Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matrix Match
Uploaded by
Ashish Gupta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pages1) One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process from A to B to C back to A.
2) The quantities in Column I are matched with their values in Column II: heat taken in path CA is equal to 0, heat taken in path AB is equal to 3PV0, and heat taken in path BC is equal to 2PV0.
3) The net work done during the full cyclic process ABCA is equal to PV0.
Original Description:
jee
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process from A to B to C back to A.
2) The quantities in Column I are matched with their values in Column II: heat taken in path CA is equal to 0, heat taken in path AB is equal to 3PV0, and heat taken in path BC is equal to 2PV0.
3) The net work done during the full cyclic process ABCA is equal to PV0.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesMatrix Match
Uploaded by
Ashish Gupta1) One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process from A to B to C back to A.
2) The quantities in Column I are matched with their values in Column II: heat taken in path CA is equal to 0, heat taken in path AB is equal to 3PV0, and heat taken in path BC is equal to 2PV0.
3) The net work done during the full cyclic process ABCA is equal to PV0.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
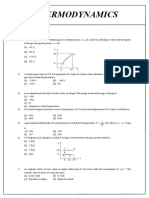
2.
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken
round the cyclic process ABCA as shown in the
figure. Then match the quantities of column I with
their values in column II.
P
0
3P
0
A
B
C
V
0
2V
0
P
V
Column I Column -II
(A) Heat taken by the gas in path CA
1.
0 0
2
5
V P
(B) Heat taken by the gas in path AB 2. 3P
0
V
0
(C) Heat taken by the gas in path BC
3.
2
0 0
V P
(D) Net work done during ABCA is
4.
0 0
V P
2. Q = Q
AB
+ Q
BC
+ Q
AC
= W = area of PV diagram = P
0
V
0
Q
CA
=
0 0
2
5
) (
2
5
V P T T R
C A
=
0 0
3 ) (
2
3
V P T T R Q
A B AB
= =
Q
BC
= ( )
2
0 0
V P
Q Q W
AC AB
= +
Net work done =
0 0
2
2
1
P V =
0 0
V P
(A) - 1, (B) - 2, (C) 3, (D) 4
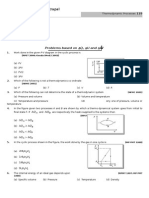
1. An ideal diatomic gas undergoes a process in which temperature (T) of the gas varies
with volume (V) as
V
T
1
. Pressure of the diatomic gas increases from P
0
to 4P
0
.
Match the following.
Column I Column II
(A) Temperature of the gas becomes 1. Half
2. 3/5
3. Double
4. 3/2
5. Triple
(B) Volume of the gas becomes
(C) For this process, ratio of heat transferred to that of
change in internal energy is
(D) For this process ratio of molar specific heat
to that of R is
1.
V
T
1
P T , R
dT n
PdV
C C
V
2
3
= + =
(A) - 3, (B) - 1, (C) 2, (D) 4
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Test Your C SkillsDocument8 pagesTest Your C SkillsBharadwaj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- 18.thermodynamics (Exercise)Document7 pages18.thermodynamics (Exercise)Viren Patel50% (2)
- Test-28 Thermo, KTG WADocument4 pagesTest-28 Thermo, KTG WAumang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- KTG & Thermodynamics (QB) For-FDocument8 pagesKTG & Thermodynamics (QB) For-FRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP Thermodynamics Nitesh DevnaniDocument26 pagesDPP Thermodynamics Nitesh DevnaniaadilNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellen0% (1)
- 02-Thermodynamic Process (Practice Problem)Document8 pages02-Thermodynamic Process (Practice Problem)Aditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Thermodynamics MCQDocument6 pagesPhysics Thermodynamics MCQkamilbismaNo ratings yet
- 02 Thermodynamic Process Practice Problem1Document8 pages02 Thermodynamic Process Practice Problem1Aman BhuttaNo ratings yet
- SSC Thermal EngineeringDocument47 pagesSSC Thermal EngineeringSteph Dela MujerNo ratings yet
- Set 5 Cat-C SolutionDocument4 pagesSet 5 Cat-C SolutionMohammad AfifNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument4 pagesThermodynamics and Kinetic Theory of GasesTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Heat1072Document3 pagesSolution of Heat1072ashaNo ratings yet
- QpaperDocument6 pagesQpaperRandeep Iyyad N CNo ratings yet
- 11 - Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument6 pages11 - Heat and ThermodynamicsAman BhuttaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument63 pagesThermodynamicsVansh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- DuihfuifhuifhuiDocument2 pagesDuihfuifhuifhui張耀恩No ratings yet
- DPP-18 (Thermodynamics)Document4 pagesDPP-18 (Thermodynamics)Dushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesThermodynamicsramchandraNo ratings yet
- P Thermo DynamicsDocument3 pagesP Thermo DynamicsJose CruzNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics20 Subhojit Maji 10HNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01 Check Your GraspDocument22 pagesExercise-01 Check Your GraspDeborshi ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- HW4VM235SU2016Document2 pagesHW4VM235SU2016tony960129No ratings yet
- Important Question Heat of Thermodynamics by PappuDocument6 pagesImportant Question Heat of Thermodynamics by PappuAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 19 Class ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics Chapter 19 Class ProblemsRuba AlNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics PYQs 1990 To 2022 110530 1670823515775 PDFDocument214 pagesThermodynamics PYQs 1990 To 2022 110530 1670823515775 PDFSandeep AsthanaNo ratings yet
- KTG Thermodynamics STUDENT COPY With Ans 1692339767740Document54 pagesKTG Thermodynamics STUDENT COPY With Ans 1692339767740sukanyab345No ratings yet
- Basic Terminology: Marked Questions Are Having More Than One Correct OptionDocument9 pagesBasic Terminology: Marked Questions Are Having More Than One Correct OptionTarun SoniNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Physics SF 016Document39 pagesThermodynamics: Physics SF 016Muhammad SolehinNo ratings yet
- 9a-Thermodynamics MC Practice ProblemsDocument14 pages9a-Thermodynamics MC Practice ProblemsFrancis Nicole V. QuirozNo ratings yet
- Problems303 2 SolDocument3 pagesProblems303 2 SolChristian Roy CNo ratings yet
- Mae 320 HW 04 SolDocument7 pagesMae 320 HW 04 SolEvan DurstNo ratings yet
- Energy BalanceDocument28 pagesEnergy BalanceEian HawNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Physics Thermodynaics MCQsDocument29 pagesNEET UG Physics Thermodynaics MCQskundrapupNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Practice Problems-2012!05!07Document17 pagesThermodynamics Practice Problems-2012!05!07Mark Abion ValladolidNo ratings yet
- 02.KTGandThermodynamics PCDocument48 pages02.KTGandThermodynamics PCDevesh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- AP Problems Database UhrichDocument18 pagesAP Problems Database UhrichMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Fundamentals For ApplicationsDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Fundamentals For ApplicationsMohamed Sayed AbdoNo ratings yet
- Heat & Thermodynamics (Practice Questions PDFDocument41 pagesHeat & Thermodynamics (Practice Questions PDFSaksham100% (2)
- Exercice Thermodynamics PART IDocument8 pagesExercice Thermodynamics PART Ichitl.23bi14075No ratings yet
- CET AssignmentDocument4 pagesCET AssignmentKAMAL HAASANNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 AnswersDocument6 pagesExam 1 AnswersAdham EmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture05 P2Document24 pagesLecture05 P2Phạm Thiên LongNo ratings yet
- Chm3410hwk01-Soln 249211458Document7 pagesChm3410hwk01-Soln 249211458Jerika ArceoNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument5 pagesPhysical ChemistryLynnden CastilloNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Ch-11 - Thermodynamics (SQP) 2023-24Document10 pages11th Physics Ch-11 - Thermodynamics (SQP) 2023-24Mahalaksshmi .DNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument19 pagesExercisesNhật MinhNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Previous Eamcet Questions EngineeringDocument14 pagesThermodynamics: Previous Eamcet Questions EngineeringAnonymous 9uu04el0% (1)
- 1st LawDocument10 pages1st LawAdyant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ME2121 - ME2121E Slides Chapter 3 (2014)Document23 pagesME2121 - ME2121E Slides Chapter 3 (2014)FlancNo ratings yet
- My 10 Question Thermodynamics: PV B RTDocument3 pagesMy 10 Question Thermodynamics: PV B RTJINU CHANDRANNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet