Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Apeastasiatimeline
Uploaded by
api-230184052Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Apeastasiatimeline
Uploaded by
api-230184052Copyright:
Available Formats
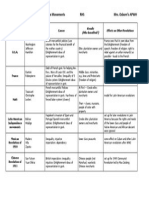
Regional Timeline/Outline for: East Asia
Politics
Economy
Social
Class/
Gender
Science/
Inventions
Art/
Architecture
Empire
Religion
RHS
PERIOD 3
600-1450
Dynasties with emperors
mandate of heaven
Start of bureaucracy
/meritocracy
Japan borrowed from China
Increased bureaucracy
Tributary system
Constant threat from North
Prince Shotoku then
daimyos
Fall of Ming from
internal/external Manchu
Japan: Warring States Period to
Tokogawa Shogunate
Centralized rule
Abdication of Qing,
unification of China
Fight for control with Mao
Japan: abolishes feudalism,
Civil code, regional govs
Nationalism = huge force
Lots of money flowing in
from Silk Roads
Otherwise agricultural
Paper money
Credit or flying money
High taxes cause peasant
revolts
Serfs bound to land
Provide labor for
plantations/mines
Meiji Restoration- quickly
industrialized in Japan
Patriarchal
Confucian principles
Women only power in
court
Scholars/officials
military artisans
Few live in cities
Iron Age
Modernized army
Paper, accurate
sundials/calendars,
agriculture improvements
(plow)
Brush painting
Palaces
Code of Bushido- chivalry
Women lost freedom in
Japan
China: trade with
Europeans in Qing
Japan: manufacturing,
merchant class get wealth and
power , urbanization, population
growth
Foreigners allowed in China
Manchus higher than Chinese
Japan: hierarchy becomes
unbreakable, samurai at top
lower class women more
free upper obey or die
Gunpowder more prevalent
Globalization of trade
British introduced opium to
China
Westernization of Japan
- steamships/railroads
Communication revolution
Artistic styles change more
rapidly and radically than ever
before
Collapse of empires in
China from internal
problems economic
depression, natural
catastrophe, social
unrest
Polytheism, animism
ancestor worship
Confucianism, Legalism
Daoism, also spread of
Buddhism from India
Mongol empires conquer
China, but fail in Japan
replaced by Ottoman Turks
and Ju Yuanzahng of Ming
dynasty
Japan: kabuki theatre
replaces restrained drama,
Woodblock prints = art
form, borrowed Korean
ceramics and western oil
painting
Japan empire centralized
Fall of the Manchu empire
Interaction with west =
China relatively isolated,
Japan- periods of isolation
and acceptance
New sects of Buddhism
from China to Japan
Neo- Confucianism increase
(ethnocentric, historicism,
rationalism)
Gunpowder for military
Boasts = junks
Navigation/block printing
Iron production
Agriculture technique
population cities
Infrastructure (roads, inns,
postal stations)
Japan: haiku, pencil
sketches, ink sketches, Noh
drama, tea ceremony
Buddhist missionaries
Shinto religion
Influenced by monotheistic
religions
Neo- Confucian thought
PERIOD 4
1450-1750
Mrs. Osborn
PERIOD 1 & 2
8000BCE-600CE
PERIOD 5
1750-1900
Rigid Tokogawa hierarchy
ended
Middle class grows power
Lower classes- horrible
conditions, taxed a lot
The fall of China opium
wars, internal rebellions,
external lasses, Boxer
Rebellion
Japanese imperialismTaiwan, Korea, Russia
Scientific/secular world
becomes dominant
PERIOD 6
1900-Present
Decolonization from Europe
Nominally democratic
Tensions- China and West
USSR/China split Birth of
Chinese Republic
Japan: parliamentary
capitalism
Modernization of Japan,
Taiwan, South Korea
Post- industrial/high-tech
Less affected by global
depression
Need natural resources
Slow to embrace/tolerate
diversity and individualism
High degree/variety social
services
Rise of feminism- suffrage
Women went worked WWII
Foot binding outlawed
Atomic bombs
Nuclear weaponry
Militarism in Japan
Computer, internet,
biotechnology and genetic
science
Theme for lit- resisting US
New style= cubism
Movie industry
Use of concrete and glass
New skepticism
Japan- WWII- invades
Manchuria, China, Siberia
taking over Southeast Asia,
Bomb Pearl Harbor brings
US into war atomic
bomb US occupies Japan
Religious fundamentalism
Western appreciation for
science spread
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Buddha's Teaching As It Is - Bhikkhu BodhiDocument44 pagesBuddha's Teaching As It Is - Bhikkhu BodhisatiNo ratings yet
- Feng Shui: More Than DecoratingDocument8 pagesFeng Shui: More Than DecoratingBaziNo ratings yet
- The Way of Shambhala ManualDocument17 pagesThe Way of Shambhala Manualsandip100% (1)
- Guidelines Paul AntonioDocument4 pagesGuidelines Paul Antonioadamkor100% (2)
- A Safe Guide For The Practitioner of Hevajra TantraDocument8 pagesA Safe Guide For The Practitioner of Hevajra TantraRandy HoweNo ratings yet
- Lineage Traditions of The Nyingma School of Tibetan BuddhismDocument3 pagesLineage Traditions of The Nyingma School of Tibetan BuddhismDudjomBuddhistAssoNo ratings yet
- Confucianism Concept NotesDocument3 pagesConfucianism Concept NotesAshley Jade Hanna Flores100% (3)
- Eckel 2008 BhavivekaDocument380 pagesEckel 2008 BhavivekaYang Nicole100% (3)
- 2017-2018 District Calendar - Boe Approved 10-18-2016 4Document1 page2017-2018 District Calendar - Boe Approved 10-18-2016 4api-230184052No ratings yet
- The Coming of Christianity To AxumDocument2 pagesThe Coming of Christianity To Axumapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Major ReviewDocument16 pagesMajor Reviewapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap RevsindDocument1 pageAp Revsindapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Apwh How To NotecardsDocument1 pageApwh How To Notecardsapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap PoldevDocument2 pagesAp Poldevapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Whap Reading Calendar 2016-17 Revised 8-8Document2 pagesWhap Reading Calendar 2016-17 Revised 8-8api-230184052No ratings yet
- Whap 2016-17 Syllabus - Student VersionDocument6 pagesWhap 2016-17 Syllabus - Student Versionapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap Week 1 How To DoDocument3 pagesAp Week 1 How To Doapi-230184052No ratings yet
- 2016-17 Bell Schedule PshsDocument1 page2016-17 Bell Schedule Pshsapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap TradeDocument2 pagesAp Tradeapi-230184052No ratings yet
- ApafricatimelineDocument1 pageApafricatimelineapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap GenderissuesDocument2 pagesAp Genderissuesapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap IndrevchartDocument1 pageAp Indrevchartapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Classical Civs Chart PDFDocument3 pagesClassical Civs Chart PDFgovandlaw4671No ratings yet
- Ap DemographicDocument3 pagesAp Demographicapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Faiths Around WorldDocument2 pagesFaiths Around Worldapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ap GlobaltradeDocument2 pagesAp Globaltradeapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Strayer Review Questions CH 20-23Document1 pageStrayer Review Questions CH 20-23api-230184052No ratings yet
- China 1900-1949Document15 pagesChina 1900-1949api-230184052100% (1)
- Globalization Visual Sources CH 23Document6 pagesGlobalization Visual Sources CH 23api-230184052No ratings yet
- Chinese DynastiesDocument34 pagesChinese Dynastiesapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Ccot 2 in Class Essay CH 22Document1 pageCcot 2 in Class Essay CH 22api-230184052No ratings yet
- Globalization Visual Sources CH 23Document6 pagesGlobalization Visual Sources CH 23api-230184052No ratings yet
- Ccot Essay & Thesis FormatDocument1 pageCcot Essay & Thesis Formatapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Apwh Period 5 ReviewDocument3 pagesApwh Period 5 Reviewapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Vanguard Video Guide - Chinese Development in AngolaDocument1 pageVanguard Video Guide - Chinese Development in Angolaapi-230184052No ratings yet
- A-Bomb SWDocument5 pagesA-Bomb SWapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Rise of StalinDocument24 pagesRise of Stalinapi-230184052No ratings yet
- Spring and Autumn Period: A Time of Decline and Conflict in Ancient ChinaDocument14 pagesSpring and Autumn Period: A Time of Decline and Conflict in Ancient ChinaEneaGjonaj100% (1)
- Works by Prof. Shanker Shanker Thapa On Nepalese Buddhism and Other Areas of HistoryDocument10 pagesWorks by Prof. Shanker Shanker Thapa On Nepalese Buddhism and Other Areas of HistoryShankerThapaNo ratings yet
- Praise of The Twelve Deeds of Buddha Shakyamuni - Composed by Pawo Tsogla Tringwa - 46Document18 pagesPraise of The Twelve Deeds of Buddha Shakyamuni - Composed by Pawo Tsogla Tringwa - 46Fairy LandNo ratings yet
- Jackie Chan Movie ListDocument5 pagesJackie Chan Movie ListSubramanian ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Gupta Rajulu EvaruDocument94 pagesGupta Rajulu EvaruRavi Kumar DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- Tingkatan 1 Allamanda (KRK-DLP) 2021: YEE2101 SMK SimanggangDocument7 pagesTingkatan 1 Allamanda (KRK-DLP) 2021: YEE2101 SMK SimanggangAndrew JohnNo ratings yet
- YogaDocument4 pagesYogasujasundarNo ratings yet
- Zen GardenDocument10 pagesZen GardenRoopali GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shoyoroku Case 1: Bodhidharma's 'Vast and VoidDocument27 pagesShoyoroku Case 1: Bodhidharma's 'Vast and VoidewbNo ratings yet
- The Three PuritiesDocument5 pagesThe Three PuritiesJessé de AndradeNo ratings yet
- Close Window TextDocument11 pagesClose Window Textwenzhuo zhangNo ratings yet
- Lamp Meditation PDFDocument12 pagesLamp Meditation PDFBalajiNo ratings yet
- 8 Versos AuspiciososDocument2 pages8 Versos AuspiciososDIEGO63No ratings yet
- Asokas Donations at Lumbini PDFDocument13 pagesAsokas Donations at Lumbini PDFShrikant Phatak100% (1)
- Sri MahavirDocument7 pagesSri Mahavirankiite4678No ratings yet
- Art Culture KushanasDocument38 pagesArt Culture KushanasAnudeep ChittluriNo ratings yet
- Vivekachudamani TranslationDocument78 pagesVivekachudamani TranslationAlejandro MachucaNo ratings yet
- White Dzambhala PlaqueDocument3 pagesWhite Dzambhala PlaqueJoseph Michael VitugNo ratings yet
- The Srimala Devi SutraDocument24 pagesThe Srimala Devi SutraSantiago JimenezNo ratings yet
- Nepal - Nepali Mss Gandhari Chinese TR of SadharmapundarikaDocument37 pagesNepal - Nepali Mss Gandhari Chinese TR of SadharmapundarikaShankerThapaNo ratings yet
- Fu Zhong Wen Taiji.2.Document9 pagesFu Zhong Wen Taiji.2.César EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Hempen Culture in JapanDocument33 pagesHempen Culture in Japanaaaaaa_No ratings yet