Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sources of Finance Table Dominic Clark
Uploaded by
api-2851969940 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
152 views4 pagesOriginal Title
sources of finance table dominic clark
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
152 views4 pagesSources of Finance Table Dominic Clark
Uploaded by
api-285196994Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
BTEC Business Studies
Assignment 3- Finance & Budgeting
P4- Sources of Finance
Name Dominic Clark
Introduction: In this piece of work I have provided accounting advice on the set up of my friends new
hairdressing business as a result of taking an accounting course to strengthen my employability skills.
I have described the various sources of potential finances from institutions, which include loans and
grants, as well as looking at government and personal sources of finance. I have then looked into
identifying how these finances are accessed.
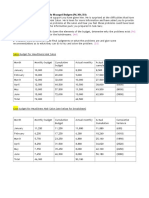
Long Term
Medium Term
Short Term
Finances the whole business
over many years
Finances major projects or
assets over a long-life
Finances day to day trading
of a business
Debentures - This works very much like shares in a
business. Investors purchase debenture certificates
from the business, and can be resold to other
investors (should the first investor need immediate
funds). The company provides each of their
debenture investors with an interest year-on-year
for a specific timeframe. Businesses must be
incorporated to use this form of finance.
Hire Purchase - This is basically a credit method for
a business to not pay for a product/service
immediately, they are entitled to pay this back over
a given timeframe. This is beneficial as the company
would not have to pay for the product/service
upfront in a large amount, but rather in small chunks
over some time.
Bank Overdraft - This is when a companys funds are in a
negative balance. A bank will allocate a maximum amount
of negative balance for firms. This is useful for short term
financing as companies can withdraw excess funds (more
than there is in the account).
Long-Term Bank Loan - This is a loan that is funded
by a bank which must be paid pack with interest
remittences. These interest rates may be fixed or
have the possibility of varying year-on-year. This
would be the result of governments raising the base
rate. Payments must be paid regularly as specified
by the lending firm.
Leasing - This is a method where a company are entitled to
use a product or service by paying regular rental
remittence. This entitles companies to utilise products and
services for a cheaper price. This is usually specified on an
official contract set over a period of time. When the
contract comes to an end, so does the lease, and the
company may use more updated goods on a new contract
that they may start.
Debt Factoring - When some companies sell good/services,
they can sometimes sell it on credit. These companies have
official records of the balance owed to them by their
debtors. For a company to seek immediate finance, they
can sell their Debtors Book to another firm at a lower price
than the actual value to raise capital.
Venture Capital - These are firms which a specially set up to invest
in companies looking for funds, which banks do not agree to finance
due to risky measures. As a result of financing these businesses,
venture capitalists take an equity of the company, if they believe
the return would be satisfactory. These could also be Business
Angels who are wealthy investors looking for opportunities to put
their money into, to gain equity in potentially successful businesses.
An example of this is seen on the UK television show Dragons Den.
Medium-term Bank Loans - This is basically a bank
loan that is paid back within a shorter term. This
means that the company must pay back their loans
faster, and should they not be able to, they may be
liable to legal consequences.
Trade Credit - Some goods and services are sold to
businesses using credit transactions. These transactions
have a timeframe in which the payment has to be made,
which could be a few weeks or even up to a month. What
this means is that the business purchasing the goods can
actually resell the product or use the product to generate
business before paying for the product/service.
Government Aid - Occasionally governments will
issue aid in regards to finances to companies. Such
funds may be sourced from governments at different
levels (i.e local or central). This is mainly popular
amongst firms looking to start up or expand in weak
economical locations.
Building Societies - These offer funds to businesses in the of
loans, business accounts, commercial mortgages or
overdraft. This is dependant on the business plan of the
business. Building societies will base the decision to invest,
as well as the interest rate, based on how risky the
business is.
Friends and Family - Investments and financial boosts from
close individuals can be the easiest form of obtaining
finances for a start-up business. This can be either paid
back as a loan, or the business director may issue shares to
these individuals.
Equity - When limited companies are established
equity would be the primary origin of finances for
that respective firm. Shares would be distributed,
and in return shareholders would provide
investments to make payments for the business start
up. The maximum capital being put into the business
must be stated in the memorandum of association
document (a legal corporation document).
Hairdressing Business Finances
The best sources of finance for starting up a hairdressing business would be for Paul to
source his hairdressing supplies form suppliers that allow him to make purchases on trade
credit, where he can begin to generate income before paying back the costs for his supplies.
He should seek funds from close friends/family to allow him to minimise loans and interest
rates. Finally, he should attempt to obtain a high overdraft maximum to allow Paul to pay
for goods/services without having the funds in his bank account if he needs to.
For paul to keep his hairdressing equipment updated regularly, without making large
payments, he should utilise hire purchases to not have to purchase equipment, but at the
same time using the best tools for the business. Regarding his establishment, it may be best
for him to rent commercial property in apposed to purchasing it, if he wishes to expand in
the future. Should Paul wish to open his hairdressing salon in a less developed location, he
may want to seek financial aid from building societies and the government. Utilising a
medium-term loan is very risky, and given the hairdressing market is so broad, I would not
recommend it.
For the expansion of Pauls salon, he should approach venture capitalists only if he has a
very unique product that would appeal to such organisations. If not, the best options for his
business would be to sell debentures or to give out equity for immediate funds. If he is
looking to expand without giving out parts of his business, the most viable option would be
to take out a long term loan for expansion.
Examine Two External Sources of Finance
that Kellett School could have used to
Finance its Capital Expenditure
Equity - This method is for Kellett school to seek investors to help with the
development and capital expenditure of the business. This would mean
giving away shares in return for finances from investors for capital
expenditure such as facilities developments. Providing equity is a source of
finance that benefits the school in the sense that they will not have to make
any loan payments or provide any interest fees. This will allow the school to
access immediate funds for capital expenditure purposes. However, giving
out equity means that less profit can be made in the future due to
distributing shares and equity of the business. This leaves less a potentially
lower budget for future capital expenditure due to smaller profit share.
Long Term Bank Loan - This method is for the management of Kellett school
to approach banks in hopes of obtaining a bank loan to pay back over a long
period of time. This means the school can receive funds and attend to the
necessary school developments through utilising the funds obtained from the
bank. This also means that the school do not need to give away any shares,
and as a result, any future profits. However this could be risky for the
school. As interest remittences could vary year-on-year, long term loans
could cost them a large sum of money year-on-year.
4
You might also like
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9api-338827544No ratings yet
- Sources of FinanceDocument3 pagesSources of Financealok19886No ratings yet
- Sources of Business Finance (Raising Capital For Enterprise)Document17 pagesSources of Business Finance (Raising Capital For Enterprise)Abiola NerdNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance DefinitionDocument6 pagesSources of Finance Definitionpallavi4846100% (1)
- BT IndvidualDocument19 pagesBT IndvidualDesmondNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance for BusinessesDocument17 pagesSources of Finance for Businessesgaurav_johnNo ratings yet
- Reference Reading 4.3Document3 pagesReference Reading 4.3Deepak MahatoNo ratings yet
- Chandan Project PDFDocument95 pagesChandan Project PDFChandan Kumar NNo ratings yet
- Final Case Study FM 108Document6 pagesFinal Case Study FM 108Jeff Beloso BasNo ratings yet
- finance internalDocument4 pagesfinance internalanupam.chatterjee23-25No ratings yet
- Definition of Business FinanceDocument4 pagesDefinition of Business FinanceClovisNo ratings yet
- MSMEDocument3 pagesMSMELrajNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument6 pagesProject ManagementEmuyeNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance and Decision MakingDocument34 pagesSources of Finance and Decision MakingWaleed Ahmad100% (1)
- Financing Business Activity: Why Does A New Business Need Finance?Document15 pagesFinancing Business Activity: Why Does A New Business Need Finance?syedanwarahmed5870No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Sources of FinanceDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Sources of Financeapi-302252730No ratings yet
- Business Finance TADocument9 pagesBusiness Finance TAOlivier MNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Business Finance: How Much Do You Need?Document4 pagesAn Introduction To Business Finance: How Much Do You Need?Wazeem AkramNo ratings yet
- Financing and Managing New VenturesDocument64 pagesFinancing and Managing New VenturesSenthil JS0% (1)
- Sources of Finance ChapterDocument4 pagesSources of Finance ChapterlojainNo ratings yet
- What Is Financing?: The Account. Bank Overdraft Is Made For Convenience in Order To PurchaseDocument3 pagesWhat Is Financing?: The Account. Bank Overdraft Is Made For Convenience in Order To PurchaseKim GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Funds LPSDocument57 pagesArrangement of Funds LPSRohan SinglaNo ratings yet
- UPPERSIXTH ENTREPRENEURSnotesDocument7 pagesUPPERSIXTH ENTREPRENEURSnotestawungalemsNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow and Credit and Background InvestigationDocument5 pagesCash Flow and Credit and Background Investigationjan francis marianoNo ratings yet
- Finance - Html#Ixzz3Su1Owgre Attribution Non-Commercial Share AlikeDocument11 pagesFinance - Html#Ixzz3Su1Owgre Attribution Non-Commercial Share AlikeDeeNo ratings yet
- Finmarket Lecture 5Document13 pagesFinmarket Lecture 5Rosie PosieNo ratings yet
- WC Sources Indicator LiquidityDocument17 pagesWC Sources Indicator LiquidityManas Pratim KachariNo ratings yet
- Short-term Financing Options ExplainedDocument18 pagesShort-term Financing Options Explainedsony4love100% (1)
- Financing Financial Resources and DecisionsDocument8 pagesFinancing Financial Resources and DecisionsmakkahihiaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Sources and Uses of FundsDocument46 pagesModule 8 - Sources and Uses of FundsKrista SuyatNo ratings yet
- T6 LendingDocument7 pagesT6 Lendingkhongst-wb22No ratings yet
- Financing The VentureDocument34 pagesFinancing The VentureYecyec, John Paul D.No ratings yet
- Equity Financing Small Business AdministrationDocument8 pagesEquity Financing Small Business AdministrationrajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-8 - Sources of Finance & Short Term FinanceDocument8 pagesChapter 6-8 - Sources of Finance & Short Term FinanceTAN YUN YUNNo ratings yet
- Where Businesses Get FundsDocument14 pagesWhere Businesses Get FundsJohn Paul GonzalesNo ratings yet
- E8 Business FinanceDocument8 pagesE8 Business FinanceTENGKU ANIS TENGKU YUSMANo ratings yet
- Choosing the Right Source of Capital for Your BusinessDocument17 pagesChoosing the Right Source of Capital for Your Businessrachanase70% (1)
- Working Capital Loan: LoansDocument5 pagesWorking Capital Loan: LoansNiharika SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHP 3.1 Sources of FinanceDocument35 pagesCHP 3.1 Sources of FinanceDana MneimneNo ratings yet
- Raising of FundsDocument5 pagesRaising of FundsSarabjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 5Document5 pagesAssignment No 5Hajra ZANo ratings yet
- A. Discuss The Advantages of Financing Capital Expenditures With DebtDocument5 pagesA. Discuss The Advantages of Financing Capital Expenditures With DebtMark SantosNo ratings yet
- Sources and Types of Short and Long Term Business FinancingDocument23 pagesSources and Types of Short and Long Term Business FinancingNishant TutejaNo ratings yet
- NOE-071 Session 2.5 Types and Sources of Financing For Start-Up BusinessesDocument5 pagesNOE-071 Session 2.5 Types and Sources of Financing For Start-Up BusinessesYogesh Kumar GaurNo ratings yet
- Sources - of - Finance - Choices 2Document5 pagesSources - of - Finance - Choices 2Svetka BNo ratings yet
- Diversify and Thrive: 10 Ideas for Multiple Sources of IncomeFrom EverandDiversify and Thrive: 10 Ideas for Multiple Sources of IncomeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Innovation & Entrepreneurship KMBN302Document21 pagesUnit 3 Innovation & Entrepreneurship KMBN302Prerna JhaNo ratings yet
- Asses The Various Methods Through Which Organization Access Funding and When To Use Different Types of FundingDocument11 pagesAsses The Various Methods Through Which Organization Access Funding and When To Use Different Types of FundingAhmad Sheikh100% (1)
- MBA 832 Chapter 3Document36 pagesMBA 832 Chapter 3shammahmuzNo ratings yet
- MODULE-7Document3 pagesMODULE-7Esier Davies Paul MalabadNo ratings yet
- A - Internal Sources: I. Various Sources of Finance Available To Phat DucDocument12 pagesA - Internal Sources: I. Various Sources of Finance Available To Phat DucnothingtosayNo ratings yet
- Source Finance 2Document17 pagesSource Finance 2Mani KandanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Criteria 1-1 Sources of FinanceDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Criteria 1-1 Sources of FinanceRyk Ramos100% (1)
- Week 5 AssignmentDocument2 pagesWeek 5 AssignmentEliza FrancisNo ratings yet
- Business Paper 2 PrepDocument30 pagesBusiness Paper 2 Prepzzw46318No ratings yet
- Financing Business Activity: Sources and Factors in Choosing FinanceDocument6 pagesFinancing Business Activity: Sources and Factors in Choosing FinanceRuvarasheNo ratings yet
- p8 Comparison Grid New Haven Firefighter ThiefDocument3 pagesp8 Comparison Grid New Haven Firefighter Thiefapi-285196994No ratings yet
- BreakevenDocument1 pageBreakevenapi-285196994No ratings yet
- p8 Comparison Grid Nhs 111Document3 pagesp8 Comparison Grid Nhs 111api-285196994No ratings yet
- StatutoryDocument2 pagesStatutoryapi-285196994No ratings yet
- Case FileDocument12 pagesCase Fileapi-285196994No ratings yet
- Task Three Consequences of Poorly Managed BudgetsDocument4 pagesTask Three Consequences of Poorly Managed Budgetsapi-285196994No ratings yet
- p8 Comparison Grid - San Antonio ArticleDocument4 pagesp8 Comparison Grid - San Antonio Articleapi-285196994No ratings yet
- Meaning of Citizenship and DiversityDocument12 pagesMeaning of Citizenship and Diversityapi-285196994100% (1)
- Diversity in The Public Services and How They Offer Equality of Service 2Document8 pagesDiversity in The Public Services and How They Offer Equality of Service 2api-285196994No ratings yet
- Government PoliciesDocument6 pagesGovernment Policiesapi-285196994No ratings yet
- Breakeven Chart Dominic Clark - Sheet1Document4 pagesBreakeven Chart Dominic Clark - Sheet1api-285196994No ratings yet
- Career Development PlanDocument20 pagesCareer Development Planapi-285196994No ratings yet
- The Business and Economic EnvironmentDocument11 pagesThe Business and Economic Environmentapi-285196994No ratings yet
- Transferable Skills AuditDocument22 pagesTransferable Skills Auditapi-285196994No ratings yet
- CPDDocument3 pagesCPDapi-285196994No ratings yet
- 2 - Self Assessed Skills AuditDocument4 pages2 - Self Assessed Skills Auditapi-285196994No ratings yet
- 101 Common Indicators of Errors: PurchasingDocument5 pages101 Common Indicators of Errors: PurchasingrasmaheeNo ratings yet
- Sage Payroll CSV TemplatesDocument50 pagesSage Payroll CSV TemplatesJosh Moore33% (3)
- IDBI Bank Project: Analysis of Products, Services, Financials and Customer SatisfactionDocument49 pagesIDBI Bank Project: Analysis of Products, Services, Financials and Customer Satisfactionshweta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Business Financial Plan Competition 2013-2014 Monta Vista High School Chapter #6477 Cupertino, California Maya Kapur & Anna TedijantoDocument16 pagesBusiness Financial Plan Competition 2013-2014 Monta Vista High School Chapter #6477 Cupertino, California Maya Kapur & Anna Tedijantoapi-285015810No ratings yet
- Environment Market Grade 9Document26 pagesEnvironment Market Grade 9Antonio Jarligo CompraNo ratings yet
- 1829618-SAP NoteDocument1,463 pages1829618-SAP NoteRyan PittsNo ratings yet
- Top 15 Questions From SCORE To Be An EntrepreneurDocument6 pagesTop 15 Questions From SCORE To Be An EntrepreneurRahmad Agus KotoNo ratings yet
- Bikila ResearchDocument57 pagesBikila ResearchBobasa S AhmedNo ratings yet
- Rural Bank of Bonbon v. Ca2Document9 pagesRural Bank of Bonbon v. Ca2Jennilyn TugelidaNo ratings yet
- Salary Slip (20267635 July, 2019)Document1 pageSalary Slip (20267635 July, 2019)anon_123683840No ratings yet
- BankingDocument377 pagesBankingUzma Shafi100% (3)
- The Stabdford Bank GameDocument101 pagesThe Stabdford Bank Gamekonstantinos10No ratings yet
- Market RiskPractice QuestionDocument99 pagesMarket RiskPractice QuestionRajivManochaNo ratings yet
- AS.567 of 2022 PDFDocument28 pagesAS.567 of 2022 PDFMani ManikandanvNo ratings yet
- Education Act of 1982 Annotated I - General ProvisionsDocument25 pagesEducation Act of 1982 Annotated I - General ProvisionsJimson GastaNo ratings yet
- Inflection Point: Unlocking Growth in The Era of Farmer FinanceDocument11 pagesInflection Point: Unlocking Growth in The Era of Farmer FinancevenucoldNo ratings yet
- Sources and Uses of Short-Term and Long-Term Funds: LessonDocument8 pagesSources and Uses of Short-Term and Long-Term Funds: LessonI am MystineNo ratings yet
- Borrower-In-Custody Program GuidelinesDocument16 pagesBorrower-In-Custody Program GuidelinesMichael FociaNo ratings yet
- Prospectus - L&T BondsDocument163 pagesProspectus - L&T Bondsajay_ghuwalewalaNo ratings yet
- Credit - Cuyco vs. CuycoDocument1 pageCredit - Cuyco vs. CuycoisangbedistaNo ratings yet
- DEMEKECH Proposal PADMDocument19 pagesDEMEKECH Proposal PADMAbdi AdanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CreditDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Creditapi-254111572No ratings yet
- Islamic Modes of Financing: Mudarabah, Shirkah and Secondary ModesDocument26 pagesIslamic Modes of Financing: Mudarabah, Shirkah and Secondary ModesUmair Ahmed UmiNo ratings yet
- Aptransco Aped Manual IIDocument315 pagesAptransco Aped Manual IISrikar Varma100% (2)
- Eligibility Criteria & Requirements For Personal LoanDocument22 pagesEligibility Criteria & Requirements For Personal LoanRitu RajNo ratings yet
- CA-Inter Advanced Accounting VOL.3Document156 pagesCA-Inter Advanced Accounting VOL.3salaarbhai2322No ratings yet
- General Mathematics Quarter 2-Module 2: Week 6 - Week 9: Department of Education - Republic of The PhilippinesDocument34 pagesGeneral Mathematics Quarter 2-Module 2: Week 6 - Week 9: Department of Education - Republic of The PhilippinesElaiza GaytaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae.: Personal DetailsDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae.: Personal Detailsneocollo100% (1)
- Commerce (Regular) Accounting For Specialised Institutions (Group A: Accounting and Finance) Paper - 3.5 (A)Document4 pagesCommerce (Regular) Accounting For Specialised Institutions (Group A: Accounting and Finance) Paper - 3.5 (A)Sanaullah M SultanpurNo ratings yet
- SCS May22 - Aug22 Mock Exam 5 PDF AnswersDocument13 pagesSCS May22 - Aug22 Mock Exam 5 PDF AnswersSanjay MehrotraNo ratings yet