Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
api-2280415730 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
752 views2 pagesOriginal Title
classification cheat sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
752 views2 pagesClassification Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
api-228041573Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CLASSIFICATION CHEAT SHEET
Domain refers to cell type:
Eukaryotic cells those with a nucleus and other membrane-bound
organelles (all plant and animal cells)
Prokaryotes no nucleus, or membrane-bound organelles (bacteria)
Archea also prokaryote but not bacteria
Kingdom In the domain Eukaryota
Animals, plant, fungus, protista, monera
Phylum
vertebrate (chordate) having a backbone,
o mammals, fish, birds, reptiles
invertebrate (non-chordate) no backbone
o Insects, shellfish
Class major classes of vertebrates:
Mammals
Reptiles
Birds
Fish
Order - Includes structurally and genetically similar organism within each
class
Family smaller grouping of similar animals by structure, DNA and life style
Genus smallest group of similar animals by structure, DNA and life style
Species identifies a specific animal
Binomial (Scientific) naming system: Each organisms scientific name is
made up of its genus and species name:
Canus lupus = wolf canus is the genus and lups the species name.
Always italicized. Genus name capitalized, species name not
Each level contains all of the levels below it in its grouping:
Keep
Privates
SO
The kingdom of animals includes ALL vertebrates, mammals,
bear, etc.
The class Mammal, however does not include ALL animals
Clean
Or
Forget
Getting
Sex
As you go down the list, the diversity of organisms included in
each category is smaller.
The most diverse level is kingdom
The least diverse level is genus
o Class includes a greater diversity of animals than
family
Organisms in any genus will be more similar to each other
than the other animals in their same family, or animals from
other families
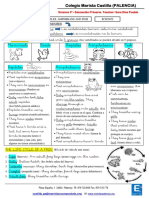
A CLADOGRAM is used to show relationships between animals
Here we see 5 animals all related at the
level of order they are all in the order
carnivora.
Within this order 3 families are identified.
Each branch shows closeness of
relationships:
Felidae (cats)
Mustelidae (weasels and skunks)
Canidae (dogs)
Within each family are different species
Mustelidae shows 2 genuses
Skunks and weasels are more closely
related to each other than either is to the
wolf
Homologous structures are those physical features that are similar between
different classes and/or families of animals, but show great similarities
like the forelimb of the cat, human, batwing and whale flipper.
Homologous structures are evidence of common ancestry.
Analogous structures are those that are similar in function but show no
evidence of common ancestry due to great differences in structure.
The bird, bat and insect wing are analogous structures
o they are functionally the same, but they are built very differently.
You might also like
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12From EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12No ratings yet
- Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDocument14 pagesCharacteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- PCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideFrom EverandPCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Cheat Sheet (Bio) 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet (Bio) 1Kelvin KohNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument25 pagesCharacteristics of Living Thingsdbhatt55No ratings yet
- Phylogenetic Trees Click Learn WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhylogenetic Trees Click Learn Worksheetfcm31450% (1)
- A Local EcosystemDocument26 pagesA Local EcosystemsandnifflerNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationDocument25 pagesHeredity and VariationDre ParkerNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology Genetics TestDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Biology Genetics TestValerieNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Kingdom AnimaliaDocument23 pagesGroup 3: Kingdom AnimaliabrettNo ratings yet
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocument82 pages6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE Biology Unit 2 Exam Revision NotesDocument18 pagesEdexcel GCE Biology Unit 2 Exam Revision NotescolachauNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Webquest AnswersDocument4 pagesThe Periodic Table Webquest AnswersshaneearlNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument31 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsOscar DamianiNo ratings yet
- Cells HW PacketDocument11 pagesCells HW PacketSandy Tana100% (2)
- Punnett Square Test ADocument3 pagesPunnett Square Test Ao969059No ratings yet
- Monster MashDocument5 pagesMonster Mashapi-507320580No ratings yet
- The Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesThe Characteristics of Living ThingsMiy El NinoNo ratings yet
- Marshmalien LabDocument9 pagesMarshmalien LabShonnefarrow14No ratings yet
- Cells Review Ws AnswersDocument4 pagesCells Review Ws AnswersTongtun TuntunNo ratings yet
- 2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFDocument9 pages2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFMelisa Anne CanilangNo ratings yet
- GENETICS Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesGENETICS Reviewer PDFMargarita RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cells 6th GradeDocument44 pagesCells 6th Gradepauleyler100% (4)
- Valence and Core ElectronsDocument19 pagesValence and Core Electronsapi-233187566No ratings yet
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Document15 pagesNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- ProkaryoticDocument8 pagesProkaryoticFraulin Leslie Sablas IrisariNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument36 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlex LlanoNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere and Weather Unit NotesDocument24 pagesAtmosphere and Weather Unit NotesRakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesVariety of Living Organismsapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Meiosis: Teacher's GuideDocument45 pagesMeiosis: Teacher's GuideLary Bags50% (2)
- Botany 102: An Introduction to Plant BiologyDocument24 pagesBotany 102: An Introduction to Plant BiologyJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Mendelian & Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument37 pagesMendelian & Non-Mendelian GeneticsJubair Al-rashid100% (2)
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocument83 pages6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture Notesledereh1No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1Document28 pagesCellular Respiration 1Maria Flor PabeloniaNo ratings yet
- Basis For Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument31 pagesBasis For Animal Kingdom ClassificationIan AlpaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyAnna MontiniNo ratings yet
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument1 pageChemical Basis of LifeChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Mitosis and Meiosis WebquestDocument3 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Webquestapi-3156932390% (1)
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument80 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument40 pagesTechniques in Cell and Molecular BiologyWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 pagesNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2, Genetic Proceses, Unit Test - 2Document5 pagesUnit 2, Genetic Proceses, Unit Test - 2hewleet100% (1)
- DNA Molecule & Central DogmaDocument43 pagesDNA Molecule & Central DogmaJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- 18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SDocument6 pages18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SkriishnaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument426 pagesLab ManualSciencefun23100% (1)
- Biome Research ProjectDocument3 pagesBiome Research Projectapi-472648158No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDocument12 pagesChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellhuy luongNo ratings yet
- Kingdom ProtistaDocument27 pagesKingdom ProtistaHELMA B. JABELLONo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 Revision Topic 3Document6 pagesBiology Unit 2 Revision Topic 3YasinKureemanNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument33 pagesVariationdejla67No ratings yet
- Blueprint of LifeDocument42 pagesBlueprint of Lifesophiehee1234No ratings yet
- AP Bio CED Scavenger HuntDocument4 pagesAP Bio CED Scavenger HuntJADEN MANN50% (2)
- HierarchyDocument4 pagesHierarchyBinazir RavanbakhshNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesClassification of Living ThingsBolu AdediranNo ratings yet
- Classifying Life Based on Evolutionary RelationshipsDocument9 pagesClassifying Life Based on Evolutionary RelationshipsWe the people Lesson 9No ratings yet
- Organizing Life's Diversity NotesDocument4 pagesOrganizing Life's Diversity NotessmedificationNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument7 pagesEnzymesapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Circulatory System CompletedDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Completedapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Emerald Necklace MapDocument1 pageEmerald Necklace Mapapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Respiratory Diagram CompletedDocument2 pagesRespiratory Diagram Completedapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Cells Summary SheetDocument2 pagesCells Summary Sheetapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Urinary Diagram CompletedDocument1 pageUrinary Diagram Completedapi-228041573No ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Review SheetDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Review Sheetapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Dna Summary SheetDocument3 pagesDna Summary Sheetapi-228041573No ratings yet
- Chordata: Salient Features and ExamplesDocument20 pagesChordata: Salient Features and Examplesasmita100% (1)
- Science Syllabus Grade 4. For PrintDocument12 pagesScience Syllabus Grade 4. For PrintNikolas Andi GitoNo ratings yet
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 1: Anatomical Terms & Introduction To Chordates AssignmentsDocument10 pagesBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 1: Anatomical Terms & Introduction To Chordates AssignmentsKerbie Jayd0% (1)
- CDU ZOOLOGY Anatomical Terminologies in Chordates and Vertebrates WorksheetDocument4 pagesCDU ZOOLOGY Anatomical Terminologies in Chordates and Vertebrates WorksheetKrisha Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 1-Anima Diversity PDFDocument9 pages1-Anima Diversity PDFMahesh Babu Chemistry 4 uNo ratings yet
- Cleveland P. Hickman-Integrated Principles of Zoology, Fourteenth Edition-Mcgraw-Hill College (2007) - 511-528Document18 pagesCleveland P. Hickman-Integrated Principles of Zoology, Fourteenth Edition-Mcgraw-Hill College (2007) - 511-528tasya dhanaNo ratings yet
- FishesDocument28 pagesFishesMilla ZahiraNo ratings yet
- 29.1A Characteristics of ChordataDocument2 pages29.1A Characteristics of ChordataEirah Gabrielle RiducaNo ratings yet
- Herbert Spencer Origin and Function of MusicDocument68 pagesHerbert Spencer Origin and Function of Musicjrhee88100% (2)
- Subtasking Luzon2 Q2Document3 pagesSubtasking Luzon2 Q2Sharmaine LappayNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument13 pages1 - IntroductionStudent 365No ratings yet
- Chordata Characteristics and ClassificationDocument32 pagesChordata Characteristics and Classificationollie tikaNo ratings yet
- Science Scrapbook Form 2 Classification of AnimalsDocument24 pagesScience Scrapbook Form 2 Classification of AnimalsAqilah Mahmud Zuhri80% (5)
- Unit 2 Lesson 8 Super Sea Animals CLIL ScienceDocument29 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 8 Super Sea Animals CLIL Sciencemylyn ortizNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology Projectmaninblac0% (1)
- Animal Classification Chart - VertebratesDocument1 pageAnimal Classification Chart - VertebratesTheTeachersDesk.info100% (1)
- Grade 5, Science CurriculumDocument3 pagesGrade 5, Science CurriculumJoel C. Yuvienco67% (3)
- 1dk Publishing First Animal Encyclopedia PDFDocument170 pages1dk Publishing First Animal Encyclopedia PDFanca12iulie100% (3)
- Science 6 Q2 Worksheet Week 14Document1 pageScience 6 Q2 Worksheet Week 14Catherine Lagario Renante100% (2)
- Quennie C Frog DissectionDocument12 pagesQuennie C Frog DissectionDhovie Mae FernandoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34: Vertebrates Study GuideDocument2 pagesChapter 34: Vertebrates Study GuideMadeline JensenNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Lab ManualDocument32 pagesGeneral Zoology Lab Manualnicole675No ratings yet
- Phylum ChordataDocument15 pagesPhylum Chordatay_khartashNo ratings yet
- Science and Health V: 38. DateDocument2 pagesScience and Health V: 38. DateRichardDumlaoNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy: (Chordates) Skeletal SystemDocument66 pagesComparative Anatomy: (Chordates) Skeletal SystemPAU FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- 24 - FishesDocument83 pages24 - FishesKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- Reptiles Amphibians and Birds Tema 5Document1 pageReptiles Amphibians and Birds Tema 5pepeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument3 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyMaria Nina Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Morfometri InvertebrateDocument9 pagesLaporan Morfometri InvertebrateFitria RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates and Non VertDocument13 pagesVertebrates and Non VertLanie Grace Sandhu100% (1)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesFrom EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (56)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (396)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesFrom EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Mitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfFrom EverandMitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)
- The Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceFrom EverandThe Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (45)
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationFrom EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeFrom EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (523)