Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ap1c24ppt (Metabolism)
Uploaded by
Mirza Shaharyar BaigCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ap1c24ppt (Metabolism)
Uploaded by
Mirza Shaharyar BaigCopyright:
Available Formats
1
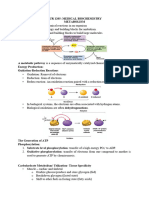
M E T A B O L I S M
Metabolism
All chemical
reactions in
cell
=
Catabolism
Degradation
+ Anabolism
Synthesis
Production and utilization of
energyATP
Anabolism
Making needed molecules
Protein synthesis (use ATP)
Catabolism
Cellular respiration (makes ATP)
Phosphorylation moving phosphate
from ATP to other molecules
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Redoxcoupled reactions
oxidation-reduction
LEO GER
Oxidationloss of electrons
Electrons must go somewhere
Electrons travel with protonsH
Dehydrogenases act as catalysts
to move H (electrons) in redox
reactions
Coenzymes temporarily hold electrons
Coenzymes become reduced when
substance is oxidized (redox)
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
flavin adenine dinucleotide
NAD and FADH
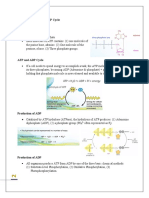
ATP Synthesis
Substrate-level Phosphorylation
Phosphate passed from substrate
to ADP
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle
2
ATP Synthesis
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
Electron Transport System
Electron energy harvested to
make ATP
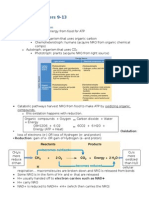
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Glycolysis
Krebs cycle, TCA, Citric acid cycle
Electron Transport System
Glucose converted to G-6-PO
4
Glucose + O
2
H
2
O + CO
2
+ 38 ATP + heat
Glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glucose-6-PO
4
2 pyruvate + 2 ATP
+ 2NADH
Substrate level phosphorylation
3
Krebs
cycle
Krebs cycle
Pyruvate Acetyl CoA + CO
2
+ NADH
Acetyl CoA 3CO
2
+ ATP + FADH
2
+
4NADH
Electron Transport System
10 NADH + 2 FADH
2
+ O
2
34 ATP + 6 H
2
O
Series of carrier molecules
cytochromes, flavins
Oxidative phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
Electrons lose energy
passing from molecule
to molecule
Energy used to pump
H
+
across membrane in
mitochondria
Electron transport
Chemiosmosis
4
Metabolic poisons (cyanide)
interrupt electron flow
Maintaining glucose levels
glycogenesis ( ATP levels)
glycogenolysis ( glucose)
gluconeogenesis
You might also like
- 1 Microbial Metabolism andDocument103 pages1 Microbial Metabolism andcalocetcerphus509No ratings yet
- Tissue RespirationDocument28 pagesTissue RespirationSheldon MillerNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and MetabolismDocument30 pagesBioenergetics and MetabolismShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 NinaDocument57 pagesLecture 7 Ninaachraf rabadiNo ratings yet
- 9 Metabolism1Document30 pages9 Metabolism1loijhonmuchillasNo ratings yet
- AP Bio MetabolismDocument3 pagesAP Bio MetabolismAniket BinwadeNo ratings yet
- Agricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyDocument63 pagesAgricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1. GlycolysisDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration 1. GlycolysisMoreen LamsenNo ratings yet
- Biologic Oxidation & Fosforilasi OksidatifDocument63 pagesBiologic Oxidation & Fosforilasi OksidatifRizky FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Nur 1205 NotesDocument10 pagesNur 1205 Noteschepngetichvalerie7No ratings yet
- Is The Process by Which Chemical Energy in OrganicDocument6 pagesIs The Process by Which Chemical Energy in Organicaiqi2712No ratings yet
- Y3 Bio Notes Unit 3Document60 pagesY3 Bio Notes Unit 3SANJAY SHIVANINo ratings yet
- Overall Equation: PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesOverall Equation: PhotosynthesisEleanorNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesisDexter Armamento Sulit100% (3)
- Bio 1130 Outline Week 9Document13 pagesBio 1130 Outline Week 9Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism 13Document87 pagesMicrobial Metabolism 13lalithaNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATPDocument38 pagesThe Structure and Hydrolysis of ATPBellony SandersNo ratings yet
- 4.4 RespirationDocument4 pages4.4 Respirationsmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Biochemistry - MetabolismDocument54 pagesBiochemistry - MetabolismDeana ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - 2012Document151 pagesTopic 2 - 2012Messen OwNo ratings yet
- NOTES 1 ATP and ADP CycleDocument4 pagesNOTES 1 ATP and ADP CycleJillian Reyes SantosNo ratings yet
- Cie Alevel BiologyDocument24 pagesCie Alevel BiologyArun Ghatan100% (1)
- Biochem Complete Reviewer JamDocument193 pagesBiochem Complete Reviewer JamArianne Jans MunarNo ratings yet
- Atp SynthesisDocument5 pagesAtp Synthesiskman0722No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document30 pagesChapter 9edomin00No ratings yet
- EMGBS Bio G11 U5 NoteDocument80 pagesEMGBS Bio G11 U5 NoteDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Module 4.4 Respiration RevisionDocument5 pagesBiology Unit 4 Module 4.4 Respiration RevisionRebekah Louise Penrice-RandalNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument52 pagesCellular Respirationjiwon hoshiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism: Metabolic ProcessesDocument45 pagesCellular Metabolism: Metabolic Processeseden bergNo ratings yet
- Section A: The Principles of Energy Harvest: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyDocument14 pagesSection A: The Principles of Energy Harvest: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyAhmedAbdelZaherNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam 2Document7 pagesBio Exam 2юрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22-Cellular Metabolic PathwaysDocument23 pagesLecture 22-Cellular Metabolic PathwaysHemanth Peddavenkatappa GariNo ratings yet
- Respiration Part 1Document35 pagesRespiration Part 1Ashley JohnsNo ratings yet
- (A) Outline The Need For Energy in Living Organisms, As Illustrated by Anabolicreactions, Active Transport, Movement and The Maintenance of Body TemperatureDocument9 pages(A) Outline The Need For Energy in Living Organisms, As Illustrated by Anabolicreactions, Active Transport, Movement and The Maintenance of Body TemperatureSammie PingNo ratings yet
- Biology: Energy & Equilibrium: RespirationDocument28 pagesBiology: Energy & Equilibrium: RespirationTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDocument60 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaAmanda PutriNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION BiologyDocument59 pagesCELLULAR RESPIRATION BiologyNur SafirahNo ratings yet
- 2238 Unit 4 Microbial Metabolic PathwaysDocument24 pages2238 Unit 4 Microbial Metabolic PathwaystitojhezielanneNo ratings yet
- Iology: 5.2 Aerobic RespirationDocument30 pagesIology: 5.2 Aerobic RespirationAdrian GohNo ratings yet
- 1 Glucose, 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 Nadh, 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 8 NADH+, 2 FADH2 34 ATPDocument3 pages1 Glucose, 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 Nadh, 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 8 NADH+, 2 FADH2 34 ATPArya BearNo ratings yet
- Biology 1113 Notes Unit 4Document17 pagesBiology 1113 Notes Unit 4Shane YacyshynNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction: PBL G5 Case 4Document42 pagesOxidation and Reduction: PBL G5 Case 4sankarNo ratings yet
- BIO 110 Photosynthesis Online Mini-LectureDocument12 pagesBIO 110 Photosynthesis Online Mini-Lectureiloveodin33No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesCellular RespirationizabelaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Oxidation: Crebs Cycle. Electron Transport ChainDocument805 pagesTissue Oxidation: Crebs Cycle. Electron Transport ChainSarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument59 pagesCitric Acid CycleSoniya BastolaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahiraDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahirasafinazahiraNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis & Kreb's CycleDocument33 pagesGlycolysis & Kreb's CycleMapple Hernandez BelenNo ratings yet
- GenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter Reviewerjoshua tejadaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short Course: Metabolism: Basic Concepts and DesignDocument30 pagesBiochemistry: A Short Course: Metabolism: Basic Concepts and DesignEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Microbial MetabolismDocument66 pagesLecture 5 Microbial MetabolismZeynep IlkNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: GlycolysisDocument4 pagesCytoplasm: Glycolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cellular Respiration 2018Document96 pagesChapter 2 Cellular Respiration 2018aliaNo ratings yet
- MetabolismeDocument31 pagesMetabolismeLalu Aldi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDocument60 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaFerybkiAyubNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism-The Chemical Crossroads of LifeDocument73 pagesMicrobial Metabolism-The Chemical Crossroads of Lifepranky neyneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 RespirationDocument55 pagesChapter 9 RespirationChaehyoung LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document19 pagesChapter 7skywalkerNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesisJan Raver SevaNo ratings yet
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- G Protein Coupled ReceptorsDocument25 pagesG Protein Coupled ReceptorsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- PAUL EHRLICH 1845-1945 Drugs Cannot Act Unless They Are Bound To ReceptorsDocument21 pagesPAUL EHRLICH 1845-1945 Drugs Cannot Act Unless They Are Bound To ReceptorsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Second Messengers Camp CGMPDocument42 pagesSecond Messengers Camp CGMPMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Ion Hannels: Voltage-Gated Channels Ligand-Gated Channels TRP ChannelsDocument33 pagesIon Hannels: Voltage-Gated Channels Ligand-Gated Channels TRP ChannelsMirza Shaharyar Baig100% (1)
- Phosphodiesterase & Its InhibitorsDocument29 pagesPhosphodiesterase & Its InhibitorsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Receptors That Stimulate Cyclic GMPDocument25 pagesReceptors That Stimulate Cyclic GMPMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- 3-Drug InteractionsDocument37 pages3-Drug InteractionsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Drug Discovery and DevelopmentDocument28 pagesDrug Discovery and DevelopmentMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- P - D: M M D A: Harmaco Ynamics Olecular Echanisms of RUG CtionDocument50 pagesP - D: M M D A: Harmaco Ynamics Olecular Echanisms of RUG CtionMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Cns DpressantDocument49 pagesCns DpressantMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Cns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Document39 pagesCns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Mirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument40 pagesSulfonamidesMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- 3 - Giardia LambliaDocument13 pages3 - Giardia LambliaMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Liver STR, Funct, Inj.Document5 pagesLiver STR, Funct, Inj.Mirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Nephro Slides in Board ExamsDocument223 pagesTop 10 Nephro Slides in Board ExamsMirza Shaharyar Baig100% (2)
- Fungal ClassificationDocument109 pagesFungal ClassificationMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Blood: General Characteristics of BloodDocument9 pagesBlood: General Characteristics of BloodMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet