2, R =88.9 N/mm2, =430(t)max= 70 N/mm2) PROBLEM 16:- A small block is 4cm long, 3cm high and 0.5cm thick. It is subjected to uniformly distribute tensile forces of resultants 1200N and 500N as shown. Compute the normal and shear stresses developed along the diagonal AB.
(Answer: n = 448.65N/cm2, t = 264.18N/cm2) PROBLEM 17:- At a point in a strained material the principal tensile stresses across two perpendicular planes, are 80 N/mm2 and 40 N/mm2. Determine normal stress, shear stress and the resultant stress on a plane inclined at 200 with the major principal plane. Determine also the obliquity. What will be the intensity of stress, which acting alone will produce the same maximum strain if Poissons ratio= . (Answer: - =75.32 N/mm2, =70 N/mm2) 12.86 N/mm2, 76.4 N/mm2, () = 9041,
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 5
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
PROBLEM 18:- The principal tensile stresses at a point across two perpendicular planes are 120MN/m2 and 60MN/m2. Find (i) (ii) The normal and tangential stress and the resultant stress and its obliquity on a plane at 200 with the major principal plane. The intensity of stress which acting alone can produce the same maximum strain. Take Poissons ratio=1/4.
(Answer: =105MN/m )
2
(t),
(shear),
PROBLEM 19:- The principal stresses acting on an element subjected to plane stresses are 12 and 4.5MN/m2 (both tensile). Find out the position of the plane AA when the resultant stress makes the maximum angle with the normal to the plane.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 6
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
(Answer: - =270) PROBLEM 20:- A piece of material is subjected to two compressive stresses at right angles, their values being 40MN/m2 and 60MN/m2. Find the position of the plane across which the resultant stress is most inclined to the normal, and determine the value of this resultant stress. (Answer: -=11032, , =39014)
PROBLEM 21:- At a point in a bracket the stresses on two mutually perpendicular planes are 35MN/m2 (tensile) and 15MN/m2 (tensile). The shear stress across these planes is 9MN/m2. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant stress on a plane making an angle of 400 with the plane of first stress. Find also the normal and tangential stresses on the plane. (Answer: (t), (shear), )
PROBLEM 22:- When a certain thin walled tube is subjected to internal pressure and torque the stresses in the tube wall are (a) 120MN/m2 (tensile) (b) 60MN/m2 in the direction of (a) and (b). (i) (ii) Calculate the normal and tangential stresses on the two planes which are equally inclined to (a) and (b). What are the results if due to an end thrust; (b) is compressive, (a) and (c) being unchanged.
Page 7
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
Answer: CASE 1: =450 (i) (ii) (t) (shear) (i) (ii) =1350 (t) (shear)
CASE 2: In the case with end thrust: =450 (i) (ii) (t) (i) (ii) =1350 (t)
PROBLEM 23:- At a point within a body subjected to two mutually perpendicular direction, the stresses are 80N/mm2 tensile and 40N/mm2 tensile. Each of the above stresses is accompanied by shear stress of 60N/mm2. Determine the normal stress, shear stress and resultant stress on an oblique plane inclined at an angle of 450 with the axis of minor tensile stress. (Answer: - n = 120N/mm2, t = 20N/mm2, R = 121.655N/mm2) PROBLEM 24:- A rectangular block of material is subjected to tensile stress of 110N/mm2 on one plane and a tensile stress of 47N/mm2 on the other plane at right angles to the former. Each of the above stresses is accompanied by a shear stress of 63N/mm2 and that associated with the former tensile stress tends to rotate the block anticlockwise. Find:
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com) Page 8
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
(i) (ii) The direction and magnitude of each of the principal stress and Magnitude of the greatest shear stress.
(Answer: - 1 = 148.93N/mm2, 2 = 8.064N/mm2, =31043, 121043, max = 70.43N/mm2) PROBLEM 25:- At a point in a material there is a tensile stress of 90MN/m2 upon the horizontal plane, and compressive stress of 45MN/m2 upon the vertical plane. There is also a shear stress of 45MN/m2 on each of these planes. Determine the planes of maximum shear stress and value of maximum shear stress at a point from the first principles. (Answer: - =61051, )
PROBLEM 26:- An element in a stressed material has tensile stress of 500MN/m2 and a compressive stress of 350MN/m2 acting on two mutually perpendicular planes and equal shear stresses of 100MN/m2 on these planes. Find the principal stresses and position of the principal planes. Find also maximum shearing stress. (Answer: (t), ) (c),
PROBLEM 27:- Direct stresses of 120N/mm2 tensile and 90N/mm2 compression exist on two perpendicular planes at a certain point in a body. They are also accompanied by shear stress on the planes. The greatest principal stress at the point due to these is 150N/mm2. (a) What must be the magnitude of the shearing stresses on the two planes? (b) What will be the maximum shearing stress at the point? (Answer: - 84.85N/mm2, 135N/mm2) PROBLEM 28:- At a point in a bracket the stresses on two mutually perpendicular planes are 400MN/m2 tensile and 300MN/m2 tensile. The shear stress across these planes is 200MN/m2. Determine graphically or otherwise the magnitude and directions of principal stresses and maximum shear stress.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com) Page 9
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
(Answer: ) PROBLEM 29:- At a certain point in a strained material, the stresses on two planes, at right angles to each other are 20N/mm2 and 10N/mm2 both tensile. They are accompanied by a shear stress of a magnitude of 10N/mm2. Find graphically or otherwise, the location of principal planes and evaluate the principal stresses. (Answer: - = 31043, 1 = 26.18N/mm2, 2 = 3.82N/mm2) PROBLEM 30:- The state of stress at a point of a machine is shown. Determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stress and its inclination. (t), (c), , ,
(Answer: -
(t), )
(c),
PROBLEM 31:- Direct stresses of 120MN/m2 in tension and 90MN/m2 in compression are applied to an elastic material at a certain point on planes at right angles to another. If the maximum principal stress is not to exceed 150MN/m2 in tension, to what shearing stress can be material be subjected? What is then the maximum resulting shearing stress in the material?
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com) Page 10
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
Also find the magnitude of the other principal stress and its inclination to 120MN/m2 stress. (Answer: (shear), (c), )
PROBLEM 32:- Two mutually perpendicular planes of an element of material are subjected to direct stresses of 10.5MN/m2 (tensile) and 3.5MN/m2 (compressive) and shear stress of 7MN/m2. Find graphically or otherwise: (i) (ii) The magnitude and direction of principal stress, and Magnitude of the normal and shear stresses on a plane on which the shear stress is maximum. (t), ) PROBLEM 33:- The normal stress in two mutually perpendicular directions are 600N/mm2 and 300N/mm2 both tensile. The complimentary shear stresses in these directions are of intensity 450N/mm2. Find the normal and tangential stresses on the two planes which are equally inclined to the planes carrying the normal stresses mentioned above. Answer: (i) Normal stress (a) When =45, 900N/mm2 (b) When =135, 0N/mm2 Tangential stress (a) When =45, 150N/mm2 (b) When =135, -150N/mm2 (c),
(Answer: -
(ii)
PROBLEM 34:- A point in a strained material is subjected to the stresses as shown in the figure. Locate the principal planes, and evaluate the principal stresses.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 11
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
(Answer: -=39021 or 129021, 1 = 76.58N/mm2, 2 =15.38N/mm2) PROBLEM 35:- The intensity of the resultant stress on the plane AB at a point in the material under stress is 800N/cm2 and it is inclined at 300 to the normal to the plane. The normal component of stress on another plane BC at right angles to plane AB is 600N/cm2. Determine the following: (i) (ii) (iii) The resultant stress on the plane BC, The principal stresses and their directions The maximum shear stresses and their planes.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 12
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
Answer: (i) (ii) (iii) Resultant stress on the plane=721N/cm2, =56.30 with the horizontal. 1049.09N/cm2 (t), 243.73N/cm2 (t), =41.690, =131.990 Maximum shear stress= 402.68N/cm2
PROBLEM 36:- At a certain point in a material under stress the intensity of the resultant stress on a vertical plane is 1000N/cm2 inclined at 300 to the normal to the plane and the stress on a horizontal plane has a normal tensile component of intensity 600N/cm2 as shown. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant stress on the horizontal plane and the principal stresses.
(Answer: -R= 781.02N/cm2, =50.190, 1 = 1250.38N/cm2, 2 =215.62N/cm2) PROBLEM 37:- At a point in a strained material, on plane BC there are normal and shear stresses of 560N/mm2 and 140N/mm2 respectively. On plane AC, perpendicular to plane BC, there are normal and shear stresses of 280N/mm2 and 140N/mm2 respectively as shown in the figure. Determine the following (i) (ii) Principal stresses and location of the planes on which they act, Maximum shear stress and the plane on which it acts.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 13
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
Answer: (i) (ii) 582.7N/mm2 (t), -302.7N/mm2, =80.670 and =170.670 442.7N/mm2, =35.780 and =125.780
PROBLEM 38:- At a point in a material under stress, the intensity of the resultant stress on a certain plane is 50MN/m2 (tensile) inclined at 300 to the normal of that plane. The stress on a plane at right angles to this has a normal tensile component of intensity of 30MN/m2. Find (i) (ii) (iii) The resultant stress on the second plane. The principal planes and stresses. The plane of maximum shear and its intensity.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 14
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
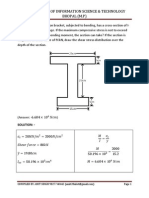
(Answer: (t) 82032) PROBLEM 39:- The state of stress at a point is shown in the figure. Determine the normal and shear stresses acting on the vertical plane using transformation equation. (t),
(Answer: -
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 15
You might also like
- Geo - Technical Engineering Question Bank by MR Sukriti DanDocument13 pagesGeo - Technical Engineering Question Bank by MR Sukriti Dansukritidan1990100% (1)
- Examples, Stress Due To Rotation and Temp.Document22 pagesExamples, Stress Due To Rotation and Temp.Addisu Ayele100% (1)
- Set 6Document15 pagesSet 6Tare Er Kshitij60% (5)
- Centrifugal Pumps BasicsDocument23 pagesCentrifugal Pumps BasicsalibahcesarayNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity by Sadhu SinghDocument7 pagesTheory of Elasticity by Sadhu Singhotonbara14% (7)
- Contact Mechanics-Barber (2018)Document592 pagesContact Mechanics-Barber (2018)Peixianjun Pei100% (3)
- Mass MIDocument12 pagesMass MIGanesh Yadav67% (3)
- MCQ - Slope and Deflection - ME Subjects - Concepts SimplifiedDocument6 pagesMCQ - Slope and Deflection - ME Subjects - Concepts SimplifiedrajkumarNo ratings yet
- Set 2 (Unit 2)Document13 pagesSet 2 (Unit 2)Tare Er Kshitij70% (10)
- Stresses and Strains in Composite BarsDocument17 pagesStresses and Strains in Composite BarsSuresh Khangembam100% (1)
- ST7103-Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesST7103-Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Question Bank PDFNiranjan Shuttler Craze100% (1)
- Equivalent Single Wheel LoadDocument12 pagesEquivalent Single Wheel LoadRajesh Khadka100% (1)
- Exercises On Fracture MechanicsDocument33 pagesExercises On Fracture Mechanicsyaswanth199260% (5)
- Design of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Blades (Chapter 3)Document10 pagesDesign of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Blades (Chapter 3)Htet Myet AgNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Bending Stress in Beam - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument37 pagesStrength of Materials - Bending Stress in Beam - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz Ameen88% (26)
- Farhan Akhtar Poem From ZNMDDocument3 pagesFarhan Akhtar Poem From ZNMDTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Theory of Simple Bending - Full1Document62 pagesTheory of Simple Bending - Full1Rahul KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- 1984 JN Reddy A Refined Nonlinear Theory of Plates With Transverse Shear Deformation IJSS 20Document16 pages1984 JN Reddy A Refined Nonlinear Theory of Plates With Transverse Shear Deformation IJSS 20fritz2000No ratings yet
- Important 2 and 3 Mark Questions and AnswersDocument23 pagesImportant 2 and 3 Mark Questions and AnswersirannaNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument13 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument13 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Petrowiki Pressure Drop EquationsDocument14 pagesPetrowiki Pressure Drop Equationsrasnowmah2012No ratings yet
- Principal Stresses and Strains: Normal, Shear, ResultantDocument3 pagesPrincipal Stresses and Strains: Normal, Shear, ResultantBasanth BabuNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Question Papers on Stress, Strain and DeformationDocument80 pagesMechanical Engineering Question Papers on Stress, Strain and Deformationommech2020100% (1)
- Numerical Problems On SOMDocument20 pagesNumerical Problems On SOMAshish0% (1)
- Manufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 15: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument54 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 15: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Aim: To Verify Maxwell's Reciprocal TheoremDocument5 pagesAim: To Verify Maxwell's Reciprocal TheoremMarisha BhattiNo ratings yet
- Unit - V Numerical SolutionsDocument35 pagesUnit - V Numerical SolutionsMuthu EzhilanNo ratings yet
- CH-1 - DC Generator Q.bank PDFDocument2 pagesCH-1 - DC Generator Q.bank PDFjaythakar8887No ratings yet
- FMM Solved Unit 1 Previous Years ProblemsDocument14 pagesFMM Solved Unit 1 Previous Years ProblemsAjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Example Problems For Tension Members SteelDocument5 pagesExample Problems For Tension Members SteelMohammed KedirNo ratings yet
- EGF316 Rotating Discs - NotesDocument11 pagesEGF316 Rotating Discs - NotesJigneshNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Design QuestionsDocument20 pagesMachine Elements Design QuestionsArjun Arumugaswamy100% (4)
- Tutorial Problem III - Vertical Petrol Engine 100 MM Diameter and 120 MMDocument9 pagesTutorial Problem III - Vertical Petrol Engine 100 MM Diameter and 120 MMParen Trivedi50% (2)
- Lect 10 B Numericals On Bending MomentDocument9 pagesLect 10 B Numericals On Bending MomentYogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Important 2-Mark QuestionsDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials Important 2-Mark QuestionsSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Design Module 2 NewDocument17 pagesTransformer Design Module 2 NewRajath SuryaNo ratings yet
- SM Lab (Tension Test)Document15 pagesSM Lab (Tension Test)sushilkumar100% (1)
- Load test on single phase induction motorDocument3 pagesLoad test on single phase induction motorthemes3x67% (3)
- Practice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Document2 pagesPractice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits Explained: Flux, Flux Density, Reluctance and MoreDocument10 pagesMagnetic Circuits Explained: Flux, Flux Density, Reluctance and MoregebreNo ratings yet
- Measurments Sheet 4 AnswersDocument5 pagesMeasurments Sheet 4 Answersahmed gamalNo ratings yet
- Roll No: Name:: Lab Experiment # 06 Verification of Kirchhoff's Current LawDocument4 pagesRoll No: Name:: Lab Experiment # 06 Verification of Kirchhoff's Current Lawsara hafeezNo ratings yet
- Gauss-Seidel Method For Power Flow SolutionDocument20 pagesGauss-Seidel Method For Power Flow SolutionEngr Syed Numan ShahNo ratings yet
- MOM2 Quiz2 SolvedDocument2 pagesMOM2 Quiz2 SolvedUsama Tariq67% (3)
- Breakdown in Insulations 2011 Update - QuizDocument23 pagesBreakdown in Insulations 2011 Update - QuizKung ChinHanNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Analysis of Bars of Varying Cross SectionsDocument15 pagesUnit II: Analysis of Bars of Varying Cross Sectionsermias0% (1)
- Determine dimensions and specs for 5kVA transformerDocument2 pagesDetermine dimensions and specs for 5kVA transformerDipesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Closed-Book Practice-Ch 15 (2015!03!28)Document21 pagesClosed-Book Practice-Ch 15 (2015!03!28)JuanNo ratings yet
- 52CDocument12 pages52CDarshit D RajNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Question Bank Unit 1-6Document6 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Question Bank Unit 1-6rashmi ashtekarNo ratings yet
- 10CV54 Unit 05 PDFDocument21 pages10CV54 Unit 05 PDFvinodh159No ratings yet
- Solved Problems On DC Machine Magnetic Circuit Continuation of Chapter 4-VkDocument14 pagesSolved Problems On DC Machine Magnetic Circuit Continuation of Chapter 4-VkmadhueeNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution Method IntroductionDocument28 pagesMoment Distribution Method IntroductionJ.R. EnginnerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document12 pagesChapter 02blooms93No ratings yet
- Set 2 - Unit 3Document8 pagesSet 2 - Unit 3Tare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 01 Combined Loading AnalyticalDocument4 pagesTutorial 01 Combined Loading Analyticalpilas_nikolaNo ratings yet
- Set 7Document11 pagesSet 7Tare Er Kshitij100% (1)
- Problems CH-8 Complex Stresses (Blank)Document18 pagesProblems CH-8 Complex Stresses (Blank)محمد خريبط100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Kibrom GebremedhinNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pages9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- D Mec Frac Fatigue Part IIDocument38 pagesD Mec Frac Fatigue Part IIsure516vNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Unit 3Document8 pagesSet 1 - Unit 3Tare Er Kshitij67% (3)
- Solution SetDocument4 pagesSolution SetPrimawati RahmaniyahNo ratings yet
- Solutions To AssignmentDocument22 pagesSolutions To AssignmentNeo TarunNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 2Document3 pagesTutorials 2Daemaro Liv Guud BremmerNo ratings yet
- rr220102 Strength of Materials IIDocument7 pagesrr220102 Strength of Materials IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Lista 3Document7 pagesLista 3Rodolfo Souza MartinsNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses & Strains Theories of Failures Unit-IvDocument2 pagesPrincipal Stresses & Strains Theories of Failures Unit-IvSujeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Unit 4Document8 pagesSet 1 - Unit 4Tare Er Kshitij0% (1)
- 1 Study of DOT NET FrameworkDocument5 pages1 Study of DOT NET FrameworkTare Er Kshitij0% (1)
- 007Document13 pages007Tare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Sunday, September 14, 2014 9:19 PMDocument2 pagesSunday, September 14, 2014 9:19 PMTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- RC Design V 2.0 UN: Rebar PS: NewtonDocument1 pageRC Design V 2.0 UN: Rebar PS: NewtonTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Steady and Unsteady Finite Element Analysis of Incompressible Viscous FluidDocument20 pagesSteady and Unsteady Finite Element Analysis of Incompressible Viscous FluidTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Why We Like To Believe The Taj Mahal Was Built On A TempleDocument4 pagesWhy We Like To Believe The Taj Mahal Was Built On A TempleTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Wiki Holy WeekDocument16 pagesWiki Holy WeekTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Jhelum Exp Jammu To Pune Time TableDocument4 pagesJhelum Exp Jammu To Pune Time TableTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument9 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Design Example For PrestressedDocument8 pagesComprehensive Design Example For PrestressedTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Jhelum Express time tableDocument4 pagesJhelum Express time tableTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular ShaftDocument12 pagesTorsion of Circular ShaftTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Thin Wall Pressure VesselsDocument20 pagesThin Wall Pressure VesselsTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress in BeamsDocument19 pagesShear Stress in BeamsTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Unit 4Document8 pagesSet 1 - Unit 4Tare Er Kshitij0% (1)
- Set 8Document5 pagesSet 8Tare Er Kshitij100% (1)
- Set 7Document11 pagesSet 7Tare Er Kshitij100% (1)
- Deflection of BeamDocument18 pagesDeflection of BeamTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 2 - Unit 3Document8 pagesSet 2 - Unit 3Tare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 4 - Unit 3Document5 pagesSet 4 - Unit 3Tare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 3 - Unit 3Document6 pagesSet 3 - Unit 3Tare Er Kshitij100% (3)
- BendingDocument12 pagesBendingTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Unit 3Document8 pagesSet 1 - Unit 3Tare Er Kshitij67% (3)
- Chapter 8 Review Activity WordDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Review Activity WordsaramafareNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 4 PDFDocument1 pageProblem Set No. 4 PDFKent Lawrence LordanNo ratings yet
- Eng Mech Lesson 1-2 PDFDocument17 pagesEng Mech Lesson 1-2 PDFAlliza Kaye CasullaNo ratings yet
- Applied Clay Science: F.A. Andrade, H.A. Al-Qureshi, D. HotzaDocument7 pagesApplied Clay Science: F.A. Andrade, H.A. Al-Qureshi, D. HotzaCarolinaNo ratings yet
- Solutions - HW 3, 4Document5 pagesSolutions - HW 3, 4batuhany90No ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument30 pagesAssignment PDFHương Hà ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Stiffness Design of Unbraced Steel Frames: h m n s E I I L P P = total story load Q ψ /h) / /LDocument3 pagesStiffness Design of Unbraced Steel Frames: h m n s E I I L P P = total story load Q ψ /h) / /LalbertoxinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 Axisymmetric Stagnation Point Flow and Tensor Algebra (Due Monday, Nov. 30 On Google Class)Document2 pagesAssignment #2 Axisymmetric Stagnation Point Flow and Tensor Algebra (Due Monday, Nov. 30 On Google Class)Hatem FaroukNo ratings yet
- Ass 11Document1 pageAss 11Hawraa AlbahadlyNo ratings yet
- Module II Lecture 4Document19 pagesModule II Lecture 4Prateek NayakNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Load Calculation - U-FA 201Document32 pagesNozzle Load Calculation - U-FA 201manish318No ratings yet
- 09 Science Chap01 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument5 pages09 Science Chap01 Matter in Our SurroundingsRopsonNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE - Proceeding PaperDocument2 pagesSAMPLE - Proceeding PaperKush DwivediNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DYNAMIC FORCE ANALYSISDocument39 pagesUnit 2 DYNAMIC FORCE ANALYSISswetha shree chavan mNo ratings yet
- LiU Turbulence SAS ModelingDocument41 pagesLiU Turbulence SAS ModelingNishNo ratings yet
- Scott & Whittle 2005 Moment Redistribution Effects in BeamsDocument13 pagesScott & Whittle 2005 Moment Redistribution Effects in BeamsRm1262No ratings yet
- 18 163052april PDFDocument11 pages18 163052april PDFMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- McqsDocument142 pagesMcqsZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration Modeling and AnalysisDocument152 pagesMechanical Vibration Modeling and AnalysisTiago Rodrigues Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lsdyna Lsprepost IntroDocument74 pagesLsdyna Lsprepost IntroBlick ZitaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Aiits Class 11 - SyllabusDocument4 pagesFiitjee Aiits Class 11 - SyllabusShaurya SinhaNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Response Analysis: I. Two Mass Spring SystemDocument5 pagesHarmonic Response Analysis: I. Two Mass Spring SystemDinesh_Tadkapa_62No ratings yet
- IIT JEE Physics Test Code – AP209Document12 pagesIIT JEE Physics Test Code – AP209Samarth TikarNo ratings yet