Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure and Function - Hylton
Uploaded by
api-2606900090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
803 views50 pagesOriginal Title
cell structure and function- hylton
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
803 views50 pagesCell Structure and Function - Hylton
Uploaded by
api-260690009Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 50
1
Basic Structure of a Cell
2
Introduction to Cells
Cells are the basic units of organisms
Cells can only be observed under
microscope
Basic types of cells:
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Bacterial Cell
3
Number of Cells
Organisms may be:
Unicellular
composed of one cell
Multicellular-
composed of many
cells that may
organize
4
Prokaryotes include bacteria &
lack a nucleus or membrane-bound
structures called organelles
Eukaryotes include most other cells
& have a nucleus and membrane-
bound organelles (plants, fungi, &
animals)
Cells May be Prokaryotic or
Eukaryotic
5
Prokaryotes
Nucleoid region
contains the DNA
Cell membrane &
cell wall
Contain ribosomes
(no membrane) to
make proteins in
their cytoplasm
6
Eukaryotic Cell
Contain 3 basic cell
structures:
Nucleus
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm with
organelles
7
Two Main Types of
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant Cell
Animal Cell
8
Organelles
Very small size
Can only be observed under a
microscope
Have specific functions
Found throughout cytoplasm
9
Organelles Found in Cells
Examples of Organelles include:
Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth)
canals for movement
Golgi Bodies wrap & export proteins
Nucleolus makes ribosomes
Lysosomes digests & gets rid of wastes
Ribosomes makes proteins
10
Golgi Bodies
Stacks of flattened
sacs
Have a shipping side &
a receiving side
Receive & modify
proteins made by ER
Transport vesicles
with modified proteins
pinch off the ends
Transport
vesicle
11
Lysosome
Contain digestive
enzymes
Break down food and
worn out cell parts for
cells
Programmed for cell
death (lyse & release
enzymes to break down
& recycle cell parts)
12
Nucleolus
Cell may have 1 to 3
nucleoli
Inside nucleus
Disappears when cell
divides
Makes ribosomes that
make proteins
13
Smooth & Rough Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Smooth ER lacks
ribosomes &
makes proteins
USED In the cell
Rough ER has
ribosomes on its
surface & makes
proteins to
EXPORT
14
Rod shape
Site of Cellular
respiration
Cell Powerhouse
Mitochondrion
( mitochondria )
15
Active cells like
muscles have more
mitochondria
Burn sugars to
produce energy ATP
In Animal Cells:
Mitochondria
16
Lies immediately
against the cell wall
in plant cells
Made of protein and
phospholipids
Selectively permeable
Cell membrane
Surrounding the Cell
17
Living layer
Controls the
movement of
materials into and
out of the cell
Selectively
permeable
Cell membrane
Cell or Plasma Membrane
18
Jelly-like substance
enclosed by cell
membrane
Provides a medium
for chemical
reactions to take
place
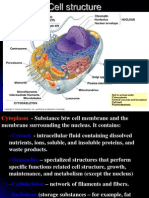
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm of a Cell
19
Contains organelles
to carry out
specific jobs
Examples:
chloroplast &
mitochondrion
Cytoplasm
More on Cytoplasm
20
Controls the normal
activities of the cell
Bounded by a
nuclear membrane
Contains chromosomes
Control Organelle
Nucleus
21
Each cell has fixed
number of
chromosomes that
carry genes
Genes control cell
characteristics
Nucleus
More on the Nucleus
22
Contain the green
pigment chlorophyll
Traps sunlight to
make to make
sugars (food)
Process called
photosynthesis
Plant Cell Organelles
Chloroplast
23
Dead layer
Large empty spaces
present between
cellulose fibers
Freely permeable
Cell wall
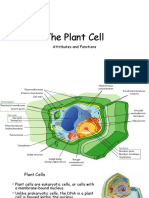
Plant Cell
24
Plant Cell
Made of cellulose
which forms very
thin fibers
Strong and rigid
Found in plant cells
Cell wall
25
Protect and support
the enclosed
substances
(protoplasm)
Resist entry of
excess water into
the cell
Give shape to the cell
Cell wall
Plant Cell
26
Have a large central
vacuole
Surrounded by tonoplast
Contains cell sap
Sugars, proteins,
minerals, wastes, &
pigments
Plant Cell Organelles
Vacuole
27
Different kinds of plant
cells
Onion Epidermal Cells
Root Hair Cell
root hair
Guard Cells
28
mitochondrion
nucleus
glycogen
granule
cell
membrane
cytoplasm
Animal cell
No cell wall or
chloroplast
Stores glycogen
in the
cytoplasm for
food energy
vacuole
29
Animal Cell Organelles
Near the nucleus
Paired structures
Help cell divide
30
Different kinds of animal
cells
white blood cell
red blood cell
cheek cells
sperm
nerve cell
muscle cell
Amoeba
Paramecium
31
Similarities between plant
cells and animal cells
Both have a cell membrane
surrounding the cytoplasm
Both have a nucleus
Both contain mitochondria
32
Differences between plant
cells and animal cells
Animal cells Plant cells
Relatively
smaller in size
Irregular shape
No cell wall
Relatively
larger in size
Regular shape
Cell wall present
33
Animal cells Plant cells
Vacuole small or
absent
Glycogen as food
storage
Nucleus at the
center
Large central
vacuole
Starch as food
storage
Nucleus near cell
wall
Differences between Plant
Cells and Animal Cells
34
Compound Microscope
Instrument for
observing small
objects
Magnify images
up to 2000X
their size
35
Different parts of
a microscope
36
Eyepiece
Fine adjustment
Arm
Stage
Condenser
control knob
Base
Body tube
Coarse
adjustment
Iris diaphragm
Revolving
nosepiece
Objective
Clip
Condenser
Mirror
37
The cell is the Basic Unit
of Life
Cell is the smallest unit of living organisms
Unicellular organisms are made of one cell
only
The cells of multicellular organisms are
specialized to perform different functions
e.g. mesophyll cells for photosynthesis
and root hair cells for water absorption
38
Levels of organization
Cells are
grouped
together and
work as a
whole to
perform special
functions
39
Tissue
A group of similar cells to
perform a particular function
Animals : epithelial tissue,
muscular tissue
Plants : vascular tissue,
mesophyll
40
Organ
Different tissues group together
to carry out specialized functions
Heart : consists of muscles,
nervous tissue and blood
vessels
Leaf : consists of epidermis,
mesophyll and vascular tissue
41
Stoma
Air Space
Spongy Mesophyll
Cell
Chloroplast
The Structures of a Leaf
(Plant Organ)
Palisade
Mesophyll Cell
42
The Structures of a Heart
(Animal Organ)
43
System
Several organs and tissues work together
to carry out a particular set of functions in a
co-ordinated way
Human : digestive, respiratory, excretory,
circulatory and reproductive systems
Plant : root and shoot systems
44
Human Body Systems
Examples of systems :
Digestive System
Respiratory System
Circulatory System
Nervous System
Reproductive System
45
Examples of a Human Body System
46
Examples of a Human Body System
The Respiratory System
47
Examples of a Human Body System
Circulatory System
48
Examples of a Human Body System
Nervous System
49
Levels of Organization
CELLS (muscle cells,nerve cells)
TISSUES (muscle, epithelium)
ORGANS (heart, lungs,
stomach)
SYSTEMS (circulatory system)
ORGANISM (human)
50
Its You!
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BIOC4610 Continuous Assessment 2021Document4 pagesBIOC4610 Continuous Assessment 2021Rainbow HuiNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Quarter 1 Science Exam Worksheets .Document7 pages6th Grade Quarter 1 Science Exam Worksheets .MohammadNassarNo ratings yet
- Page 151 Jeopardy GenesDocument1 pagePage 151 Jeopardy Genesapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Public Library-Scavenger-Hunt-ListDocument1 pagePublic Library-Scavenger-Hunt-Listapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Page 163 Codominace Blood PowerpointDocument3 pagesPage 163 Codominace Blood Powerpointapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Page 165 Sex Chromosomes and Sex Linked ChromosomesDocument3 pagesPage 165 Sex Chromosomes and Sex Linked Chromosomesapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Page 162-3 CominananceDocument3 pagesPage 162-3 Cominananceapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Writing Workshop Session 5Document17 pagesWriting Workshop Session 5api-260690009100% (1)
- Biology Unit 3b Growth and Heredity - Mendelian Genetics KudDocument1 pageBiology Unit 3b Growth and Heredity - Mendelian Genetics Kudapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Bikini Bottom Genetics - Punnett SquaresDocument3 pagesBikini Bottom Genetics - Punnett Squaresapi-307565882No ratings yet
- Page 151 Jeopardy MeiosisDocument1 pagePage 151 Jeopardy Meiosisapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Genetics Vocabulary1Document1 pageGenetics Vocabulary1api-260690009100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument21 pagesMeiosisapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Mitosis Cheat Sheet PDocument1 pageMitosis Cheat Sheet Papi-260690009No ratings yet
- Gen Spbobgenetics2Document3 pagesGen Spbobgenetics2api-259614222No ratings yet
- Jeopardy - Dna Rna and MitosisDocument27 pagesJeopardy - Dna Rna and Mitosisapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Dna WorksheetDocument3 pagesDna Worksheetapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Transcription - TranslationDocument34 pagesTranscription - Translationapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Study Guide Growth and Reproduction and Nucleic Acids KeyDocument1 pageStudy Guide Growth and Reproduction and Nucleic Acids Keyapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Rna Jeopardy QuestionsDocument1 pageRna Jeopardy Questionsapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Vocabulary 2 Growth and ReproductionDocument2 pagesVocabulary 2 Growth and Reproductionapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Transcription - TranslationDocument34 pagesTranscription - Translationapi-260690009No ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Dna and RnaDocument4 pagesThe Structure and Function of Dna and Rnaapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Usa Tesst PrepDocument1 pageUsa Tesst Prepapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Jeopardy - Dna Rna and MitosisDocument27 pagesJeopardy - Dna Rna and Mitosisapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Parent Letter For Usa Test Prep, Grades, Last Two Cdas Page 146 in NotebookDocument1 pageParent Letter For Usa Test Prep, Grades, Last Two Cdas Page 146 in Notebookapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Color and Construct A Dna Model DirectionsDocument1 pageColor and Construct A Dna Model Directionsapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Mitosis and The Cell Cycle Cloze NotesDocument2 pagesMitosis and The Cell Cycle Cloze Notesapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument19 pagesMitosis and The Cell Cycleapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Mitosis Jeopardy QuestDocument1 pageMitosis Jeopardy Questapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument19 pagesMitosis and The Cell Cycleapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Karyotype Picture Picture DirectionsDocument1 pageKaryotype Picture Picture Directionsapi-260690009No ratings yet
- What Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of OrganellesDocument18 pagesWhat Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of Organellestdukes546No ratings yet
- SPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Document4 pagesSPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Felicia LingNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-8 Composite Diagram of An Animal Cell: AnimatedDocument1 pageFigure 4-8 Composite Diagram of An Animal Cell: AnimatedElrey AnatolNo ratings yet
- The Plant CellDocument30 pagesThe Plant CellMichael GentilesNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document4 pagesCH 1Viraaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The CellDocument68 pagesChapter 3 The CellCarlos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Cell CityDocument1 pageCell Cityapi-233757247No ratings yet
- How To Create 3D Plant Cell and Animal Cell Models For Science Class - OwlcationDocument1 pageHow To Create 3D Plant Cell and Animal Cell Models For Science Class - OwlcationMethuli FernandoNo ratings yet
- SIM 7 Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument17 pagesSIM 7 Plant Cell and Animal CellSheryl Jane P. Silang100% (4)
- Cell Model ProjectDocument3 pagesCell Model ProjectAmelia Fernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Cell Types & Cell ModificationDocument41 pagesCell Types & Cell ModificationShane Marcande Calicdan78% (18)
- Cell - Formative Assessment - MT 6315 2021Document1 pageCell - Formative Assessment - MT 6315 2021REGINE COELI LANSANGANNo ratings yet
- Cell CytoplasmDocument55 pagesCell Cytoplasmnicolaer111100% (1)
- Plant Cell:: Ultra Structure and Functions of Typical Plant and Animal CellDocument8 pagesPlant Cell:: Ultra Structure and Functions of Typical Plant and Animal CellMaleehaNo ratings yet
- Cells - Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesCells - Basic Unit of Lifeapi-202349222No ratings yet
- (Long Quiz) Buyco, Althea Kattrize M. - Stem111-12Document3 pages(Long Quiz) Buyco, Althea Kattrize M. - Stem111-12Buyco, Nicole Kimberly M.No ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingDocument24 pagesCell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingWina MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life Practice Worksheet: (B) Golgi Apparatus (C) Cell Wall (D) Cytoplasm (E) NucleoplasmDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life Practice Worksheet: (B) Golgi Apparatus (C) Cell Wall (D) Cytoplasm (E) NucleoplasmSarwan KumarNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Mya Bennett - Intro To Cells Recap by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesKami Export - Mya Bennett - Intro To Cells Recap by Amoeba SistersMya BennettNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5, The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesChapter-5, The Fundamental Unit of LifeMonika Mehan100% (20)
- Chapter Practice Problems: FiitjeeDocument2 pagesChapter Practice Problems: FiitjeeSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Student Slides - Fill in The BlanksDocument20 pagesStudent Slides - Fill in The Blanksapi-663039855No ratings yet
- 7 Grade Life Science Cell Biology UnitDocument4 pages7 Grade Life Science Cell Biology UnitAngelica Rumbaua GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Mystery Cell Model: Teacher GuideDocument5 pagesMystery Cell Model: Teacher GuideGrace EliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 TestDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Testkwilliams1994No ratings yet
- Differences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellDocument1 pageDifferences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellSunidhi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument5 pagesPlant CellEster Ariza CruzadoNo ratings yet