Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Intro Notes
Uploaded by
api-251874912Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Intro Notes
Uploaded by
api-251874912Copyright:
Available Formats
Energy
Notes: 10/6/2014
What is Energy?
Energy is the ABILITY TO DO WORK
Energy can:
Produce light
Produce heat
Produce motion
Produce sound
Produce growth
Power technology
When you see any of
the above, you know that
energy is present!
Forms of Energy
There are many different forms of energy, but
they all fall into two categories: Potential or
Kinetic Energy
Potential Energy: Stored energy; the energy
of position; gravitational energy
Kinetic Energy: Motion; motion of waves,
electrons, atoms, molecules, substances, and
objects
Potential Energy:
stored energy; the energy of position;
gravitational energy
Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and
molecules (Example: FOOD)
Stored Mechanical Energy: Energy stored in objects by an
application of force (Examples: a SPRING; a STRETCHED
RUBBER BAND)
Nuclear Energy: Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
(when atoms are split, the energy that holds the nucleus
together is released) (Examples: Nuclear Power Plants
split Uranium atoms in a process called FISSION. The sun
combines atoms in a process called FUSION.)
Gravitational Energy: Energy of position or place
(Examples: Water behind a DAM; a ROCK at the top of a
HILL).
Kinetic Energy:
motion; the motion of waves, electrons,
atoms, molecules, substances, and objects
Electrical Energy: the movement of electrons (Examples:
ELECTRICITY; LIGHTENING)
Radiant Energy: Electromagnetic Energy that travels in
waves (Examples: SUNLIGHT; LIGHT FROM A LAMP)
Thermal Energy: the internal energy in substances, known
as HEAT (Examples: GEOTHERMAL; FRICTION.)
Motion Energy: the movement of objects from one place to
another (Example: WIND)
Sound Energy: the movement of energy through
substances in longitudinal waves (Examples: MUSIC from
a speaker; KNOCKING)
The Law of Conservation of
Energy
Energy can be transformed from
one form to another, but it can
NEVER be created or destroyed
This means that all the energy on Earth is
transformed from some other energy
source Lets look at some examples!
On the next five slides, there will be one picture on each slide. Your job
is to figure out ONE energy conversion (or transformation) that is taking
place in each picture.
Example
Stretching and releasing a
rubber band converts
Stored Mechanical
(Potential) Energy
into
Motion (Kinetic) Energy
A Jack-in-the-Box
Stored Mechanical Energy (Potential)
Motion (Kinetic) and Sound (Kinetic)
A Flashlight
Chemical Energy (Potential) Radiant
(Kinetic) and Heat (Kinetic)
A Radio
Electrical Energy (Electricity, Kinetic) Sound (Kinetic) and
Thermal (Kinetic) or, if batteries are used
Chemical Energy (Potential) Sound (Kinetic) and Thermal
(Kinetic)
An athletelike this bicyclist.
Chemical Energy (Potential) Motion
(Kinetic), Sound (Kinetic), and Thermal
(Kinetic)
Bouncy Balls
Gravitational (Potential) Motion (Kinetic),
Sound (Kinetic), Thermal (Kinetic)
Question #1 Question #2
Practice Questions
Question #3
Question #4
Question #5
You might also like
- What Is Energy: Ansunlight Makes Our DaytimeDocument16 pagesWhat Is Energy: Ansunlight Makes Our DaytimeMuhamad Afif100% (2)
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument28 pagesForging New Generations of EngineersDarshan MbNo ratings yet
- Energy of SystemDocument14 pagesEnergy of SystemRovshen BayramovNo ratings yet
- Forms of EnergyDocument4 pagesForms of Energybrian marchenaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 W4 - EnergyDocument37 pagesSCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 W4 - EnergyRex AlcistoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Sources of EnergyDocument48 pagesTopic 6 Sources of EnergyNur AmalinaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument7 pagesScienceAletheia BlatzNo ratings yet
- What is Energy? ExplainedDocument38 pagesWhat is Energy? Explainednasir siyarNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy Sources 1 NewDocument38 pagesAlternative Energy Sources 1 Newnasir siyarNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument38 pagesEnergy Forms and ChangesllsinclairNo ratings yet
- Copy This Chart and Complete The Missing InformationDocument33 pagesCopy This Chart and Complete The Missing InformationOlivia RidleyNo ratings yet
- Types of EnergyDocument30 pagesTypes of EnergyabdikarimmohamoudNo ratings yet
- Forms of Energy NotesDocument24 pagesForms of Energy NotesCassidy BellNo ratings yet
- Forms and Sources of EnergyDocument60 pagesForms and Sources of EnergyCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- Energy-Forms and ChangesDocument17 pagesEnergy-Forms and ChangesantoniodellisantiNo ratings yet
- الجزء الأولDocument31 pagesالجزء الأولMustafa MandourNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Grade 7 Intro Energy Forms and ChangesDocument67 pagesWeek 4 Grade 7 Intro Energy Forms and ChangesmkraemerNo ratings yet
- 6 9C-EnergyFormsConversionsDocument5 pages6 9C-EnergyFormsConversionsTracy Nicole MaurilloNo ratings yet
- 14-Energy Transformations Test ReviewDocument3 pages14-Energy Transformations Test Reviewapi-235364651No ratings yet
- What Is EnergyDocument14 pagesWhat Is EnergyNILO, CZARINA A.No ratings yet
- What Is EnergyDocument12 pagesWhat Is Energyapi-379952307No ratings yet
- Types of EnergyDocument3 pagesTypes of EnergyPABLO REYNERIO CRUZ ROCHA100% (1)
- Energy FormsDocument41 pagesEnergy FormsHamza MujahidNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument20 pagesEnergy Forms and ChangesMonica JavierNo ratings yet
- Energy OverviewDocument39 pagesEnergy OverviewHimani RaoNo ratings yet
- Energy - Forms 2017Document54 pagesEnergy - Forms 2017ElahMae AriateNo ratings yet
- Fuels & Energy: Checkpoint PhysicsDocument18 pagesFuels & Energy: Checkpoint PhysicslplkwvNo ratings yet
- Work-Power-Energy Physsics 12 LectureDocument12 pagesWork-Power-Energy Physsics 12 LecturefilchibuffNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Types of EnergyDocument23 pagesLesson 2 Types of Energyapi-408493824No ratings yet
- Competency 6 Ay 2023 2024 2Document14 pagesCompetency 6 Ay 2023 2024 2chaibalinNo ratings yet
- Forms of EnergyDocument6 pagesForms of Energyapi-279793282No ratings yet
- Content SourcesofenergyDocument24 pagesContent SourcesofenergyZainurain Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy Form 1Document24 pagesSources of Energy Form 1Sivam DhanabalNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument22 pagesRocksdina1712No ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument44 pagesEnergy Forms and Changesdoudouthekiller100% (1)
- Energy and It's Types.Document17 pagesEnergy and It's Types.usmansherdinNo ratings yet
- Forms of Energy: The Big 6Document3 pagesForms of Energy: The Big 6Maria Christine A. MonterdeNo ratings yet
- KS3 Physics: 7I Energy ResourcesDocument87 pagesKS3 Physics: 7I Energy ResourcesRahaf ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Identify All The Forms of Energy You See in The Picture BelowDocument54 pagesIdentify All The Forms of Energy You See in The Picture Belowmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes Year 7Document5 pagesSummary Notes Year 7Cinara Rahimova100% (1)
- Energy TransfersDocument36 pagesEnergy TransfersMai HamadaNo ratings yet
- Forms of Energy ReadingDocument20 pagesForms of Energy Readingapi-25797854150% (6)
- EnergyDocument28 pagesEnergy吕洁儿No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Energy Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages8th Grade Energy Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- P6 PAL Science L11 Forms and Uses of Energy-1Document24 pagesP6 PAL Science L11 Forms and Uses of Energy-1XuaN XuanNo ratings yet
- What is Energy? Exploring Chemical and Kinetic FormsDocument7 pagesWhat is Energy? Exploring Chemical and Kinetic FormsJothsna PraveenaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Energy Sources and TypesDocument7 pagesThe Basics of Energy Sources and TypesLakshanaNo ratings yet
- Exploring the Main Forms of EnergyDocument17 pagesExploring the Main Forms of EnergyEmily MangraNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion: Dr. Mohamed ElsamahyDocument42 pagesEnergy Conversion: Dr. Mohamed ElsamahyHossamKamalNo ratings yet
- Energy: Forms and ChangesDocument43 pagesEnergy: Forms and ChangesDian WestbyNo ratings yet
- files_2_2021_September_NotesHubDocument_1632364774Document41 pagesfiles_2_2021_September_NotesHubDocument_1632364774ANKIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Energy and EnvironmentDocument39 pagesEnergy and EnvironmentAkinwunmi OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Energy and Energy TR Ansform at Ions: Kinetic Energy Potential EnergyDocument5 pagesEnergy and Energy TR Ansform at Ions: Kinetic Energy Potential EnergyhextobinaryNo ratings yet
- Energy: Forms and Changes: BBBBBBBBBBDocument41 pagesEnergy: Forms and Changes: BBBBBBBBBBSam AwanNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of EnergyDocument4 pagesLaw of Conservation of Energyapi-189616674No ratings yet
- Energy: 25 Projects Investigate Why We Need Power & How We Get ItFrom EverandEnergy: 25 Projects Investigate Why We Need Power & How We Get ItNo ratings yet
- Atkinson 14te802 Gltunit2Document19 pagesAtkinson 14te802 Gltunit2api-251874912No ratings yet
- Atkinson 15te804 SyllabusDocument7 pagesAtkinson 15te804 Syllabusapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Carly Atkinson: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesCarly Atkinson: Objectiveapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Thunderstorms Note SheetDocument3 pagesThunderstorms Note Sheetapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Viscosity Lab 2 WPDocument6 pagesViscosity Lab 2 WPapi-251874912No ratings yet
- AprilDocument1 pageAprilapi-251874912No ratings yet
- MarchDocument2 pagesMarchapi-251874912No ratings yet
- ThunderstormssocrativeDocument2 pagesThunderstormssocrativeapi-251874912No ratings yet
- TornadonotesDocument11 pagesTornadonotesapi-251874912No ratings yet
- HurricanesDocument17 pagesHurricanesapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Forces of NatureDocument6 pagesForces of Natureapi-251874912No ratings yet
- There Is Energy in The WindDocument3 pagesThere Is Energy in The Windapi-251874912No ratings yet
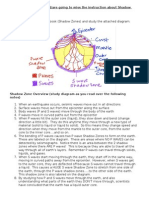
- Shadow ZonesDocument1 pageShadow Zonesapi-251874912No ratings yet
- FebruaryDocument1 pageFebruaryapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Air Pressure NotesDocument2 pagesAir Pressure Notesapi-251874912No ratings yet
- GetthegistDocument1 pageGetthegistapi-251874912No ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument7 pagesVolcanoapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Volcano and Earthquake PatternsDocument2 pagesVolcano and Earthquake Patternsapi-251874912No ratings yet
- EarthquaketrackDocument5 pagesEarthquaketrackapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Earthquake Depth InvestigationDocument3 pagesEarthquake Depth Investigationapi-251874912No ratings yet
- ShadowzoneDocument2 pagesShadowzoneapi-251874912No ratings yet
- EqtsunamiDocument7 pagesEqtsunamiapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Slinky Lab: Introduction. Earthquakes Release Large Amounts of Energy in The Form of Seismic WavesDocument4 pagesSlinky Lab: Introduction. Earthquakes Release Large Amounts of Energy in The Form of Seismic Wavesapi-251874912No ratings yet
- MagnitudeDocument7 pagesMagnitudeapi-251874912No ratings yet
- SeismicDocument2 pagesSeismicapi-251874912No ratings yet
- PlatetecstudyguideDocument1 pagePlatetecstudyguideapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Seismic Waves-2Document3 pagesSeismic Waves-2api-251874912No ratings yet
- JanuaryDocument2 pagesJanuaryapi-251874912No ratings yet
- EarthquakeelasticreboundDocument5 pagesEarthquakeelasticreboundapi-251874912No ratings yet
- Interactive Map QuestionsDocument4 pagesInteractive Map Questionsapi-251874912No ratings yet
- MWSS v. CADocument15 pagesMWSS v. CAAlexander AbonadoNo ratings yet
- Soal IntroducingDocument2 pagesSoal IntroducingBibah ZulfaNo ratings yet
- 99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)Document11 pages99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)api-26870382100% (1)
- Puregold SWOT AnalysisDocument3 pagesPuregold SWOT AnalysisRizza Mae CabigasNo ratings yet
- GSP Action PlanDocument2 pagesGSP Action PlanTen Victa-Milano100% (3)
- Bonaventure Sentences Doctorisseraphic11bonaDocument1,014 pagesBonaventure Sentences Doctorisseraphic11bonaChad Deffler100% (1)
- Jean Elizabeth HamptonDocument3 pagesJean Elizabeth HamptonTamannaNo ratings yet
- ABC Pre School: (Please Refer Advertisement in This Section)Document5 pagesABC Pre School: (Please Refer Advertisement in This Section)hemacrcNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 4: Explorer's Rainforest Trip and Blind AdventurerDocument6 pagesPractice Test 4: Explorer's Rainforest Trip and Blind AdventurerKhang Nguyen TienNo ratings yet
- Qualys WAS and OWASP Top 10 2017 CoverageDocument5 pagesQualys WAS and OWASP Top 10 2017 CoverageoobyddNo ratings yet
- Sereno's Dissenting Opinion Re TruthCommDocument35 pagesSereno's Dissenting Opinion Re TruthCommGerald MagnoNo ratings yet
- CoverDocument6 pagesCoverFani Dwi Putra100% (2)
- God's Refining Process Removes Character DefectsDocument5 pagesGod's Refining Process Removes Character DefectsPercen7No ratings yet
- Past Simple - Present PerfectDocument5 pagesPast Simple - Present PerfectAnonymous MCobwixNo ratings yet
- 5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsDocument5 pages5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsSendhil RevuluriNo ratings yet
- Wegsheider's Role Theory in Substance Abusing FamiliesDocument5 pagesWegsheider's Role Theory in Substance Abusing FamiliesLouisa KouklaNo ratings yet
- Urology Semiology Guide for Renal Colic & HematuriaDocument30 pagesUrology Semiology Guide for Renal Colic & HematuriaNikita KumariNo ratings yet
- Sap HCM loclalization-EGDocument124 pagesSap HCM loclalization-EGrania abdelghanyNo ratings yet
- A Study on Student Budgeting HabitsDocument41 pagesA Study on Student Budgeting Habitsbornak BonalasNo ratings yet
- Week4.pdf 82849 1 1583836882000 PDFDocument17 pagesWeek4.pdf 82849 1 1583836882000 PDFsssmmm8No ratings yet
- Go Int 6 Unit 2 Extension TestDocument4 pagesGo Int 6 Unit 2 Extension TestMiguel Anabalón TorresNo ratings yet
- AEF3 File4 TestADocument5 pagesAEF3 File4 TestAdaniel-XIINo ratings yet
- Homework #3 - Coursera CorrectedDocument10 pagesHomework #3 - Coursera CorrectedSaravind67% (3)
- Timeline of The Human SocietyDocument3 pagesTimeline of The Human SocietyAtencio Barandino JhonilNo ratings yet
- Quieting of TitleDocument11 pagesQuieting of TitleJONA PHOEBE MANGALINDANNo ratings yet
- New Edition ThesisDocument100 pagesNew Edition Thesisniluka welagedaraNo ratings yet
- ME8513 & Metrology and Measurements LaboratoryDocument3 pagesME8513 & Metrology and Measurements LaboratorySakthivel KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- English Language (1122)Document26 pagesEnglish Language (1122)TD X Mzinda100% (1)
- Tiếng Anh 6 Smart World - Unit 10 - CITIES AROUND THE WORLD - SBDocument33 pagesTiếng Anh 6 Smart World - Unit 10 - CITIES AROUND THE WORLD - SBponyoNo ratings yet
- Group Project Assignment Imc407Document4 pagesGroup Project Assignment Imc407Anonymous nyN7IVBMNo ratings yet