Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3 Study Guide - Teacher
Uploaded by
api-198603477Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 3 Study Guide - Teacher
Uploaded by
api-198603477Copyright:
Available Formats
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Lesson 1 From Cells to Organs
Vocabulary:
Tissue- a group of cells that work together to perform a certain function
Organ a group of different tissues that work together to perform a specific
function
Organ System - a collection of organs that function together to perform a major
function
Notes:
All systems in an organism must work together to keep the organism alive.
What happens when a system is weakened?
o If one part of a system is damaged, the entire system may fail. If one system
fails, the entire organism is at risk.
How do cells know to become a certain type of cell?
o
It follows the instructions in it DNA, as a result the cell becomes
specialized. Each type of cell in your body has a different function (job)
Levels of Organization:
CellsTissuesOrgansSystemsOrganism
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Lets Practice
Using this information, fill in the blanks below. This first one is
done for you.
CellsTissuesOrgansSystemsOrganism
1. Lung cells make up lung __tissue___.
2. Brain tissues make up the brain, the brain is an __organ___.
3. Muscle tissue is made of muscle _cells___.
4. Organisms are made of different __systems_____, like the immune
system.
Label the diagram below using the words:
organ, cells, organ systems, tissues, organism
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Systems
Organism
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Lesson 2 Muscular and Skeletal Systems
Vocabulary:
Muscular system- responsible for the movement of the human body
Skeletal system-supports and protects the body
Exoskeleton- the hard outside body covering of some animals. Ex: crabs, insects
Joint-where two bones meet, makes movement possible
Ligaments-connects bone to bone
Cartilage- end of the bones shock absorber
Skeletal muscle- attaches to bone, you can relax and contract these muscles
Cardiac muscle- found only in the heart
Smooth muscle- found in the walls of organs, cannot voluntarily contract
Tendon-connects muscle to bone
Notes
For many animals, the skeletal and muscular systems work together to maintain the
animals form and let the animal move.
Lets Practice!
Label the diagram below with these words:
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle
Lesson
Respiratory System
4:
3
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Vocabulary
Respiratory System-picks up oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide in the body
Notes
The structures in the respiratory system include the:
1. Mouth and nose
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Pharynx part of the throat
Trachea -- windpipe
Lungsair sacs
Bronchi-- tubes leading to lungs
Bronchioleswhere air passes to the
alveoli
7. Alveoli-where
Oxygen
exchange
happens via DIFFUSION
8. Diaphragm-- sheet of internal skeletal
muscle that extends across the bottom
of the rib cage. As the diaphragm
contracts, air is drawn into the lungs
Here you can see the oxygen in an
alveolus is being passed to the blood
stream, while carbon dioxide is being
passed to the alveoli, where it will be
exhaled.
Lets Practice!
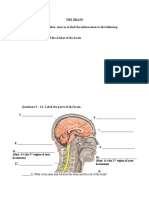
Use the notes to help you finish labeling this diagram of the respiratory
system.
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Nose
Mouth
Pharynx
Larynx-voice
box
Trachea
Lung
Bronch
i
Bronch
i
Bronchioles
Diaphra
Alveoli
gm
Lesson 5: Circulatory System
Vocabulary
Circulatory System-transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes wastes
from them
5
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Notes
The structures in the circulatory system of most animals include the:
1. Blood vesselstubes that carry blood, includes, arteries, veins, and
capillaries
2. Arteries-carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
3. Veins-carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
4. Capillaries-very tiny blood vessels that connect veins and arteries,
also found in the lungs for oxygen exchange
5. Bloodmade of water and blood cells
6. Heart organ that pumps blood through body
How is the respiratory system connected to the circulatory system?
o The respiratory system brings in oxygen and the circulatory
system transports it around the body.
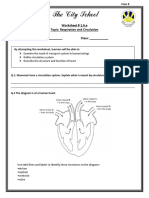
Diagram of the blood
vessels in a human.
Diagram of the human heart
Lets Practice!
Directions:
1
Color all the veins in blue and all the arteries in red and color in the key.
2
Fill in the missing words in the sentences below. Use these words: pump, capillaries, lung,
heart, oxygen
6
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
heart
pump
lung
oxygen
capillaries
Lesson 5: Digestive and Excretory Systems
Vocabulary
Digestive Systembreaks down food so the body can use the nutrients
Excretory Systemremoves waste products from the body
7
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Notes
Pathway of human digestion:
Mouth esophagus stomach small intestinelarge intestine expelled through
anus
Two types of digestive systems:
Incomplete--Digestive System- a single opening where food enters and
undigested food exits ex. Hydra, jellyfish, flatworm
Complete-- Digestive System-tube-like form, mouth at one end where food enters,
and an anus where undigested food exits ex. Earthworm, humans and most
animals
The structures of the excretory systems include the:
Liver-- converts ammonia into urea and then the kidneys remove urea from the blood
and send it to the ureter and the bladder for urination
Kidneys--the main organ, filter the blood
Bladder--holds urine
**Sweating is part of excretion as well***
Lets Practice!
Use the vocabulary to help find the correct match! Draw lines to
match them up!
8
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Liver
Bladder
Excretory
System
Kidneys
Digestive
system
Mouth
Organ that holds urine
Removes waste products from the body
Breaks down food so the body can use
the nutrients
The main organ, filter the blood
Organ in the digestive system that helps
us chew our food
Converts ammonia into urea and then the
kidneys remove urea from the blood and
send it to the ureter and the bladder for
urination
Lesson 5: Immune System
Vocabulary
Immune System- recognizes and destroys disease causing organisms
Pathogenscause diseases. Some examples are bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi
9
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
White blood cellsdefend the body against invaders
Notes
The Immune system is all over the body. It is a network of cells, tissues, and organs that
work together to destroy invaders
The four main organs of the immune system are:
1. Thymustrains/develops white
blood cells
2. Spleenstores white blood cells
3. Bone marrowmakes white blood
cells
4. Tonsiltraps and kills germs you
breathe in
The skin, tears, saliva, and nose hair are also part of the immune system, and they are
the first line of defense, keeping invaders out!!!
Lets Practice!
10
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Lesson 8: How Systems work
Together
Vocabulary
Nervous System-Control center, the brain,
analyzes the information and delivers chemical
messages
and
instructions
to all parts
the body.
spinal cord, and nerveswhich
of
Endocrine
System- produces and secretes hormones
that help
control many body functions, including
growth, metabolism, sexual development, and reproduction.
Reproductive System- The reproductive system makes it possible for an organism to
pass its genes on to new organisms.
Skin SystemCovers and protects organisms
11
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Notes
If one part of a system is damaged, the entire system may fail. If one system fails, the
entire organism is at risk. In this way, all systems work together.
Lets Practice!
Fill in the function and organs/structures of the systems below. Use the info from the
study guide!
SYSTEM
FUNCTION ORGANS/STRUC
TURES
Skeletal
Muscular
To support and protect
the body
Respiratory
picks up oxygen and
gets rid of carbon
dioxide in the body
SYSTEM
FUNCTION ORGANS/STRUC
TURES
Circulatory
transports oxygen and
nutrients to cells and
removes wastes from
them
Digestive
responsible for the
movement of the human
body
breaks down food so
the body can use the
nutrients
bones
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle,
skeletal muscle, ligaments, tendons
Mouth and nose
Pharynx
Trachea
Lungs
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Diaphragm
Blood vessels
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Blood
Heart
Mouth esophagus stomach
small intestinelarge intestine
expelled through anus
12
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Excretory
Immune
removes waste
products from the body
recognizes and
destroys disease
causing organisms
Nervous
Control center, the
brain, spinal cord, and nerves
brain, spinal cord, and
nerveswhich analyzes
the information and
delivers chemical
messages and
instructions to all parts
of the body.
To produce hormones
Glands such as thymus, pituitary,
adrenal
makes it possible for an Male: Sperm from male organs
organism to pass its
Female: eggs from ovaries, baby
genes on to new
develops in the uterus
organisms.
Endocrine
Reproductiv
e
Skin
Liver, bladder, kidneys
Thymus
Spleen
Bone marrow
Tonsils
skin
Covers and protects
organisms
Use the above notes for the Unit 3 Lessons 1-8
Body Systems Test in Sapphire
Lesson 11: Continuation of a Species and Lesson 12: Cells for
Reproduction
Vocabulary
Reproduction- when organisms make new organisms
Parent- The original organism that will make the offspring
Offspring- the new organism created by the parent(s)
13
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Asexual reproduction- simplest form of reproduction requiring only one parent; can be
fission or budding. Each new offspring is an exact copy of the parent.
Sexual Reproduction- the most common form of reproduction requires two parents.
The cells from two parents join (fertilization)
Fertilization- when a male and female reproductive cell join together to create a new
organism
Gametes- Sex cells=sperm and egg cells
Notes
How does life continue on earth?
Living things are able to make others like themselves through the
process of reproduction.
If living things never reproduced again, life on earth would not
continue.
Lesson 13: Life Cycles
Vocabulary
Life Cycle- the distinct stages of growth, development, and reproduction an organism
goes through during its life
Metamorphosis- distinct changes in physical appearance during life cycle
Incomplete metamorphosis- the insect that hatches from an egg and looks like a
miniature version of the adult, but it lacks working wings and reproductive organs.
14
Life Science Unit 3: Living Systems
Complete metamorphosis- insect will hatch from an egg and start off as a wormlike
larva, which looks nothing like the adult. Caterpillars, maggots, and mealworms are
all larvae of different insects.
Notes
All organisms have life cycles and they can be very different. Below are a
few examples:
Human Life Cycle
Cycle
**Use
the
notes from Lesson
3 L 11-13 quiz in
Chicken Life
11-13 for the Unit
Sapphire
15
You might also like
- Exploring the Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesExploring the Nervous SystemMcLargoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms (4º) PDFDocument2 pagesKingdoms (4º) PDFRocío MadolellNo ratings yet
- The Units of Living ThingsDocument2 pagesThe Units of Living ThingsAnonymous he4hP6Y06CNo ratings yet
- 01 The Living ThingsDocument6 pages01 The Living ThingsBelen MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsLea IoaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Terms: Physiology Point of View Soewono Department of PhysiologyDocument21 pagesThe Human Body Terms: Physiology Point of View Soewono Department of PhysiologyRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Characteristics of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Characteristics of LifeNicholas LeongNo ratings yet
- NS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 2Document4 pagesNS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 2Anabel Sánchez RubiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 NATURAL SCIENCE 6th GRADE, TEACHER PILAR CARRASCO PDFDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 NATURAL SCIENCE 6th GRADE, TEACHER PILAR CARRASCO PDFVicenteAguilarSanchezNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Document1 pageQUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Tego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- Entire Lab Report Due Nov. XX - Equivalent To A Quiz GradeDocument5 pagesEntire Lab Report Due Nov. XX - Equivalent To A Quiz GradeJaga_Sahsiny_1No ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODYDocument9 pagesChapter1-AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODYKie MusstisqueNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument2 pagesClassification of Living Thingsquick learnerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1Document2 pagesLesson 3.1Evangelia GkNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - Human Body and SensitivityDocument8 pagesStudent's Booklet - Human Body and SensitivityRafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Darwin and EvolutionDocument39 pagesCH 14 Darwin and EvolutionJane Heidi MomonganNo ratings yet
- The Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDocument49 pagesThe Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDaezel DeuxNo ratings yet
- Energy Processing in PlantsDocument2 pagesEnergy Processing in Plantsapi-32756760650% (2)
- Reinforcement and Extension 5th.23-26Document4 pagesReinforcement and Extension 5th.23-26magrotasNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: Key Concepts for CBSE Class 9 ScienceDocument11 pagesAtoms and Molecules: Key Concepts for CBSE Class 9 ScienceSrividhya ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesNervous System WorksheetaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.6.aDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.6.aNadia AmeerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 - Nebular TheoryDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 - Nebular TheoryMaria Adeza PereñaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. RickDocument17 pagesThe Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. Rickapi-464344582No ratings yet
- NS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 4Document4 pagesNS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 4Anabel Sánchez RubiaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of FlowerDocument1 pageStructure and Function of Flowersuma deviNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellDaryl De LeonNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - Climates and Vegetation of SpainDocument11 pagesStudent's Booklet - Climates and Vegetation of SpainRafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- 25 VertebratesDocument41 pages25 Vertebratespurple crocNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Kingdom AnimaliaDocument23 pagesGroup 3: Kingdom AnimaliabrettNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2 Cell Specialisation in Multicellular OrganismsDocument18 pages2.2.2 Cell Specialisation in Multicellular Organismsche sal100% (1)
- Cladograms ActivityDocument6 pagesCladograms ActivityziribiriNo ratings yet
- RSU Environmental Science SyllabusDocument8 pagesRSU Environmental Science SyllabusMelch Champion RufonNo ratings yet
- Science 3 ºprimaria PlantsDocument1 pageScience 3 ºprimaria PlantsElectronica PscNo ratings yet
- Basic English Grammar Module Unit 2A: The Verbal Group: Finites and Non - FinitesDocument21 pagesBasic English Grammar Module Unit 2A: The Verbal Group: Finites and Non - FinitesSantiago TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Reference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EDocument11 pagesReference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EAnnalei GagnéNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Digestive SystemSBNoadNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument20 pagesDigestive System Guiderocky2219No ratings yet
- Vocabulary U 02Document1 pageVocabulary U 02MarieNo ratings yet
- STK1211 Practical Analytical ChemistryDocument39 pagesSTK1211 Practical Analytical Chemistrylox agencyNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument15 pagesCellsMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Worksheet: I. Read The Passage and Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesMuscular System Worksheet: I. Read The Passage and Answer The Questions That FollowJulie Anne Bergado CortezNo ratings yet
- Biology 3rd ESO Full DossierDocument54 pagesBiology 3rd ESO Full DossierNinaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Parts and FunctionsDocument9 pagesIntegumentary System: Parts and FunctionsJat GomezNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Kingdoms Webquest 2019Document4 pagesTaxonomy and Kingdoms Webquest 2019Aakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Classification of AnimalsDocument4 pagesClassification of Animalsisabella gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - NUTRITION I (Digestion and Respiration)Document8 pagesStudent's Booklet - NUTRITION I (Digestion and Respiration)Rafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesWorksheet Respiratory SystemAnonymous piAtTTKkNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesDigestive SystemMargaret Xaira Rubio MercadoNo ratings yet
- Human Body Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesHuman Body Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Cells-1Document3 pagesLesson Plan Cells-1api-371640211No ratings yet
- 2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFDocument9 pages2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFMelisa Anne CanilangNo ratings yet
- Muscles: Dr. Maung MyintDocument54 pagesMuscles: Dr. Maung MyintIntan AinNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells - WorksheetDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal Cells - WorksheetsabaNo ratings yet
- Revision Series-1 Science - Part II ADocument4 pagesRevision Series-1 Science - Part II AmumniyasNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument9 pagesTissuesAtharv AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - The Axial and Appendicular SkeletonDocument5 pagesLab 7 - The Axial and Appendicular Skeletonsidro123100% (3)
- Digestive System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesDigestive System: Anatomy & PhysiologyBaltazar MarcosNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Study Guide Filled inDocument6 pagesUnit 8 Study Guide Filled inapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Life Science Foundations Quarter 4 TgaDocument1 pageLife Science Foundations Quarter 4 Tgaapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Guide TeacherDocument12 pagesUnit 6 Guide Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Guide TeacherDocument17 pagesUnit 5 Guide Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Unit+7+study+guide AnswersDocument14 pagesUnit+7+study+guide Answersapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Guide - TeacherDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide - Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Life Science Foundations Quarter 3 TgaDocument1 pageLife Science Foundations Quarter 3 Tgaapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Life Science Foundations Quarter 3 TgaDocument1 pageLife Science Foundations Quarter 3 Tgaapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study Guide Filled inDocument17 pagesUnit 1 Study Guide Filled inapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Ls Resources-1Document23 pagesLs Resources-1api-207621290No ratings yet
- Sagan Satellites Pssa CalendarDocument2 pagesSagan Satellites Pssa Calendarapi-198603477No ratings yet
- 3a ReproductionDocument25 pages3a ReproductionThaarvena Retina100% (1)
- Harr. Cap 114Document7 pagesHarr. Cap 114tkovats.lopes2No ratings yet
- Haralabia BoletiDocument5 pagesHaralabia BoletiHellenic Pasteur Institute - Athens, GreeceNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Trends in Skin Mycoses Worldwide: Blanka Havlickova, Viktor A. Czaika and Markus FriedrichDocument14 pagesEpidemiological Trends in Skin Mycoses Worldwide: Blanka Havlickova, Viktor A. Czaika and Markus FriedrichRS Tk IV PekanbaruNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tonsil Limfoma Non HodgkinDocument5 pagesJurnal Tonsil Limfoma Non HodgkinAhmad RamadhanuNo ratings yet
- The House of Usher EssayDocument5 pagesThe House of Usher EssayJohn Garza100% (1)
- Human CloningDocument2 pagesHuman Cloningapi-318868666No ratings yet
- Salivary Gland - Part3Document27 pagesSalivary Gland - Part3Prince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Points For Diabetes PDFDocument4 pagesAcupressure Points For Diabetes PDFRanganathanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/41HamidNo ratings yet
- Coccidia 10 - 11Document40 pagesCoccidia 10 - 11microperadeniya100% (1)
- Understanding Autoimmune Disease PDFDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Autoimmune Disease PDFLiz TaylorNo ratings yet
- MRCP Recalls May 2014Document15 pagesMRCP Recalls May 2014sohailsu100% (1)
- PHILIPPINES Asthma Consensus Guidelines 2009Document134 pagesPHILIPPINES Asthma Consensus Guidelines 2009Sirias_black50% (2)
- MRNA VaccineDocument23 pagesMRNA VaccineIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- ANENCEPHALYDocument10 pagesANENCEPHALYSharmaine SimonNo ratings yet
- Test Questionairre FormatDocument149 pagesTest Questionairre FormatSantosh Kumar TataNo ratings yet
- EmbeddingDocument6 pagesEmbeddingVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Submerged Cultivation of Medicinal MushroomsDocument30 pagesSubmerged Cultivation of Medicinal Mushroomsbravohr98No ratings yet
- Respiratory System HistologyDocument32 pagesRespiratory System HistologyMohib HassanNo ratings yet
- The Variability in The Fungal Ribosomal DNA (Korabecna, 2007)Document6 pagesThe Variability in The Fungal Ribosomal DNA (Korabecna, 2007)annisa pramestiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Nodular PrurigoDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Nodular Prurigoranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Current GM Crops & Transgenic AnimalsDocument12 pagesCurrent GM Crops & Transgenic AnimalsJhayce Christian S. CapanayanNo ratings yet
- FHSC1234 Tutorial 9S 202210Document5 pagesFHSC1234 Tutorial 9S 202210Zhi YongNo ratings yet
- Functions of Blood and ComponentsDocument15 pagesFunctions of Blood and ComponentsayuNo ratings yet
- Imidacloprid Aumenta Permeabilidad IntestinalDocument11 pagesImidacloprid Aumenta Permeabilidad IntestinalNuria Areli Márquez PérezNo ratings yet
- PCR 5 Lab SetupDocument22 pagesPCR 5 Lab Setupptz1965No ratings yet
- Improving Eyesight With Red Light TherapyDocument23 pagesImproving Eyesight With Red Light TherapyMark Sloan100% (8)
- Ers 2015Document358 pagesErs 2015Dejan ŽujovićNo ratings yet