Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Somatoform&dissociative Disorders Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
api-284104206Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Somatoform&dissociative Disorders Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
api-284104206Copyright:
Available Formats
Psychological Disorders > Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
Somatoform Disorders
Dissociative Disorders
Psychological Disorders > Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
Somatoform Disorders
There are at least five forms of somatoform disorders: Somatization Disorder,
Hypochondriasis, Conversion Disorder, Body Dysmorphic Disorder, and Pain
Disorder.
Somatization Disorder is characterized by seeking treatment for at least seven
illnesses which impair functioning, and after investigation, are unfounded as a
medical condition.
Hypochondriasis is characterized by a persistent fear of becoming ill.Individuals
with Hypochondriasis focus on the fear of the illness or disease.
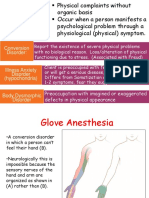
Conversion disorder is characterized by a functional loss with no accompanying
physiological or neurological disorder to account for such loss.The functional loss
could be anything such as paralysis, seizures, tunnel vision, etc.
Body Dysmorphic Disorder is characterized by a perceived body-related defect in
appearance that significantly impairs functioning (social, occupational, etc.), and
cannot be explained by another mental illness.
Pain Disorder is characterized by pain in one or more places, impairs functioning
(social, occupational, etc.),is determined to have a psychological onset, and is
not accounted for by mood disorders or other mental disorders.
Hypochondriac
Psychological Disorders > Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
Dissociative Disorders
Dissociation can range from mild detachment from immediate surroundings to
more severe detachment from physical and emotional experience.While some
dissociation is normal, there are four kinds of dissociation that are considered
psychopathological.
Dissociative amnesia occurs when an individual is suddenly unable to recall
personal information, which cannot be explained by common
forgetfulness.Dissociative fugue is characterized by a sudden leave from one's
location and the assumption of a new identity in a new location.
Depersonalization disorder occurs when an individual feels that they are a
detached observer outside of themselves.Dissociative identity disorder (DID) is a
controversial disorder characterized by and individual displaying at least two
distinct identities.
Severe childhood trauma has been proposed as an explanation for the
development of DID; traumatic events are thought to disrupt the development of
a unified personality, and memories and emotions related to the trauma are
relegated to alternate personalities.
Some argue that individuals who are diagnosed with DID are highly suggestible,
and may be subconsciously acting out a role that they believe the therapist is
expecting.
Dissociative Identity Disorder
Psychological Disorders
Key terms
dissociate to experience a wide array of conditions from mild detachment from immediate surroundings to more severe
detachment from physical and emotional experience.
dissociative Removing or separating from some association.
hypochondriasis A mental disorder characterized by excessive fear of or preoccupation with a serious illness, despite medical
testing and reassurance to the contrary.
somatoform disorder A psychiatric disorder in which physical symptoms are experienced, but for which no apparent physical
cause can be found.
Psychological Disorders
An individual with a conversion disorder might present to a
physician in which of the following ways?
A) A women who is convinced she has elephantiasis in her right arm
when her arm is completely healthy.
B) An individual with paralysis of the right leg with no identifiable
neurological origin.
C) A patient who is concerned he has meningitis despite being tested and
cleared several times.
D) A foreign exchange student who complains of stomach problems the
night before a big test.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Psychological Disorders
An individual with a conversion disorder might present to a
physician in which of the following ways?
A) A women who is convinced she has elephantiasis in her right arm
when her arm is completely healthy.
B) An individual with paralysis of the right leg with no identifiable
neurological origin.
C) A patient who is concerned he has meningitis despite being tested and
cleared several times.
D) A foreign exchange student who complains of stomach problems the
night before a big test.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/
Psychological Disorders
Somatoform disorders are characterized by which of the
following?
A) Concern that something is physically wrong, but no accompanying
medical condition.
B) Concern that something is psychologically wrong, but no
accompanying medical condition.
C) Concern that something is physically wrong, with a medical diagnosis
to back up the concern.
D) Concern that something is psychologically wrong, with a medical
diagnosis to back up the condition.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Psychological Disorders
Somatoform disorders are characterized by which of the
following?
A) Concern that something is physically wrong, but no accompanying
medical condition.
B) Concern that something is psychologically wrong, but no
accompanying medical condition.
C) Concern that something is physically wrong, with a medical diagnosis
to back up the concern.
D) Concern that something is psychologically wrong, with a medical
diagnosis to back up the condition.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/
Psychological Disorders
What is the post-traumatic model of Dissociative Identity Disorder
(DID)?
A) The idea that DID results from childhood abuse which disrupts the
development of a unified identity.
B) The idea that individuals with DID are more prone to trauma while they
are in a dissociated state.
C) The idea that DID is a form of post-traumatic stress disorder.
D) The idea that DID is a form of re-enacting past traumas, akin to posttraumatic flashbacks.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Psychological Disorders
What is the post-traumatic model of Dissociative Identity Disorder
(DID)?
A) The idea that DID results from childhood abuse which disrupts the
development of a unified identity.
B) The idea that individuals with DID are more prone to trauma while they
are in a dissociated state.
C) The idea that DID is a form of post-traumatic stress disorder.
D) The idea that DID is a form of re-enacting past traumas, akin to posttraumatic flashbacks.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/
Psychological Disorders
Why did DID become a popular diagnosis in the latter half of the
20th century?
A) Because research was able to confirm the existence of the condition
during this period.
B) Because of a significant increase in recreational drug use and
alcoholism during this period.
C) Unclear if there were more instances of DID, or if it was simply better
recognized by clinicians.
D) Because there was an increase in people seeking to overcome
childhood traumas during this period.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Psychological Disorders
Why did DID become a popular diagnosis in the latter half of the
20th century?
A) Because research was able to confirm the existence of the condition
during this period.
B) Because of a significant increase in recreational drug use and
alcoholism during this period.
C) Unclear if there were more instances of DID, or if it was simply better
recognized by clinicians.
D) Because there was an increase in people seeking to overcome
childhood traumas during this period.
Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com
Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/
You might also like
- Guilt and ChildrenFrom EverandGuilt and ChildrenJane BybeeNo ratings yet
- Helping Men Recover: Addiction, Males, and The Missing PeaceDocument8 pagesHelping Men Recover: Addiction, Males, and The Missing Peacetadcp100% (1)
- Dissociative NewDocument15 pagesDissociative NewJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- FibromyalgiaDocument1 pageFibromyalgiashailesh284100% (1)
- Revisa Pagina 37Document74 pagesRevisa Pagina 37Donald Cabrera AstudilloNo ratings yet
- QS: Social Exchange Theory: FoundersDocument2 pagesQS: Social Exchange Theory: FounderssoulxpressNo ratings yet
- ConversionPsychiatric Symptoms and Dissociation in Conversion, Somatization and Dissociative Disorders15Document7 pagesConversionPsychiatric Symptoms and Dissociation in Conversion, Somatization and Dissociative Disorders15Amir MirzaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology: Social Influences and RelationshipsDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Psychology: Social Influences and RelationshipsIqbal Baryar100% (1)
- 2015 - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (Review)Document22 pages2015 - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (Review)Andrés Felipe SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal BehaviorDocument22 pagesAbnormal BehaviorKieth DagondongNo ratings yet
- 9-Somatoform Dissociative DisordersDocument27 pages9-Somatoform Dissociative DisordersSara Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Is Schizoaffective Disorder A Distinct Categorical Diagnosis? A Critical Review of The LiteratureDocument22 pagesIs Schizoaffective Disorder A Distinct Categorical Diagnosis? A Critical Review of The Literaturedr.cintaNo ratings yet
- Depersonalization in Response To Life-Threatening DangerDocument10 pagesDepersonalization in Response To Life-Threatening DangeryochaiatariaNo ratings yet
- Dissociative DisordersDocument7 pagesDissociative DisordersHugoNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisordersDocument2 pagesSomatoform DisordersZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Parts: of PsycheDocument10 pagesParts: of PsycheFlower100% (1)
- Notes On PsychiatryDocument10 pagesNotes On PsychiatryMark VillenaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety The Omni Present in 21 CenturyDocument17 pagesAnxiety The Omni Present in 21 CenturyYaadrahulkumar MoharanaNo ratings yet
- Dissociative FugueDocument9 pagesDissociative Fugueapi-254434112No ratings yet
- Somatic Symptom Disorders and Personality DisordersDocument15 pagesSomatic Symptom Disorders and Personality Disordersapi-287575009No ratings yet
- PsyDocument12 pagesPsyImaneNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity DisorderDocument42 pagesDissociative Identity DisorderGsdhdbNo ratings yet
- Jane R. Wheatley-Crosbie - Healing Traumatic Reenactment: Psyche's Return From Soma's UnderworldDocument5 pagesJane R. Wheatley-Crosbie - Healing Traumatic Reenactment: Psyche's Return From Soma's UnderworldCanola_Olive0% (1)
- Quality of Life in Cancer: by Sanish SebastianDocument55 pagesQuality of Life in Cancer: by Sanish Sebastiansanish4u100% (1)
- Anxiety Disorder - Nayan MaharjanDocument52 pagesAnxiety Disorder - Nayan MaharjanNayan MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Slides CHPT 5 - Trauma and Stress DisordersDocument45 pagesSlides CHPT 5 - Trauma and Stress DisordersSofiaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Disorder The Modern HysteriaDocument6 pagesConversion Disorder The Modern HysteriaGiiszs AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Depersonalzation DisorderDocument7 pagesDepersonalzation DisorderJeramyah RuiNo ratings yet
- PTSD EssayDocument2 pagesPTSD Essayapi-338213804No ratings yet
- Liotti Trauma Attachment 2004Document39 pagesLiotti Trauma Attachment 2004samathacalmmindNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric MisadventuresDocument10 pagesPsychiatric MisadventuresRob_212No ratings yet
- Guided Imagery and Recovered Memory Therapy - Considerations and Cautions 2006Document12 pagesGuided Imagery and Recovered Memory Therapy - Considerations and Cautions 2006Hashem Al-attasNo ratings yet
- Depression in Older PeopleDocument4 pagesDepression in Older PeopleAlina AlinaNo ratings yet
- Addicted To BlissDocument19 pagesAddicted To BlissInternational Journal of Transpersonal StudiesNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity DisorderDocument2 pagesDissociative Identity DisorderAnca Crețu0% (1)
- CH 5 Psychointetherap 2Document17 pagesCH 5 Psychointetherap 2Elif AktaşNo ratings yet
- Effect of Stress On Executive Performance by Saathwik Chandan NuneDocument8 pagesEffect of Stress On Executive Performance by Saathwik Chandan NuneSaathwik Chandan100% (1)
- Modified Emdr Resource Development & Installation ProtocolDocument5 pagesModified Emdr Resource Development & Installation ProtocolYanina Andrea Fernandez PintoNo ratings yet
- PNES ClinicalApproachesDocument19 pagesPNES ClinicalApproachesClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Stress and TraumaDocument19 pagesStress and TraumaprabhuthalaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Disorder, Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder, and Chronic Pain - Comorbidity, Assessment, and TreatmentDocument10 pagesConversion Disorder, Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder, and Chronic Pain - Comorbidity, Assessment, and TreatmentViviana CalderónNo ratings yet
- Nicotine WithdrawalDocument4 pagesNicotine Withdrawalhasan jamiNo ratings yet
- 7A Psychological DisordersDocument5 pages7A Psychological DisordersJonathanNo ratings yet
- Icd V/S DSM: Aneena JohnDocument9 pagesIcd V/S DSM: Aneena JohnAneena JohnNo ratings yet
- Gestalt, Psy PDFDocument17 pagesGestalt, Psy PDFAdriana Bogdanovska ToskicNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Stress - Effects On The Brain PDFDocument17 pagesTraumatic Stress - Effects On The Brain PDFDaniel Londoño GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Day 2015Document5 pagesDiagnosis Day 2015api-261267976No ratings yet
- Dissociative Dis, SeminarDocument11 pagesDissociative Dis, Seminarastha singh100% (1)
- DAY 1 - Thursday, April 29, 2021: Central My Time ZoneDocument2 pagesDAY 1 - Thursday, April 29, 2021: Central My Time ZoneNerissa ArvianaNo ratings yet
- ECTDocument24 pagesECTEdgar ManoodNo ratings yet
- Memories For TraumaDocument17 pagesMemories For TraumaTANIA DONOSONo ratings yet
- Podcast Anxiety and DepressionDocument5 pagesPodcast Anxiety and DepressionSyifa Olyfiani SariNo ratings yet
- EMDR and Mesmerism: A Comparative Historical AnalysisDocument12 pagesEMDR and Mesmerism: A Comparative Historical AnalysisKamiNo ratings yet
- Obsessive Compulsive DisorderDocument26 pagesObsessive Compulsive DisorderMhaane Desepeda VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Mental Disorders: Sub Ject: Clinical Psychology Presented By: PHD - Mariana CernitanuDocument34 pagesMental Disorders: Sub Ject: Clinical Psychology Presented By: PHD - Mariana CernitanuAlbert PruteanuNo ratings yet
- Assessment & Management of Dissociative Disorders: Chairperson: DR - Safeekh A.T. Presenter: Dr.D.ArchanaaDocument62 pagesAssessment & Management of Dissociative Disorders: Chairperson: DR - Safeekh A.T. Presenter: Dr.D.Archanaadrkadiyala2No ratings yet
- Paper 2 Compassion FatigueDocument4 pagesPaper 2 Compassion Fatigueapi-401934380No ratings yet
- Integrative Dual Diagnosis Treatment Approach to an Individual with Alcoholism and Coexisting Endogenous DepressionFrom EverandIntegrative Dual Diagnosis Treatment Approach to an Individual with Alcoholism and Coexisting Endogenous DepressionRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Childhood Disorders Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesChildhood Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Personality Disorders Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesPersonality Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Mood Disorders Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesMood Disorders Lesson Planapi-2841042060% (1)
- Personality Disorders Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesPersonality Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders Lesson PlanDocument32 pagesAnxiety Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Mood Disorders Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesMood Disorders Lesson Planapi-2841042060% (1)
- Anxiety Disorders Lesson PlanDocument32 pagesAnxiety Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Introduction To Psych Disorders Lesson PlanDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Psych Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS)Document3 pagesAdult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS)amaandrei100% (1)
- Literature Review - Pankhuri Saxena 3Document3 pagesLiterature Review - Pankhuri Saxena 3api-610037275No ratings yet
- Psychopatholgy of Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pagePsychopatholgy of Bipolar Disorderthr3adzNo ratings yet
- Differences in Mood Instability in Patients With Bipolar Disorder Type I and II: A Smartphone Based StudyDocument8 pagesDifferences in Mood Instability in Patients With Bipolar Disorder Type I and II: A Smartphone Based StudyAndre PhanNo ratings yet
- Malignant Self Love Narcisism RevisitedDocument139 pagesMalignant Self Love Narcisism Revisitedbedou100% (3)
- Icd 10Document4 pagesIcd 10ÜnŶäÜnClubEverydayNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Question Bank - 65 Multiple Choice Questions On - Psychiatry in India - PDFDocument21 pagesPsychiatry Question Bank - 65 Multiple Choice Questions On - Psychiatry in India - PDFAnkit Gupta44% (9)
- Anxiety Disorders in WomenDocument52 pagesAnxiety Disorders in WomenZakkiyatus Zainiyah100% (1)
- Wender Utah PDFDocument3 pagesWender Utah PDFFco CanaleNo ratings yet
- Changes From Dsm-IV-tr To Dsm-5Document19 pagesChanges From Dsm-IV-tr To Dsm-5Sofia Cabezas Ordóñez100% (1)
- Holla 2015Document10 pagesHolla 2015Bima GhovaroliyNo ratings yet
- Borderline Personality Disorder Write Up 2Document8 pagesBorderline Personality Disorder Write Up 2Sreejita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case For Exam and Control of Survival of KnowledgeDocument15 pagesClinical Case For Exam and Control of Survival of KnowledgeSherif KhaledNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument35 pagesPersonality DisordersEsraRamosNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan ContentDocument9 pagesUnit Plan ContentS KANIMOZHINo ratings yet
- Adhd Add Adult TestDocument1 pageAdhd Add Adult Testlogan50% (2)
- Young MRSDocument2 pagesYoung MRSAnonymous KgUtPlkjNo ratings yet
- The Master Disorder Document SPR 2015Document6 pagesThe Master Disorder Document SPR 2015api-261267976100% (1)
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument27 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderFrenstan Tan100% (2)
- Psychological DisordersDocument7 pagesPsychological Disorderskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Adults and Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) : Diagnostics, Treatments, ChallengesDocument33 pagesAdults and Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) : Diagnostics, Treatments, Challengeskawaiijanai gfNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument42 pagesBipolar Disorder: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- The Soloist PaperDocument6 pagesThe Soloist Paperapi-326282879No ratings yet
- A Companion To Fish's Clinical PsychopathologyDocument77 pagesA Companion To Fish's Clinical PsychopathologyRobbydjan Christopher80% (5)
- Provisional: Borderline Personality Disorder Differential DXDocument6 pagesProvisional: Borderline Personality Disorder Differential DXhernandez2812No ratings yet
- Oppositional Defiant DisorderDocument2 pagesOppositional Defiant DisorderNikhil MohanNo ratings yet
- A Fractured Mind by Robert BDocument5 pagesA Fractured Mind by Robert Bapi-4550416880% (4)
- AbDocument13 pagesAbSeahorse ClamNo ratings yet
- Instrumen ADULT MANIFEST ANXIETY SCALE - Iqbal FauziDocument7 pagesInstrumen ADULT MANIFEST ANXIETY SCALE - Iqbal Fauziamenda puspa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Delirium, Dementia & Amnestic Cognitive DisordersDocument33 pagesDelirium, Dementia & Amnestic Cognitive Disordersapi-369624875% (4)