Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure: Lauren Saunders 12 September 2014
Uploaded by
LaurenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atomic Structure: Lauren Saunders 12 September 2014
Uploaded by
LaurenCopyright:
Available Formats
Lauren Saunders
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
12th September 2014
12th September 2014
Lauren Saunders
Subatomic
particle
Symbol
(inc.
mass &
atomic
nos.)
Mass
Charge
kg
Relativ
e
Relativ
e
proton
1.672 x 10
+1.602
x10 -19
+1
neutron
1.674 x 10
electron
9.109 x 10
1/1836 -1.602 x10
-1
-27
-27
-31
-19
Description of an atom (in terms of sub-atomic
particles) :
Effect of
electric or
magnetic
fields
Positively
charged and
so would be
deflected on
a curving
path towards
the negative
plate.
Don't have a
charge, and
so would
continue on
in a straight
line.
Negatively
charged and
so would be
deflected on
a curving
path towards
the positive
plate.
Diagram of atomic
Each atom has a nucleus at its centre,
containing protons and neutrons. Most of
the mass of the atom is concentrated
here. The diameter of the nucleus is very
small compared to the rest of the atom.
Electrons are in clouds (shells) around
the nucleus. These shells take up most
of the volume of the atom.
structure
Explain the meaning of the following terms :Isotope:
Atoms of the same element which have the same atomic number
but different mass numbers.
Same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Atomic number:
The number of protons in the nucleus.
This identifies the element. All atoms of the same element have the
same number of protons- same atomic number.
Lauren Saunders
12th September 2014
Mass number:
Total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Can subtract the atomic from the mass number to work out the
number of neutrons.
Relative atomic mass:
Average mass of an atom of an element on a scale where a carbon12 atom has a mass of exactly 12 units.
Explain the meaning of nuclear fusion :
Two light atomic nuclei fuse together to form a single heavier
nucleus of a new element.
The process releases enormous quantities of energy.
Conditions for nuclear fusion:
Very high temperature - gives the (hydrogen) nuclei enough energy
to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between the protons. The
hotter a molecule is, the faster it will move and the more likely it is
to collide
High pressure- the nuclei need to be very close together to fuse,
approximately a million millionth of a millimetre.
Example of nuclear fusion (equation)
Hydrogen nuclei combine to make helium nuclei, releasing huge
amounts of energy. This is happening inside our suns core.
+
You might also like
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- 12 Nuclear Physics and IsotopesDocument12 pages12 Nuclear Physics and IsotopesProf.Dr.Mohamed Fahmy Mohamed HusseinNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics NotesDocument80 pagesA Level Physics NotesAsghar Abbas100% (2)
- Chapter Four (Nuclear Power)Document121 pagesChapter Four (Nuclear Power)luter alexNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR01x 2016 1.2 The Atomic Model-TranscriptDocument2 pagesNUCLEAR01x 2016 1.2 The Atomic Model-TranscriptArnoldo DanielNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics NotesDocument81 pagesA Level Physics NotesJames Chong100% (1)
- A Level Physics NotesDocument92 pagesA Level Physics NotesMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- Energy Unit 4Document22 pagesEnergy Unit 4Joseph MartinNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics NotesDocument93 pagesA Level Physics NotesAdam BaldwinNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics NotesDocument80 pagesA Level Physics NotesFireFrostNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document13 pagesChapter 13Shyam 07No ratings yet
- Atomic Nucleus and Nuclear EnergyDocument41 pagesAtomic Nucleus and Nuclear EnergyArundhati KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 1 1Document15 pagesChapitre 1 1Ri HabNo ratings yet
- As Physics NotesDocument43 pagesAs Physics Notesleelakdd108100% (1)
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesNuclear PhysicsShubh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Atomic Structure The Structure of The Atom A) Protons, Neutrons and ElectronsDocument21 pagesChapter 1: Atomic Structure The Structure of The Atom A) Protons, Neutrons and ElectronsTeneshwaran Muniandy MunusamyNo ratings yet
- Ch02 AtomicNucleusDocument8 pagesCh02 AtomicNucleusPrichindel MorocanosNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics (Lecture 22-24) - Compatibility ModeDocument41 pagesNuclear Physics (Lecture 22-24) - Compatibility ModeBibhu Prasad SahooNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry 20-10-2020Document16 pagesNuclear Chemistry 20-10-2020Manohar MaripeNo ratings yet
- Note For EJUDocument18 pagesNote For EJUmr.draungnaingwinNo ratings yet
- Nuclei: Chapter ThirteenDocument17 pagesNuclei: Chapter ThirteenBhoomika VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument29 pagesNucleiVaibhav Singh100% (1)
- Nuclear Physics and Examples-2022Document14 pagesNuclear Physics and Examples-2022OSCARNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant. EEE-481, CUETDocument96 pagesNuclear Power Plant. EEE-481, CUETbaruaeee100% (1)
- Nuclear Fission and Fusion: Unit IV: Atomic Physics Welter Class NotesDocument5 pagesNuclear Fission and Fusion: Unit IV: Atomic Physics Welter Class Notesbharathy100% (1)
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 13 PDFSuresh Babu KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Nuclei 22912Document7 pagesNuclei 22912user 003No ratings yet
- Module Nuc - Phys I (Phys382) New1Document26 pagesModule Nuc - Phys I (Phys382) New1davididosa40No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument3 pagesStructure of AtomabiramirajalaksmiNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear AtomDocument4 pagesThe Nuclear AtomMantiki QhobosheaneNo ratings yet
- 23 Nuclear PhysicsDocument52 pages23 Nuclear Physicsdayana hanis hassanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesVijithaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Nuclei2012-Notes UnlockedDocument29 pagesAtoms and Nuclei2012-Notes Unlockedapi-250079701No ratings yet
- Lecture 36Document27 pagesLecture 36Jaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Objectius Del Tema: Isotopes of An Element Are Atoms That Have The Same Number ofDocument9 pagesObjectius Del Tema: Isotopes of An Element Are Atoms That Have The Same Number ofAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- 08 Physics 11se Ch08Document42 pages08 Physics 11se Ch08pecan_lisa38No ratings yet
- Atoms and NucleiDocument53 pagesAtoms and NucleiGirish Arora100% (1)
- Physics NotesDocument80 pagesPhysics NotesDanielNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Basic PhysicsDocument26 pagesLec 2 Basic PhysicsHashir AliNo ratings yet
- 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 1 (9/6/06) Basic Nuclear ConceptsDocument13 pages22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 1 (9/6/06) Basic Nuclear ConceptsDeniz Cihan GündüzNo ratings yet
- Basic Rad Phy1Document99 pagesBasic Rad Phy1Rashmi RajanNo ratings yet
- Helium Atom: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesHelium Atom: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchWYNNo ratings yet
- 10.radiometry and DosimetryDocument17 pages10.radiometry and DosimetryAchraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- 'NUCLEIDocument39 pages'NUCLEIRITIKANo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding 2.2 Fundamental ConceptsDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding 2.2 Fundamental Conceptshirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document40 pagesChapter 1Lea EtengNo ratings yet
- 14 - Nucleus 14.1 Nucleus - General InformationDocument12 pages14 - Nucleus 14.1 Nucleus - General InformationHrishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StabilityDocument7 pagesNuclear StabilityWaqas SaeedNo ratings yet
- Nuclei: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedDocument29 pagesNuclei: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedMridul GuptaNo ratings yet
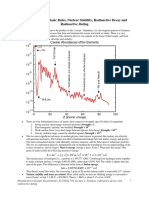
- 12.744/12.754 The Basic Rules, Nuclear Stability, Radioactive Decay and Radioactive DatingDocument8 pages12.744/12.754 The Basic Rules, Nuclear Stability, Radioactive Decay and Radioactive Datingshawnah jamesNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument17 pagesNucleiliebertj221No ratings yet
- Ib HL Study Guide Organizer-Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesIb HL Study Guide Organizer-Nuclear PhysicsCarlos Andres Vásquez100% (1)
- Notes 2 - Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument6 pagesNotes 2 - Atoms and Atomic Theoryochiengjoseph122No ratings yet
- TRM 12Document96 pagesTRM 12KayKhaing OoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument27 pagesNuclear ChemistryveluselvamaniNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument8 pagesNucleiZahaan SajidNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Chem 9thDocument6 pagesStructure of Atom Chem 9thPrashant ZadeNo ratings yet
- Maths Transcript 1Document1 pageMaths Transcript 1LaurenNo ratings yet
- English GCSE - The Falling LeavesDocument1 pageEnglish GCSE - The Falling LeavesLaurenNo ratings yet
- Position of EquilibriumDocument5 pagesPosition of EquilibriumLaurenNo ratings yet
- Elements From The SeaDocument11 pagesElements From The SeaLaurenNo ratings yet
- C2HDocument16 pagesC2HLaurenNo ratings yet
- English GCSE - FutilityDocument1 pageEnglish GCSE - FutilityLaurenNo ratings yet
- English GCSE - Next To of Course God America IDocument1 pageEnglish GCSE - Next To of Course God America ILaurenNo ratings yet
- English GCSE - The Charge of The Light BrigadeDocument1 pageEnglish GCSE - The Charge of The Light BrigadeLaurenNo ratings yet
- English GCSE - Bayonet ChargeDocument1 pageEnglish GCSE - Bayonet ChargeLaurenNo ratings yet
- M2 Summary SheetDocument1 pageM2 Summary SheetLaurenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Ideas 1.2Document2 pagesChemical Ideas 1.2LaurenNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Using Equations To Work Out Reacting MassesDocument1 page1.3 Using Equations To Work Out Reacting MassesLaurenNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Concentration of SolutionsDocument2 pages1.5 Concentration of SolutionsLaurenNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Calculations Involving GasesDocument2 pages1.4 Calculations Involving GasesLaurenNo ratings yet