Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answers
Uploaded by
api-281108263Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answers
Uploaded by
api-281108263Copyright:
Available Formats
[Teacher Copy]
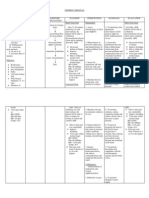
Disorders of the Circulatory System
(Disorders of the Circulatory System)
Disorder:
Atherosclero
sis
(Narrowing of the
arteries)
Arrhythmia
(Irregular
Heartbeat)
Heart Attack
Stroke
Symptoms:
Causes:
Treatment:
-Silent Killer
-Shortness of breath
-Dizziness
-Headaches
-Vision problems
-High blood
pressure
-Smoking
-High cholesterol
-Plaque buildup
-Lifestyle changes
-Medication
-Angioplasty
-Bypass surgery
-Palpitations (a
feeling of skipped
heart beats, or
feeling that your
heart is running
away)
-Dizziness or feeling
light-headed
-Fainting
-Weakness or fatigue
-Discomfort,
pressure, heaviness,
or pain in the chest,
arm, or below the
breastbone
-Indigestion, or
choking feeling (may
feel like heartburn)
-Sweating, nausea,
vomiting, or dizziness
-Extreme weakness,
anxiety, or shortness
of breath
-Rapid or irregular
heartbeats
-Weakness or
numbness of the
face, arm, or leg on
one side of the body
-Loss of vision or
dimming (like a
curtain falling) in one
or both eyes
-Loss of speech,
difficulty talking, or
understanding what
others are saying
-Sudden, severe
headache with no
known cause
-Loss of balance or
unstable walking,
-Coronary artery
disease
-Electrolyte
imbalances in your
blood (Na or K)
-Injury from a heart
attack
-Healing process
after heart surgery
-In some cases, no
treatment may be
required
-Lifestyle changes
-Medication
-Surgical
procedures
-Coronary heart
disease (arteries
clogged with fatty,
calcified plaques)
-High blood
pressure
-High cholesterol
-Smoking
-Diabetes
-Sedentary lifestyle
-Stress
-Genetics
-Medication to
break up or
prevent blood
clots, prevent
platelets from
gathering and
sticking to the
plaque, or stabilize
the plaque
-Surgical
procedures (open
heart surgery &
angioplasty)
-Blockage in blood
flow to the brain
caused by a blood
clot
-Buildup of plaque
in the artery wall
-Bleeding into the
brain or around the
brain
-High blood
pressure
-Injections
-Blood pressurelowering
medications
-Cholesterollowering
medications
-Surgical
procedures (e.g.,
carotid
endarterectomy)
-Lifestyle changes
[Teacher Copy]
Anemia
(Blood lacks
enough healthy
red blood cells or
hemoglobin)
Varicose
Veins
Heart Murur
usually combined
with another
symptom
-Extreme fatigue
-Pale skin
-Weakness
-Dizziness or
lightheadedness
-Headache
-Frequent infections
-Blood loss
-Decreased or
faulty red blood
cell production
-Destruction of red
blood cells
-Aching, cramping at
night, swelling, and a
feeling of fullness in
the legs (These
symptoms become
worse before
menstruation or after
standing for a long
time)
-Spider-web of raised
veins over most of
the leg or only one
vein
-The valves that
push blood through
the varicose veins
stop working
properly, causing
blood to collect in
areas in the veins
-Standing for long
periods of time
-Being overweight
-Age
-Gender
-Genetic
-No symptoms;
underlying structural
issue of the heart
-Difficulty breathing
-Swelling
-Chest pain,
palpitations
-When blood
rushes through the
heart quickly
during normal
function
-Underlying
medical condition
-Abnormalities in
the valves, septae,
arteries, or veins
-Blood transfusion,
oxygen infusion,
iron supplements
-Diet changes
(increasing the
amount of iron in
your diet)
-Iron injections or
given
intravenously
-Leg elevation
while sitting or
sleeping
-Compression
dressings with
single or
multilayered
systems
-Compression
stockings
-Sclerotherapy
(injection of a
liquid or foam into
the vein to form a
clot and
permanently
destroy the vessel)
-Ablation
(destruction) of
abnormal veins
with techniques
using laser,
radiofrequency or
other modalities
-Surgery (removal
of the varicose
veins, including
"phlebectomy" or
vein stripping).
-Many times just
monitored
-Infected
valvesantibiotics
-Damaged
valvessurgical
repair
You might also like
- Cardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atLilly DayeNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1Document34 pagesArrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1preethi preethaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesLiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- CVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologyDocument13 pagesCVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologySherwan R Shal100% (5)
- CH 11 Heart NotesDocument2 pagesCH 11 Heart Notesummnicole0% (1)
- Patho Exam 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesPatho Exam 3 Study GuideFarzanaAziziNo ratings yet
- HEENT Cheat SheetDocument22 pagesHEENT Cheat SheetKatrina FeriNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNo ratings yet
- 1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefDocument35 pages1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefJade EdanoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument86 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument29 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum Marie50% (2)
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)Document4 pagesRespiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)PkernNo ratings yet
- PharynxDocument2 pagesPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Heart Failure RevisionDocument4 pagesHeart Failure RevisionBlanaid MargaretNo ratings yet
- Mesenteric Ischemia in Dilated CardiomyopathyDocument30 pagesMesenteric Ischemia in Dilated CardiomyopathyJo AnneNo ratings yet
- Guide To Oxygen Delivery SystemDocument3 pagesGuide To Oxygen Delivery SystemDarwin Villestas0% (1)
- Notes in Physiology 2nd PDFDocument37 pagesNotes in Physiology 2nd PDFDany SamuelNo ratings yet
- OSCE Chart Cough (KK)Document4 pagesOSCE Chart Cough (KK)api-26938624No ratings yet
- Frank-Starling LawDocument5 pagesFrank-Starling LawNTA UGC-NETNo ratings yet
- Jugular Venous PressureDocument9 pagesJugular Venous Pressuremoh86-No ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular ChecklistDocument3 pagesPeripheral Vascular ChecklistPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment ChecklistDocument1 pagePhysical Assessment ChecklistDMRMNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic PharmacologyDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Pharmacologyjess6001No ratings yet
- Rhythm Interpretation and Its ManagementDocument6 pagesRhythm Interpretation and Its Managementjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- CardiopathophysiologyDocument63 pagesCardiopathophysiologyapplesncoreNo ratings yet
- Right Bundle Branch BlockDocument13 pagesRight Bundle Branch BlockKweenie QueenieNo ratings yet
- Latihan Ekg KD A III 2016Document15 pagesLatihan Ekg KD A III 2016Syamsul PutraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSDocument56 pagesPhysiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Action PotentialDocument41 pagesCardiac Action PotentialRadijska Postaja KoprivnicaNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease 2Document46 pagesValvular Heart Disease 2Topea BogdanNo ratings yet
- 3-Major Veins of The BodyDocument26 pages3-Major Veins of The BodyTJPlayz100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Cad2Document182 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Cad2Mamot MotNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis: An Autoimmune Neurologic DisorderDocument16 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: An Autoimmune Neurologic DisorderHibba NasserNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle: Chapter 19Document62 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle: Chapter 19BishwambherNo ratings yet
- Patho Exam 3Document7 pagesPatho Exam 3menickel3No ratings yet
- Ekg Full BibleDocument6 pagesEkg Full BibleTJNo ratings yet
- AH2 Hesi ReviewDocument46 pagesAH2 Hesi ReviewJamie Antonini Grant100% (1)
- Hip Dislocation Reduction ManueverDocument6 pagesHip Dislocation Reduction ManueverAdam IrsyaddyraNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease. KulDocument60 pagesValvular Heart Disease. KulIntan Kumalasari RambeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Blood VesselDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Blood Vesselneleh grayNo ratings yet
- My Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomNo ratings yet
- Chest TubesDocument12 pagesChest TubesMark Hammerschmidt100% (4)
- Urinalysis OSCE GuideDocument11 pagesUrinalysis OSCE GuideYu Hsuen Yang0% (1)
- Lillico NR511 SOAP Note Week 3 KatieDocument7 pagesLillico NR511 SOAP Note Week 3 Katie최인선100% (1)
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- HW InotropesDocument3 pagesHW InotropesNatalie YeohNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Document7 pagesConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227No ratings yet
- MS2 Cards Wigger DiagramDocument1 pageMS2 Cards Wigger DiagramCharlieNo ratings yet
- Diuretic eDocument2 pagesDiuretic ejustme_adryNo ratings yet
- Properties of Cardiac Muscle and Conducting SystemsDocument38 pagesProperties of Cardiac Muscle and Conducting Systemsnirilib100% (4)
- Complete Guide To ECGDocument78 pagesComplete Guide To ECGAnas YahyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicDocument13 pagesPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- Study Guide #10 With HEENT ChecklistDocument4 pagesStudy Guide #10 With HEENT ChecklistPrince DuNo ratings yet
- Literacy Tutoring Lesson Plan For Superior: Lesson Parts Lesson Activities Possible Questions ObservationsDocument2 pagesLiteracy Tutoring Lesson Plan For Superior: Lesson Parts Lesson Activities Possible Questions Observationsapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Culminating ActivityyDocument2 pagesCulminating Activityyapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Portfolio AssessmentDocument2 pagesPortfolio Assessmentapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Animals: Structure and Function - Unit TestDocument6 pagesAnimals: Structure and Function - Unit Testapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Respiratory System QuizDocument2 pagesRespiratory System Quizapi-281108263100% (1)
- Differentiated Instruction TechniqueDocument2 pagesDifferentiated Instruction Techniqueapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Circulatory System QuizDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Quizapi-281108263No ratings yet
- "Dancing Raisins" Experiment: Assignment 11-Scientific InquiryDocument3 pages"Dancing Raisins" Experiment: Assignment 11-Scientific Inquiryapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Why ScienceDocument4 pagesWhy Scienceapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Educ 3236 - Prayer ServiceDocument3 pagesEduc 3236 - Prayer Serviceapi-281108263No ratings yet
- EssayDocument5 pagesEssayapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Educ 4262 - Di TechniqueDocument3 pagesEduc 4262 - Di Techniqueapi-281108263No ratings yet
- 4262 Monique Czaczkowski Reportonsdl Table2Document3 pages4262 Monique Czaczkowski Reportonsdl Table2api-281108263No ratings yet
- Teaching Exceptional Students: IEP Project: Step 1: Case StudyDocument5 pagesTeaching Exceptional Students: IEP Project: Step 1: Case Studyapi-281108263No ratings yet
- 4262 Monique Czaczkowski Kevin Vanhaaren Assig6 OnepagerDocument1 page4262 Monique Czaczkowski Kevin Vanhaaren Assig6 Onepagerapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Aortic SurgeryDocument355 pagesAortic SurgeryPaola Rojas GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Notes AtherosclerosisDocument1 pageNotes AtherosclerosisElizabeth de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 pagesHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionPamela DomingoNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument19 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument11 pagesHEART1NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKANo ratings yet
- Braunwald MSCT CompiledDocument127 pagesBraunwald MSCT CompiledAlvin BudionoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 MsDocument16 pagesUnit 3 MsYoussef ElgedelyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Recent Advances - Cardiac CT: Journal ClubDocument130 pagesTopic: Recent Advances - Cardiac CT: Journal Clubjai256No ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Document37 pagesIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Yowan SusantiNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Case StudyDocument7 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Case StudySana RazaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: A Powerpoint PresentationDocument105 pagesLecture Notes: A Powerpoint PresentationDutchsMoin Mohammad100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy OF Acute Coronary Syndrome: Girum SebsibeDocument71 pagesPharmacotherapy OF Acute Coronary Syndrome: Girum SebsibeABREHAM BUKULONo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument19 pagesAtherosclerosissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Achim 2022Document8 pagesAchim 2022BözskeNo ratings yet
- Preventing Chronic Disease:: Physical Activity and Healthy EatingDocument54 pagesPreventing Chronic Disease:: Physical Activity and Healthy EatingCHANGEZ KHAN SARDARNo ratings yet
- Notes On Forensic MedicineDocument59 pagesNotes On Forensic Medicineranjithreddy916gmailNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac RehabilitationDocument35 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac Rehabilitationsdsd100% (1)
- The Cholesterol Myths Uffe RavnskovDocument195 pagesThe Cholesterol Myths Uffe Ravnskovpeedaagee100% (7)
- 10.1038@s41572 019 0090 3Document20 pages10.1038@s41572 019 0090 3sari100% (1)
- Smartscore 4.0 Operator Manual: Ge HealthcareDocument89 pagesSmartscore 4.0 Operator Manual: Ge HealthcareargenisNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Biomechanics of Coronary ArteriesDocument62 pagesA Review On The Biomechanics of Coronary ArteriesAbhishek KarmakarNo ratings yet
- National Clinical Guidelines For Stroke Fourth EditionDocument232 pagesNational Clinical Guidelines For Stroke Fourth EditionRosa Mabel Sanchez RoncalNo ratings yet
- Case Study in NutritionDocument27 pagesCase Study in NutritionTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial Infarctionbanyenye2593% (14)
- Characteristics, Prevention, and Management of Cardiovascular Disease in People Living With HIV - AHA 2019Document27 pagesCharacteristics, Prevention, and Management of Cardiovascular Disease in People Living With HIV - AHA 2019Michael Amarillo CorreaNo ratings yet
- NCMMSN Notes - Sacramento, Karl SebastianDocument96 pagesNCMMSN Notes - Sacramento, Karl SebastianRHEA MAY CAPORNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis A Review: Imedpub JournalsDocument6 pagesPathogenesis of Atherosclerosis A Review: Imedpub JournalsHaydee RocaNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol GuideDocument26 pagesCholesterol GuideRavi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Chelation Therapy, Oral Detoxification For HealthDocument12 pagesChelation Therapy, Oral Detoxification For HealthMuhammad Sajid Abdulgani JambagiNo ratings yet
- What Is AtherosclerosisDocument5 pagesWhat Is AtherosclerosisYến NgọcNo ratings yet