Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSE
Uploaded by
gurdeepsarora87380 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views1 pageMaths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMaths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views1 pageMaths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSE
Uploaded by
gurdeepsarora8738Maths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
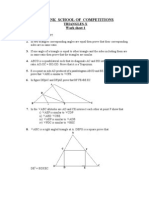
MATHS ASSIGNMENT CLASS 9
CHAPTER AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS
1. Area of a parallelogram ABCD is 96 cm2. Diagonals AC and BD divide the parallelogram into
four triangles. Find the area of AOB.
2. ABCD is a parallelogram in which BC is produced to E such that BC = CE. AE intersect DC at
F. If ar DFB = 3 cm2. Find the area of gm ABCD.
3
3. ABCD is a gm. E and F are mid points of BC and DC respectively. Prove that ar (AEF) =
8
ar(gm ABCD).
4. A quadrilateral ABCD is such that the diagonal BD divides its area in two equal parts. Prove that
BD bisects AC.
5. AD is a median of ABC and G is the mid point of AD, prove that ar (BGC) = 2 ar (AGC).
6. PQRS is a gm. ABPS and meets PQ at A and SR at B. O is any point on AB. Prove that
ar (SOR) + ar (POQ) = ar (SAR)
7. A point D is taken on the side BC of a triangle ABC such that BD = 2DC. Prove that ar (ABD)
= 2 ar (ADC).
8. ABCD is a quadrilateral. A line through D, parallel to AC, meets BC produced in P. prove that
ar (ABP) = ar (quad ABCD).
9. In ABC, D is the mid point of AB. P is any point of BC. CQ,
PD meets AB in Q and D. show that ar(BPQ) =
1
ar(ABC).
2
10. In the given figure ABCD is a gm.
Prove that ar (BCP) = ar (DPQ).
11. D is the mid point of side BC of ABC and E is the mid point of
BD. If O is the mid point of AE, prove that ar(BOE) =
1
8
ar(ABC)
12. ABCD is a quadrilateral in which diagonals AC and BD intersect at E. Show
that ar(AED) ar (BEC) = ar(ABE) ar (CDE).
13. ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid point of BC.
Prove that (i)ar (BDE) =
1
1
ar (ABC) (ii) ar (BDE). = ar (BAE).
4
2
14. ABCD is a parallelogram and BC is produced to Q such that AD =
CQ . If AQ intersects DC at P , show that ar(BPC) = ar(DPQ).
You might also like
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-9Document18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-9funson123No ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: Properties and RelationshipsDocument3 pagesQuadrilaterals: Properties and RelationshipsSssohannNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: Grade 9 Mathematic WorksheetDocument22 pagesQuadrilaterals: Grade 9 Mathematic Worksheethuang pok manNo ratings yet
- Grade 11Document1 pageGrade 11Tr LynnNo ratings yet
- MATH ASSIGNMENT - AREAS OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLESDocument4 pagesMATH ASSIGNMENT - AREAS OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLESgurdeepsarora87380% (2)
- Area of Parallelogram and Its TrianglesDocument3 pagesArea of Parallelogram and Its Trianglesaman5hazarikaNo ratings yet
- Trapezium ABCD with diagonals AC and BD intersecting at PDocument8 pagesTrapezium ABCD with diagonals AC and BD intersecting at PUnnieNo ratings yet
- L-9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesDocument37 pagesL-9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesferozamedNo ratings yet
- Geometry I AssignmentDocument114 pagesGeometry I AssignmentSAHIL KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Geometry by False PrideDocument15 pagesGeometry by False PrideSamSharmaNo ratings yet
- Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles FormulasDocument13 pagesAreas of Parallelograms and Triangles FormulasnNo ratings yet
- Geometry AssignmentDocument17 pagesGeometry AssignmentDaksh Bhardwaj VIII-A Roll No 250% (2)
- Congruent Triangles Assignment 2Document6 pagesCongruent Triangles Assignment 2UNKNOWN LEGENDNo ratings yet
- 9th Triangle Test Paper-3Document1 page9th Triangle Test Paper-3vishal_bokaroNo ratings yet
- TrianglesDocument13 pagesTrianglessudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- 6.triangles Marks BoosterDocument19 pages6.triangles Marks BoosterDROZON GAMING YTNo ratings yet
- Area of Parallelograms and Triangles Math AssignmentDocument3 pagesArea of Parallelograms and Triangles Math AssignmentSanjay SihagNo ratings yet
- Traingle Class 10thDocument6 pagesTraingle Class 10thAarthiKalyanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7Document22 pagesNcert Sol For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7VANSHNo ratings yet
- 9maths 8 QuadrilateralsDocument28 pages9maths 8 QuadrilateralsLEARN WITH SOUNDARYANo ratings yet
- Class IX Chapter 8 - Quadrilaterals Maths: Exercise 8.1 Question 1Document28 pagesClass IX Chapter 8 - Quadrilaterals Maths: Exercise 8.1 Question 1Usha SaliNo ratings yet
- TRIANGLES-X Worksheet Similarity ProblemsDocument2 pagesTRIANGLES-X Worksheet Similarity Problemsjindalyash1234No ratings yet
- Ix Maths Chapter 8 QuadrilateralsDocument20 pagesIx Maths Chapter 8 QuadrilateralsDVAC-SERVERNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals IX QDocument7 pagesQuadrilaterals IX QRitwikTandonNo ratings yet
- Circles, Tangent-Chord Theorem, Intersecting Chord Theorem and Tangent-Secant TheoremDocument11 pagesCircles, Tangent-Chord Theorem, Intersecting Chord Theorem and Tangent-Secant TheoremStefanie BargoNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 (Areas of Parallelograms & Triangles) : Exercise 9.1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document18 pagesUnit 9 (Areas of Parallelograms & Triangles) : Exercise 9.1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)renu tomarNo ratings yet
- Triangle 5Document11 pagesTriangle 5Vilas ShindeNo ratings yet
- Concise Selina Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 16 Area TheoremsDocument34 pagesConcise Selina Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 16 Area Theoremsbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9Document27 pagesNcert Sol For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9Arundhati ShaktawatNo ratings yet
- WS Quadrilateral IX QuestionsDocument3 pagesWS Quadrilateral IX Questionsaks252625No ratings yet
- NCERT-Solutions-for-Class-9-Maths-Chapter-8-Quadrilaterals-Exercise-8-1 (1)Document14 pagesNCERT-Solutions-for-Class-9-Maths-Chapter-8-Quadrilaterals-Exercise-8-1 (1)rudratrivedi011No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral Assignment Class 9Document2 pagesQuadrilateral Assignment Class 9gurdeepsarora873850% (2)
- Areas of Similar Triangles TutorialDocument2 pagesAreas of Similar Triangles Tutorialjuliet holbNo ratings yet
- Geomtery II AssignmentDocument20 pagesGeomtery II AssignmentHimanshu Chahar100% (1)
- If ΔABC, is right angled at B, thenDocument2 pagesIf ΔABC, is right angled at B, thenKamleshKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit Test: Sub: Mathematicstopic: Area Related To Triangle and Parallelogram Time: 01:00HrDocument1 pageUnit Test: Sub: Mathematicstopic: Area Related To Triangle and Parallelogram Time: 01:00HrSuman DasNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Subjective QuadrilateralsDocument1 pageClass 9 Subjective QuadrilateralsAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- 9 Maths Exemplar Chapter 9Document13 pages9 Maths Exemplar Chapter 9Sarthak RajNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals and Midpoints (HOTSDocument5 pagesQuadrilaterals and Midpoints (HOTSChetanNo ratings yet
- Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesDocument4 pagesAreas of Parallelograms and TrianglesChetanNo ratings yet
- PRMO Test Series DiscountDocument19 pagesPRMO Test Series Discountsudhir singh100% (3)
- Areas of P and TDocument2 pagesAreas of P and TSandeep BrajNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Geometry of TrianglesDocument21 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Geometry of Trianglessuresh muthuramanNo ratings yet
- NCERT SOLUTION CLASS - 10 Ex 6.3Document20 pagesNCERT SOLUTION CLASS - 10 Ex 6.3Pardeep MittalNo ratings yet
- Geometry II AssignmentDocument102 pagesGeometry II Assignmentkoushik reddyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Revision AssignmentsDocument17 pagesCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Revision AssignmentslauranistNo ratings yet
- Triangle 3Document12 pagesTriangle 3Vilas ShindeNo ratings yet
- AfrykaDocument12 pagesAfrykaryszard_lubicz100% (1)
- GeometryDocument22 pagesGeometrynitcvisheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TrianglesDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Trianglesmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Holiday Home Work-Oct 31Document6 pagesClass 9 Holiday Home Work-Oct 31zxcvbnmkhannaNo ratings yet
- 9maths 9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesDocument44 pages9maths 9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesHitesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument69 pagesSimilarityavinandan chandraNo ratings yet
- Class IX Triangles WorksheetDocument1 pageClass IX Triangles WorksheetgagahujaNo ratings yet
- KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Ex 11.3 - KSEEB SolutionsDocument18 pagesKSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Ex 11.3 - KSEEB SolutionsHifzur IfzurNo ratings yet
- PRMO - INCENTER - QuestionsDocument4 pagesPRMO - INCENTER - QuestionsAnshika MishraNo ratings yet
- ML Aggarwal Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Theorems On AreaDocument29 pagesML Aggarwal Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Theorems On AreaSurbhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Triangles: Sample Question 1Document9 pagesTriangles: Sample Question 1soumikbhNo ratings yet
- Circles Chapter Class IX Key ConceptsDocument3 pagesCircles Chapter Class IX Key Conceptsgurdeepsarora8738100% (2)
- Linear Equations Assignment-1Document3 pagesLinear Equations Assignment-1gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Assignment Class 9 CBSE Heron's FormulaDocument2 pagesAssignment Class 9 CBSE Heron's Formulagurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Euclids Geometry Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument2 pagesEuclids Geometry Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Science Practice-Model Paper Class IX SA2Document5 pagesScience Practice-Model Paper Class IX SA2gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Separation of Substances Assignment Class 5 CBSEDocument1 pageSeparation of Substances Assignment Class 5 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Body Movement Assignment CBSE Class 6Document3 pagesBody Movement Assignment CBSE Class 6gurdeepsarora8738100% (3)
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument2 pagesSurface Area and Volumegurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- English Assignment Class 8 - 1Document3 pagesEnglish Assignment Class 8 - 1gurdeepsarora873833% (6)
- Exponents and Powers - Assignment Class 8 CBSEDocument2 pagesExponents and Powers - Assignment Class 8 CBSEgurdeepsarora873850% (2)
- Class IX Practice Test SA2 PaperDocument5 pagesClass IX Practice Test SA2 Papergurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Heat Assignment Chapter 4 Science CBSE Class 7Document1 pageHeat Assignment Chapter 4 Science CBSE Class 7gurdeepsarora873867% (3)
- Separation of Substances MethodsDocument2 pagesSeparation of Substances Methodsgurdeepsarora87380% (1)
- Solar System Class 8 CBSE TestDocument1 pageSolar System Class 8 CBSE Testgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Comparing Quantities Assignment Class 8 Maths CBSEDocument3 pagesComparing Quantities Assignment Class 8 Maths CBSEgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- Working of Institutions AssignmentDocument2 pagesWorking of Institutions Assignmentgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- Motion - Worksheet Ch-8 CBSE Class 9Document2 pagesMotion - Worksheet Ch-8 CBSE Class 9gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Lines and Angles Maths Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument2 pagesLines and Angles Maths Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora873867% (3)
- Social Science Assignment Class IX Electoral PoliticsDocument2 pagesSocial Science Assignment Class IX Electoral Politicsgurdeepsarora8738100% (2)
- PHYSICS Revision Assignment SA1Document5 pagesPHYSICS Revision Assignment SA1gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Assignment Why Do We Fall IllDocument1 pageBIOLOGY Assignment Why Do We Fall Illgurdeepsarora873867% (3)
- CHEMISTRY Revision Assignment Class IX CBSEDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY Revision Assignment Class IX CBSEgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Friction Assignment Class 8 CBSEDocument2 pagesFriction Assignment Class 8 CBSEgurdeepsarora873867% (3)
- Making of The National MovementDocument1 pageMaking of The National Movementgurdeepsarora87380% (1)
- Social Science SA2 Revision AssignmentDocument11 pagesSocial Science SA2 Revision Assignmentgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Assignment Human Resources and Law & Social Justice Class 8Document2 pagesAssignment Human Resources and Law & Social Justice Class 8gurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- Social Science Assignment Class 8 CBSEDocument3 pagesSocial Science Assignment Class 8 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Social Science Understanding Secularism Class 8 Cbse AssignmentDocument1 pageSocial Science Understanding Secularism Class 8 Cbse Assignmentgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Social Science Assignment CBSE Class 8 IndustriesDocument2 pagesSocial Science Assignment CBSE Class 8 Industriesgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet