Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respirasi: Dr. Irawan Fajar K Fakultas Kedokteran Unej
Uploaded by
Elvira Wisakhadewi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views35 pagesThe document discusses the functions of the respiratory system, including gas exchange, moving air in and out of the lungs, and protecting respiratory surfaces. It describes external respiration processes like breathing, gas diffusion, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport, and gas exchange between blood and tissues. Compliance is discussed in relation to connective tissue structure, surfactant production, and thoracic cage mobility. Muscles involved in inhalation include the diaphragm, sternocleidomastoid, serratus anterior, pectoralis minor, scalenes, and external intercostals. Muscles for exhalation include the internal intercostals, transversus thoracis, external and internal obliques, transversus
Original Description:
respirasi
Original Title
2. respirasi
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the functions of the respiratory system, including gas exchange, moving air in and out of the lungs, and protecting respiratory surfaces. It describes external respiration processes like breathing, gas diffusion, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport, and gas exchange between blood and tissues. Compliance is discussed in relation to connective tissue structure, surfactant production, and thoracic cage mobility. Muscles involved in inhalation include the diaphragm, sternocleidomastoid, serratus anterior, pectoralis minor, scalenes, and external intercostals. Muscles for exhalation include the internal intercostals, transversus thoracis, external and internal obliques, transversus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views35 pagesRespirasi: Dr. Irawan Fajar K Fakultas Kedokteran Unej
Uploaded by
Elvira WisakhadewiThe document discusses the functions of the respiratory system, including gas exchange, moving air in and out of the lungs, and protecting respiratory surfaces. It describes external respiration processes like breathing, gas diffusion, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport, and gas exchange between blood and tissues. Compliance is discussed in relation to connective tissue structure, surfactant production, and thoracic cage mobility. Muscles involved in inhalation include the diaphragm, sternocleidomastoid, serratus anterior, pectoralis minor, scalenes, and external intercostals. Muscles for exhalation include the internal intercostals, transversus thoracis, external and internal obliques, transversus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 35
Respirasi
dr. Irawan Fajar K
FAKULTAS KEDOKTERAN
UNEJ
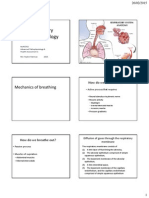
FUNGSI SYSTEM
RESPIRATORY
1. Area untuk gas exchange
2. Menggerakkan udara ke dan dari paru.
3. Melindungi permukaan respiratory dari dehydrasi,
perubahan temperatur, dan dari invasi bakteri pathogen
4. Bersuara.
5. Mencium /membau
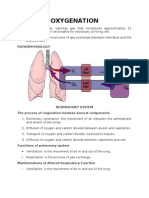
Respiration
external respiration
internal respiration
External respiration
1. Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, which
involves the physical movement of air into and
out of the lungs.
2. Gas diffusion across the respiratory membrane
between the alveolar air spaces and the alveolar
capillaries.
3. The storage and transport of oxygen and
carbon dioxide between the alveolar capillaries
and capillary beds in other tissues.
4. The exchange of dissolved gases between the
blood and the interstitial fluids.
Compliance
The connective tissue structure of the lungs. The
loss of supporting tissues resulting from alveolar
damage, as in emphysema, increases compliance.
The level of surfactant production. The collapse
of alveoli on expiration, due to inadequate
surfactant, as in respiratory distress syndrome,
reduces compliance.
The mobility of the thoracic cage. Arthritis or
other skeletal disorders that affect the articulations
of the ribs or spinal column will also reduce
compliance.
Otot I nhalation
Diaphragma 75 percent. elevating the ribs.
25 percent
Sternocleidomastoid
serratus anterior,
pectoralis minor
scalenes,
external intercostals
Otot Exhalation
The internal intercostals
transversus thoracis
external and internal obliques
the transversus abdominis, and
the rectus abdominis
You might also like
- Atelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Hole'S Human Anatomy and Physiology: Powerpoint Lecture Outlines To AccompanyDocument52 pagesHole'S Human Anatomy and Physiology: Powerpoint Lecture Outlines To AccompanyEllen LiberaceNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory SystemvhieeelgbmNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-277775953No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesRespiratory Systemamulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- I. Review of Respiratory System A.ppt 2Document115 pagesI. Review of Respiratory System A.ppt 2arielleortuosteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Student Version The Respiratory System 2020.ppt (1186)Document18 pagesChapter 13 Student Version The Respiratory System 2020.ppt (1186)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases-HumansDocument14 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases-Humansnihalbolla2023No ratings yet
- 1-Respiratory MechanicsDocument56 pages1-Respiratory MechanicsDoha JKNo ratings yet
- M132 Respiratory 2022Document28 pagesM132 Respiratory 2022Bana ItanNo ratings yet
- ImrozDocument57 pagesImrozSyed Imroz KhanNo ratings yet
- NUR5703 Respiratory Advanced PathophysiologyDocument16 pagesNUR5703 Respiratory Advanced PathophysiologyLee MeyerNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes in Elderly RespiDocument23 pagesPhysiological Changes in Elderly RespiIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- Assignment NO 1: Name:Adeel Afzal Section: C Sap I'd: 70126263 Assignment: Physiology Submitted To: DR Urfah ZaighamDocument6 pagesAssignment NO 1: Name:Adeel Afzal Section: C Sap I'd: 70126263 Assignment: Physiology Submitted To: DR Urfah ZaighamAdeel AfzalNo ratings yet
- 0 Toxic Responses of The Respiratory SystemDocument67 pages0 Toxic Responses of The Respiratory SystemfianceeleeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System-1Document38 pagesRespiratory System-1KelvinNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document40 pagesModule 2Sharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Ila College of Health: Respiratory PhysiologyDocument29 pagesIla College of Health: Respiratory PhysiologyDaniel DendaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemRhod Jayson RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Air 213 2Document56 pagesAir 213 2gr0442No ratings yet
- Respiratory System: M.AzhariDocument142 pagesRespiratory System: M.AzhariLili ManaoNo ratings yet
- NCM 118Responses-to-Altered-Ventilatory-FunctionDocument169 pagesNCM 118Responses-to-Altered-Ventilatory-FunctionAddah, Dhenaraiza H.No ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document28 pagesChapter 12Ammar SmadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document28 pagesChapter 12براءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemMotiourNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Blessy-1Document51 pagesRespiratory System Blessy-1Naveen ChNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemArjunNo ratings yet
- Breathing MechanismDocument25 pagesBreathing Mechanismilikegay2dmensNo ratings yet
- 12.respiratory SystemDocument52 pages12.respiratory SystemRulani PrinceNo ratings yet
- Beige and Brown Vintage Risograph Illustration Cutout Scrapbook Animated PresentationDocument38 pagesBeige and Brown Vintage Risograph Illustration Cutout Scrapbook Animated PresentationKyla Macauba VHNo ratings yet
- Mtless 8 F 99 RespiratoryDocument28 pagesMtless 8 F 99 RespiratorytiejeitorresNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Document27 pagesSains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Nadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Kim LesterDocument6 pagesKim LesterKim Lester ValeraNo ratings yet
- NursingBulletin Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesNursingBulletin Respiratory Systemseigelystic100% (3)
- Oksigenasi ACHMADDocument24 pagesOksigenasi ACHMADMuhammad Angger wijaksonoNo ratings yet
- fileConcept20of20Oxygenation202620Suctioning - Pdftoken AWznOZUw2d1 DzDmnT6ByvrL NX2FKwf6OGYFwFDocument105 pagesfileConcept20of20Oxygenation202620Suctioning - Pdftoken AWznOZUw2d1 DzDmnT6ByvrL NX2FKwf6OGYFwFJullana ImperialNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Basis of The Human Respiratory System: Erial Bahar 2018Document103 pagesAnatomical Basis of The Human Respiratory System: Erial Bahar 2018AmNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System and AnemiaDocument112 pagesRespiratory System and AnemiaJorie RocoNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Gas ExchangeDocument8 pagesBreathing and Gas ExchangeSumaiya AnwarNo ratings yet
- Lec-6 Respiratory SystemDocument42 pagesLec-6 Respiratory SystemOnkar RaiNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity Nostrils Pharynx AIRDocument4 pagesNasal Cavity Nostrils Pharynx AIRDarwin CauilanNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distres SyndromeDocument17 pagesAcute Respiratory Distres SyndromeLalrinchhani PautuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesRespiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Organs of The Respiratory System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document13 pagesThe Respiratory System Organs of The Respiratory System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- Problems in OxygenationDocument2 pagesProblems in OxygenationCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and Physiology: Marianne Belleza, RNDocument18 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and Physiology: Marianne Belleza, RNTiara GustiwiyanaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Respiratory System HandoutDocument10 pages2018 Respiratory System HandoutMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Respiration and Gas Exchange-2Document28 pagesUnit 10 - Respiration and Gas Exchange-2thraaaladyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemWilson chumpukaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Second HalfDocument35 pagesRespiratory System: The Second HalfnicopiiNo ratings yet
- DR Zainuri - Anatomi RespiratoriDocument55 pagesDR Zainuri - Anatomi RespiratoriratuhamimNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Gaseous Exchnage by Sherrie-Ann Wilson-BrownDocument85 pagesBreathing and Gaseous Exchnage by Sherrie-Ann Wilson-BrownNayoka EnnisNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemOyrik Mukhopadhyay100% (1)
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument37 pagesGaseous ExchangeSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 1Document29 pagesRespiratory System 1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesDiffusion and Gas ExchangeMariam Al.hellaniNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Air and Bioaerosols: ENVR 133 Mark D. SobseyDocument35 pagesMicrobes in Air and Bioaerosols: ENVR 133 Mark D. SobseyMuhamad ZakyNo ratings yet
- Analisis Data FFQ SQ-FFQDocument4 pagesAnalisis Data FFQ SQ-FFQElvira WisakhadewiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Low Mediu M High Very High Wasting 15 Underwei GHT 10 10-19.9 20-29,9 30Document1 pageLow Mediu M High Very High Wasting 15 Underwei GHT 10 10-19.9 20-29,9 30Elvira WisakhadewiNo ratings yet
- The Kind of Pollination and Ability To Parthenocarpy of Pepino (Solanum Muricatum Ait.)Document7 pagesThe Kind of Pollination and Ability To Parthenocarpy of Pepino (Solanum Muricatum Ait.)Elvira WisakhadewiNo ratings yet