Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ملخص رقم2
Uploaded by
عبد الله البطحاني احمدCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ملخص رقم2
Uploaded by
عبد الله البطحاني احمدCopyright:
Available Formats
Summaries in Partial Differential Equations
)(
)Summary (2
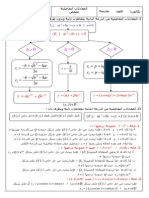
Solution of P.D.E :
:
=
=
,
:
. )( Exact (complete) solution :
.
It is a solution of the P.D.E which contains arbitrary
constants.
+
: :
,
+
=
=
. General solution :
.
It is a solution of the P.D.E which contains arbitrary
functions are equal to the order of the PDE
+2 ( +
: ) :
=2
= :
=2
+
+
=2
=2 +2
( 2 )=2
* **
( 2 ) =
:
=2
+2 ( +
+
= .
Particular solution : .
.
It is a solution of the P.D.E can be obtained from the
general solution by a particular selection of the arbitrary
functions.
:
( , )=
: :
=2
( ,0 ) =
(0, ) = ( , ) = 0 :
:
( , )=
( ,0 ) =
2 =
(0, ) =
2(0) = 0
( , )=
2( ) = 0
=2
= 8
= 4
2
2
=2
Singular solution : .
.
It is a solution of the P.D.E can't be obtained from the
general solution by a particular selection of the arbitrary
functions.
:
: trivial solution :
All coefficients are equal to zero .
: isoclines :
.
.
A line or curve formed by plotting constant values of the
first differential, i.e. points at which the slope is uniform.
This is not necessarily a solution of the differential
equation.
: separable :
.
A differential equation in which the dependent and
independent variables can be algebraically separated on
opposite sides of the equation.
: explicit :
.
An explicit solution of a differential equation is one in
which y may be written in terms of x only. Otherwise it is
an implicit solution
:
If the differential equation containing the partial
derivative one can be solved by direct integration:
.
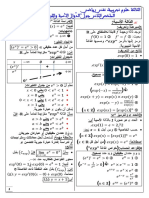
:
:
=
1.
:
.
) (:
1
=
=
) ( +
2
1
.
=
+ ( ).
2
1
=
) ( + ( )+
6
) ( ) ( .
) (2 + 2
:
=
(2 + 2 ) .
2.
) ( (2 + 2 ) +
1
2
(2 + 2 ) + ( ).
) ( (2 + 2 ) + ( ) +
) (
1
2
=
1
4
.
=
Appendix :
Rules integration :
You might also like
- ملخص رقم 1Document11 pagesملخص رقم 1عبد الله البطحاني احمد73% (15)
- ملخص معادلات تفاضلية 1Document43 pagesملخص معادلات تفاضلية 1Salem100% (7)
- المعادلات التفاضلية رياضيات3 2019 PDFDocument90 pagesالمعادلات التفاضلية رياضيات3 2019 PDFYosha AlassadNo ratings yet
- حل المعادلات التفاضلية بااستخدام المتسلسلات 2 PDFDocument71 pagesحل المعادلات التفاضلية بااستخدام المتسلسلات 2 PDFRosa AlbaNo ratings yet
- التكامل غير المحدود - 3صيدلةDocument10 pagesالتكامل غير المحدود - 3صيدلةmojojoNo ratings yet
- معادلات تفاضلية تمارين محلولةDocument4 pagesمعادلات تفاضلية تمارين محلولةBasel A MorayNo ratings yet
- تمارين في المعادلات التفاضلية 1 PDFDocument64 pagesتمارين في المعادلات التفاضلية 1 PDFAbderrazak AferyadNo ratings yet
- الدوال القابلة للتكامل الريمانيDocument53 pagesالدوال القابلة للتكامل الريمانيS P A C ENo ratings yet
- تحليل المتجهات في الرياضياتDocument12 pagesتحليل المتجهات في الرياضياتalkalkiaNo ratings yet
- طرق حل المعادلات التفاضليةDocument33 pagesطرق حل المعادلات التفاضليةعلي العماري100% (6)
- سلسلة تمارين في الاعداد المركبةDocument13 pagesسلسلة تمارين في الاعداد المركبةARmani Khaled0% (1)
- 38 تمرين الاعداد الم ركبة و التحويلات النقطيةDocument13 pages38 تمرين الاعداد الم ركبة و التحويلات النقطيةخلف الله مخلوفNo ratings yet
- سسلة تمارين الدوال اللوغاريتمية بخدة أمـــين PDFDocument23 pagesسسلة تمارين الدوال اللوغاريتمية بخدة أمـــين PDFEnjoy with football إستمتع مع كرة القدم100% (1)
- التوزيعات الاحتمالية المتقطعة Discrete Distribution1Document1 pageالتوزيعات الاحتمالية المتقطعة Discrete Distribution1sam100% (3)
- الهندسة التحليلية تاليف الاستاذ احمد ابو نبوت 3Document325 pagesالهندسة التحليلية تاليف الاستاذ احمد ابو نبوت 3AmanyalhasanNo ratings yet
- قواعد التكامل المحددDocument4 pagesقواعد التكامل المحددOmran King100% (3)
- تمارين في حساب التكاملDocument4 pagesتمارين في حساب التكاملcol302011dz100% (2)
- حساب مركز الثقلDocument3 pagesحساب مركز الثقلAmr Mahmoud Ali RAGAP80% (5)
- حل المعادلات التفاضلية الخطية المتجانسة و الغير متجانسة من الرتبة ن ذات المعادلات الثابتة PDFDocument54 pagesحل المعادلات التفاضلية الخطية المتجانسة و الغير متجانسة من الرتبة ن ذات المعادلات الثابتة PDFTam Alasadi75% (4)
- احصاء - المحاضرة السادسةDocument4 pagesاحصاء - المحاضرة السادسةMohammed Rabie ElfallalNo ratings yet
- تحويلات لابلاسDocument15 pagesتحويلات لابلاسALALAM OFFECNo ratings yet
- تحليل عددي PDFDocument4 pagesتحليل عددي PDFجمال سينغNo ratings yet
- المعادلات التفاضلية-ملخصDocument1 pageالمعادلات التفاضلية-ملخصUnkownKïllêr100% (3)
- ملخص قوانين الرياضيات المدرسية والجامعية - اهداء الاستاذ ابراهيم الاحمدى ابراهيمDocument24 pagesملخص قوانين الرياضيات المدرسية والجامعية - اهداء الاستاذ ابراهيم الاحمدى ابراهيمHAMADA1972No ratings yet
- سلسلة في العد و التحليل التوفيقي و الإحتمالات للنهائي شعب علمية إعداد الأستاذ حليلات عمـــارDocument12 pagesسلسلة في العد و التحليل التوفيقي و الإحتمالات للنهائي شعب علمية إعداد الأستاذ حليلات عمـــارMourad Mouradbensalem100% (1)
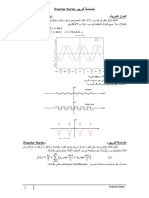
- Fourier SeriesDocument8 pagesFourier SeriesKarim MANSOURINo ratings yet
- تحويلات لابلاس البحثDocument71 pagesتحويلات لابلاس البحثAbdulsalam SNo ratings yet
- تمارين في الدوال اللوغاريتمية للأستاذ كيــــحــالDocument12 pagesتمارين في الدوال اللوغاريتمية للأستاذ كيــــحــالMourad Mouradbensalem100% (2)
- قوانين التكاملDocument3 pagesقوانين التكاملOmran King80% (5)
- تمرين محلول حفلة زفاف اللوغاريتم والأسية مع استدعاء فرقة القيمة المطلقةDocument2 pagesتمرين محلول حفلة زفاف اللوغاريتم والأسية مع استدعاء فرقة القيمة المطلقةMourad Mouradbensalem67% (3)
- الامتحان + التصحيحDocument6 pagesالامتحان + التصحيحXrg WahabNo ratings yet
- المصفوفات المتعامدةDocument38 pagesالمصفوفات المتعامدةMohamed alqadasiNo ratings yet
- طرق حل المعادلات التفاضلية #موقع الفيزياء.كوم PDFDocument45 pagesطرق حل المعادلات التفاضلية #موقع الفيزياء.كوم PDFYazan BaniBakerNo ratings yet
- ا المتجهاتDocument29 pagesا المتجهاتShifa Al.Musalhi100% (1)
- الوحدة 01 سلسلة 02 السنة ثالثةDocument1 pageالوحدة 01 سلسلة 02 السنة ثالثةÊš Pőîř100% (1)
- تحويلات فورييه PDFDocument30 pagesتحويلات فورييه PDFhammoud73% (15)
- Methods for the Solution of Linear Programming Models طرق حل نماذج البرمجة الخطيةDocument32 pagesMethods for the Solution of Linear Programming Models طرق حل نماذج البرمجة الخطيةDr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-NaimiNo ratings yet
- تكاملات مثلثيهDocument25 pagesتكاملات مثلثيهMohammed Al-saa'bary100% (2)
- 05.1-4 lnوexp ملخص شامل حول PDFDocument4 pages05.1-4 lnوexp ملخص شامل حول PDFUmut Gul Gul100% (2)
- سلسلة تمارين الاعداد المركبة Word1616438352Document4 pagesسلسلة تمارين الاعداد المركبة Word1616438352layatiNo ratings yet
- Dzexams Docs 3as 904418Document37 pagesDzexams Docs 3as 904418abdelhafidtlmNo ratings yet
- 2 5454136225675872497 PDFDocument45 pages2 5454136225675872497 PDFbassam lateefNo ratings yet
- معالجة الإشارة - الجلسة الرابعةDocument5 pagesمعالجة الإشارة - الجلسة الرابعةjmarkoNo ratings yet
- التكامل الثلاثيDocument13 pagesالتكامل الثلاثيm3amer bouhelal100% (1)
- التكامل وتطبيقاتهDocument12 pagesالتكامل وتطبيقاتهMalik SelawiNo ratings yet
- مبرهنة القيم المتوسطةDocument4 pagesمبرهنة القيم المتوسطةUnkownKïllêrNo ratings yet
- معادلة الحرارةDocument73 pagesمعادلة الحرارةlazhor100% (1)
- الامتحان + التصحيحDocument6 pagesالامتحان + التصحيحXrg WahabNo ratings yet
- دراسة دالة لوغاريتمية رقم 6 (رائعة)Document6 pagesدراسة دالة لوغاريتمية رقم 6 (رائعة)bouss2013100% (1)
- المعادلات التفاضليةDocument1 pageالمعادلات التفاضليةموقع التعليم الجزائريNo ratings yet
- ترييض مشكلDocument2 pagesترييض مشكلAhmed Salem0% (1)
- درس رائع في الإحتمالات للنهائي شعبة علوم تجريبيةDocument25 pagesدرس رائع في الإحتمالات للنهائي شعبة علوم تجريبيةMourad Mouradbensalem73% (11)
- معادلات التفاضليه الجزئيهDocument39 pagesمعادلات التفاضليه الجزئيهنزار الدهامي100% (1)
- مصطلحات ورموز التعامد والتوازيDocument2 pagesمصطلحات ورموز التعامد والتوازيMilou AmalNo ratings yet
- قواعد الاشتقاقDocument2 pagesقواعد الاشتقاقSANAAMOHAMMED4388No ratings yet
- المعادلات التفاضلية الاعتيادية م.جليل طلب عبداللهDocument13 pagesالمعادلات التفاضلية الاعتيادية م.جليل طلب عبداللهSaeed AlsudanyNo ratings yet
- مفاهيم أساسية Basic ConceptsDocument3 pagesمفاهيم أساسية Basic Conceptsحسام الشاعرNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثالثة والرابعة قسم التقنياتDocument5 pagesالمحاضرة الثالثة والرابعة قسم التقنياتمصطفى أحمد عبد الرزاق هاديNo ratings yet
- المحور 3 المعادلات التفاضليةDocument4 pagesالمحور 3 المعادلات التفاضليةʚĩɞ ŞéRįñã ʚĩɞNo ratings yet