Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essential Curriculum Map Units
Uploaded by
api-2427395750 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views12 pagesOriginal Title
essential curriculum map units
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views12 pagesEssential Curriculum Map Units
Uploaded by
api-242739575Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Unit: Routines & Procedures (Week 1, 5 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Life-long learners use reading and writing as
tools for discovery.
Reading independently and discussing
reading leads to clearer understanding.
Proficient readers use a variety of strategies
to navigate through text.
Writers communicate in appropriate and
meaningful ways using multiple techniques to
achieve their purpose.
Effective writers use a multi-stage process to
change or clarify ideas in their work.
Strong listening and speaking skills lead to
new and unique understandings and
solutions.
Proficient speakers convey their message by
utilizing language, content, and media.
Words are powerful. Vocabulary knowledge is
important for effective communication and
expression.
Essential Questions
How does independent reading and collaboration
through meaningful discussions aid in understanding of
a text?
How do proficient readers and writers interact with the
text?
How does reading a variety of text enrich an
individual's life?
How can writers develop a well-written narrative using
voice, conventions, content, and organization?
How can the writing process help shape and clarify
ideas?
How can you present information effectively and
concisely while engaging the audience?
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. Synonyms
2. Definition
3. Subjective Pronouns
4. Objective Pronouns
5. Possessive Pronouns
6. Intensive Pronouns
(myself, ourselves)
7. Point of View
8. Third Person
9. First Person
10. Dramas
11. Nonfiction
12. Narrative
13. Sequence
14. Details
15. Tone
16. Formal language
17. Informal language
18. Graphic Organizer
19. Thinking Map
20. Narrator
21. Characters
22. Dialogue
23. Events
24. Transition Words
25. Phrases
26. Introductory clause
27. Main clauses
28. Subordinate clauses
29. Descriptive Language
30. Sensory Language
31. Conclusion
32. Purpose
33. Organization
34. Conventions
35. Punctuation
36. Development
37. Audience
38. Planning
39. Revising
40. Editing
41. Brainstorming
42. Complex sentences
43. Compound sentences
44. Elaborating sentences
45. Rewriting
46. Claims
47. Pronounciation
Content
A. Genre: Narrative (e.g. memoir, fiction)
B. Plan: Ideas, Organization, Brainstorming, Voice, and Content
C. Draft: Ideas, Organization, Voice, and Content
D. Revision: Word Choice, Elaborating Sentences, and Sentence Fluency
E. Editing: Conventions
F. Point of View: First person, Third person
G. Presentation: Clear voice, volume, eye contact
H. Sequence: Logical sequence of ideas
I. Vocabulary: Definition, synonyms, antonyms
Unit: Anaylzing Literature (Week 6, 5 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Life sculpts literature and literature molds life.
Imaginative texts can provide rich and
timeless insights in universal themes,
dilemmas, and social realities of the world.
Students need to learn to use writing as a
way to convey real or imagined experiences
or events.
Writers communicate in appropriate and
meaningful ways to achieve their intended
purpose.
Effective writing is the result of a multi-stage,
reflective process in which the writer must
develop, plan, revise, edit, and rewrite work.
Essential Questions
How do a variety of techniques
enrich narratives?
How does the writing process lay out the writer's
thinking?
How do character thoughts and actions shape the theme
of a text and cause the theme to develop?
How does a reader analyze literary elements, structure,
and language to discern and validate themes in a text?
How can a reader draw on prior knowledge to make a
connection with the text?
How does summarizing or paraphrasing in writing help
us understand complex text?
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. scene
2. stanza
3. setting
4. point of view
5. narrator
6. sequence
7. descriptive details
8. dialogue
9. transition words
10. sensory language
11. conclusion
12. organization
13. purpose
14. audience
15. inference
16. textual evidence
17. theme
18. central idea
19. summary
20. supporting details
21. opinions
22. plot
23. resolution
24. conflict
25. rising action
26. falling action
27. exposition
28. internal conflict
29. external conflict
30. nature vs. man
31. man vs. man
32. man vs. self
33. man vs. society
34. dialogue
35. monologue
36. climax
37. drama
38. planning
39. revising
40. editing
41. rewriting
42. bias
43. judgement
44. third person limited
45. third person
omniscient
46. third person objective
47. first person
48. second person
49. direct
characterization
50. indirect
characterization
51. flat characters
52. round characters
53. static characters
54. dynamic characters
Content
A. Genre: Narrative (e.g. memoir, fiction)
B. Plan: Ideas, Organization, Brainstorming, Voice, and Content
C. Draft: Ideas, Organization, Voice, and Content
D. Revision: Word Choice, Elaborating Sentences, and Sentence Fluency
E. Editing: Conventions
F. Inference/Drawing Conclusions: Prior knowledge, textual evidence
G. Theme: lesson, author's message, main idea/central idea
H. Comprehension: summarize without bias, point of view (first person, second person, third person
objective, third person omniscient, and third person limited), and drama (including stage directions,
dialogues, and monologues)
I. Characterization: static, dynamic, flat, round, indirect, direct
J. Elements: Plot, characterization, setting, conflict, resolution, climax, rising action, falling action
K. Analysis: Structure (sentence, chapter, scene, stanza)
Unit: Comparing & Contrasting Text (Week 11, 2 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Writers share information, opinions and ideas
by using multiple techniques and text types.
Writers communicate in appropriate and
meaningful ways to achieve their intended
purpose.
Essential Questions
Why do writers need evidence within their text to
support their purpose?
How do writers use precise language and specific
vocabulary to explain their topic?
How does the use of comparing and contrasting assist in
examining a topic?
Content
A. Genre: narrative (memoir, historical fiction, fairy tales, poetry, tall tales, fantasy, mystery, realistic
fiction, science fiction, folktales), informational (reports, inquiry), expository/explanatory,
persuasive/argumentative (editorials, essays, speeches), multimedia, descriptive, research
B.Comprehension: Compare/Contrast
C. Valid Claims: Argument, reasons, evidence, secondary and primary sources
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. research
2. analysis
3. compare
4. contrast
5. genres
6. fantasy
7. historical fiction
8. novels
9. poems
10. folktales
11. fairy tales
12. tall tales
13. myths
14. mystery
15. fiction
16. nonfiction
17. science fiction
18. realistic fiction
19. themes
20. topics
21. claims
22. primary source
23. secondary source
Unit: Informational Text: Main Idea / Summary (Week 13, 4 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Imaginative texts can provide rich and
timeless insights into universal themes,
dilemmas, and social realities of the world.
Literary text represents complex stories in
which the thoughts and actions of human
beings are revealed.
Writers use multiple techniques to share
information, opinions, and ideas.
To achieve their intended purpose, writers
communicate in meaningful ways.
Effective writers use a multi-step process to
reflect and improve on their work.
Writing is a tool for thinking and problem-
solving.
Essential Questions
How does a reader analyze literary elements, structure,
and language within a text?
How can a reader draw on prior knowledge to make a
connection with the text?
How does summarizing or paraphrasing in writing help
us understand complex text?
In argumentative writing, how does a writer support
claims made?
Using a multi-stage process, how does a writer
incorporate various components in an
informative/explanatory text to convey concepts and
ideas?
How do writers gather relevant information from
multiple sources and redefine questions to refocus their
research?
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. inference
2. bias
3. propaganda
4. textual evidence
5. central idea
6. summary
7. supporting details
8. opinions
9. planning
10. revising
11. editing
12. rewriting
13. publish
14. transition words
15. events
16. illustrations
17. anecdotes
18. arguments
19. claims
20. valid reasoning
21. relevant evidence
22. credible source
23. primary source
24. secondary source
25. clarify
26. formal style
27. concluding statement
28. informative text
29. explanatory text
30. content
31. organization
32. content
33. voice
34. conventions
35. topic
36. cause/effect structure
37. compare/contrast
structure
38. classification
39. definition
40. format
41. text features
42. headings
43. subheadings
44. bold print
45. font
46. captions
47. italic print
48. graphic features
49. charts
50. tables
51. maps
52. facts
53. quotations
54. concrete details
55. domain-specific
vocabulary
56. development
57. organization
58. purpose
59. audience
60. inquiry
61. refocus
Content
A. Genre: persuasive/argumentative (editorials, essays, speeches), expository/explanatory, research
B. Plan: Ideas, Organization, Brainstorming, Voice, and Content
C. Draft: Ideas, Organization, Voice, and Content
D. Revision: Word Choice, Elaborating Sentences, and Sentence Fluency
E. Editing: Conventions
F. Inference/Drawing Conclusions: Prior knowledge, textual evidence
G. Theme: lesson, author's message, main idea/central idea
H. Comprehension: summarize without bias
I. Characterization: static, dynamic, flat, round, indirect, direct
J. Elements: Plot, characterization, setting, conflict, resolution, climax, rising action, falling action
K. Credible sources: Primary and secondary sources
L. Styles of Writing: Formal, Informal
M. Publication: Presentation
N. Text Features: text elements, graphic features, and functional text features
Unit: Informational Text: Text Structure (Week 18, 4 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Writers use multiple techniques as well as
technology to share information, opinions,
and ideas.
To achieve their intended purpose, writers
communicate in meaningful ways.
Effective writers use a multi-step process to
reflect and improve on their work.
Writing is a tool for thinking and problem-
solving.
Essential Questions
In argumentative writing, how does a writer support
claims made?
How does a writer incorporate various components in
an informative/explanatory text to convey concepts and
ideas?
How does a writer use a multi-stage process to clarify
ideas?
How can a writer use technology to share written
work?
Content
A. Genre: Persuasive/argumentative (editorials, essays, speeches), multimedia
B. Plan: Ideas, Organization, Brainstorming, Voice, and Content
C. Draft: Ideas, Organization, Voice, and Content
D. Revision: Word Choice, Elaborating Sentences, and Sentence Fluency
E. Editing: Conventions
F. Publication: Presentation
G. Credible Sources: Primary and secondary
K. Styles of Writing: Formal, Informal
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. publish
2. argument
3. claim
4. relevant evidence
5. valid reasoning
6. organization
7. content
8. voice
9. conventions
10. credible source
11. primary source
12. secondary source
13. clarify
14. formal style
15. concluding statement
16. planning
17. revising
18. editing
19. rewriting
Unit: Figurative Language / Poetry (Week 22, 3 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Literary text provides creative craftsmanship
through word choice.
Comparing and contrasting text in a variety of
forms or genres provides a full understanding
of the author's message/theme as well as the
ideas being explored.
Words are powerful and vocabulary
knowledge is essential for learning.
Essential Questions
How do specific word choices shape meaning or tone in
a text?
How can you incorporate different strategies when
reading to determine the meaning of words?
How can a reader effectively compare text and
multimedia?
How can a reader compare and contrast different
genres through themes and topics?
How does understanding figurative language help in
interpreting the author's message?
Content
A. Figurative Language: Meaning of words/phrases (including figurative, technical, and connotative)
B. Comprehension: Compare and contrast
C. Genres: Nonfiction, Fiction (drama, poetry, etc), multimedia
D. Vocabulary: Definition, Word Relationships, Parts of Speech, Context clues, prefixes, affixes,
synonyms/antonyms, nuances, tone
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. connotative meaning
2. technical meaning
3. figurative meaning
4. tone
5. mood
6. drama
7. poem
8. compare/contrast
9. evaluate
10. genre
11. historical fiction
12. fantasy
13. fiction
14. nonfiction
15. tall tale
16. fairy tale
17. folktale
18. science fiction
19. mystery
20. realistic fiction
21. themes
22. topics
23. figurative language
24. personification
25. metaphors
26. similes
27. idioms
28. hyperbole
29. onomatopoeia
30. allusion
31. oxymoron
32. alliteration
33. word relationships
34. definition
35. cause/effect
36. part/whole
37. item/category
38. connotations
39. denotations
40. context
Unit: The Genres of Writing (Week 25, 3 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Writers use a multi-step process to develop
and improve ideas through collaboration with
others.
Essential Questions
How does a writer use a multi-
stage process to clarify ideas?
How does the insight and suggestions of
peers help in strengthening and shaping a
piece of writing?
Content
A. Genre: persuasive/argumentative (editorials, essays, speeches), expository/explanatory, research,
narrative (mystery, memoir, realistic fiction, science fiction, historical fiction), poetry
B. Plan: Ideas, Organization, Brainstorming, Voice, and Content
C. Draft: Ideas, Organization, Voice, and Content
D. Revision: Word Choice, Elaborating Sentences, and Sentence Fluency
E. Editing: Conventions
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. coherent writing
2. content
3. voice
4. conventions
5. development
6. organization
7. style
8. purpose
9. audience
10. planning
11. revising
12. editing
13. rewriting
Unit: Information & Argument (Week 29, 4 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Analyzing informational text empowers the
reader to make informed choices in life.
Writing is a device for thinking and problem
solving in which to create new
understandings.
Essential Questions
How can you identify a reliable source of information?
How can an author's outlook on an event differ from
another?
How can the writer draw evidence from text to support
their thinking?
How can the comparison of themes and topics through
a variety of genres differ between texts?
Content
A. Credible Sources: Primary and Secondary
B. Genres: poems, historical fiction, fiction, nonfiction, drama, science fiction, fantasy, fairy tales, folk
tales, tall tales
C. Comprehension: Compare and Contrast
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. argument
2. claims
3. evaluate
4. supporting evidence
5. validity
6. themes
7. topics
8. compare/contrast
9. events
10. genres
11. historical fiction
12. realistic fiction
13. science fiction
14. nonfiction
15. folktales
16. fantasy
17. fairy tales
18. poetry
19. fiction
20. tall tales
21. mystery
22. research
23. informational text
24. literary text
Unit: Visual Learning (Week 35, 4 Weeks)
Stage One: Essential Map (District)
Enduring Understandings
Competent readers can synthesize
information from a variety of sources
including print, audio and visual.
Strong listening and speaking skills are
critical for communicating the understanding
of a topic or issue under study.
Proficient speakers make deliberate choices
regarding language, content and media to
capture and maintain the audience in order to
convey their message.
Essential Questions
How can readers compare text to multimedia using
various components?
How does different information in a multitude of
formats aid in contributing to a deeper understanding
of a topic?
How can different forms of multimedia enhance the
understanding of a presentation?
Content
A. Genre: fiction, poetry, drama, multimedia (video, audio)
B. Presentation: Multimedia, Visual Displays (graphics, images)
C. Comprehension: Interpretation, Explanation
Disciplinary Vocabulary
1. evaluate
2. format
3. content
4. compare/contrast
5. drama
6. poem
7. visually
8. quantitatively
9. surveys
10. data
11. statistics
12. orally
13. topic
14. multimedia
15. graphics
16. images
17. music
18. sound
19. visuals
You might also like
- Multimodal Composing: Strategies for Twenty-First-Century Writing ConsultationsFrom EverandMultimodal Composing: Strategies for Twenty-First-Century Writing ConsultationsLindsay A. SabatinoNo ratings yet
- DA & Pragmatics Course OutlineDocument4 pagesDA & Pragmatics Course Outlineamenmes22No ratings yet
- Memorial ProgramDocument18 pagesMemorial Programapi-267136654No ratings yet
- 1st QuarterDocument24 pages1st QuarterLui Harris S. CatayaoNo ratings yet
- QH 2021 D1 Semantics Syllabus GradDocument10 pagesQH 2021 D1 Semantics Syllabus GradNgọc BíchNo ratings yet
- MemorialDocument18 pagesMemorialS TANCRED100% (2)
- Fogarty Literacy PlannerDocument9 pagesFogarty Literacy Plannerapi-318709080No ratings yet
- FILE - 20220417 - 133622 - QH 2021.D2 Syllabus GradDocument10 pagesFILE - 20220417 - 133622 - QH 2021.D2 Syllabus GradHoa ĐàoNo ratings yet
- The Great Kapok Tree S2Document24 pagesThe Great Kapok Tree S2S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Creative WritingDocument13 pagesCreative WritingShaheeraMobarakNo ratings yet
- Reading U3w3 Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesReading U3w3 Lesson Planapi-239626791No ratings yet
- The Arrival S3Document24 pagesThe Arrival S3S TANCRED100% (1)
- RW Module 1 and 2 Q3Document10 pagesRW Module 1 and 2 Q3danilo roblico jr.No ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument17 pagesENGLISHvimala maharajaNo ratings yet
- Let The Celebrations Begin S3Document18 pagesLet The Celebrations Begin S3S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Fahrenheit 451 UnitDocument83 pagesFahrenheit 451 UnitJulia Maturo100% (1)
- Grade 8 English ModuleDocument47 pagesGrade 8 English ModuleIra100% (1)
- An Analysis of Students' Writing Skill in Descriptive TextDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Students' Writing Skill in Descriptive TextRichard RayNo ratings yet
- April 28-May2 PDFDocument2 pagesApril 28-May2 PDFLee MeiNo ratings yet
- Creus, Billy JoyDocument6 pagesCreus, Billy JoyBilly Joy E. Creus100% (2)
- Reading U3w2 Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesReading U3w2 Lesson Planapi-239626791No ratings yet
- Grade8qtr1l1 130812032648 Phpapp02Document47 pagesGrade8qtr1l1 130812032648 Phpapp02Anthony Miguel RafananNo ratings yet
- RWS Interviewer First SummativeDocument10 pagesRWS Interviewer First SummativelucilNo ratings yet
- Ued 401 Mcmaster Priscilla Unit Plan 8thDocument7 pagesUed 401 Mcmaster Priscilla Unit Plan 8thapi-540885055No ratings yet
- Resource PacketDocument38 pagesResource Packetapi-238546478No ratings yet
- SHS Reading and Writing Q3 W2Document20 pagesSHS Reading and Writing Q3 W2Renz De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning CompetenciesDocument5 pagesLearning CompetenciesGracelyn Jhing Racoma CamasuraNo ratings yet
- Expository TextDocument21 pagesExpository TextRosmalia Kasan100% (1)
- Bridge To Terabithia Unit S3 UpdatedDocument23 pagesBridge To Terabithia Unit S3 UpdatedS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Tep Secondary Curriculum MapDocument4 pagesTep Secondary Curriculum Mapapi-393406373No ratings yet
- Y7 Narrative Writing SowDocument8 pagesY7 Narrative Writing SowMustafa Al QadyNo ratings yet
- English Unit - NanberryDocument12 pagesEnglish Unit - Nanberryapi-237136245100% (6)
- Wotw Unit PlanDocument6 pagesWotw Unit Planapi-317825538No ratings yet
- Teaching ReadingDocument3 pagesTeaching Readingapi-458431283No ratings yet
- English Communication Arts and Skills Through Anglo-American and Philippine Literatures Ecas 10Document8 pagesEnglish Communication Arts and Skills Through Anglo-American and Philippine Literatures Ecas 10Jonathan M. AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Speeches and RhetoricDocument7 pagesSpeeches and RhetoricTom HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Communication ExamsDocument6 pagesCommunication ExamsLesley Liavoga SandeNo ratings yet
- Stage 3 Author Craft mk2Document11 pagesStage 3 Author Craft mk2api-237136245No ratings yet
- Docengpowerofonemultigenre ProjectDocument7 pagesDocengpowerofonemultigenre Projectapi-146484992No ratings yet
- Grandad's Gifts S2Document30 pagesGrandad's Gifts S2S TANCRED100% (1)
- WRD 513: Semiotics: Course DescriptionDocument2 pagesWRD 513: Semiotics: Course DescriptionMaria del Carmen Alvarado AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Porterm Information Literacy PlanDocument10 pagesPorterm Information Literacy Planapi-164885499No ratings yet
- Grade 12 - Creative Writing Q2 Weeks 7-8Document4 pagesGrade 12 - Creative Writing Q2 Weeks 7-8Cloue Faye I. Basallo71% (7)
- EN6-w9-day 1-5Document31 pagesEN6-w9-day 1-5ivy quirog100% (1)
- Grade 10 UBD FIRST QUARTER (2019-2020)Document38 pagesGrade 10 UBD FIRST QUARTER (2019-2020)Donna GeonzonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - CabaneroDocument16 pagesLesson Plan - CabaneroJelly SedeñoNo ratings yet
- Third Trimester Grade 8 BOOKLETDocument51 pagesThird Trimester Grade 8 BOOKLETHaya Al HassanNo ratings yet
- 7th ReadingDocument23 pages7th ReadingasdNo ratings yet
- Lesson Mysteries of Harris BurdickDocument4 pagesLesson Mysteries of Harris Burdickapi-260469323No ratings yet
- Unit 4 StandardsDocument12 pagesUnit 4 Standardsapi-265442361No ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Final 2 Numbered 1Document71 pagesReading and Writing Final 2 Numbered 1Daisy CabaseNo ratings yet
- Tomorrow When The War Began UbdDocument14 pagesTomorrow When The War Began Ubdapi-25742789650% (2)
- Unit Plan ThemeDocument33 pagesUnit Plan Themeapi-281781118No ratings yet
- Come On, Rain! S1Document24 pagesCome On, Rain! S1S TANCRED100% (1)
- Literacy Planner OnlyDocument8 pagesLiteracy Planner Onlyapi-284319044No ratings yet
- Curriculum DocumentDocument6 pagesCurriculum Documentapi-266091068No ratings yet
- Educ5208 Multimedia AssignmentDocument19 pagesEduc5208 Multimedia Assignmentapi-542567609No ratings yet
- s2 The Lost Thing English UnitDocument19 pagess2 The Lost Thing English Unitapi-233094051No ratings yet
- Ubd Unit PlanDocument32 pagesUbd Unit Planapi-469833896No ratings yet
- Writers Workshop Fractured Fairy Tale RubricDocument1 pageWriters Workshop Fractured Fairy Tale Rubricapi-242739575No ratings yet
- Twisted Fairytale ProjectDocument2 pagesTwisted Fairytale Projectapi-242739575No ratings yet
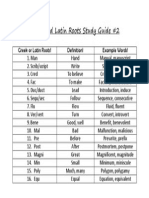
- Greek or Latin Roots Study Guide 2Document1 pageGreek or Latin Roots Study Guide 2api-242739575No ratings yet
- Ms Kennealys 2014-2015 Ela SyllabusDocument4 pagesMs Kennealys 2014-2015 Ela Syllabusapi-242739575No ratings yet
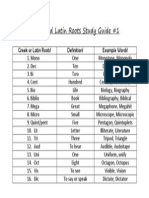
- Greek or Latin Roots Study Guide 1Document1 pageGreek or Latin Roots Study Guide 1api-242739575No ratings yet
- Speech Recognition Abilities in Noise For Children With Severe To Profound Unilateral Hearing ImpairmentDocument9 pagesSpeech Recognition Abilities in Noise For Children With Severe To Profound Unilateral Hearing ImpairmentKhaled Al-GhamdiNo ratings yet
- Eswara Lec Fbbhet HDocument35 pagesEswara Lec Fbbhet Hron100% (1)
- 1.escreva Os Verbos A Seguir No GerúndioDocument3 pages1.escreva Os Verbos A Seguir No Gerúndiopatriciasaires100% (1)
- 17071-02 B13R D13C CHN 125761-132856 PDFDocument120 pages17071-02 B13R D13C CHN 125761-132856 PDFAnonymous EDNsviNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Regular Verbs Informative SheetDocument2 pagesSimple Past Regular Verbs Informative SheetPedro FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ielts Task 1: 1. Rubic of Ielts Task Understanding The Rubric Writing Task 1Document23 pagesIntroduction To Ielts Task 1: 1. Rubic of Ielts Task Understanding The Rubric Writing Task 1Linh Trang Lê ThịNo ratings yet
- Alexander Coan Unit 5 Lesson Plan 229922 1641768921Document2 pagesAlexander Coan Unit 5 Lesson Plan 229922 1641768921api-665959454No ratings yet
- Green To GoldDocument3 pagesGreen To Goldapi-326627986No ratings yet
- Spectroquant Prove 600: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesSpectroquant Prove 600: Technical Data SheetGunawan Alim CahyoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Progression Test English Question Paper 2 PDF FreeDocument10 pagesCambridge Primary Progression Test English Question Paper 2 PDF FreeladeahmagdalyneNo ratings yet
- Reading Response 2Document5 pagesReading Response 2api-577366559No ratings yet
- Teach English Now - Technology Enriched TeachingDocument4 pagesTeach English Now - Technology Enriched TeachingveverexNo ratings yet
- 73. THCS ĐIỆN BIÊN CHẴN KEYSDocument2 pages73. THCS ĐIỆN BIÊN CHẴN KEYSLe Thi Hai AnhNo ratings yet
- 3-Minute German S1 #2 Greetings: Lesson NotesDocument4 pages3-Minute German S1 #2 Greetings: Lesson NotesThuong StriegelNo ratings yet
- Comparison of CompilerDocument4 pagesComparison of CompilerMuhammad Waqas AnwarNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechgtygyuDocument2 pagesIndirect SpeechgtygyuKiriakos IfantidisNo ratings yet
- Makalah Materi B InggrisDocument14 pagesMakalah Materi B InggrisYogi IpiNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1) School RegisterDocument3 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1) School RegisterAlberto SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Later Vedic AgesDocument3 pagesLater Vedic AgesKanupriya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- 05 - 1 - StarUML 5.0 User Guide (Modeling With UseCase Diagram)Document10 pages05 - 1 - StarUML 5.0 User Guide (Modeling With UseCase Diagram)Juan Carlos Flores LNo ratings yet
- Error CorrectionDocument9 pagesError CorrectionJesus PerezNo ratings yet
- Aim High - 1st Year Secondary 2015Document158 pagesAim High - 1st Year Secondary 2015yassoi50% (2)
- NounDocument2 pagesNounGustavo Henrique AraújoNo ratings yet
- Writing Application LetterDocument4 pagesWriting Application LetterSiswati OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics PapersDocument13 pagesPsycholinguistics PapersDaneshaa BillNo ratings yet
- When Two Subjects Are Joined by And', The Verb Is Plural. Sally and Sam Ride Their Bikes To SchoolDocument12 pagesWhen Two Subjects Are Joined by And', The Verb Is Plural. Sally and Sam Ride Their Bikes To SchoolPrecious ChristineNo ratings yet
- Half Race Design GuidelinesDocument5 pagesHalf Race Design GuidelinesDrackGamerbrNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument2 pagesAdjective OrderNoreen NoyinNo ratings yet
- Comparative of AdjectivesDocument27 pagesComparative of AdjectivesapgalanNo ratings yet
- Commonly Confused Words PresentationDocument21 pagesCommonly Confused Words PresentationJunaid NazirNo ratings yet