Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Family Letter
Uploaded by
api-247555999Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Family Letter
Uploaded by
api-247555999Copyright:
Available Formats
Name
STUDY LINK
Date
Time
7 13
3
Unit 8: Family Letter
Perimeter and Area
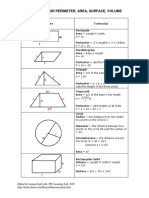
In previous grades, your child studied the perimeter (distance around) and the area (amount of surface) of various geometric figures. This next unit will extend your childs understanding of geometry by developing and applying formulas for the areas of figures such as rectangles, parallelograms, and triangles. Area of a Rectangle Area = base height (or length width) A = b h (or l w) height (width) Area of a Parallelogram Area = base height A=bh
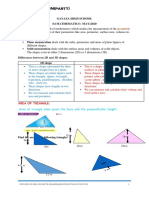
base (length) Area of a Triangle 1 Area = _ of (base height)
2 1 bh A=_ 2
base
Copyright Wright Group/McGraw-Hill
base Students will learn how to make scale drawings and apply their knowledge of perimeter, area, and scale drawing by analyzing the arrangement of the appliances in their kitchens and the furniture in their bedrooms. Students will also calculate the area of the skin that covers their entire body. A rule of thumb is that the area of a persons skin is about 100 times the area of one side of that persons hand. Ask your child to show you how to calculate the area of your own skin. The World Tour will continue. Students will examine how geographical areas are measured and the difficulties in making accurate measurements. They will compare areas for South American countries by using division to calculate the ratio of areas. Please keep this Family Letter for reference as your child works through Unit 8.
height
height
243
STUDY LINK
7313
Unit 8: Family Letter cont.
Vocabulary
Important terms in Unit 8:
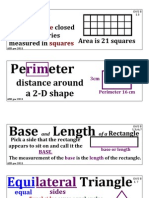
area The amount of surface inside a closed 2-dimensional (flat) boundary. Area is measured in square units, such as square inches or square centimeters.
Area of a triangle h b A=
1 2
perpendicular Crossing or meeting at right
angles. Lines, rays, line segments, and planes that cross or meet at right angles are perpendicular. The symbol means is perpendicular to, as in line CD line AB. The symbol indicates a right angle. C
Area of a rectangle
h b A=bh
A D
bh
Area of a parallelogram
Perpendicular lines
scale The ratio of
h b A=bh the distance on a map, globe, drawing, or model to an actual distance.
West Entrance Highway 61 East Entrance
Campground Hi kin g
Tr
ai
Beach 0 1 2 miles Lake
formula A general rule for finding the value of
something. A formula is often written using letter variables, which stand for the quantities involved.
Scale: 1 inch =
1 2
mile
scale drawing A drawing of an object or a region
in which all parts are drawn to the same scale as the object. Architects and builders often use scale drawings.
length The distance between two points on a
1-dimensional figure. Length is measured in units such as inches, meters, and miles.
perimeter The distance
around a 2-dimensional shape along the boundary of the shape. The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference. The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides.
Perimeter of a rectangle w l P=l+w+l+w = 2 (l + w )
square unit A unit used to measure area. For example, a square that measures one inch on each side has an area of one square inch. variable A letter or other symbol that represents
a number. A variable can represent one specific number, or it can stand for many different numbers.
Copyright Wright Group/McGraw-Hill
width The length of one side of a rectangle or
rectangular object, typically the shorter side.
244
STUDY LINK
7313
Unit 8: Family Letter cont.
Do-Anytime Activities
To work with your child on concepts taught in this unit, try these interesting and engaging activities: 1. Have your child pretend that he or she is a carpenter whose job is to redesign a roomfor example, a bedroom, the kitchen, or the living room. Have him or her make a rough estimate of the area of the room. Then help your child check the estimate by finding the actual area using a tape measure or, if possible, blueprints. 2. Have your child pretend that he or she is an architect. Give him or her some dimensions and space requirements to work with. Then have your child design a dream house, dream bedroom, or sports stadium, and make a scale drawing for that design. 3. Work with your child to make a scale drawing of your neighborhood. Or have your child make a scale drawing of the floor plan of your house or apartment. 4. Have your child compare the areas of continents, countries, states, or major cities.
Building Skills through Games
In this unit, your child will calculate perimeter and area, compare fractions, identify equivalent fractions, find fractions of collections, and calculate expected probabilities by playing the following games. For detailed instructions, see the Student Reference Book. Fraction Match See Student Reference Book, page 243. This is a game for 2 to 4 players and requires a deck of Fraction Match Cards. The game provides practice recognizing equivalent fractions. Fraction Of See Student Reference Book, pages 244 and 245. This is a game for 2 players and requires 1 deck of Fraction Of Fraction Cards, 1 deck of Fraction Of Set Cards, and 1 Fraction Of Gameboard and Record Sheet. The game provides practice finding fractions of collections. Fraction Top-It See Student Reference Book, page 247. This is a game for 2 to 4 players and requires a set of Fraction Cards 1 and 2. The game provides practice comparing fractions. Grab Bag See Student Reference Book, page 249. This is a game for 2 players or two teams of 2 players. It requires 1 deck of Grab Bag Cards, 2 Grab Bag Record Sheets, and 3 six-sided dice. The game provides practice with variable substitution and calculating probabilities of events. Rugs and Fences See Student Reference Book, pages 260 and 261. This is a game for 2 players and requires a Rugs and Fences Polygon Deck and an Area and Perimeter Deck. The game provides practice finding and comparing the area and perimeter of polygons.
Copyright Wright Group/McGraw-Hill
245
STUDY LINK
7313
Unit 8: Family Letter cont.
As You Help Your Child with Homework
As your child brings assignments home, you may want to go over the instructions together, clarifying them as necessary. The answers listed below will guide you through some of the Study Links in this unit.
Study Link 831
1. 17 feet 3.
B 3 cm L 5 cm U M 2 cm A 6 cm
m
2., continued Sample answer: 2. 54 inches
E
Sample answer:
4.
F
Sample answer:
3. 2,072
4. 11,740
5. 3,593
6. 2,848
Study Link 834
1. 87,500; 35 grid squares 2. 17,500; 7 grid squares 6.
1 in.
3 1 in. 4 4 1 in. 4 1 1 in. 1 in. 4 2 4 3 in. 4
R 11 in. 4
3. 88.71
in. in.
4. 58.08
5. 386.174
6. 18.098
5.
3c
3 cm
m 1c
Study Link 835
1. 48 square feet 2. 21 square inches 3. 864 square centimeters 4. 300 square meters 5. 9 inches 7. 9, 15, 18, 21 6. 10 centimeters 8. 28, 35, 49, 56 10. 24, 48, 72, 84
1 cm
3 cm
2 cm m 2c
1 2
in. 11 4 in.
15 centimeters
7 inches
Study Link 832
1. a. 52 miles 1 c. 32 _ miles
2
b. 117 miles 1 d. 175 _ miles
2
9. 36, 54, 60, 66
Study Link 836
Actual Height
12 ft 30 ft 48 ft 42 ft 24 ft
3.
Rectangle
A B C D E
Height in Drawing
1 _ in. 2 1 1_ in. 4
1. 9 4 = 36 3. 4 6 = 24 5. 13 inches
2. 3 8 = 24
Copyright Wright Group/McGraw-Hill
4. 65 72 = 4,680 6. 85 meters
2 in. 1_ 4 in.
3
Study Link 837
1 1. _ (8 4) = 16 2 1 3. _ (10 2) = 10 2 1 4. _ (34 75) = 1,275 2 1 2. _ (12 5) = 30 2
1 in.
Study Link 833
1. 24 square centimeters 2. 24 square centimeters
5. 3 inches 7. 27, 36, 54, 72
6. 6 meters 8. 8, 24, 40, 48
246
You might also like
- Grade 4 Unit 8 PDFDocument8 pagesGrade 4 Unit 8 PDFapi-237196236No ratings yet
- History Comes Alive Homework TimelineDocument3 pagesHistory Comes Alive Homework Timelineapi-237196236No ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 7Document9 pagesGrade 4 Unit 7api-237196236No ratings yet
- Unit 7 gr42Document4 pagesUnit 7 gr42api-237196236No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Junior Kangaroo 2019: SolutionsDocument4 pagesJunior Kangaroo 2019: SolutionsAges Teacher 11No ratings yet
- Self Learning Module For Senior High School LearnersDocument14 pagesSelf Learning Module For Senior High School LearnersMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Patterns and AlgebraDocument263 pagesLearning Module: Patterns and AlgebraMaria Martina Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Word Problems SolvedDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Math Word Problems Solvedjiokoijiko100% (1)
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFsagar sagarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3Document36 pagesPractice Test 3Jaymark DNo ratings yet
- SEQUENCE OF NUMBERS AND ARITHMETIC PROBLEMSDocument7 pagesSEQUENCE OF NUMBERS AND ARITHMETIC PROBLEMSAzka Ghossani AminNo ratings yet
- Maxima and MinimaDocument12 pagesMaxima and MinimaDennis Dale60% (5)
- MAT 070 Algebra I Word ProblemsDocument37 pagesMAT 070 Algebra I Word ProblemsZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFharikrishnanpd3327No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Aircraft Structures: Warping in Circular BarsDocument46 pagesMechanics of Aircraft Structures: Warping in Circular Barsroundstorm1100% (1)
- Class 6 Algebra: Answer The QuestionsDocument11 pagesClass 6 Algebra: Answer The QuestionsssNo ratings yet
- GRE Math Practice Tests 1-7Document12 pagesGRE Math Practice Tests 1-7pramodkb_cusat100% (2)
- 1st Practice Test 2 Levels 6-8 - With Calculator (439kB)Document24 pages1st Practice Test 2 Levels 6-8 - With Calculator (439kB)Nguyen Thi Anh TrangNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of the Isoperimetric ProblemDocument41 pagesThe Evolution of the Isoperimetric ProblemallysonmgabrielNo ratings yet
- Ncert 5th ClassDocument21 pagesNcert 5th ClassShishir HalaharviNo ratings yet
- G3 MMC Reviewer - Perimeter and Area - Part 1Document2 pagesG3 MMC Reviewer - Perimeter and Area - Part 1Harry Magbanua PradoNo ratings yet
- 5592Document174 pages5592Nazir RashidNo ratings yet
- MTAP Reviewer 3Document2 pagesMTAP Reviewer 3Vaughn Elbert P. Ybanez100% (2)
- Brian Leaf - Top 50 SAT Math Skills 2021Document177 pagesBrian Leaf - Top 50 SAT Math Skills 2021omid100% (2)
- Grade 9 Math Worksheet IVDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Math Worksheet IVtae hyungNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 Metrobank MTAP DepEd Math Challenge worksheet answersDocument14 pagesGrade 2 Metrobank MTAP DepEd Math Challenge worksheet answersKrizel100% (1)
- EMAC8 HOT Integrated 090211Document32 pagesEMAC8 HOT Integrated 090211vnmuyen2316No ratings yet
- Math PronunciationDocument59 pagesMath PronunciationPrince Dark0% (1)
- 4 Applications of Linear EquationsDocument11 pages4 Applications of Linear EquationsJun MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument12 pagesLesson Plan in MathematicsJANICE TIONGSONNo ratings yet
- Calculate Perimeter of Composite ShapesDocument8 pagesCalculate Perimeter of Composite ShapesAarti PadiaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic CaculationDocument66 pagesHydraulic CaculationgagajainNo ratings yet
- Perimeter, Area, and Volume: Shape Formula VariablesDocument4 pagesPerimeter, Area, and Volume: Shape Formula VariablesLucele Pasinag CorderoNo ratings yet
- MENSURATION (Part1) : Geometric ShapesDocument9 pagesMENSURATION (Part1) : Geometric ShapesAthiyo MartinNo ratings yet