Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Engineering Basics
Uploaded by
Ivar Nilasta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views6 pagesAn electrical drafter performs the following key tasks:
1) Produces technical drawings and documentation by conferring with engineers, visiting installation sites, and drafting diagrams.
2) Checks drawings for accuracy and conformity to standards before reproduction.
3) Explains drawings to construction teams and provides adjustments as needed.
Original Description:
Job Description of Electrical Drafts Person
Original Title
sample Job Description of Electrical Drafts Person
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn electrical drafter performs the following key tasks:
1) Produces technical drawings and documentation by conferring with engineers, visiting installation sites, and drafting diagrams.
2) Checks drawings for accuracy and conformity to standards before reproduction.
3) Explains drawings to construction teams and provides adjustments as needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views6 pagesElectrical Engineering Basics
Uploaded by
Ivar NilastaAn electrical drafter performs the following key tasks:
1) Produces technical drawings and documentation by conferring with engineers, visiting installation sites, and drafting diagrams.
2) Checks drawings for accuracy and conformity to standards before reproduction.
3) Explains drawings to construction teams and provides adjustments as needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
What is Electrical Engineering?
What is "electrical engineering"? Electrical engineering is concerned with research, design,
development, manufacture, installation, operation, maintenance and management of equipment,
plant and systems within the electrical, electronic, communication and computer systems areas.
These activities can apply to electricity generation, transmission, distribution, electrical
installations in buildings and on industrial sites, electrical equipment manufacture,
instrumentation and control systems applications in industry, communications networks,
electronic plant and equipment, and also the integration and control of computer systems.
Previously the Electrical College covered all these areas of interest, however the formation of a
separate ITEE College (the College of Information, Telecommunications and Electronics
Engineering) means that the ITEE is now available to support and promote the work of engineers
in Communications Engineering, Computer Systems Engineering, Electronics Engineering,
Information Engineering and Software Engineering.
The Electrical College's activities therefore now apply to electricity generation, transmission,
distribution (generally referred to as the electricity supply side), the utilisation side covering
electrical installations (power distribution, lighting control systems etc) in buildings and on
industrial sites, electrical equipment manufacture, instrumentation and control systems
applications in industry.
Job Duties and Tasks for: "Electrical Drafter"
1) Assemble documentation packages and produce drawing sets which are then
checked by an engineer or an architect.
2) Confer with engineering staff and other personnel to resolve problems.
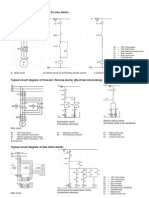
3) Draft working drawings, wiring diagrams, wiring connection specifications or
cross-sections of underground cables, as required for instructions to installation
crew.
4) Draw master sketches to scale showing relation of proposed installations to
existing facilities and exact specifications and dimensions.
5) Measure factors that affect installation and arrangement of equipment, such as
distances to be spanned by wire and cable.
6) Study work order requests to determine type of service, such as lighting or
power, demanded by installation.
2) 7) Visit proposed installation sites and draw rough sketches of location.
8) Determine the order of work and the method of presentation, such as
orthographic or isometric drawing.
9) Explain drawings to production or construction teams and provide adjustments
as necessary.
3) 10) Prepare and interpret specifications, calculating weights, volumes, and stress
factors.
11) Reproduce working drawings on copy machines or trace drawings in ink.
12) Review completed construction drawings and cost estimates for accuracy
and conformity to standards and regulations.
13) Supervise and train other technologists, technicians and drafters.
14) Write technical reports and draw charts that display statistics and data.
15) Use computer-aided drafting equipment and/or conventional drafting stations,
technical handbooks, tables, calculators, and traditional drafting tools such as
boards, pencils, protractors, and T-squares.
Job Duties and Tasks for: "Electrical Drafter"
4) 1) Assemble documentation packages and produce drawing sets which are then
checked by an engineer or an architect.
2) Confer with engineering staff and other personnel to resolve problems.
3) Draft working drawings, wiring diagrams, wiring connection specifications or
cross-sections of underground cables, as required for instructions to installation
crew.
4) Draw master sketches to scale showing relation of proposed installations to
existing facilities and exact specifications and dimensions.
5) Measure factors that affect installation and arrangement of equipment, such as
distances to be spanned by wire and cable.
6) Study work order requests to determine type of service, such as lighting or
power, demanded by installation.
5) 7) Visit proposed installation sites and draw rough sketches of location.
8) Determine the order of work and the method of presentation, such as
orthographic or isometric drawing.
9) Explain drawings to production or construction teams and provide adjustments
as necessary
6) 10) Prepare and interpret specifications, calculating weights, volumes, and stress
factors.
11) Reproduce working drawings on copy machines or trace drawings in ink.
12) Review completed construction drawings and cost estimates for accuracy
and conformity to standards and regulations.
13) Supervise and train other technologists, technicians and drafters.
14) Write technical reports and draw charts that display statistics and data.
15) Use computer-aided drafting equipment and/or conventional drafting stations,
technical handbooks, tables, calculators, and traditional drafting tools such as
boards, pencils, protractors, and T-squares.
1)
Getting Information -- Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining
information from all relevant sources.
2) Drafting, Laying Out, and Specifying Technical Devices, Parts, and
Equipment -- Providing documentation, detailed instructions, drawings, or
specifications to tell others about how devices, parts, equipment, or structures
are to be fabricated, constructed, assembled, modified, maintained, or used.
3) Inspecting Equipment, Structures, or Material -- Inspecting equipment,
structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or
defects.
4) Estimating the Quantifiable Characteristics of Products, Events, or
Information -- Estimating sizes, distances, and quantities; or determining
time, costs, resources, or materials needed to perform a work activity.
5) Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards -Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether
events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
6) Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events -- Identifying information by
categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting
changes in circumstances or events.
2)
) Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events -- Identifying information by
categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting
changes in circumstances or events.
7) Documenting/Recording Information -- Entering, transcribing, recording,
storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic form.
8) Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates -- Providing
information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in
written form, e-mail, or in person.
9) Making Decisions and Solving Problems -- Analyzing information and
evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
10) Handling and Moving Objects -- Using hands and arms in handling,
installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things.
11) Analyzing Data or Information -- Identifying the underlying principles,
reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into
separate parts.
Skills Needed for: "Electrical Drafter"
7) 1) Mathematics -- Using mathematics to solve problems.
2) Operations Analysis -- Analyzing needs and product requirements to create a
design.
3) Equipment Selection -- Determining the kind of tools and equipment needed
to do a job.
4) Judgment and Decision Making-- Considering the relative costs and benefits
of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
5) Reading Comprehension -- Understanding written sentences and paragraphs
in work related documents.
6) Complex Problem Solving -- Identifying complex problems and reviewing
related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
7) Critical Thinking -- Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and
weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
8) Quality Control Analysis -- Conducting tests and inspections of products,
services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
9) Speaking -- Talking to others to convey information effectively.
10) Systems Evaluation -- Identifying measures or indicators of system
performance and the actions needed to improve or correct performance, relative
to the goals of the system.
11) Monitoring -- Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other
individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
12) Management of Personnel Resources -- Motivating, developing, and
directing people as they work, identifying the best people for the job.
13) Systems Analysis -- Determining how a system should work and how
changes in conditions, operations, and the environment will affect outcomes.
14) Writing -- Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs
of the audience.
15) Active Listening -- Giving full attention to what other people are saying,
taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as
appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
16) Coordination -- Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
17) Active Learning -- Understanding the implications of new information for
both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
18) Time Management -- Managing one's own time and the time of others.
19) Management of Financial Resources -- Determining how money will be
spent to get the work done, and accounting for these expenditures.
20) Management of Material Resources -- Obtaining and seeing to the
appropriate use of equipment, facilities, and materials needed to do certain work.
Abilities Needed for: "Electrical Drafter"
8) 1) Number Facility -- The ability to add, subtract, multiply, or divide quickly and
correctly.
2) Near Vision -- The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the
observer).
Knowledge, Experience, Education Required for: "Electrical
Drafter"
9) 1) Design -- Knowledge of design techniques, tools, and principles involved in
production of precision technical plans, blueprints, drawings, and models.
2) Engineering and Technology -- Knowledge of the practical application of
engineering science and technology. This includes applying principles,
techniques, procedures, and equipment to the design and production of various
goods and services.
3) Administration and Management-- Knowledge of business and management
principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources
modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people
and resources.
4) Mathematics -- Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus,
statistics, and their applications.
5) Building and Construction -- Knowledge of materials, methods, and the tools
involved in the construction or repair of houses, buildings, or other structures
such as highways and roads.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Car Electrical SystemsDocument10 pagesCar Electrical SystemsIvar Nilasta100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Basics of Engineering DrawingDocument23 pagesBasics of Engineering DrawingKamal Uddin100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Understanding Working DrawingDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Working DrawinghanihusainiNo ratings yet
- TD SBA Guide BookletDocument62 pagesTD SBA Guide BookletBIANCA IRVINGNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Engineering Drawing Abbreviations and SymbolsDocument18 pagesEngineering Drawing Abbreviations and SymbolsDhinesh Kumar R (Baju)No ratings yet
- Microstation V8 - Accu Draw BasicsDocument80 pagesMicrostation V8 - Accu Draw BasicsEschtzNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Blueprint Reading NAVEDTRA 14040 1994Document200 pagesBlueprint Reading NAVEDTRA 14040 1994dawnk31297% (39)
- Star Delta DiagramDocument2 pagesStar Delta Diagramgarv84090% (10)
- Star Delta DiagramDocument2 pagesStar Delta Diagramgarv84090% (10)
- As 1100.201-1992 Technical Drawing Mechanical Engineering DrawingDocument8 pagesAs 1100.201-1992 Technical Drawing Mechanical Engineering DrawingSAI Global - APAC0% (2)
- Electric Thump RuleDocument3 pagesElectric Thump RuleAnwar Pariyarath100% (1)
- Fundamentals of GD&TDocument7 pagesFundamentals of GD&TPalani TrainerNo ratings yet
- Service, Feeders, Standby Systems Required Lighting OutletsDocument1 pageService, Feeders, Standby Systems Required Lighting OutletsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Piping Coordination SystemsDocument38 pagesPiping Coordination SystemsSathiyaseelan Sakthi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Lux Level Standards List by AreaDocument1 pageLux Level Standards List by AreaIvar Nilasta0% (1)
- Engineering Drawing 1st Sem FinalDocument122 pagesEngineering Drawing 1st Sem FinalGopal LoharNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing PDFDocument173 pagesEngineering Drawing PDFWiseman SiriroNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - Units of MeasurementDocument5 pagesWork Sheet - Units of MeasurementIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Prerequisites To Learn Selenium: I) Software Testing FundamentalsDocument10 pagesPrerequisites To Learn Selenium: I) Software Testing FundamentalsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Selenium Intrview QuestionsDocument3 pagesSelenium Intrview QuestionsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- TIASA - Thermal Insulation HandbookDocument58 pagesTIASA - Thermal Insulation HandbookSirGawain99No ratings yet
- Names For Dispaly Board in WorkshopDocument16 pagesNames For Dispaly Board in WorkshopIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- DOL Starter: Plastic Enclosure To IP65 IEC947-4-1 Issue 1 Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesDOL Starter: Plastic Enclosure To IP65 IEC947-4-1 Issue 1 Installation InstructionsRam KuthrapaliNo ratings yet
- EAL All Units Guided HourssDocument12 pagesEAL All Units Guided HourssIvar Nilasta0% (2)
- WiringsDocument1 pageWiringsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Types of Screws and Nuts Used For Wiring InstallationsDocument1 pageTypes of Screws and Nuts Used For Wiring InstallationsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- A. Match The Following Words.: Worksheet No: 11Document2 pagesA. Match The Following Words.: Worksheet No: 11Ivar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Question WordsDocument1 pageQuestion WordsANDREWEARNo ratings yet
- 50 Lux. Additional Lighting Equipment Is Often Necessary To Compensate The Low LevelsDocument2 pages50 Lux. Additional Lighting Equipment Is Often Necessary To Compensate The Low LevelsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Year 2018 Calendar - OmanDocument1 pageYear 2018 Calendar - OmanIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- ETAP System Requirements PDFDocument1 pageETAP System Requirements PDFIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- IBPS Prelims Mock Test Numerical Ability QuestionsDocument2 pagesIBPS Prelims Mock Test Numerical Ability QuestionsIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument22 pagesCathodic ProtectionFakhr-e-Alam100% (1)
- ELCBDocument8 pagesELCBIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Project On WaterDocument3 pagesProject On WaterIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety PDFDocument12 pagesFunctional Safety PDFGabriel BolatitoNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument8 pagesTensesIvar Nilasta100% (1)
- Machines Lab Sample Details PDFDocument9 pagesMachines Lab Sample Details PDFIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Fuse Box Rating ChartDocument2 pagesFuse Box Rating ChartIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Fuse Box Rating ChartDocument2 pagesFuse Box Rating ChartIvar NilastaNo ratings yet
- Ie 1 1 PDFDocument11 pagesIe 1 1 PDFNilesh AvhadNo ratings yet
- ECM415 Group Project Report and Presentation InstructionsDocument3 pagesECM415 Group Project Report and Presentation InstructionsdaniaNo ratings yet
- Lettering Techniques in DrawingDocument7 pagesLettering Techniques in DrawingASFNo ratings yet
- Simplification of Workshop Calculation & Science (WCS) and Engineering Drawing (ED) syllabus and merging with Trade TheoryDocument415 pagesSimplification of Workshop Calculation & Science (WCS) and Engineering Drawing (ED) syllabus and merging with Trade TheorySourav ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer Resume - 7+ Years ExperienceDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineer Resume - 7+ Years ExperienceMOHAMMAD ARSHAD ANSARINo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab 2023Document2 pagesOpen Ended Lab 2023Dragon Ball zNo ratings yet
- Learn Civil Engineering Drawings & GraphicsDocument3 pagesLearn Civil Engineering Drawings & Graphicskhan khanNo ratings yet
- CADCAM PortfolioDocument5 pagesCADCAM PortfolioGuhan MNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design Standard: Document Number: EDS 00-0001 Date: 10/07/2012Document27 pagesEngineering Design Standard: Document Number: EDS 00-0001 Date: 10/07/2012sebipaNo ratings yet
- CAD LAB - FinalDocument28 pagesCAD LAB - FinalgocoolonNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument99 pagesEngineering DrawingBinu ChandranNo ratings yet
- ECE 2101 ENGINEERING DRAWING II NotesDocument7 pagesECE 2101 ENGINEERING DRAWING II NotesJohn Ng'ang'aNo ratings yet
- EG Lecture 1Document21 pagesEG Lecture 1Avinash ShindeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Views & Basics Explained FractoryDocument15 pagesEngineering Drawing Views & Basics Explained FractoryParas GuptaNo ratings yet
- Entering Survey Data in AutoCAD using Lines, Curves and LinetypesDocument36 pagesEntering Survey Data in AutoCAD using Lines, Curves and LinetypesuntoniNo ratings yet
- @00 MenggambarTeknik - PengenalanDocument32 pages@00 MenggambarTeknik - PengenalanwidiNo ratings yet
- Piping Design & DraftingDocument2 pagesPiping Design & DraftingSuvidya Institute of TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Drafting ConventionsDocument20 pagesDrafting ConventionsmeNo ratings yet
- Drafting 9 - DimensioningDocument1 pageDrafting 9 - DimensioningHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet