Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Levels Hydrogen
Uploaded by
skruzerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Levels Hydrogen
Uploaded by
skruzerCopyright:
Available Formats
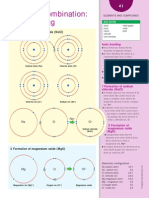
AT O M I C ST RUCT URE
Energy levels
G Electronsare arranged i n defi ni te
energy levels( also called shellsor
orbitals) , at a consi derable di stance
from the nucleus.
G Electronsjump between the orbi tsby
emi tti ng or absorbi ng energy.
G The energy emi tted or absorbed i s
equal to the di fference i n energy
between the orbi ts.
Energy levels of hydrogen
G The graph showsthe energy levelsfor
the hydrogen atom. Each level i s
descri bed by a quantum number
( labeled by the i nteger n ) .
G The shell closest to the nucleushas
the lowest energy level. I t i sgenerally
termed the ground state. The states
farther from the nucleushave
successi vely more energy.
Transition from n level to
ground state
G Transi ti on from n = 2 to the ground
state, n = 1 :
Frequency = 2 4 . 6 6 x 1 0
1 4
H z
G Transi ti on from n = 3 to the ground
state, n = 1 :
Frequency = 2 9 . 2 3 x 1 0
1 4
H z
G Transi ti on from n = 4 to the ground
state, n = 1 :
Frequency = 3 0 . 8 3 x 1 0
1 4
H z
Line spectrum
G Thi sradi ati on i si n the ultraviolet
regi on of the electromagneti c
spectrum and cannot be seen by the
human eye.
Energy levels: hydrogen
atom
ground state
orbital
quantum number
shell
ultraviolet
Key words
23
D
i
a
g
r
a
m
V
i
s
u
a
l
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
L
t
d
.
Fre q u e n c y / 1 0
1 4
H z
G ro u n d sta te
E
n
e
r
g
y
Energy-level schematic
Line spectrum
n = ?
n = 5
n = 4
n = 3
n = 2
n = 1
3 0 . 8 3 2 9 . 2 3 2 4 . 6 6
You might also like
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Electronic Structure of Elements - RozainaDocument75 pagesChapter 3 - Electronic Structure of Elements - RozainaEzzarenNo ratings yet
- NCERT 12th Physics Chapterwise Exempler Solution Important For Neet Aipmt IIT JEE Main and Advanced 12th Boards Exams Book Bank Publication PDFDocument266 pagesNCERT 12th Physics Chapterwise Exempler Solution Important For Neet Aipmt IIT JEE Main and Advanced 12th Boards Exams Book Bank Publication PDFSana Aiman100% (1)
- SkewT and StabilityDocument54 pagesSkewT and StabilityYazanNo ratings yet
- Models of Stellar Atmospheres: Department of Astronomy Vienna UniversityDocument46 pagesModels of Stellar Atmospheres: Department of Astronomy Vienna UniversityGloria Evelin Vargas SirpaNo ratings yet
- Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences From Line Emission: Profiles Not Often Suitable For Inversion, E.G. HollowDocument21 pagesPlasma Spectroscopy Inferences From Line Emission: Profiles Not Often Suitable For Inversion, E.G. HollowkurakidNo ratings yet
- Statistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CramerDocument7 pagesStatistical Molecular Thermodynamics: Christopher J. CrameradiazNo ratings yet
- Ncert Summary Class 12th PhysicsDocument29 pagesNcert Summary Class 12th Physicsmeghraj.socialNo ratings yet
- A HidrogenatomDocument33 pagesA HidrogenatomRévész CsabiNo ratings yet
- HyperfineDocument15 pagesHyperfinesediha5178No ratings yet
- General Physics CH 23Document31 pagesGeneral Physics CH 23Wei HuangNo ratings yet
- Notes On Black BodyDocument5 pagesNotes On Black BodyHamza HanifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document39 pagesChapter 4Sameal LabibNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Light: Chapter 1, Light Propagation in MediaDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Light: Chapter 1, Light Propagation in MediaLee Kar HuoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Structure of AtomDocument81 pagesChemistry Structure of AtomlololberuhlololNo ratings yet
- Reiche 2001 0124Document3 pagesReiche 2001 0124Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Atomic StructureDocument60 pages2.1 Atomic StructureKamariah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Gauss LawDocument6 pagesGauss LawmesahooNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Unit I: ElectrostaticsDocument79 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Unit I: ElectrostaticsShubham KNo ratings yet
- Manonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.Sc. Physics - Ii YearDocument80 pagesManonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.Sc. Physics - Ii Yeardushyantgiri0001No ratings yet
- Physics Unacademy Iconic NotesDocument52 pagesPhysics Unacademy Iconic NotesSANJAY J100% (2)
- General SB12 2005Document14 pagesGeneral SB12 2005Asif HameedNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS (Page 7 - 13)Document5 pagesELECTROSTATICS (Page 7 - 13)fireNo ratings yet
- Phy 2 Marks Imp Ques With Answers (1) - 1Document12 pagesPhy 2 Marks Imp Ques With Answers (1) - 1Amrita LecturesNo ratings yet
- Autumn Classes Week 1 PSC 2019Document38 pagesAutumn Classes Week 1 PSC 2019rcb6mfk5vwNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Week 6Document19 pagesLecture 9 Week 6mona ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Piee 1973 0312Document8 pagesPiee 1973 0312Armando MaloneNo ratings yet
- SSM E5Document3 pagesSSM E5Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics 2 Mark and 3 Mark Study Material em 217417Document57 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics 2 Mark and 3 Mark Study Material em 217417Kumar NNo ratings yet
- De La Elctricidad A La Generacion de Energia ElectricaDocument21 pagesDe La Elctricidad A La Generacion de Energia ElectricamikeNo ratings yet
- Ems ch2 NT PDFDocument16 pagesEms ch2 NT PDFAli khan7No ratings yet
- Studysheet For GREDocument15 pagesStudysheet For GREMuqarraulAhmadNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument5 pagesElectric Charges and Fieldsabijitchettrigoalkeeper01No ratings yet
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDocument181 pagesModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNo ratings yet
- ESR Lab ReportDocument4 pagesESR Lab ReportVargheseAbinNo ratings yet
- R Sum AtomedeBohr-enDocument5 pagesR Sum AtomedeBohr-enmilina moliNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 ECE3010 TH VL2021220101865 Reference Material I 06-Aug-2021 Module-1Document24 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 ECE3010 TH VL2021220101865 Reference Material I 06-Aug-2021 Module-1anchitNo ratings yet
- 1 ElectrostaticsDocument17 pages1 ElectrostaticsAyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics: UNIT-2Document5 pagesMagnetostatics: UNIT-2Joel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Electro StaticsDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Electro StaticsNagai KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Models - Plasma.positive Column 2dDocument24 pagesModels - Plasma.positive Column 2dFabianBarraganNo ratings yet
- Basic Ideas History (Background Material) : Fi - DecaysDocument5 pagesBasic Ideas History (Background Material) : Fi - DecaysRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan3-Sampling and Quantization in MATLABDocument23 pagesPertemuan3-Sampling and Quantization in MATLABEstika Vriscilla GintingNo ratings yet
- Radiation Formula SheetDocument5 pagesRadiation Formula SheetJakeJosephNo ratings yet
- Ekt 241-3-ElectrostaticsDocument73 pagesEkt 241-3-ElectrostaticsAbdirahman ElmiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pre-U Chemistry Sem 1 Chap 2Document48 pagesChemistry Pre-U Chemistry Sem 1 Chap 2Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- Phys507 Lect 1Document18 pagesPhys507 Lect 1noura haqNo ratings yet
- Elecrtrostatics 1Document29 pagesElecrtrostatics 1yeshwanth-203873No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet by VishalDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet by Vishalabhinav yadavNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Electromagnetism, UP 203: Problem Set IIIDocument1 pageIntermediate Electromagnetism, UP 203: Problem Set IIIarjun__123No ratings yet
- Gravity NotesDocument7 pagesGravity NotesRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 StudentDocument47 pagesLecture 7 StudentDiane G-GaytanNo ratings yet
- XII Phy Ch1 Electric Charges and Fields Chapter Notes JulyDocument5 pagesXII Phy Ch1 Electric Charges and Fields Chapter Notes JulyAakriti Goel50% (2)
- GLE 594: An Introduction To Applied Geophysics: Electrical Resistivity MethodsDocument9 pagesGLE 594: An Introduction To Applied Geophysics: Electrical Resistivity MethodsAsmaniarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Four Kinds of Fundamental Forces or InteractionsDocument38 pagesElectromagnetism: Four Kinds of Fundamental Forces or InteractionsLong JunNo ratings yet
- Coulombs Law and Electric FieldDocument11 pagesCoulombs Law and Electric FieldMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Lect10 PDFDocument8 pagesLect10 PDFDicia KesumaNo ratings yet
- The Hydrogen 21-cm Line and Its Applications To Radio AstrophysicsDocument7 pagesThe Hydrogen 21-cm Line and Its Applications To Radio AstrophysicsKush BhatiaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument1 pageThe Periodic Tableskruzer100% (1)
- Variation of Atomic NumbersDocument1 pageVariation of Atomic NumbersskruzerNo ratings yet
- Structure of Some Ionic CrystalsDocument1 pageStructure of Some Ionic CrystalsskruzerNo ratings yet
- Organizing The ElementsDocument1 pageOrganizing The ElementsskruzerNo ratings yet
- Planet CompositionDocument1 pagePlanet CompositionskruzerNo ratings yet
- Planetary Density, Size, and AtmosphereDocument1 pagePlanetary Density, Size, and AtmosphereskruzerNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Electron 2Document1 pageInvestigating The Electron 2skruzerNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure of Metals Efficient PackingDocument1 pageCrystal Structure of Metals Efficient PackingskruzerNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Electron 1Document1 pageInvestigating The Electron 1skruzerNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure of Metals Lattice Structure 0Document1 pageCrystal Structure of Metals Lattice Structure 0skruzerNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Molecular Mass of CompoundsDocument1 pageCalculate The Molecular Mass of CompoundsskruzerNo ratings yet
- Geiger and Marsden's ApparatusDocument1 pageGeiger and Marsden's ApparatusskruzerNo ratings yet
- Atomic MassDocument1 pageAtomic MassskruzerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Combination-IONIC BONDINGDocument1 pageChemical Combination-IONIC BONDINGskruzerNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument1 pageSolar SystemskruzerNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and SolutionsDocument1 pageMixtures and SolutionsskruzerNo ratings yet