Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Bank
Uploaded by
ANKITPATEL6233Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank
Uploaded by
ANKITPATEL6233Copyright:
Available Formats
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
I.
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
Part A (Power Maintenance)
SELECT THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Turbine pumps are used up to a suction head of
( b )
a. 1000 ft.
c. 20 ft
b. 100 ft
d. 50 ft
The yard stick for provision of Electrical points in staff quarters can
( a )
be changed by the Zonal railways with the approval of
a. Railway Board
c. General Manager
b. EIG
d. CSO
Who functions as Electrical Inspector to Government of India in
( c )
Indian Railways?
a. Chief Electrical Loco Engineer c. Chief Electrical Engineer
b. Chief Electrical Services Engineer d. Chief Safety Officer
The illumination is measured in term of
( c )
a Tesla
c. Lux
b. Candela/m2
d. Gauss
The EIG draws his powers from
( c )
a. TheRailwayElectricity Act c. The Indian Railways Act
b. TheIndian Electricity Rules
d. The Electricity Act, 2003
Both the pump and motor are inside water in case of
( b )
a. Turbine pump
c. Centrifugal pump
b. Submersible pump
d. Jet pumps
To reduce Electrical energy bill, power factor should be kept
( d )
a. as less as possible
c. power factor does not affect energy bill
b. as high as possible
d. as close to unity as possible
Which type of overlap is formed at the end of every tension length:- ( b )
a.
9)
10)
11)
12)
13)
Insulated overlap
c.
either Insulated overlap or un-insulated
overlap
b. un-insulated overlap
d. none of the above.
Earth pit value resistance is measures in which type of meter
a. Insulation megger
c. Earth megger
volt
meter
b.
d. Am meter
Insulation value resistance of a cable is measures in which type of
meter
a. Clip on meter
c. Lux meter
b. Insulation megger
d. Earth megger
How many neutrals earth pits are there for one transformer in a
sub-station
a. One
c. Two
b. Three
d. Four
Minimum how many earth pits are there in a 11 KVsub-station
a. Four
c. Six
b. Eight
d. Ten
Schedule maintenance for CLS panel is done
a.
b.
Weekly
Monthly
c.
d.
Page 1 of 33
Fortnightly
Yearly
c )
( b
b )
( c
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
14)
What is the earth resistance value for residential quarters
a. 1 Ohm
c. 8 Ohms
b.
15)
16)
a. plate type
c. strip type
b. pipe type
d. none of the above
Which type fire extinguisher is used for electrical fire
c.
d.
Water
Co2 & dry powder
Foam
None of the above
WRITE DOWN THE ABBREVIATIONS:
1
Watts
KW
Kilowatts
KWH
Kilowatt Hour
KVA
Kilo Volt Amps
KVAR
Kilo Volt Ampers Reactive
H.P.
Horse Power
A.H.
Ampere Hours
P.F.
Power Factor
R.P.M.
Revolutions per minute
10
O.H.
Over Head
11
L.T.
Low Tension
12
H.T.
High Tension
13
E.H.T.
Extra High Tension
14
C/S
Cycles per second
15
A.C.
Alternating current
16
D.C.
Direct current
17
C.L.S.
Colour Light Signalling
18
A.T.
Auxillary Transformer
19
L.E.D.
Light Emitting Diode
20
E.M.F.
Electro Motive Force
Page 2 of 33
10 Ohms
What type of earthing is found in 11 KV sub-station
a.
b.
II.
d.
6 Ohms
( c
b )
( b
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
21
P.D.
Potential difference
22
M.D.B.
Main Distribution Board
23
S.D.B.
Sub-Distribution Board
24
C.B.
Circuit Breaker
25
D.B.
Distribution Board
26
M.C.B.
Miniature Circuit Breaker
27
A.C.B.
Air Circuit Breaker
28
O.C.B.
Oil Circuit Breaker
29
C.F.L.
Compact Flourocent Lamp
30
F.T.
Flourosent Lamp
31
M.H.
Metal Halide
32
S.V.
Sodium Vapour
33
I.C.
Incandecent
34
U.P.S.
Un-interuptable Power Supply
35
L.T.U.G
Low Tension Under Ground
36
P.V.C.
Poly Vinly Chloride
37
H.R.C.
High Rapturing Capacity
III.
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1)
The process of removing heat from low temperature level and rejecting at high
temperature is called. REFRIGERATION.
Any substances for change of its state at constant temperature absorbs/give up heat is
called LATENT HEAT.
The sum of sensible heat and latent heat of substance in process is called ENTHALPY.
The latent heat of fusing ice is 144 BTU/LB.
The unit of refrigeration is TON OF REFREGIRATION 12000 Btu/Hr or 3023.98
K.Cal/Hr.
The temperature measured by ordinary thermometer is called SENSIBLE HEAT.
What is the boiling point of water 100 C at Atmospheric Pressure
AT what temperature water starts freezing_ 0 C. at Atmospheric Pressure
The unit of heat is BTU OR K.CAL
RMPU means ROOF MOUNTED PACKAGE AC UNIT
The setting of HP cutout in RMPU coaches is 415 psi.
The setting of LP cutout in under slung coaches is 35 psi.
The boiling point of refrigerant R22_ -40.8 C.
The boiling point of refrigerant R12. 29.8 C.
Artificial respiration is required to the person met with electrical accident.
The rating of alternator in TL coaches is 4.5 KW.
The latent heat of evaporation IS THE HEAT REQUIRED TO CHANGE THE LIQUID INTO
VAPOUR.
Page 3 of 33
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
12)
13)
14)
15)
16)
17)
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
18)
19)
20)
21)
22)
23)
24)
25)
26)
27)
28)
29)
30)
31)
32)
33)
34)
35)
36)
37)
38)
39)
40)
41)
42)
43)
44)
45)
46)
47)
48)
49)
50)
51)
52)
53)
54)
55)
56)
57)
58)
59)
60)
61)
62)
63)
The temperature maintained in the refrigerator is LESS then 0 C.
The dry bulb and vet bulb temperatures equals then the RH is 100%
The moisture absorption in refrigeration circuit is done by DEHYDRATOR CUM FILTER.
The commonly used refrigerants are R 12 & R 22
The lubrication of system in the sealed compressors is done by FREEZOL
The 3-phase voltage unbalance in supply should not exceed 2.5. % To 5%
For maintaining power supply quality the rate of change of frequency should not exceed. 1
HZ/Sec.
The voltage of 11 KV supply is 11000V
Tender Notice is to be published for. Open tender
Copper is the good conductor of electricity.
Completion estimate is not required for calling tender.
Contingencies charges mean Transportation charges.
Detailed estimate is to be prepared for sanctioned works.
Detailed estimate needs sanction of HOD.
The fire extinguisher used for Electrical fire is CO2 and DCP
Fire is the combination of material and temperature & Oxygen.
B Type of fire extinguisher used to nullify the oil fires.
Electric type of fire is clarified as D type.
CO2 type fire extinguisher is used for electrical fires.
Ordinary fire can be extinguished by water.
RUBBER HAND GLOVES are to be used while operating isolator handle in substations.
Ordinary fire can be extinguished by WATER OR SAND.
Artificial respiration is required to the person met with ELECTRICAL accident.
What is IOD? INJURED ON DUTY
What is meant by fatal accident? THE ACCIDENT CAUSES WITH LOSS OF HUMAN LIFE
If a man touches a live wire, he gets SHOCK. /electrocuted.
CTC type extinguisher is used for ELECTRICAL fire.
If a transformer catches fire FOAM type of fire extinguisher to be used.
The fire extinguisher used for Electrical fire is CO2 TYPE.
Fire is the combination of Material, temperature and oxygen
B type of fire extinguisher used to nullify the oil fires.
Electric type of fire is clarified as D type.
CO2 type fire extinguisher is used for ELECTRICAL fires.
Soda ash type fire extinguisher is used for GENERAL fires.
CTC OR FOAM type of fire extinguishers will be used to extinguisher chemical fires.
The system voltage in TL coaches is 110 V DC supply.
Monoblock type & 120 Ah capacity of batteries are used in TL coaches.
The codal life of lead acid batteries is 04 years.
The codal life of VRLA batteries is 04 years.
The 35 SWG size of fuse wire is used for each fan or light in distribution fuse board.
The voltage setting of 4.5 KW alternator at regulator is 123 0.5 volts.
If a cell is found less than 1.7 volts, it is considered as defective.
The wattage of 400 mm DC fan in TL coach is 35 watts.
The specific gravity of sulphuric acid which is used to make as electrolyte is 1.210.
The working voltage of 20W/TL inverter is 110 volts DC.
16A HRC fuse is used for L1, L2 & fan circuit in RJB of TL coaches.
Page 4 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
67)
68)
100 VA inverter capacity is used for cell phone charger in TL coaches.
The gap between wheel edge to axle pulley edge is 145mm 3mm.
The gap between the mounting bracket to adjustment nut of tension device for 4.5 KW
alternator is 75mm.
Earth fault can be detected by using double test lamp or multi-meter.
The capacity of alternator, batteries & fans in TL coach are 4.5KW, 120Ah & 35W.
IV.
INDICATE TRUE OR FALSE TO THE FOLLOWING:
64)
65)
66)
1) MCB is used in circuits for Overload protection. True or False
Ans True
2) We can improve the earth resistance by packing common salt charcoal & water. (True or
False)
Ans True
3) Silica gel used in breathers to absorbs moisture (Ture or false) (True or False)
Ans True
4) Three phase motor is an example of balanced 3o load. (True or False)
Ans True
5) The voltage of 11 KV supply is 11000V
Ans true
6) A ceiling fan shall be hung at a height not less than 3M from the floor. (True or false)
Ans) True
7) Cells are connected in parallel to Increase the current capacity carrying (True or false)
Ans) True
8) Co2 type fire extinguisher is not used for Electrical fires. (True or false)
Ans) false
9) DCP type of fire extinguisher used for electrical fire. (True or false)
Ans True
10) What is IOD? INJURED ON DUTY (True or false)
Ans True
11) For maintaining power supply quality the rate of change of frequency should not
exceed.1HZ/Sec.(True or false)
Ans False
12) RUBBER HAND GLOVES are to be used while operating isolator handle in substations. (True or false)
Ans True
13) If a man touches a live wire, he gets SHOCK. /electrocuted. (True or false)
Ans True
14) The width of alternator pulley of 4.5 KW 110V is 140mm. (True or false)
Ans False
15) Shorting of power diode test to be conducted at full load. (True or false)
Ans True
Page 5 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
V SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1) What are the loses in Transformers, Explain?
Ans. (1) Iron loses (2) Copper loses
Iron Loss : Iron loss occurs in the transformers Iron core due to hysteresis and eddy
currents taking place. They are almost fixed irrespective of loading of transformers.
Copper Losses: Copper losses are I2 R losses in the primary and the secondary windings of
the transformer which with the loading of transformer.
2) Why a transformer requires cooling. What are the methods of cooling transformers?
Ans. Transformers requires cooling as they get heated up due to various losses taking place in the
transformer. (like iron of copper losses)
Following are the methods of cooling of transformer.
a.
Natural cooling by Air.
b. Oil Natural cooling Air natural (ONAN).
c.
Forced oil air Natural Cooling (OFAN).
d. Forced oil and forced Air cooling (OFAF).
3) What are the schedules of maintenance done on transformers?
Ans. Following are the schedules of maintenance on transformers.
a. Daily maintenance.
b. Monthly maintenance.
c. Quarterly maintenance.
d. Half yearly maintenance.
e. Yearly maintenance.
f. 5 Yearly maintenance.
4) Explan different types of pumps used in Railways?
Ans: Following are the different types of pumps used in Railways.
a. Submersible pumps.
b. Mono block submersible pumps.
c. Centrifugal pumps.
d. Jet pumps.
5) Explain how double test lamp used for testing earth?
Ans: Double test lamp having three leads. Centre lead should be connected to earth, left side lead to
be connected on positive side (+ve), right side to be connected on negative side (-ve) If both bulbs
glow dimly it indicates no earth in the coach. If left side bulb glows brightly it indicates negative
earth (-ve) in the coach. If right side bulb glows brightly it indicates positive earth (+ve) in the
coach.
6) Explain the functioning of Submersible pumps?
Ans. Submersible pump by name it works in the water immersed condition. Generally, they are
used in Bore-well. It consists of two parts, one motor and other pump. The motor is similar either a
single phase or three phase induction motor. It is specially designed as its armature is comparatively
longer and diameter is less impeller stages and made to work in water. The pump consists of
impeller and guide wanes similar to a turbine generally for more delivery of water, number of
stages are added to suit our requirement.
When supply is given the electric motor works. The water is sucked into impeller it gains
kinetic energy and goes over stages. During this, it gains kinetic energy. By casing it converts as
pressure energy. At the end, the water is delivered through delivery pipe.
7) What are the maintenance schedules of a pumping station and type of starters?
Ans. Following are maintenance schedule of the pumping installation:
Page 6 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Switch gear in every quarter and the motor & pump section every half yearly.
Starters are DOL starter, star delta starter, Auto T/F starter.
8) What are the hydraulic data required for designing a pump capacity?
Ans: Following are the hydraulic data required for designing the pump capacity
a. The depth of the Bore or well (suction height/ below ground level)
b. The delivery light.
c. The yield of the Borewell.
d. The horizontal distance of the pumping from bore well where planned to deliver.
9) What is BHP, How do you calculate the BHP of pump BHP-> Brake horse power?
Ans The following formula is used for calculating the BHP capacity of the pump.
Q H/4500 = in horse power
i.e., P = Discharge in Liters/minute
H= Head in Meters
10) What do you mean by energy conservation? why it is required and how it can be done?
Ans Energy conservation means saving of Electricity without fore going its utility.
Conservation is required in present scenario of growing demand of power, depleting of
natural resources and increase of and lack of Proportional, global worming
Conservation can be achieved by many methods some of the growing supply of power.
a.
Use of star rated equipments like AC, methods geysers, Pumps, fans etc.
b. Provision CFL/.T5 in place of IC lamps.
c.
By using non conventional sources of energy by reducing consumption of
conventional sources of energy.
d. Switching OFF of lights/Fans when not required.
e.
Use of solar water heater.
f.
Use of solar plants.
g.
Use of 70% & 30%.
h. Use of segregation timers for water wderse high mast lights pumps.
i.
Use of APFC panels
j.
Use of copper wiring inplace of Aluminum wiring.
11) What are the test and measuring instrument required in an Electrical depots?
Ans. Following are the test and measuring instruments required in an Electrical depots.
a. Test lamp
b. Line Tester
c. Continuity tester
d. Volt meter
e. Ammeter
f. Earth megger
g. Megger
h. Lux meter
i. Power analyzer
j. Infrared thermometer
12) What are the schedule maintenance to be carried out OH mains & UG Cables?
Ans. Following are the schedule to be maintained of HO mains and UG cables.
a. OH mains Every Half yearly
b. UG.Cables Every Yearly.
During those schedules, for OH, Guarding condition of insulators, sag in OH line are to be
checked for UG cables, cables are to be beggared for their IR values.
Page 7 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
13) What is CLS panel. Explain its importance?
Ans. CLS panel is the abbreviation of colour light signaling panel. It is the equipment which
supplies uninterrupted power supply to signaling equipment by providing three power
sources Supply, i.e UP AT, DN AT and local if power supply fails to signaling systems, it will result in
detention of trains. Hence CLS panel is very important.
14) What is UPS how it works?
Ans. An UPS is a device which supply un interrupted power supply. This works on the principle of
charging the batteries when normal power is available and take power during power is failed.
15) What is stabilizer?
Ans. Stabilizer is a device which supplies constant voltage irrespective of variation in the incoming
power supply.
16) What is electricity?
Ans. It is a form of energy, which is invisible but can be felt by its effect.
17) What is Ohm's Law?
Ans. The electric current is directly proportional to electro motive force and inversely proportional
to the resistance at constant temperature.
18)What is DC?
Ans. It is a unidirectional current which changes its magnitude but not the directions.
19) What is AC?
Ans. It is the current which changes its magnitude and direction periodically.
20) What is an earth?
Ans.Any wire of supply line touches the earth is called an earth.
21) What is fuse?
Ans. Fuse is used to protect an electric circuit when the rated current exceeds in the circuit the fuse
wire melts and opens the circuit.
22) What is an alternator?
Ans. Alternator is a machine which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
23) What is a motor?
Ans. Motor is a machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
24) What do you mean by turn?
Ans. Two conductors connected in series by end connection is called turn.
25) What do you mean by coil?
Ans. Having one or more turns connected in series is called coil.
26) Why starter is used in flourescent tube?
Ans. Starter is used in flourescent tube for automatic make & break in the circuit for starting
purpose. It generates voltage in choke to aid in series with supply so as to stabilize gas discharge in
Flourescent tubes.
27) Why the choke is used with tube light?
Ans. Choke is used as inductance and check voltage surge at starting and limit the current in
Running.
28) What is a transformer?
Ans. Transformer is a static device which transforms power from one circuit to the other circuit.
Step up Transformer is used to increase voltage from primary to secondary and Step down
transformer is used to reduce voltage from primary to secondary.
29) What do you mean by domestic air conditioner?
Ans. It is a closed self conducted cooling unit in a cabinet. It is modular in nature. It works on the
principle of Thermodynamics second law and works on refrigeration cycle.
Page 8 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
30) What is a battery?
Ans. Battery is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It stores energy in
form of chemical energy. Types a) Primary cell batteries b) Secondary batteries.
31) What is the advantage of HRC fuses when compared with rewireable fuses?
Ans.HRC fuses have high rupturing capacity, high speed of operation and no aging effect.
32) What is meant by Power factor?
Ans. Power factor means ratio of true power to apparent power. It is cosine of phase angle between
voltage and current. Its value is 1 for Unity P.F. Loads, 0 to 1 lagging for inductive loads and o to 1
leading for capacitive loads.
33) How can the state of charge of battery is best indicated?
Ans. The state of charge of battery is best indicated by specific gravity of electrolyte and voltage.
34)What is the purpose of Overload Protection in a motor circuit?
Ans. The Overload Protection is used in a motor circuit to protect it from sustained over
currents.
35) Explain Briefing the half yearly schedule maintenance of OH mains?
Ans. "(a) Check all the jumper connections (b) Check any connections of the strands of the
conductor (c ) Check and ensure proper earth connection (d) Check proper fixation of insulators,
stay wires, guard wires, etc. (e) Check proper tensioning and connection of service wires."
36) FAN Trouble Shooting
Ans a. Replacement of Regulator
b. Replacement of Capacitor.
c. Dismantle.
d. Erect a Fan
e. Cleaning.
37) Light Trouble Shoot
Ans a. Tube
a.
b.
c.
d.
Wire Cut
Switch
Erect
Dismantle
38) Wiring types
Ans) a. Casing & Capping
b. Concealed wiring
c. Cleat Wiring
d. Conduit Wiring Cutting of wall.
39) Identification of Safety Items in the Sub-Station & Why they are Used?
Ans. Horn gap fuse, circuit breakers, fire extinguishers, lightening arrestors, earth pits, hand
gloves, rubber mats, etc.
They are used for stopping of low and high voltages, to stop fire, to stop damages against
thunders, etc.
40) D.G. Set
Ans.
ON/OFF
Daily Inspection about leakages, battery voltage, lub oil pressure, water temperature.
Trouble Shooting about any faults.
Reading Noting about parameters voltage, current, frequency, lub oil pressure.
Page 9 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
41)
Ans
42)
Ans.
Use of Discharged Rod ?
It is used to connect circuits to earth after disconnection from supply.
Types of Fire Extinguishers? Use of Fire Extinguisher ?
CO2 Type Fire Extinguishers, DCP type Fire Extinguishers
Used for extinguishing fires of (1) Solid fires (2) Liquid fires (3) Gasfires(4)Electric
43)
CLS Panels
Ans(A) Schedule Maintenance fortnightly
(B)Identification Parts- UP AT, DN AT, Local Supply.
(C) Trouble Shooting of above components failures, auto change over switch, to identify
failure
of
components for rectification of failure.
44) Pumps
Ans. a. Centrifugal Pump Parts: Impeller, casing, diffuser, suction pipe, delivery pipe.
b. How to Switch ON & OFF: It is usually run by motor. Motor is usually 3 phase induction motor.
It is usually started and stopped by DOL Starter upto 5 HP., beyond 5 HP, star delta starter is used
to switch it ON and OFF.
C.DOL Starter Maintenance
(1) Disconnecting Supply.
(2) Cleaning of dust accumulated
(3) IR values measurement
(4) Testing of all MCBs for their proper functioning.
45) Earth Electrode
Ans. a. Size & Length of Pipe
b. Earth Values at different locations.
c. Schedule Maintenance HY & Y.
46) Distribution Boards
Ans.
a. Sub & Main Distribution Boards
b. Schedule Maintenance.
47) WP Tapping?
Ans. Means weather proof tapping. WP mains provision of 3 phase. 4 wire OH lines running under
COP. WP tapping means tapping supply to lights and fans, circuits under COP at all stations
48) Pole Climbing & Attention to Street Light, Jumpers & Insulator Checking &
Replacement of Insulator?
Ans. (a)
Before pole climbing, supply to be disconnected
(b)
While climbing safety belt, helmet to be used.
(c)
While attending street light, safety board to be displayed.
(d)
While providing jumpers, replacement of insulators, safety is must. Hence
safety belt and safety helmet, safety shoes should be worn compulsorily.
(e)
1st Normal supply to be kept off.
(f)
Segregate loads, which have essential and non-essential
(g)
Essential loads to be brought to single point.
(h)
Then connect UPS supply.
49) UPS- How to give Connection?
Ans. Means Uninterrupted power supply. To give UPS connection, first normal supply is kept off.
Then, loads of essential and non essential are to be segregated. Essential loads are to be
brought under single point of control. Then, UPS can be connected.
Page 10 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
50) Batteries Maintenance
a) Specific gravity.
b)
Voltage/Cell. ON Load/OFF Load(2.2V when fully charged and 1.8 when fully
discharged.
51) When an employee is deemed to possess proficiency in Hindi?
Ans: The employee is deemed to be proficiency in Hindi
a) If he has passed Metric or equivalent or higher examination with Hindi as medium
b) If he took Hindi as an elective subject in a Degree or Equivalent or higher
examination
c) If he declares that he possess proficiency in Hindi
52) When an employee is deemed to have acquired working knowledge of Hindi?
Ans: An employee is deemed to have acquired working knowledge of Hindi
a) if he has passed Metric or equivalent or higher examination with Hindi as subject
b) If he has passed Pragya examination under governments Hindi teaching scheme
c) Other examinations specified by the government
d) if he declares that he has acquired a working knowledge of Hindi.
53) What incentives are given for passing various Hindi examinations?
Ans: Passing of Prabodh
--Rs.250/Praveen
--Rs.250/Pragya
--Rs.300/Hindi Typewriting
--Rs.150/Hindi Stenography
--Rs.300/Other Hindi examinations
Conducted by voluntary
bodies
--Rs.300/Those passed with 60% or above will be given an increment. Special casual leave may be granted
for appearing to such examinations.
54) What is the importance of Hindi Divas?
Ans: 14th September is celebrated as Hindi Day because the constitution Assembly of India had
adopted in Devanagari script as the official language of the union on that day.
55) Which is the official language of government of India and what is its scripts & minerals
prescribed?
Ans: As per Article 343 of constitution of India, Hindi in Devanagari script is the official
language of India & the international form of Indian numerals are prescribed for Official
language.
56) What are states come under Region A, Region B & Region C?
Ans: Region A: Bihar, Hariyana, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar
Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand & Chatisgarh, NCR Delhi & Union territories
of Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
Region-B: Gujarat, Maharashtra & Punjab, Union territories of Chandigarh.
Region-C: All states & Union territories other than region A & B.
Page 11 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
VI. QUESTION & ANSWERS:
Essay Answer Type Questions
Q.1 Explain about Circuit Breaker
Ans: CIRCUIT BREAKERS:
In the case of outdoor type installation, the circuit breakers have fixed location and the
station layout is such that adequate section clearances are always available from the live parts.
In case of indoor type of installation, the circuit breakers of the draw-out type are used so as to
facilitate removal of the breaker to a safe place for maintenance purposes.
(b) Maintenance of circuit breakers:
Of many items which need inspection and maintenance, the circuit -breaker is
perhaps the most important. Because of the duty on circuit- breakers, their relative
complexity and the fact that they contain moving parts and elements subject to deterioration,
circuit-breakers usually need more frequent and more prolonged maintenance. In general, for
maintenance of CB the instructions of the manufacturer should be followed. A few salient
points on maintenance of CB are given below:
Under normal operating conditions during regular inspections following checks
should be made.
The contacts should be checked for proper alignment and their surfaces should bear with
firm , uniform pressure.
The oil level should be checked and maintained.
The oil condition should be tested and if dielectric strength is lower than
specified, oil should be filtered While taking oil samples normal precautions should
be followed.
All insulating parts should be thoroughly cleaned to remove all traces of carbon
which may remain after the oil has been drained from the tank.
Check the tripping of the breaker through devices which will have to function on
fault or overload.
Check indicating devices such as mechanical on and off indication, as an incorrect
indication may at some times lead to a fatal accident.
Check auxiliary switches for cleanliness and contact making.
Check all bolts and nuts for tightness.
Check links of operating mechanism for smooth movement. A small quantity of
appropriate lubricant should be applied at joints.
If a CB operates under fault conditions to interrupt a fault, then maintenance after
such occurrence should be carried out giving special attention to the following items.
Current carrying parts: All contacts including isolator contacts should be examined,
dressed or replaced if necessary.
Insulation should be cleaned of carbon deposits. Examination be made of cracks,
tracking or other damages.
Arc control devices should be checked and dismantled, if any carbon or metallic
deposits are found these should be removed.
All joints and seals should be examined for tightness.
Oil should be checked in case of oil circuit breaker.
Page 12 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
The general inspection of mechanical damage or distortion of the structure and
mechanism should be made . The switchgear should be closed and tripped by each of the
methods provided.
In addition to the periodical maintenance carried out as above, every circuit
breaker will be completely overhauled after five year interval.
Q.2 Explain about Electric Energy Conservation? How Energy conservation can be done in
Lighting?
Ans: Today in India, the per capita availability of energy is much less than the energy in
developed countries. The demand for energy is always out placing availability, the shortfall being
ten percent per annum. The present cost of thermal power is about Rs. 4.00crores per MW and the
others are higher. So, to tackle this demand of power, an enormous amount of investment is
necessary. A review of the entire situation demands that to overcome the grim situation, some
useful immediate measures have to be taken. One of the most fundamental step is to find the
possibilities of conservation of energy by all means. Energy conservation practice can provide
equivalent or improved visual performance and visual comforts while producing substantial energy
and power savings. Referring back to the time when incandescent lamps gave way to fluorescent
lamps in commercial buildings", other trends such as rising urban land costs, the advent of
building air-conditioning systems and low cost electricity combined to eliminate daylight as an
essential element in building design.
Any lighting system with an energy conservation objective and with the intention of
providing increased productivity and safety should comply with six basic rules in order to
produce the most cost effective results.
Use of the most efficient light source practicable.
Use of the lamp light output efficiently.
Maintain lighting equipments in good order.
Use well designed energy effective lighting schemes.
Control the switching operation and usage of the lighting installation.
Consider the utilization of daylight and the effect of the surrounding dcor
(i) Efficient light Source
The need is clearly, to use the type of lamp which gives the maximum amount of light
(lumens) for each watt of electrical energy consumed, consistent with the colour rendering and
other needs of the installation. For lighting, the commonly used light sources are incandescent,
fluorescent lamps, T5 fluorescent lamps, CFL, high pressure mercury (HPMV), metal halide
lamps and high pressure sodium vapour (SON) lamps, and the the LED lamps.
The high pressure sodium vapour lamp is undoubtedly a very efficient light source. This
high efficacy lamp is ideal for all applications where colour rendition is not important.. But due to
poor colour rendering index , they are being replaced by high luminous efficacy metal halide
lamps except in general road highways and some rail yards. Modern T5 lamps are available
with luminous efficacies ranging from 90 to 104 Lumens/watt and are now preferred for use in
indoor lighting in offices, street lighting and in railway platforms. Future holds a lot of potential
for LED lighting. Already street light luminaries with luminous efficacy of 120 Lumens/watt are
available which are most energy efficient.
In India, many industries still use incandescent lamps because of their low cost.
Vast amount of savings in energy are possible by replacing the high wattage incandescent lamps
with CFLs or appropriate fluorescent luminaries.
Two types of fluorescent lamps are available in our country, namely the cool daylight
(colour 54) with a colour temperature of 6500 K and the white (colour 33) with a colour
temperature of 4300K. The white fluorescent lamp gives 14% more light than the cool
daylight fluorescent lamp and thus for the same illuminance a 14% saving of energy is possible,
Page 13 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
although the colour rendition of cool daylight fluorescent lamp is better than that of the white
fluorescent lamp.
For home lighting, the incandescent lamp can be conveniently replaced by CFL.
In the recent years, developments in the field of low wattage gas discharge lamps and
High Frequency, Electronic lighting have changed the situation dramatically. The new generation
'fluorescent HF electronic lamps have achieved a luminous efficacy of more than
100 lumen power Watt. These lamps operate on a frequency of more than 25kHz and give
exceptional performance. The important features of these lamps are
Instant starting,
Superb colour appearance with high colour rendering index.
No stroboscoplc effects.
Excellent lumen maintenance, and
Wide temperature range.
(ii) Efficient Use of lamp light output
It is all too common in many lighting installations to see instances of energy
wastage with consequent total money-wastage due to poor quality or inefficient luminaries for
either commercial, industrial, or road light use, purchased possibly on the grounds only of less
capital cost
Generally, provided that the light distribution is acceptable and care is taken to reduce
glare, the light output ratio is a reasonable indicator of efficiency. In addition to the photometric
efficiency account should be taken of the power consumed by the luminaire control gear, e.g.
ballast. The total wattage consumption of any discharge lamp circuit is always greater than the
rated wattage of the lamp at a given reference voltage. The power loss in the control gear is
dissipated as heat within the luminaire causing problem there.
Fur commercial interiors, from the energy saving point of view, use the fluorescent
lamps without any screening louvre or diffuser. However, from the point of view of illumination
engineering, this is not advisable because bare lamps give rise to considerable amount of
discomfort glare. lt is therefore, necessary to use louvres/diffusers, not only to screen the lamp
from view in order to reduce glare, but also to give a aesthetic appearance to the room.
For industrial Interiors where decorative appearance is not important, the
fluorescent lamps are normally used with through type reflectors, For mounting heights of 7m
and above the work plane it is found that the use of highway luminaires with metal halide lamps
are many times preferable.
For street lighting, the design of the luminaire is very important. This is because
only by proper design of the luminaire it is possible to ensure that maximum light leaches the
road surface.. In streets of rural areas and side streets, street lighting luminaires with fluorescent
lamps are used.
Q.3 who is designated EIG on Indian Railways? What is his role?
Ans.
Chief Electrical Engineer is designation as EIG of Indian Railways. No person shall be
appointed to be a Chief Electrical Engineer/inspector unless he possess a degree in Electrical
Engineering or its equivalent from recognized university or institution.
The inspector may enter, inspect and examine any place in generation, transmission,
distribution, conversion of use of energy and may carry out the tests therein.
He has been regularly engaged for a period of at least 20 years in the practice of Electrical
Engineering.
Q.4 A tube light rated 50 watts (electric powers) is used for 10 hours per day for 30 days in a
month. How much electric energy is being consumed by it per month? Similary per year, how
much energy will be consumed?
Ans. 50 x 10 x 30 = 15000watts = 15000/1000= 15 units per month.
Per units consumed: 15X12= 180units per year.
Page 14 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Q.5 Please indicate the illumination levels provided at following locations?
Ans. a. ASM Room: 100 lux and above
b. Booking Window:400 lux and above
c. Officers Chamber: 120 lux and above.
d. Operation theatre in Hospital.
Q.6 Write various advantages of using high mast tower lighting viz a vIz Sodium lamps in
circulating areas?
Ans. (i) Better illumination
(ii) Vide area illumination
(iii)where mass public movement
(iv) Where loading & unloading of materials
(v) At goods coaches & passenger coaches formation, checking and maintenance.
Q.7 Draw a schematic diagram of Power supply distribution substation for a Rly. Colony?
Ans. Schematic diagram of power supply
Q.8 Write advantages of Underground cable with respect to Overhead line?
Ans.
FEATURE
Layout
U. G. CABLE
1. Safe in any terrain And layout
2. Practicable for any And layout
3. Acceptable for any
environment and weather
conditions
Investment
Generally costly.
Maintenance
Practically Maintenance
Page 15 of 33
OH LINE
Unsafe in certain terrains and layouts
Impracticable for densely populated areas.
Not acceptable for certain environments
(viz. High speed of wind, varying climatic
patterns
Becomes costly with Special considerations
like High masts, zig-zag configurations.
Costly maintenance
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Failure rate Or Free. Generally not affected by
Reliability
natural calamities like
Storms, lighting or snow.
Aerial
Interference
Nil
Prone to natural calamities like storms
Lighting or snow.
May infringe the layout of Air Ports and
airways.
Will not affect the beauty or get up of Will affect the beauty and at times the
the Settlements.
Surroundings.
Cheaper because, either the conductor or
Replacement Costly
the Insulators can be strengthened without
affecting the cost of supports at times.
Limited to maximum of 132 KV and Can be used for any Voltage and power
Application
becomes costly as well as bulky to application.
handle beyond this voltage.
Troubleshooting Difficult to locate Faults
Easy to localize faults and hence their
rectification.
Aesthitics
Q.9. What are the different type of fire extinguishers used for different type of fires. Describe
in brief working of fire extinguisher used for electrical fire?
Ans The types of extinguishers normally used are:
Soda acid type
Foam type
Dry powder type
Carbon dioxide type &
Halol (chloro bromo methane) type
Soda acid type of extinguisher is suitable for only class 'A' for eg. fires in ordinary combustible
materials such as wood paper etc. It can be used in such areas as office rooms.
Foam type is suitable for oil fires (class 'B') and can be used in oil storage areas.
Both these types are not suitable for electrical apparatus.
Dry powder type, CO2 type & chloro bromo methane type are suitable for classes 'A' & 'B' as
well as Class 'F' (electrical apparatus) fires and should be provided in adequate quantities in areas
housing electrical apparatus such as switch-gear rooms.
Dry powder type equipment being relatively cheaper can be used in all less important areas and
CO2 type apparatus must be used near more important equipment. In addition to wall mounted
equipment one or two wheeled portable apparatus of CO2 and dry powder type equipment
depending on the size of the substation should be placed at strategic spots from where it can
be readily taken to affected areas. Halol gas system is preferred for the protection of control
rooms. All fire protection equipment shall be covered by a regular and strict maintenance
and test routine.
Portable equipment should be charged at specified intervals and checked regularly for loss of
charge, damage etc. Records of all tests and checks must be maintained.
Page 16 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Q.10. Indicate power of following electrical appliances?
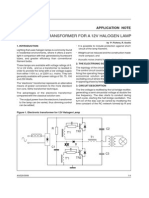
Ans. Incandescent Lamp
The incandescent lamp is the oldest electric light source still in general use.The incandescent
lamp produces its light by the electrical heating of a wire (the filament), usually tungsten filament
to such a high temperature that radiation in the visible region of the spectrum is emitted.
Performance characteristics
Energy balance
Fig. 1 shows the energy balance in an incandescent Lamp. An incandescent lamp operates at
about 2800K and emits radiation throughout the visible spectrum with a bias towards the higher
wavelengths. The outer glass envelope is filled typically with a mixture of nitrogen and argon
whose function is to limit the evaporation of tungsten and also to prevent arcing across the
filament. The luminous efficacy of practical tungsten incandescent lamps is always considerably
low since most of the radiation is in the infra red range of wavelengths. For example, for modern
GLS lamps with a rated operating life of 1000 hours it varies between 8 and 21.5 Lm/W.
b. T5 Tube light
The latest development in the fluorescent lamp is the T5 lamp. This lamp has a diameter of only
5/8 (15 mm) and has an inbuilt electronic ballast of high quality. The main advantage of T5
lamps are very high luminous efficacy between 85 to 90 lumens/watt for the 2T5 tube and up to
104 Lumens/watt for the 28 W 4 T5 tube. The T5 lamp also a very high power factor greater
than 0.85 and colour rendering index Ra of 90.
The T5 uses less quantity of mercury vapour in the tube. A coating of calcium nitrate on
the inside surface prevents absorption of mercury by the walls of the tube thereby prolonging the
life of the lamp. The narrow tube along with the powerful electronic ballast substantially
improves the luminous efficacies to the range of 90 to 104 Lumens/watt. The life of T5 lamp
is between 15000 to 18000 burning hours.
C. Ceiling fan
Ceiling fans shall be installed at a height of 2.75 m or more from floor. The fan rod shall be
preferably one piece. The suspension hook for ceiling fans should be fixed in roofs during
construction stage. All ceiling fans should be wired to ceiling-roses or to a special connector
boxes. The fan including its suspension, should confirm to IS:374 (Specification for ceiling fan
and regulator).
e. Window type AC System
Air conditioners of the window type, are completely self-contained units, with the compressor,
condenser, evaporator, refrigerant piping and air filter, all assembled in a very compact assembly. The
window units are usually of 1/2 to 2 tons capacity and fitted with 230 V motor upto 3 HP. Modern
tendency is to employ sealed type motor-compressor units with the refrigerant piping system sealed-in
with brazed joints, so that the leakage of gas is virtually eliminated and the unit may serve for long
Page 17 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
periods with hardly any attention. In these units expansion valve and liquid receiver are not provided.
The refrigerant is controlled with the capillary system. The unit is so designed that it can be mounted on
the window with small bracket from outside. Window units are particularly adopted when only few
rooms are to be air-conditioned and they are widely separated.
f. Electric iron
An electric iron consist of basically a heating coil and heat control circuit viz thermostat.
Thermostat act as a switch. When we switch on the electric iron current flows through the heating
coil. The heat in the heating coil causes expansion in the thermostat which gradually disconnects
the supply.
Q.11. Write short note on UPS and its usage in railway system.
Ans. Ideally, the voltage supply by the utility system should be perfect sine wave without any
harmonics, at its nominal frequency of 50 Hz and at its nominal magnitude. In practice however
voltage can significantly depart from the ideal condition due to power line disturbances e.g.
overvoltage, under voltage (brown out), outage (blackout), voltage spikes, harmonics and
electromagnetic interference. Sustained over voltage and under voltages may cause equipments, to
trip out, while voltage spikes may cause hardware problems. Power conditioners i.e. metal oxide
varistors (MOVs), EMI filters, isolation transformers; Ferro resonant transformers provide an
effective way of suppressing some or all of these disturbances.
An Uninterruptible Power Supply system is used for supplying critical loads like computer/data
processing machines, hospitals, control and instrumentation, communication equipment and
critical processes in industries. This provides protection against power outages as well as voltage
regulation during power line over voltage and under voltage conditions.
UPS TOPOLOGIES:
The UPS system can be classified into two types.
a)
On load UPS
b)
Off load UPS
On load UPS
The input rectifier feeds to battery as well as the load all the time. Battery remains in
floating condition and takes over as soon as the mains goes off. This gives conditioned output
of fixed frequency, fixed voltage irrespective of line condition.
OFF load UPS
In off load UPS system, battery bank is usually not connected to the load. lt comes into
circuit only when the mains is off.
In the normal mode, the switching converter operates as rectifier, charging the battery bank.
In addition, it can draw, inductive or capacitive currents from the mains, thus providing a
fine regulation of the voltage supplied to the load. In case of a main power outage, the power is
isolated and the switching convener operates as an inverter, supplying power to the load from
the battery bank. This arrangement is also referred to as the "standby power supply'. The
response time of the OFF LINE UPS is slower compared to ON LINE UPS system.
Static Bypass switch
In on load UPS systems, the battery takes care of mains failure but there is no standby system to
take care of the failure of inverter. Hence, for additional reliability the power line itself is used as
a backup to the UPS and static bypass switch is provided to transfer the load from the UPS to the
mains in case of any problem in the UPS. Whenever a static transfer switch is used the inverter
Page 18 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
output should be synchronized to the line voltage so that transferring the load from one source to
the other results in the least amount of disturbance seen by the load.
Q.12. Write short note on following
Ans. Types of Insulators
There are several types of insulators but the most commonly used are pin type, suspension
type, strain insulator and shackle insulator.
1. Pin type Insulators
Pin Type Insulator
As the name suggests, the pin type insulator is secured to the cross-arm on the pole. There is a
groove on the upper end of the insulator for housing the conductor. The conductor passes through
this groove and is bound by the annealed wire of the same material as the conductor.
Pin type insulators are used for transmission and distribution of electric power at voltages up to 33
kV. Beyond operating voltage of 33 kV, the pin type insulators become too bulky and hence
uneconomical.
2.Suspension Type
Suspension Type
For high voltages (>33 kV), it is a usual practice to use suspension type insulators shown in Figure.
Consist of a number of porcelain discs connected in series by metal links in the form of a string.
The conductor is suspended at the bottom end of this string while the other end of the string is
secured to the cross-arm of the tower. Each unit or disc is designed for low voltage, say 11 kV. The
Page 19 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
number of discs in series would obviously depend upon the working voltage. For instance, if the
working voltage is 66 kV, then six discs in series will be provided on the string.
3. Strain Insulators
Strain Type Insulator
When there is a dead end of the line or there is corner or sharp curve, the line is subjected to greater
tension. In order to relieve the line of excessive tension, strain insulators are used. For low voltage
lines (< 11 kV), shackle insulators are used as strain insulators. However, for high voltage
transmission lines, strain insulator consists of an assembly of suspension insulators as shown in
Figure. The discs of strain insulators are used in the vertical plane. When the tension in lines is
exceedingly high, at long river spans, two or more strings are used in parallel.
4. Shackle Insulators
Shackle Type Insulator
In early days, the shackle insulators were used as strain insulators. But now a day, they are frequently used
for low voltage distribution lines. Such insulators can be used either in a horizontal position or in a vertical
position. They can be directly fixed to the pole with a bolt or to the cross arm.
Q.13. What is electric tariff? What are different tariffs?
Ans. ELECTRICAL TARIFF:
Electrical Tariff represents the basis on which charges are recovered from the consumers for supply of
electricity. The main objectives of the tariff is to distribute equitably the cost of supplying electrical
energy among the various classification of use such as lighting, heating, industrial and, bulk supply etc. All
types of tariffs must cover the following costs :
Recovery of cost of capital investment in generating plant, transmission and
distribution system equipments and in other forms of the operating equipment.
Recovery of cost of operation and maintenance of equipments and plant.
Recovery of cost of auxiliary equipment, metering equipment, billing and collection
expenses and miscellaneous services.
The principle factors involving the formulation of tariff are enumerated below:
Page 20 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Proper return is secured from each consumer of electric energy. Consumers are made to make more
extended use of electric energy. Consumers of electric energy are charged according to what the energy
costs. The tariff should be simple and cheap and should be easy to understand by the consumers.
TYPES OF TARIFF :
The different kinds of tariffs in common use are as under
Simple tariff
Flat rate tariff
Block rate tariff
Two-part tariff
Maximum demand tariff
Power factor tariff
Three part tariff
Off peak tariff
Simple tariff
This is the simplest kind of tariff. Here the cost of energy is charged on the basis of units consumed. The
rate per unit can be calculated as,
Charges per Kwh = (Annual Fixed charges + Annual running charges)
Total number of units supplied to consumer
This method has following drawbacks although the procedure for fixing the rates is very simple for the
supplier and calculation, verification by the consumer.
The cost per KWh delivered is higher.
There is no discrimination among the different categories (such as domestic, commercial
and industrial) of consumers.
The simple tariff can be made suitable by having some modifications mentioned below.
By allowing a discount to the consumer who consumes more electricity than an average
consumer.
Special tariff be framed for different categories of consumers such that the
domestic
consumers may be charged light rates than in case of industrial consumers and commercial consumers.
By encouraging the consumers of electric energy to use electricity during off peak load period
thereby giving them a special discount. Its use is restricted to industrial loads only.
Flat rate tariff
This kind of tariff differs from the former (simple tariff) one in the sense that the different
categories of consumers are charged at different rates, In this case the flat rate thus is slightly higher for
domestic (light and fan) loads than for industrial (power) loads. The rate for each category of
consumers is derived by taking into account its load factor and diversity factor.
This method is very popular with the consumers since it can be easily understood by the
consumers and the calculations at the supplier's end are very simple. If the energy consumed by an
industrial consumer is x units and the fat rate per unit is Rs. a per unit then the total charges of the bill
are Rs. A x
The disadvantage of this tariff is that separate meters are required for different types of supply.
Two-part tariff :
The charges include fixed charges independent of energy consumed and proportional to per kW
of maximum demand and a;nning (operating) charges per kWh of the total energy consumed.
The tariff can be expressed as. C = Rs. (a. kw + b. kwh)
Where Rs. a is The charge per Kw of maximum demand assessed and Rs. b is the charge per
kWh of energy consumed.
This tariff is mostly applicable to the medium industrial consumers.
Here, the charges made on the maximum demand covers the fixed charges such as interest and
depreciation on the capital cost of building and equipment, taxes and insurance charges and operating
Page 21 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
cost which is independent of energy supplied by it. The charge varies with the variation in energy
supplied.
Q.14. What is object of earthing? What are types of earthing (Electric power supply
Ans)
OBJECT OF EARTHING
The object of earthing system is, to provide as nearly as possible a surface under and
around a station, which shall be at a uniform potential and as nearly to zero or absolute earth
potential as possible. This is in order to ensure that, in general, all parts of apparatus other than
live parts shall be at earth potential, as well as, to ensure that operators and attendants shall be at
earth potential at all times, so that there exists no potential difference, to cause shock or injure a
person, when short circuit or any type of earth fault takes place in the system.
CLASSIFICATION OF EARTHING
Earthing can be broadly classified as follows
System earthing.
Equipment earthing.
Static and lightning protection earthing.
System earthing is designed primarily to preserve the security of the system by ensuring that the
potential on each conductor is restricted to such a value as is consistent with the level of insulation
applied. From the point of view of safety, it is equally important that earthing should ensure efficient and
fast operation of protective gear in the case of earth faults. The system earth resistance should be such
that, when any fault occurs against which earthing is designed to give protection, the protective gear
will operate to make the faulty main or plant harmless. In most cases such operation involves
isolation of the faulty main or plant by circuit breakers or fuses.
In case of underground systems, there is no difficulty whatever, but, in case of overhead line
systems protected by fuses or circuit breakers, fitted with over protection only, there may be difficulty in
arranging the value of the system earth resistance in such a way that a conductor falling and making
good contact with the ground results in operation of the protection systems. A low system earth
resistance is required even in the cases where an arc suppression coil is installed, as its operation may be
frustrated by too high an earth electrode resistance.
Earthing may not give protection against faults that are not essentially earth faults. For
example, if a phase conductor on an overhead spur line breaks and the part remote from the supply falls
to the ground, it is unlikely that any protective gear relying on earthing, other than current balance
protection at the sub-station, will operate since the earth fault current circuit includes the impedance of
the load that would be high relative to the rest of the circuit.
When the insulation of the motor windings breaks down, current starts leaking into the metal
body of the apparatus which would get charged with the supply voltage and become alive and
dangerous, unless the charge is drained to earth by an earth connection. When the body is
earthed, a fault in the winding would cause a heavy current to flow into the earth, which would
then blow out the fuse, thereby disconnecting the supply to the motor.
The permissible value of the earth resistance is directly related to the system voltage, maximum
fault current and the sensitivity of the protective equipment and the reasonable potential rise. If the
resistance to earth is high, the protective system will not function under a fault, creating a dangerous
condition.
Q.15. What are power cables? Explain about them?
Ans)
TYPES AND APPLICATIONS
Presently PVC and XLPE cables are being used in electrical installations. The discussion is
restricted to these two types only. The voltage ratings covered are up to and including 33 KV.
Page 22 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
a) PVC INSULATED CABLES
PVC insulated cables, covered by IS 1554 are used where combination of ambient
temperature and temperature rise due to load results in conductor temperature not exceeding 70C
under normal operation and 160C under short circuit conditions.
b)XLPE INSULATED CABLES
XLPE insulated cables, covered by IS 7098 are used where combination of ambient
temperature and temperature rise due to load results in conductor temperature not exceeding 90C
under normal operation and 250C under short circuit conditions.
XLPE cables are particularly suitable in following situations.
On vertical runs of unlimited difference in level,.
At locations having severe vibration problems,
At locations having higher ambient temperatures up to 70C,
At conditions demanding short time overload up to 120C and,
In systems having higher short circuit levels.
Q.16. what are types of wiring systems based on method of connection?
Ans) Wiring systems based on method of connection are of two Wiring systems based on
method of connection are of two types viz.,
(i) Joint box and,
(ii) Looping in system.
Joint Box System
Here load is connected to its controlling switch in series. Positive supply is connected to one
end of control-switch by making a T joint in the main-line-positive and the other end of load is
connected to neutral by similar T joint in main line neutral. These points are kept inside a wooden box
(called joint box)
Joint-box system of wiring
Loop in System of wiring
Instead of puncturing the main lines, here lines are brought to first load and its
control switch as shown below. Now lines are brought from first load and control switch to
another load and control switch. This process is repeated.
Page 23 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Loop in system wiring
Q.17. What are different types of pumps used in Railway colony. Write short note on any one
of them?
Page 24 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Page 25 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Q.18. what are the criteria taken in to consideration while deciding pump capacity?
Page 26 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
VII. Official Language Act and Rules.
Page 27 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Page 28 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
(VIII) Meanings:-
Page 29 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
VIII. Industrial Electrical Symbols:
Page 30 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Page 31 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Page 32 of 33
QUESTION BANK FOR Tech-III/PM LDCE Quota
Page 33 of 33
You might also like
- Thermal Stability of I.T. at SiteDocument4 pagesThermal Stability of I.T. at SiteBalubhai KarsanbhaiNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesFrom EverandMarine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- DSC 1280Document11 pagesDSC 1280nhiahm nhiahmNo ratings yet
- HF-525Plus Service Manual (Rev. 2.2 Latest) 16 11 2011 PDFDocument142 pagesHF-525Plus Service Manual (Rev. 2.2 Latest) 16 11 2011 PDFFélix Nicolau100% (1)
- ELECTRICAL - QUESTION BANK FOR HWH DIVISIONDocument17 pagesELECTRICAL - QUESTION BANK FOR HWH DIVISIONNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- EmsDocument7 pagesEmssujaraghupsNo ratings yet
- Three factors and electrical safety in fire causesDocument5 pagesThree factors and electrical safety in fire causesSUJIT KUMAR MONDALNo ratings yet
- Questions For ElectricianDocument87 pagesQuestions For ElectricianMohammad TammamNo ratings yet
- Building Management ElectricalDocument51 pagesBuilding Management Electricalmanikyam begariNo ratings yet
- IES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2006Document10 pagesIES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2006aditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Thermal DesignDocument28 pagesChapter 7 Thermal DesignettypasewangNo ratings yet
- Electrical UtilitiesDocument10 pagesElectrical UtilitiesSuresh K KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- EgyE 201 Assignment On Energy Conversion SystemsDocument2 pagesEgyE 201 Assignment On Energy Conversion SystemsAngel de DiosNo ratings yet
- Facilities BasicsDocument51 pagesFacilities BasicsMubarak HoseinNo ratings yet
- Busbar Sizing CalculationDocument7 pagesBusbar Sizing Calculationchenshiva100% (1)
- How to properly size busbars in electrical panelsDocument5 pagesHow to properly size busbars in electrical panelsZaferullah Khan100% (1)
- EWT Earthing TransformersDocument4 pagesEWT Earthing TransformersSibolis NaburjuNo ratings yet
- MC Des Final 2011Document1 pageMC Des Final 2011Puneet AroraNo ratings yet
- Busbar Sizing CalculationDocument5 pagesBusbar Sizing CalculationZaferullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Four Types of High Voltage Current TransformersDocument3 pagesFour Types of High Voltage Current TransformersSudhakar KethireddyNo ratings yet
- CKP Notes Vol 2 VERSION 2Document116 pagesCKP Notes Vol 2 VERSION 2Sivasankar AkcNo ratings yet
- PART 3 ElectrificationDocument20 pagesPART 3 ElectrificationglymayNo ratings yet
- MRT and ProtectionDocument4 pagesMRT and ProtectionAlexander AnthonyNo ratings yet
- SREDA Energy Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesSREDA Energy Exam ReviewAbu Hasnat Md. ShaedNo ratings yet
- Dce 20% DKH To Tech-Iii (Electrical) 2015 Descriptive Type Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesDce 20% DKH To Tech-Iii (Electrical) 2015 Descriptive Type Questions and AnswersmajjisatNo ratings yet
- Electrical FileDocument52 pagesElectrical FilebabuNo ratings yet
- Current Transformers (72.5 kV to 420 kV) SpecificationsDocument4 pagesCurrent Transformers (72.5 kV to 420 kV) SpecificationsPaulo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Power and Control CablesDocument27 pagesPower and Control CablesAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- RRB Jobs Question Bank Junior Engineer Non Ac Write Short NotesDocument6 pagesRRB Jobs Question Bank Junior Engineer Non Ac Write Short Noteskunalg293No ratings yet
- Write Short Notes:: Question Bank For Jee Non - AcDocument6 pagesWrite Short Notes:: Question Bank For Jee Non - Ackunalg293No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument15 pagesAssignmentSumit ShindeNo ratings yet
- 1800 Ω with ± 10% tolerance e. 7621 VA c. decrease cDocument19 pages1800 Ω with ± 10% tolerance e. 7621 VA c. decrease cAbas S. AcmadNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis University: Chemical Engineering PrinciplesDocument6 pagesSaint Louis University: Chemical Engineering PrinciplesAileen MayaNo ratings yet
- Design Philosophy Design Criteria: Transformers Will Be Provided by OthersDocument8 pagesDesign Philosophy Design Criteria: Transformers Will Be Provided by OthersMunish GaurNo ratings yet
- 6.manage Troubleshooting and Restoration of Electrical and Electronic ControlDocument15 pages6.manage Troubleshooting and Restoration of Electrical and Electronic ControlDaru ArusukeNo ratings yet
- Ee 1 April 2017 Part 2bDocument2 pagesEe 1 April 2017 Part 2bBugoy2023No ratings yet
- Induction Cooker PaperDocument7 pagesInduction Cooker PaperSyed Salman AliNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transfer DeviceDocument65 pagesWireless Power Transfer DevicebhagathnagarNo ratings yet
- Instrument TransformersDocument16 pagesInstrument Transformersnitinatp1978No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0960148112000821 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0960148112000821 MainJaspreet Singh ChahalNo ratings yet
- Canalis KTA Characteristics GuideDocument32 pagesCanalis KTA Characteristics Guideodin_auerNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering PapersDocument34 pagesMechanical Engineering PapersshivarajeshNo ratings yet
- Vocational training report on power generation processes and components at KBUNL power plantDocument33 pagesVocational training report on power generation processes and components at KBUNL power plantShanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Transistorised IntercomDocument13 pagesLow Cost Transistorised IntercomaymangafferNo ratings yet
- GROUND REFERENCE TRANSFORMER SIZING EXAMPLEDocument5 pagesGROUND REFERENCE TRANSFORMER SIZING EXAMPLEmehrbloor@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Kerite Engineering Catalog PDFDocument20 pagesKerite Engineering Catalog PDFTIAGO3045No ratings yet
- 20Th National Certification Examination FOR Energy Managers & Energy Auditors - September, 2019Document13 pages20Th National Certification Examination FOR Energy Managers & Energy Auditors - September, 2019Albert SekarNo ratings yet
- Merlin Gerin Medium VoltageDocument10 pagesMerlin Gerin Medium VoltagekjfenNo ratings yet
- HV Cable SizingDocument11 pagesHV Cable Sizingvikasmit2k2100% (3)
- EL Transf 12VDocument4 pagesEL Transf 12VmarjanchoNo ratings yet
- Transformador Electrnico para La Lmpara Del Halgeno 12cv 214Document5 pagesTransformador Electrnico para La Lmpara Del Halgeno 12cv 214billy_lxNo ratings yet
- Energy Harvesting EstimatesDocument12 pagesEnergy Harvesting EstimatesShashikiran HPNo ratings yet
- MCQs in EC, Electrical, Electronics, and General AwarenessDocument6 pagesMCQs in EC, Electrical, Electronics, and General Awarenesserjayprakashpatel0% (2)
- Electrical Engineering 5Document19 pagesElectrical Engineering 5manikandaprabhuNo ratings yet
- 5r110 Thermistor Sunstar RemacheDocument4 pages5r110 Thermistor Sunstar RemacheHeriberto Flores Ampie0% (1)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Eep Practical File: IndexDocument17 pagesEep Practical File: IndexAkash GandharNo ratings yet
- CKT No. Load Description AB BC CA AT AFDocument8 pagesCKT No. Load Description AB BC CA AT AFChrisanto AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 4 Characteristics of Welding TransformerDocument5 pagesExperiment No: 4 Characteristics of Welding TransformerKunal TanwarNo ratings yet
- Transformers: Spec Tech Industrial 203 Vest Ave. Valley Park, MO 63088 Phone: 888 SPECTECHDocument12 pagesTransformers: Spec Tech Industrial 203 Vest Ave. Valley Park, MO 63088 Phone: 888 SPECTECHEngineerOmarNo ratings yet
- Good Earthing Practices For Generator System (Presentation) PDFDocument20 pagesGood Earthing Practices For Generator System (Presentation) PDFMokr AchourNo ratings yet
- Questions On Armature WindingsDocument18 pagesQuestions On Armature Windingskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- Lab #3: Linear Voltage Regulators: GoalsDocument15 pagesLab #3: Linear Voltage Regulators: GoalsManuel EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- TR25-1 Annex DDocument2 pagesTR25-1 Annex DDarshit VyasNo ratings yet
- Is 9921 3 1982 PDFDocument12 pagesIs 9921 3 1982 PDFsridharNo ratings yet
- Standard Ac Eng PDFDocument324 pagesStandard Ac Eng PDFPranav KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument53 pagesPe Lab ManualKada JashNo ratings yet
- MSD Digital, 6al Ignition Control, PN 6425Document20 pagesMSD Digital, 6al Ignition Control, PN 6425Alberto Delgado100% (1)
- G6H PCB Relay: Ordering InformationDocument8 pagesG6H PCB Relay: Ordering InformationLuis Enrique De los Santos FarfánNo ratings yet
- Acs 5000 BrochureDocument24 pagesAcs 5000 BrochureRagilNo ratings yet
- 500kVA DG Set Comparative AnalysisDocument7 pages500kVA DG Set Comparative Analysisअभिषेक कुमार उपाध्यायNo ratings yet
- Voltage Drop GuideDocument2 pagesVoltage Drop Guidemherold2No ratings yet
- 400A 4-Pole Transfer SwitchDocument3 pages400A 4-Pole Transfer Switchbachir oussamaNo ratings yet
- Mom Pump Storage Plants-201706 PDFDocument259 pagesMom Pump Storage Plants-201706 PDFweiboNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Analysis of 5MW Osmanabad Solar PV Power ProjectDocument52 pagesFeasibility Analysis of 5MW Osmanabad Solar PV Power ProjectAnkur PathakNo ratings yet
- Power Factor - Calculation and Power Factor Improvement - Electrical4uDocument6 pagesPower Factor - Calculation and Power Factor Improvement - Electrical4uANo ratings yet
- Feasibility Analysis of Stand-Alone Renewable Energy Supply For Telecommunication Tower Using HomerDocument6 pagesFeasibility Analysis of Stand-Alone Renewable Energy Supply For Telecommunication Tower Using Homerjuan ceronNo ratings yet
- Investigation of A Unified Power Flow Controller: AbstractDocument9 pagesInvestigation of A Unified Power Flow Controller: AbstractChaibHabibNo ratings yet
- Ul 1283 BulletinDocument4 pagesUl 1283 BulletinMboriko MwashaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 6 Electrical Installation and Maintenance I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan 6 Electrical Installation and Maintenance I. Objectivescecille mañacapNo ratings yet
- Australian Standard: Grid Connection of Energy Systems Via Inverters Part 3: Grid Protection RequirementsDocument20 pagesAustralian Standard: Grid Connection of Energy Systems Via Inverters Part 3: Grid Protection RequirementsLoganNo ratings yet
- Grid-tied System Design NY: Calculating Module and Inverter NeedsDocument52 pagesGrid-tied System Design NY: Calculating Module and Inverter Needsbedilu77No ratings yet
- Hormann Lineamatic Gate OperatorsDocument46 pagesHormann Lineamatic Gate Operatorsineskhiari2204No ratings yet