Professional Documents
Culture Documents
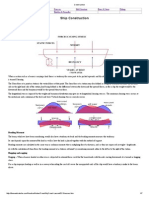
Tumble Home
Uploaded by
Sumit Sinha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageTumblehome
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTumblehome
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageTumble Home
Uploaded by
Sumit SinhaTumblehome
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
I found this explaination: 1.
The American-Built Clipper Ship 1850-1856,
Characteristics, Construction, Details. W.L.Crothers, McGraw Hill (1997). p54.
Tumblehome has the effect of making the top deck (weatherdeck) smaller. The clai
m
is that this was introduced during the galleon era when large numbers of canons
could make the hull top-heavy. A smaller top deck lowers the centre of gravity,
but it also reduces the righting moment quite significantly. Another reason for
tumblehome might be to keep the lee rail out of the water when heeling. A more
sensible excuse is the strengthening effect of a barrel shaped hull, approaching
the cylindrical shape of a submarine or pressure vessel. Significant tumblehome
is
virtually absent on modern ships, the sides are more likely to be vertical or ev
en
slightly outward sloping (flare).
A small amount of tumblehome is normal in many designs in order to allow any
small projections at deck level to clear wharves.
Freeboard (f) on Oil Tankers
It can be seen from the given H/D percentages that the summer freeboard
for the General Cargo ships will be approximately 25%. For the Oil Tankers
it is more likely to be nearer 20%.
Freeboard on Oil Tankers have less freeboard than General Cargo ships of
similar length for several reasons, six of them being:
1. Smaller deck openings in the Upper Deck.
2. Greater sub-division by transverse and longitudinal bulkheads.
3. Density of cargo oil is less than grain cargo.
4. Much larger and better pumping arrangements on tankers to control any
ingress of bilge water.
5. Permeability for an oil-filled tank is only about 5% compared to permeability
of a grain cargo hold of 6065%. Hence ingress of water in a
bilged compartment will be much less.
6. Larger Transverse Metacentric Height (GMT) values for an Oil Tanker,
especially for modern wide shallow draft tanker designs.
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Brochure 2022 23Document28 pagesBrochure 2022 23Sumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Electrical Oral Question & AnswersDocument14 pagesElectrical Oral Question & AnswersKranthi KiranNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- TDS Pidifin 2K Eng Rev.09 23 07 19Document3 pagesTDS Pidifin 2K Eng Rev.09 23 07 19Sumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) - Maritime WikiDocument11 pagesShip Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) - Maritime WikiSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- PumpsDocument8 pagesPumpsDeeran CarieNo ratings yet
- LifeboatDocument74 pagesLifeboatSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- IMO - Action DatesDocument4 pagesIMO - Action DatesSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Centrifugal Purifiers ClarifiersDocument9 pagesCentrifugal Purifiers ClarifiersSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Oil Spill KitDocument8 pagesOil Spill Kitnqt14283No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Notes On Ball BearingsDocument10 pagesNotes On Ball BearingsSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Function of Thermostatic Expansion Valve in Refrigeration SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of Thermostatic Expansion Valve in Refrigeration SystemSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Clover Lapping Compounds and Grinding Compound, Clover Brand, Clover, Fel-Pro, Felpro, Loctite Lapping Compounds, Lapping PasteDocument4 pagesClover Lapping Compounds and Grinding Compound, Clover Brand, Clover, Fel-Pro, Felpro, Loctite Lapping Compounds, Lapping PasteSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Ship StressesDocument7 pagesShip StressesSumit Sinha50% (2)
- Rudder and PropellerDocument5 pagesRudder and PropellerSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- c0n Rod Ovality For ADocument2 pagesc0n Rod Ovality For ASumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)