Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Physiology
Uploaded by
anglogalibo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
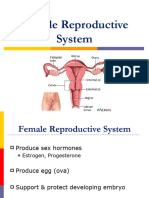
54 views2 pagesCervix is the lower narrower portion of the uterus. Fallopian tubes Extending upper part of Egg transportation from ovary to uterus. Canal about 10-8 cm long Provides the route for the menstrual blood (menses) from going from the cervice to the uterine wall, to leave the body.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCervix is the lower narrower portion of the uterus. Fallopian tubes Extending upper part of Egg transportation from ovary to uterus. Canal about 10-8 cm long Provides the route for the menstrual blood (menses) from going from the cervice to the uterine wall, to leave the body.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology
Uploaded by
anglogaliboCervix is the lower narrower portion of the uterus. Fallopian tubes Extending upper part of Egg transportation from ovary to uterus. Canal about 10-8 cm long Provides the route for the menstrual blood (menses) from going from the cervice to the uterine wall, to leave the body.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
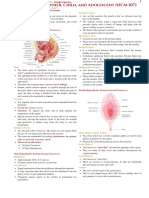
Anatomy and Physiology:
LOCATION &
STRUCTURE FUNCTION
DESCRIPTION
During childbirth, contractions of the uterus will dilate the
The lower narrower cervix up to 10 cm in diameter to allow the child to pass
Cervix
portion of the uterus. through. During orgasm, the cervix convulses and the
external is dilates
Extending upper part of Egg transportation from ovary to uterus (fertilization
Fallopian tubes
the uterus on either side. usually takes place here).
Provides an environment for maturation of oocyte.
Pelvic region on either
Ovaries (female gonads) Synthesizes and secretes sex hormones (estrogen and
side of the uterus.
progesterone).
Receives penis during mating. Pathway through a
woman’s body for the baby to take during childbirth.
Canal about 10-8 cm long
Provides the route for the menstrual blood (menses) from
Vagina going from the cervix to
the uterus, to leave the body. May hold forms of birth
the outside of the body.
control, such as an IUD, diaphragm, neva ring, or female
condom
Located in the center of
the pelvic cavity House and nourishes the fetus.
Uterus
The innermost layer of Contains glands that secrete fluids that bathe the uterine
Endometrium
uterine wall.Smooth lining.
Myometrium
muscle in the uterine Contract to help expel the baby.
Perimetrium
wall.Outer layer of the Covers the uterus
uterus
ESTROGEN
It is the most important hormone during puberty in female and is responsible
for secondary sexual characteristics (e.g. breast enlargement, menstruation, pelvic enlargement, long
bones). Generally secreted by the ovary specifically secreted by the Grafian follicle.
You might also like
- PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPhysiologyapi-19762967No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- Ana Physio ReprodDocument8 pagesAna Physio ReprodTeodoro Lemuel Ramos Gaela100% (1)
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Summary (Modifications) - AnasayaDocument15 pagesModule 8 Summary (Modifications) - Anasayafroosedd777No ratings yet
- OB CA2 ReviewerDocument34 pagesOB CA2 Reviewercresia hidalgoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Review of female reproductive anatomy and physiologyDocument8 pagesReview of female reproductive anatomy and physiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Topic 1 Normal ObDocument68 pagesReproductive System Topic 1 Normal ObNur-Sallah AbbasNo ratings yet
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002No ratings yet
- Biology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 7 Remediation Female Reporductive System Card SortDocument6 pagesBiology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 7 Remediation Female Reporductive System Card SortTeachTappyNo ratings yet
- Archive: Biology of Reproduction of GoatsDocument8 pagesArchive: Biology of Reproduction of GoatshassanNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Child Print 1-10Document11 pagesMaternity and Child Print 1-10ZYRHIL ANANONo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybadgurl08No ratings yet
- Part, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemDocument31 pagesPart, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemSavia NaldiNo ratings yet
- MORANDocument3 pagesMORANCubillas P. DerNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System FunctionsDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System FunctionsDoc_NeurologistNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System For ReviewerDocument50 pagesReproductive System For Reviewerzyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- Femalereproductivesystem 120329125448 Phpapp02Document18 pagesFemalereproductivesystem 120329125448 Phpapp02Crapster GamingNo ratings yet
- 2 The Reproductive SystemDocument122 pages2 The Reproductive SystemBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatNo ratings yet
- Gensic Reviewer2 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesGensic Reviewer2 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductionexplorers.beamaepetracortaNo ratings yet
- Female reproductive anatomy assignmentDocument8 pagesFemale reproductive anatomy assignmentDr. Mohammad JamaliNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive SystemDocument113 pagesQuarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive Systemsano.kthNo ratings yet
- MCN LEC (Prelims)Document19 pagesMCN LEC (Prelims)BIANCA ANGELICA GERARDONo ratings yet
- Gender & Sexuality AnatomyDocument27 pagesGender & Sexuality AnatomyÆRO YT CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Gender & Society Lo4Document6 pagesGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EDocument51 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EGwyneth100% (1)
- Aula 1 - Aparelho ReprodutorDocument35 pagesAula 1 - Aparelho ReprodutorLeticia MeirellesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesReproductive SystemDoc Zay VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Reproduction AnfismanDocument43 pagesReproduction AnfismanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System AnatomyDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive System AnatomyAldjen SetiasNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive Organs GuideDocument2 pagesMale and Female Reproductive Organs GuidePink EaintNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Female reproductive organs, menstrual cycles, and fertilization explainedDocument13 pagesFemale reproductive organs, menstrual cycles, and fertilization explainedNurinnisa ShiddiqiyahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemseongeokNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy PhysiologyRouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMDocument5 pagesREPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Discussion of The Diseases ProcessDocument4 pagesDiscussion of The Diseases ProcessMica CoveyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3melanielampera17No ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System OverviewDocument84 pagesFemale Reproductive System OverviewAtie IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- The female reproductive system explainedDocument3 pagesThe female reproductive system explainedAngie Sanchez-GalvezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemElla PaezNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- The uterus and its functionsDocument21 pagesThe uterus and its functionsdoreen03100% (1)
- PARTSDocument2 pagesPARTSMary joy DominguezNo ratings yet
- Bahan UASDocument4 pagesBahan UASislamiah sybNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesThe Female Reproductive SystemKhristin Joy GamponiaNo ratings yet
- Ana ReproDocument4 pagesAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinNo ratings yet
- Module 1..lesson 1,2&3Document26 pagesModule 1..lesson 1,2&3Carlyn100% (1)
- Maternal Lec Week 1 3Document4 pagesMaternal Lec Week 1 3Althea ManarpiisNo ratings yet
- 1 Grade 9 TerminologyDocument6 pages1 Grade 9 Terminologyhanbin kimNo ratings yet
- Organ Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraDocument5 pagesOrgan Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraNur AleahNo ratings yet
- Organ Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraDocument5 pagesOrgan Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraSabana MedtimbangNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gNo ratings yet
- List of Endocrine DiseasesDocument6 pagesList of Endocrine DiseasesPreethiHonavarNo ratings yet
- Human Rep - DPP 1 (2.0)Document42 pagesHuman Rep - DPP 1 (2.0)Upal PramanickNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing I Chap 1Document27 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing I Chap 1Rouwi DesiatcoNo ratings yet
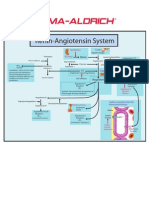
- Renin-Angiotensin SystemDocument1 pageRenin-Angiotensin SystemSigma-Aldrich100% (2)
- Disorders of Blood Pressure Regulation - 10Document31 pagesDisorders of Blood Pressure Regulation - 10Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Test and Its Effect On The Human BodyDocument4 pagesThyroid Stimulating Hormone Test and Its Effect On The Human BodyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- RAAS System and Drugs That Affect ItDocument22 pagesRAAS System and Drugs That Affect ItChandra pranataNo ratings yet
- Describing Skin LesionsDocument4 pagesDescribing Skin LesionsChris TayNo ratings yet
- Riwayat Pendidikan Riwayat PekerjaanDocument36 pagesRiwayat Pendidikan Riwayat PekerjaanRam PrototokonNo ratings yet
- Diagnose Pituitary Tumor with Acromegaly SymptomsDocument3 pagesDiagnose Pituitary Tumor with Acromegaly SymptomsMazin obeidNo ratings yet
- Penelitian Ilmiah: Pengaruh Konsumsi Jantung Pisang Terhadap Produksi Asi Pada Ibu NifasDocument9 pagesPenelitian Ilmiah: Pengaruh Konsumsi Jantung Pisang Terhadap Produksi Asi Pada Ibu Nifasima nurvita permatasariNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and RamadanDocument4 pagesDiabetes and Ramadan80082583No ratings yet
- 1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39Document94 pages1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39hamidNo ratings yet
- Matary MCQ 2011Document197 pagesMatary MCQ 2011Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (3)
- Vitamin D and Thyroid Test ResultsDocument4 pagesVitamin D and Thyroid Test ResultsEkta SinhaNo ratings yet
- My MCAT Bio NotesDocument14 pagesMy MCAT Bio NotesCarishma BudhuNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Metabolism: The Roles of Insulin and GlucagonDocument45 pagesHormones in Metabolism: The Roles of Insulin and GlucagonAciNo ratings yet
- 2 Nurfadilah 3Document9 pages2 Nurfadilah 3Khalid Hidayat Al IkhsanNo ratings yet
- A Case Discussion of Management of Primary Infertility Due To EndometriosisDocument35 pagesA Case Discussion of Management of Primary Infertility Due To EndometriosisVarsha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Effects of Aging in Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEffects of Aging in Endocrine Systemapi-3718174No ratings yet
- Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)Document19 pagesAndrogen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)arief206_eighteenNo ratings yet
- Glanela Manaloto: Clinical ChemistryDocument48 pagesGlanela Manaloto: Clinical ChemistryGlanela M. BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Ray Peat Various TopicsDocument4 pagesRay Peat Various TopicsTamaraBlickhan100% (3)
- 2007 Menstrual History QuestionnaireDocument2 pages2007 Menstrual History QuestionnaireAnonymous kieXEbsGeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Profile (Total T3, Total T4, TSH), Serum: EcliaDocument3 pagesThyroid Profile (Total T3, Total T4, TSH), Serum: EcliaRoopa gowdaNo ratings yet
- Care of A Child With Diabetes Mellitus: Guidelines For ParentsDocument12 pagesCare of A Child With Diabetes Mellitus: Guidelines For ParentsNivedita MishraNo ratings yet
- Demo DLLDocument4 pagesDemo DLLFlorenz AsiadoNo ratings yet
- AntaraDocument13 pagesAntaraDeepti KukretiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 7 Integumentary System and Body TemperatureDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Chapter 7 Integumentary System and Body Temperaturesann1992No ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Science 5 Quarter 2, Week 1: Parts of The Reproductive System and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesActivity Sheets in Science 5 Quarter 2, Week 1: Parts of The Reproductive System and Their Functionsricardo salayonNo ratings yet