Professional Documents
Culture Documents
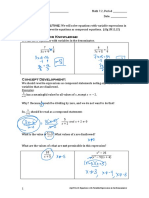
g8m7 Study Guide Key Irrational Numbers
Uploaded by
api-276774049Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
g8m7 Study Guide Key Irrational Numbers
Uploaded by
api-276774049Copyright:
Available Formats
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
Square Roots and Cube Roots
Positive Square Roots
A positive number whose square is equal to a positive number b is denoted by the
symbol . The symbol is automatically denotes a positive number. The number
is called the positive square root of b.
Cube Roots: The cube root of a number, x, is the number, y which satisfy the
!
equation = ! . The notation we use is as follows: =
!
Example: 8 = 2! and 8 = 2
Simplifying Square Roots
You can simplify square roots by rewriting the radicand (number inside the radical
symbol) as a product containing perfect squares (such as 4, 9, 16, 25, etc). The
square root of perfect squares are integers.
Example: 48 = 16 3 = 4 3
Solving Equations with Square and Cube Roots
We can simplify the expressions until we have the form of ! = ! = and
then take the square root or cube root of both sides of the equation to solve for x.
Example:
3 ! = 48
(divide by 3)
! = 16
(take square root of each side) = 4
For more refreshers, go to www.khanacademy.com. Work on the following
exercises and watch associated videos:
Square roots of perfect squares
Cube roots
Simplifying square roots
Simplifying square roots 2
Cube roots 2
Estimating Square Roots
For more information, check out Lessons 67-71 on
http://mrrogove.weebly.com
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Rational and Irrational Numbers
!
Rational
Numbers:
Any
number
that
can
be
expressed
as
a
fraction
!
where
p
and
q
are
both
integers
and
0.
!
!!!
Example:
41.13, ! , !"# , 64. 9
Finite
Decimals:
A
subset
of
rational
numbers
which
have
terminating
decimals.
Written
as
fractions,
the
denominators
are
products
of
only
2s
and
5s.
!
Example:
!" , 1.05, 4.253
Repeating
Decimals:
A
subset
of
rational
numbers
that
have
infinite
decimals
that
repeat.
Written
as
fractions,
the
denominators
are
products
of
numbers
other
than
2
and
5.
!
!"
Example:
! , !" , 0.4545454545 .
Irrational
Numbers:
The
set
of
numbers
that
have
infinite
decimals
that
DO
NOT
repeat.
!
Example:
, , 8, 25
For more refreshers, go to www.khanacademy.com. Work on the following
exercises and watch associated videos:
Converting fractions to
decimals
Approximating irrational
Recognizing rational and
irrational exercises
Comparing rational numbers
numbers
For more information, check out Lessons 72-74 on
http://mrrogove.weebly.com
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean
theorem
is
+ =
We
can
prove
this
using
squares,
similar
triangles,
and
area.
Refer
to
lesson
75
for
specific
information
on
the
proofs.
Distance
on
a
coordinate
plane:
We
can
use
the
Pythagorean
Theorem
to
find
the
distance
of
diagonals
on
a
coordinate
plane.
Formula:
= ! ! ! + ! ! !
For more refreshers, go to www.khanacademy.com. Work on the following
exercises and watch associated videos:
Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean Theorem Proofs
Distance Formula
Pythagorean Theorem word
problems
For more information, check out Lessons 75-78 on
http://mrrogove.weebly.com
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
PROBLEM SET
I
strongly
suggest
you
solve
these
problems
by
hand.
You
will
NOT
be
allowed
to
use
a
calculator
on
the
assessment.
In
order
to
get
ANY
credit,
you
MUST
SHOW
YOUR
WORK!!!
Please
initial
here
to
indicate
that
you
read
this
paragraph.
__________
Simplify:
128
Simplify:
576
24
8 2
Simplify:
3 80
Simplify:
512
12 5
16 2
!
!
Simplify:
729
Simplify:
1024
!
9
8 2
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Solve
for
x.
2 ! 12 = 6(2 ! 9)
= 3
Solve
for
x.
2 !
!
!
+ 2 = 4
+ 216
!
2
= 6
Convert
to
a
decimal.
Classify
as
a
repeating
or
finite
decimal.
7
12
0.583
repeating
Solve
for
x.
3 ! 4 + 13 = 2 2 + 29
= 4
Solve
for
x.
3
= 1
1
=
9
Convert to a decimal. Classify as a
repeating or finite decimal.
42
48
0.875
finite
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Convert to a decimal. Classify as a
repeating or finite decimal.
13
15
0.86
Repeating
Convert to a fraction.
0. 72
8
11
Convert to a fraction.
0. 234
26
111
Convert to a decimal. Classify as a
repeating or finite decimal.
13
125
0.104
Finite
Convert
to
a
fraction.
0.072
13
180
Convert
to
a
fraction.
4.12
371
11
4
90
90
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Approximate to the nearest hundredth
80
8.94
Approximate to the nearest hundredth
20
4.47
Which is greater: 21 4.4?
21 > 4.4
Approximate to the nearest hundredth
90
9.49
Approximate to the nearest hundredth
30
5.48
Which is greater: 47 6.8
47 > 6.8
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
NAME:___________________________
Math 7.2, Period ____________
Mr. Rogove
Date:__________
Label these numbers on a number line in their approximate place.
10
!
29 , 9 , , 3. 2 , 13
3
10
!
9,
29 ,
3. 2,
,
13
3
all between 3 and 4.
Prove the Pythagorean Theorem for a triangle that has sides of 12, 16, and 20 using
the similar triangles proof.
In order to prove the Pythagorean theorem using similar triangles, draw a right
triangle with legs of 12 and 16 and a hypotenuse of 20. Then make a line from the
right angle perpendicular to the hypotenuse. From this create three triangles that
are similar (because of AA similarity). Create proportions based on corresponding
sides of similar triangles and use this fact to prove that ! + ! = ! .
Find the distance between (1, 2) and
Find the distance between (6, 10) and
(8, 6) on the coordinate plane
(15, 2) on the coordinate plane
15
65
Irrational Numbers Study Guide
You might also like
- Assignment 3 Algebra PDFDocument74 pagesAssignment 3 Algebra PDFAmi NewtonNo ratings yet
- 2 NdfinalDocument11 pages2 NdfinalDhanetth Kim ReyesNo ratings yet
- Learn Square Roots & Plot on Number LineDocument11 pagesLearn Square Roots & Plot on Number LineADAM CRISOLOGONo ratings yet
- End-of-the-Year Test Grade 4Document17 pagesEnd-of-the-Year Test Grade 4Jorge KrjdNo ratings yet
- Mathmatics Year - 6 PDFDocument91 pagesMathmatics Year - 6 PDFK M Zahidul Islam80% (5)
- Century Learner, Alen L. Tuliao., Et - Al.2020, Mathematics Learner'S Material, Deped 2013, Elizabeth R. Aseron, Et - AlDocument5 pagesCentury Learner, Alen L. Tuliao., Et - Al.2020, Mathematics Learner'S Material, Deped 2013, Elizabeth R. Aseron, Et - AlReyboy TagsipNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PI - FinalDocument13 pagesMathematics PI - FinalThoko SimbeyeNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Math Daily Warm UpsDocument73 pages5th Grade Math Daily Warm UpsEva WangNo ratings yet
- Equations Expressions HomeworkDocument25 pagesEquations Expressions HomeworkHakim Yahiaoui100% (1)
- Final Mathematics Paper II Neno District MockDocument16 pagesFinal Mathematics Paper II Neno District MockThoko SimbeyeNo ratings yet
- Math 4 LAS 2 RTPDocument4 pagesMath 4 LAS 2 RTPJonalvin KENo ratings yet
- 2017 Metrobank - MTAP - DepeEd Math ChallengeDocument2 pages2017 Metrobank - MTAP - DepeEd Math ChallengeBERNADETTENo ratings yet
- III Do As Directed III ModifiedDocument23 pagesIII Do As Directed III Modifiedshailesh2984No ratings yet
- Number TheoryDocument52 pagesNumber TheoryshazarafiaNo ratings yet
- End of Year Test Grade4Document17 pagesEnd of Year Test Grade4Mónica Illanes RodríguezNo ratings yet
- MMW Ch3 Problem Solving and Reasoning 2Document54 pagesMMW Ch3 Problem Solving and Reasoning 2Maxene Jane AngalaNo ratings yet
- Saint James Academy Mathematics 7 TestDocument2 pagesSaint James Academy Mathematics 7 TestMeace Javier Gallinero DrilonNo ratings yet
- Summer8math Package PDFDocument34 pagesSummer8math Package PDFAnonymous EmjOwXNo ratings yet
- Secondary 1 Maths TestDocument9 pagesSecondary 1 Maths TestAMKONo ratings yet
- Secondary 2 Normal (A) Mathematics Test 5 Simultaneous Linear Equations 1 HourDocument7 pagesSecondary 2 Normal (A) Mathematics Test 5 Simultaneous Linear Equations 1 HourHira Hassan100% (1)
- Unit 1 Numbers 1ws Grade 5Document3 pagesUnit 1 Numbers 1ws Grade 5Jeya Surya VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 4 Worksheet For 2nd Mid TermDocument6 pagesMath Grade 4 Worksheet For 2nd Mid Termobakhit91No ratings yet
- 7thgrademath Unit2Document25 pages7thgrademath Unit2RINALYN CANITESNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 Mathematics TestDocument32 pagesGrade 2 Mathematics TestLucille Gacutan Aramburo67% (3)
- mms9 Workbook 03 Unit3Document48 pagesmms9 Workbook 03 Unit3api-265180883100% (2)
- Math7 q1 Week 6 EnhancedDocument11 pagesMath7 q1 Week 6 EnhancedADAM CRISOLOGONo ratings yet
- Math7 Q1 Week 6 EnhancedDocument11 pagesMath7 Q1 Week 6 EnhancedADAM CRISOLOGONo ratings yet
- Use The Diagram Below When Answering Question #S 1-6. AssumeDocument6 pagesUse The Diagram Below When Answering Question #S 1-6. Assumeapi-544979663No ratings yet
- 7 TH Grade Math Final Study Guide EquatiDocument7 pages7 TH Grade Math Final Study Guide EquatiAbhay MohunramNo ratings yet
- 2$20 ReasoningDocument28 pages2$20 ReasoningShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Study Guide and Intervention Workbook Course 2 EditionDocument92 pagesStudy Guide and Intervention Workbook Course 2 Editionapi-261894355100% (1)
- Tabaco National High School students learn set operations and integersDocument2 pagesTabaco National High School students learn set operations and integersMaisieNo ratings yet
- g5 Math p1 End Term 1 2023-2024Document9 pagesg5 Math p1 End Term 1 2023-2024TWAKIIRE AbiusNo ratings yet
- Day 5: New Equations, New Numbers: Important StuffDocument5 pagesDay 5: New Equations, New Numbers: Important Stuffjoe_ochiltreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Notes Algebra 2Document26 pagesChapter 3 Notes Algebra 2sesirekha@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Operation SenseDocument10 pagesCH 2 Operation SenseFady NagyNo ratings yet
- $R12SETIDocument28 pages$R12SETIbirrajNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Math3 q1 Module 5a&5bDocument2 pagesSummative Test in Math3 q1 Module 5a&5bAlma MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4api-306720213No ratings yet
- Mathematics For Grade 3 TeachersDocument15 pagesMathematics For Grade 3 Teachersnecro threadNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet1 - g5 With Answer KeyDocument9 pagesRevision Worksheet1 - g5 With Answer KeySarahNo ratings yet
- Prime Composite Square and Triangular Numbers WorkbookDocument9 pagesPrime Composite Square and Triangular Numbers Workbookrithanya.nagaraj.rnNo ratings yet
- G5 Math P1 End Term 1 2023-2024Document9 pagesG5 Math P1 End Term 1 2023-2024TWAKIIRE AbiusNo ratings yet
- IB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter4Document52 pagesIB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter4aa1cc2100% (4)
- E VR E: Question BankDocument9 pagesE VR E: Question BankAKSHARA MIRYALANo ratings yet
- PermutationDocument17 pagesPermutationPranav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-18 at 8.41.36 PMDocument19 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-18 at 8.41.36 PMdina.timo4ever.isaNo ratings yet
- Heep203 PDFDocument32 pagesHeep203 PDFAjiteshPaddaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Exponential and Linear FunctionsDocument8 pagesStudy Guide Exponential and Linear Functionsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Packet 2 NotesDocument25 pagesPacket 2 NotesNightwing10No ratings yet
- Magdalen College School 9 Plus Maths Practice PaperDocument9 pagesMagdalen College School 9 Plus Maths Practice PaperSheena YuNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Summative & Performance Test Q3Document9 pagesMath 6 Summative & Performance Test Q3Cherry Ocampo SalesNo ratings yet
- 02a Algebraic Proof - H - Question PaperDocument1 page02a Algebraic Proof - H - Question PaperWalid GadallaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Plan Week 1 and 2Document14 pagesGrade 7 Plan Week 1 and 2Saleha ShoaibNo ratings yet
- SMK DATO’ SRI AMAR DIRAJA MATHEMATICS SUBJECT FORMDocument8 pagesSMK DATO’ SRI AMAR DIRAJA MATHEMATICS SUBJECT FORMzarina binti jusohNo ratings yet
- Math - Ratio and ProportionDocument41 pagesMath - Ratio and ProportionninigraceNo ratings yet
- Maths Revision Test STD 5Document17 pagesMaths Revision Test STD 5rachymuponda71No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 5 Maths Revision WorksheetsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 5 Maths Revision WorksheetspraspravinNo ratings yet
- Brain Benders, Grades 3 - 5: Challenging Puzzles and Games for Math and Language ArtsFrom EverandBrain Benders, Grades 3 - 5: Challenging Puzzles and Games for Math and Language ArtsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Alg1m3l7 - Patterns and FunctionsDocument5 pagesAlg1m3l7 - Patterns and Functionsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Study Guide Key Exponential and Linear FunctionsDocument10 pagesStudy Guide Key Exponential and Linear Functionsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l11 7 1 - Finding Missing Angle MeasurementsDocument5 pagesg8m2l11 7 1 - Finding Missing Angle Measurementsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l10 - Comparing Growth Rates 2Document4 pagesAlg1m3l10 - Comparing Growth Rates 2api-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l6 - Exponential Decay 2Document5 pagesAlg1m3l6 - Exponential Decay 2api-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l5 7 1 - Sequencing Reflections and Translations and RotationsDocument5 pagesg8m2l5 7 1 - Sequencing Reflections and Translations and Rotationsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l9 7 1 - Angle Sum Theorem For TrianglesDocument4 pagesg8m2l9 7 1 - Angle Sum Theorem For Trianglesapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l10 7 1 - Angle Sum Theorem and Missing Interior and Exterior AnglesDocument5 pagesg8m2l10 7 1 - Angle Sum Theorem and Missing Interior and Exterior Anglesapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l4 - Compound Interest and Simple InterestDocument5 pagesAlg1m3l4 - Compound Interest and Simple Interestapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l8 7 1 - Angle Measures of Parallel LinesDocument4 pagesg8m2l8 7 1 - Angle Measures of Parallel Linesapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l5 - The Power of Exponential GrowthDocument3 pagesAlg1m3l5 - The Power of Exponential Growthapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l7 7 1 - CongruenceDocument5 pagesg8m2l7 7 1 - Congruenceapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l2 7 1 - Graphing Reflections On The Coordinate PlaneDocument6 pagesg8m2l2 7 1 - Graphing Reflections On The Coordinate Planeapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l6 7 1 - Sequences of Rigid MotionsDocument4 pagesg8m2l6 7 1 - Sequences of Rigid Motionsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l3 - Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 2Document5 pagesAlg1m3l3 - Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 2api-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l2 - Writing Sequences With Recursive and Explicit Formulas 2Document3 pagesAlg1m3l2 - Writing Sequences With Recursive and Explicit Formulas 2api-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l4 7 1 - Sequencing TranslationsDocument5 pagesg8m2l4 7 1 - Sequencing Translationsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m1l10 - Operations With Scientific Notation 3Document4 pagesg8m1l10 - Operations With Scientific Notation 3api-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l3 7 1 - Graphing Rotations On The Coordinate PlaneDocument5 pagesg8m2l3 7 1 - Graphing Rotations On The Coordinate Planeapi-276774049No ratings yet
- g8m2l1 7 1 - Transformations and Translations On The Coordinate PlaneDocument6 pagesg8m2l1 7 1 - Transformations and Translations On The Coordinate Planeapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m3l1 - Introduction To Sequences 2Document5 pagesAlg1m3l1 - Introduction To Sequences 2api-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m1 SG Solns To Eqns and InequalitiesDocument7 pagesAlg1m1 SG Solns To Eqns and Inequalitiesapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m1l13 - Equations Involving Variable Expressions in The Denominator 2Document3 pagesAlg1m1l13 - Equations Involving Variable Expressions in The Denominator 2api-276774049No ratings yet
- Alg1m1l12 - Equations Involving Factored ExpressionsDocument4 pagesAlg1m1l12 - Equations Involving Factored Expressionsapi-276774049No ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document4 pagesQuiz 3dEEP THE hELPERNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 18 (Final)Document3 pagesLesson Plan 18 (Final)ryan agustianNo ratings yet
- Types of Nuclear Reactors GuideDocument19 pagesTypes of Nuclear Reactors GuideUgur GuvenNo ratings yet
- Brown Stock WashingDocument22 pagesBrown Stock Washingtreese2No ratings yet
- Yr 6 Maths G-6 E P-I PDFDocument168 pagesYr 6 Maths G-6 E P-I PDFdina171279No ratings yet
- Oracle Database - Introduction To SQL Ed 2Document5 pagesOracle Database - Introduction To SQL Ed 2Miguel Alfonso DIAZ MORRISNo ratings yet
- RWM61 Data SheetDocument3 pagesRWM61 Data SheetBarth XaosNo ratings yet
- Skripsi #2 Tanpa HyperlinkDocument19 pagesSkripsi #2 Tanpa HyperlinkindahNo ratings yet
- Applied Combinatorics, Second Edition by Fred S Roberts, Barry TesmanDocument889 pagesApplied Combinatorics, Second Edition by Fred S Roberts, Barry TesmanAnil kumarNo ratings yet
- RMI Verif NAFEMS 3 2 PDFDocument28 pagesRMI Verif NAFEMS 3 2 PDFFernando MartinezNo ratings yet
- Babcock University Bookshop An Babcock University BookshopDocument11 pagesBabcock University Bookshop An Babcock University BookshopAdeniyi M. AdelekeNo ratings yet
- Is It Simple To Explain Simple Experiments The Heavy Newspaper' Stick BreakDocument6 pagesIs It Simple To Explain Simple Experiments The Heavy Newspaper' Stick Break이온유No ratings yet
- GGGDocument3 pagesGGGAnkitNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument43 pagesResearch Methodologyswaroophoppy100% (3)
- OOPS using C++ Question BankDocument32 pagesOOPS using C++ Question BankPushpa Bg100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis: N N N N A A A ADocument15 pagesChapter 3 - Methods of Analysis: N N N N A A A AvampakkNo ratings yet
- CHM 556 Experiment 5Document12 pagesCHM 556 Experiment 5Amar Safwan100% (1)
- Newtons CowsDocument9 pagesNewtons CowsLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- MQTT RGB Light For HomeDocument3 pagesMQTT RGB Light For HomearevazhagunvcNo ratings yet
- To Design and Simulate Priority EncoderDocument6 pagesTo Design and Simulate Priority EncoderShubham GargNo ratings yet
- Brochure Innerynx Mechanical SealsDocument12 pagesBrochure Innerynx Mechanical SealsErivelton ScaldelaiNo ratings yet
- Install and Configure Computer SystemsDocument18 pagesInstall and Configure Computer SystemsAlbino LarozaNo ratings yet
- Seguridad Electrica 4Document28 pagesSeguridad Electrica 4salo081018No ratings yet
- Magic The Gathering - Masquerade Cycle 2 - NemesisDocument386 pagesMagic The Gathering - Masquerade Cycle 2 - Nemesisapi-3804457100% (4)
- Star and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesStar and Its PropertiesRemond BalabaNo ratings yet
- HMT Data Book-kothandaramanDocument2 pagesHMT Data Book-kothandaramanNikhil T G0% (1)
- External DC fuse board for Sunny Island battery invertersDocument2 pagesExternal DC fuse board for Sunny Island battery invertersrhadammantysNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack Script Docx PDF FreeDocument2 pagesBlockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack Script Docx PDF FreeHealing Relaxing Sleep Music100% (1)
- Prescurtari PDFDocument67 pagesPrescurtari PDFהוד אנדרוNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: in Order To Decrease Cross Sectional Area of Structural Members, Ultra High StrengthDocument16 pagesSynopsis: in Order To Decrease Cross Sectional Area of Structural Members, Ultra High StrengthHector Alberto Garcia LopezNo ratings yet