Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCP
Uploaded by
dericOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCP
Uploaded by
dericCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Nurses Community
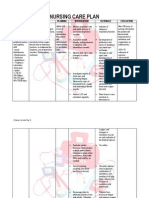
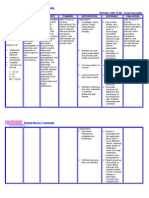
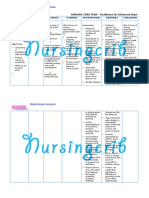
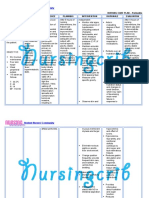
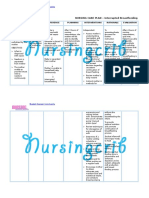
NURSING CARE PLAN Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
Napakasakit ng
tiyan ko (Im
having severe
stomach pain) as
verbalized by the
patient.
OBJECTIVE:
Abdominal
guarding
Rigid body
posture
Facial
grimacing
V/S taken as
follows
T: 37.3C
P: 89
R: 19
BP: 110/ 80
DIAGNOSIS
Acute or
chronic pain
maybe related
to chemical
burn of gastric
mucosa, oral
cavity and
physical
response such
as flex muscle
spasm in the
stomach wall.
INFERENCE
PLANNING
Acid, pepsin, and
helicobacter
infection play an
important role in
the development
of gastric ulcers.
The gastric
mucosal barrier
overlies the
epithelium. The
secretion of
mucus and
bicarbonate
provides a first
line defense in
maintaining a
near-normal pH
on the gastric
epithelium and
protects the
mucosal barrier
against acid.
Gastromucosal
prostaglandins
increase the
barriers
resistance to
ulceration. The
integrity of the
barrier is
enhanced by the
rich blood supply
of the mucosa of
the stomach and
duodenum.
After 4 hours of
nursing
interventions, the
Patient verbalize
relief of pain and
demonstrate
relaxed body
posture and be
able to sleep or
rest properly.
INTERVENTION
Independent
Note reports of
pain, including
location, duration,
and intensity (0-10
scale).
Review factors that
aggravate or
alleviate pain.
Note nonverbal
pain cues.
Provide small
frequent meals.
Identify and limit
foods that create
discomfort.
Assist with active
and passive range
of motion
exercises.
Provide frequent
oral care and
comfort measures
including back rub
and position
change.
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Pain is not always
present, should
be compared with
patients previous
pain symptoms.
The comparison
may assist in
diagnosis of
etiology of
bleeding and
development of
complications.
After 4 hours of
nursing
interventions, the
Patient was able to
verbalize relief of
pain and
demonstrate relaxed
body posture and be
able to sleep or rest
properly.
Helpful in
establishing
diagnosis and
treatment needs.
Non-verbal cues
may be both
physiological and
psychological and
may be use in
conjunction with
verbal cues to
evaluate extent
and severity of
the problem.
Food has an acidneutralizing effect
and dilutes the
gastric contents.
Student Nurses Community
Collaborative
Provide and
implement dietary
modifications.
Use regular than
skim milk, if milk is
allowed.
Administer
medications as
indicated such as
analgesics.
Small meals
prevent distention
and the release of
gastrin.
Specific foods that
cause distress
vary among
individuals. Spicy
foods, alcohol,
and coffee can
precipitate
dyspepsia.
Reduces joint
stiffness,
minimizing pain
and discomfort.
Halitosis from
stagnant oral
secretions is
unappetizing and
can aggravate
nausea.
Client may receive
nothing by mouth
initially. When
oral intake is
allowed, food
choices depend
on the diagnosis
and etiology of
the bleeding.
Student Nurses Community
Fat in regular milk
may decreases
gastric
secretions. The
calcium and
protein content
especially in skim
milk increases
secretions.
Helps relive acute
or severe pain.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitGenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesEnteral Feeding Nursing Care PlanChebz Zy0% (1)
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument4 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPBrylle Capili100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Vii. NCP and Case Study: Learn The DemonstrateDocument4 pagesVii. NCP and Case Study: Learn The DemonstrateVenus Glaze Verzola100% (2)
- NCP CholangitisDocument4 pagesNCP CholangitisJanica C. BayauaNo ratings yet
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Ugib NCPDocument5 pagesUgib NCPJhuRise Ann Mangana100% (1)
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Case StudyDocument5 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Case StudyClaudine Lacaden0% (1)
- Ugib Case StudyDocument33 pagesUgib Case StudyRosemarie Cunanan Grifoni100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was SeenDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was Seenkaren kate ablesNo ratings yet
- NCP: Patient With Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument3 pagesNCP: Patient With Peptic Ulcer DiseaseICa Marlina0% (1)
- CAREPLAN For CholangitisDocument3 pagesCAREPLAN For CholangitisNatty-oneBonafide100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerAntonio G. Cordillon100% (1)
- GERDDocument5 pagesGERDSteve Randolph67% (3)
- Relief of Acute Gastric PainDocument4 pagesRelief of Acute Gastric PainJhaypee Soriano100% (3)
- NCP CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesNCP Cholelithiasiskmpg11100% (2)
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDocument3 pagesNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- BPN NCPDocument6 pagesBPN NCPJoart EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Due To Gastritis Care Plan-G.a.Document1 pageAcute Pain Due To Gastritis Care Plan-G.a.Kristin Bienvenu85% (13)
- Self Care DeficitDocument4 pagesSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezNo ratings yet
- NCP GastroenteritisDocument1 pageNCP GastroenteritisFranchesca PaunganNo ratings yet
- NCP Peptic Ulcer DsDocument4 pagesNCP Peptic Ulcer Dsplug0650% (10)
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- ThyroidectomyDocument2 pagesThyroidectomyYenyen Legas100% (2)
- Assessing and Managing Gastric PainDocument2 pagesAssessing and Managing Gastric PainMichael Joaquin0% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnneNo ratings yet
- NCP For DengueDocument1 pageNCP For DengueyelbonifacioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: DiagnosisDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: DiagnosisCharmaine100% (1)
- Hiatal Hernia Nursing Care Plan - Risk For AspirationDocument1 pageHiatal Hernia Nursing Care Plan - Risk For AspirationCyrus De Asis100% (12)
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- NCP For Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesNCP For Acute Cholecystitisnarucute01224100% (3)
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesAcute PancreatitisAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- NCP For Patient With GastritisDocument1 pageNCP For Patient With GastritisBer Anne33% (3)
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocument3 pagesAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitisdon-timothy-abenojar-795686% (7)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntolerancedohbleNo ratings yet
- NCP For GERD (Risk For Aspiration)Document2 pagesNCP For GERD (Risk For Aspiration)Ma Kristina Apolonio63% (8)
- NCP3 Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP3 Skin IntegritySheng Arquiza67% (3)
- Multiodular non toxic goiter nursing care planDocument1 pageMultiodular non toxic goiter nursing care plankzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- Final NCP HerniaDocument5 pagesFinal NCP HerniaDenisse Shazz Mae Maret100% (2)
- CHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanMiguelito Galagar GultianoNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis Discharge PlanDocument1 pageAcute Gastroenteritis Discharge PlanDiana Jeanne PaculananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 47 Management of Patient With Gastric and Duodenal DisorderDocument7 pagesChapter 47 Management of Patient With Gastric and Duodenal DisorderMae Navidas Digdigan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peptic Ulcer DiseaseWardinatul ImanNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDIES L3 A Group 3Document10 pagesCASE STUDIES L3 A Group 3Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane TimbalopezDocument14 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane Timbalopezjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCP EndoDocument8 pagesNCP EndoJan Rainier Carlos BalariaNo ratings yet
- Course Task DysphagiaDocument4 pagesCourse Task DysphagiaExile RoleplayNo ratings yet
- RubelinDocument7 pagesRubelinPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Upper Git Medical Nutrition Therapy 2Document32 pagesUpper Git Medical Nutrition Therapy 2KHALEEL SALEHNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument5 pagesCues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleJamie IcabandiNo ratings yet
- Imbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument3 pagesImbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementselheezaNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination:: DiarrheaDocument44 pagesBowel Elimination:: DiarrheaBashracel Marie M. SALMORINNo ratings yet
- NCP LymphomaDocument3 pagesNCP LymphomaJohn Emmanuel Tatad TudNo ratings yet
- 7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument8 pages7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru Takishima91% (23)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Thesis NewDocument55 pagesThesis NewHasan juwelNo ratings yet
- Inner Ear Balance ProblemsDocument6 pagesInner Ear Balance ProblemsaleiyoNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide for Pineapple JuiceDocument5 pagesReference Guide for Pineapple JuiceLayfloNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy Blood, Micro-OrganismDocument4 pagesPhlebotomy Blood, Micro-Organismapi-372107867% (3)
- Sample Format PDFDocument5 pagesSample Format PDFRhod R. AvisoNo ratings yet
- Gulliver's Travels Misogyny or MisanthropyDocument3 pagesGulliver's Travels Misogyny or MisanthropyKingshuk MondalNo ratings yet
- 4.6.6 Lab View Wired and Wireless Nic InformationDocument4 pages4.6.6 Lab View Wired and Wireless Nic InformationThắng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviDocument148 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University BelagavichetanbvNo ratings yet
- Optimize Your Portfolio With Modern TheoriesDocument65 pagesOptimize Your Portfolio With Modern Theoriesastro9jyotish9asim9mNo ratings yet
- SAP Untangled: An Introductory Guide To SAP For New HomesDocument28 pagesSAP Untangled: An Introductory Guide To SAP For New HomestempuserNo ratings yet
- VR 2200 CatalogueDocument4 pagesVR 2200 Catalogueh.torabyNo ratings yet
- Key concepts in biology examDocument19 pagesKey concepts in biology examAditya RaiNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: Thermal Activity and Fluid MotionDocument14 pagesHeat Exchangers: Thermal Activity and Fluid Motionishu vohraNo ratings yet
- WHIRLPOOL AWE 2214 User ManualDocument19 pagesWHIRLPOOL AWE 2214 User ManualSilvestru NemorovNo ratings yet
- MR - Abhishek JiDocument4 pagesMR - Abhishek Jimalikgaurav01No ratings yet
- Analyzing Visual TextsDocument4 pagesAnalyzing Visual Textsapi-582845240No ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Kelsen's Pure Theory of LawDocument20 pagesSubmitted By:: Kelsen's Pure Theory of Lawjyoti chouhanNo ratings yet
- SYKES Home Equipment Agreement UpdatedDocument3 pagesSYKES Home Equipment Agreement UpdatedFritz PrejeanNo ratings yet
- Text Book Development 1Document24 pagesText Book Development 1Iqra MunirNo ratings yet
- Impact of Aadhaar On Different Sectors of SocietyDocument5 pagesImpact of Aadhaar On Different Sectors of SocietyPunyak SatishNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Layout and SpecificationsDocument1 pagePlumbing Layout and SpecificationsLiza P. PaculanangNo ratings yet
- Essay #01 (First Draft)Document2 pagesEssay #01 (First Draft)thanhtam3819No ratings yet
- ADJECTIVES ENDING IN Ing and EdDocument1 pageADJECTIVES ENDING IN Ing and EdRafael FloresNo ratings yet
- Ford Taurus Service Manual - Disassembly and Assembly - Automatic Transaxle-Transmission - 6F35 - Automatic Transmission - PowertrainDocument62 pagesFord Taurus Service Manual - Disassembly and Assembly - Automatic Transaxle-Transmission - 6F35 - Automatic Transmission - Powertraininfocarsservice.deNo ratings yet
- Hussam Al-Furqan Ala Mann Haajj Al-Qur'anDocument34 pagesHussam Al-Furqan Ala Mann Haajj Al-Qur'anNoori al-Qadiri0% (1)
- The Neyveli Lignite Deposits (Cauvery Basin), India: Organic Composition, Age and Depositional PatternDocument53 pagesThe Neyveli Lignite Deposits (Cauvery Basin), India: Organic Composition, Age and Depositional PatternAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- Turning Frequency in Adult Bedridden Patients To Prevent Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcer: A Scoping ReviewDocument12 pagesTurning Frequency in Adult Bedridden Patients To Prevent Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcer: A Scoping ReviewfajaqaNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument6 pagesFuture TenseMuhammad Ibnu LaksonoNo ratings yet
- Filipino Catholic Wedding Ceremony LiturgyDocument8 pagesFilipino Catholic Wedding Ceremony LiturgyHoney Joy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SyllabusDocument23 pagesGrade 9 SyllabusClopzNo ratings yet