Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Color
Uploaded by
David (Dave) MelsnessOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Color
Uploaded by
David (Dave) MelsnessCopyright:
Available Formats
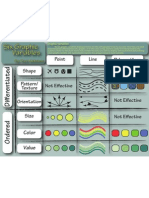
What is Color?
Color Design Issues:
Color Scheme Complimentary Colors Context
By: Dave Melsness Color Printing Color and Figure/Ground
Color Use in Cartography Hue:
RGB Color CMYK Color Color is our most important graphic
Wavelength of Light Emitted by a Color
Model Model variable. How it is used can sway thinking,
change actions and cause reactions. Physi-
cally, it can sooth or irritate ones eyes,
raise blood pressure, and suppress ones Value:
appetite. Amount of Black Contained in a Color
How cartographers use color can
help or hinder the messages, or themes of
their maps. For example, if a cartographer Low High
were to make a map of local businesses
Chroma:
RGB Colors are additive The CMYK colors are
colors, the model above subtractive colors. The Amount of White Contained in a Color
that are increasing their environmental
demonstrates how the model above demonstrates
three primary colors of how the use of cyan, awareness, or “going green,” would it not
red, green, and blue can be magenta, yellow, and the make sense to use more greens throughout
combined to create various “key” black are combined in the map than reds? Or how about making a Low High
other hues of the color the printing process to
spectrum. These are the create various other hues in politically themed map of the last U.S. Warm and Cool Color Spectrum
colors we see in projected, the color spectrum. These election, would it not be more appropriate
Cool Warm
visible light. are the colors commonly to use red, white, and blue than orange,
used in printing.
yellow, and pink? Through examples like
these color can help or hinder an
White Light is Dispursed by a Prism into the overall message of a map or graphic.
Colors of the Optical Spectrum
Color
Wavelength patterns
Color and physical
Wavelength colors, as specifications
represented in this prism figure of colors are determined
derived from the spectrum of by the object, material,
light, or the distribution of light light source, etc. perceived to have
energy versus wavelength, and color. The color it takes is based on its
how they interact in the eye physical properties of light absorption,
with the spectral sensitivi- reflection, or emission spectra. Color we see
ties of light receptors. comes from the visual range of the
(Continued on other electromagnetic radiation in the visible range,
Side) commonly referred to as light.
You might also like
- Colours Form An Integral Part of Our LivesDocument4 pagesColours Form An Integral Part of Our LivesIreneStampNo ratings yet
- Basics Design 05 Colour Sample Chapter Using ColourDocument34 pagesBasics Design 05 Colour Sample Chapter Using ColourAVAAcademia100% (1)
- 4.repetition, Rhythm & MovementDocument37 pages4.repetition, Rhythm & MovementKavya100% (1)
- The Evolution of Basic Color Terms in ChineseDocument47 pagesThe Evolution of Basic Color Terms in ChineseJianshe WuNo ratings yet
- Identity PaperDocument6 pagesIdentity PaperamygracelearyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Color For VisualizationDocument3 pagesIntro To Color For VisualizationBartholomew Wleh SNOH JRNo ratings yet
- Color in Cartographic Design 8Document11 pagesColor in Cartographic Design 8Jovial O'BrianNo ratings yet
- SelectiveDocument9 pagesSelectivehamza iliyasNo ratings yet
- Design Elements Color Fundamentals by Aaris SherinDocument161 pagesDesign Elements Color Fundamentals by Aaris Sherinpixeljoy100% (6)
- AGD Toolkit Summary Notes - Colour TheoryDocument28 pagesAGD Toolkit Summary Notes - Colour TheorybernbilazonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7sevenDocument21 pagesChapter 7sevenGalatom YadetaNo ratings yet
- Image ProcessingDocument49 pagesImage ProcessingJyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To ColourDocument8 pagesA Simple Guide To ColourMiguel A V FuscoNo ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument13 pagesColor Image ProcessingBrijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- HSI Color SpaceDocument13 pagesHSI Color Spacehuechhoac100% (3)
- 05 - Introduction To Digital Image ProcessingDocument14 pages05 - Introduction To Digital Image ProcessingSabinaNo ratings yet
- Gray To ColorDocument6 pagesGray To Colorvidi87No ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument17 pagesColor Image ProcessingShravani ChettineniNo ratings yet
- Art of Infographics 2015Document39 pagesArt of Infographics 2015Aline GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- What Is ColorDocument9 pagesWhat Is ColorPankon TharlayNo ratings yet
- Color Theory: Complementary ColorsDocument2 pagesColor Theory: Complementary ColorsShannara21No ratings yet
- Tekompres 10 - ColorDocument18 pagesTekompres 10 - ColorFahmi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Color Patterns PDFDocument58 pagesColor Patterns PDFMihir PantNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Color SystemDocument28 pagesLecture 8 Color SystemAbdelRahman MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Primary Colors of Light and Pigment - Learn.Document6 pagesPrimary Colors of Light and Pigment - Learn.munzirstudioNo ratings yet
- Senior ColorDocument28 pagesSenior ColorRaj GhimireNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Question & AnswersDocument13 pagesDigital Image Processing Question & AnswershemavathyrajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Q&ADocument13 pagesDigital Image Processing Q&AVENKATNo ratings yet
- Colors SudanDocument26 pagesColors SudanYousif ElgenaidNo ratings yet
- Color Theory Guide: RGB, CMYK, Psychology & UsesDocument12 pagesColor Theory Guide: RGB, CMYK, Psychology & UsesRachana GoliNo ratings yet
- Design Arcade Comp Game Graphics 07Document33 pagesDesign Arcade Comp Game Graphics 07acefogoNo ratings yet
- Id 121 Module 2 Lecture 1Document41 pagesId 121 Module 2 Lecture 1fernandezpetalsNo ratings yet
- Color SystemsDocument6 pagesColor Systemsbsnt.a7md23No ratings yet
- © UW CSE Vision FacultyDocument62 pages© UW CSE Vision FacultyDuong TheNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Colour SystemsDocument19 pagesLecture 4 Colour SystemsdaveNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Question & AnswersDocument13 pagesDigital Image Processing Question & AnswerstescopolitanNo ratings yet
- Map SymbolsDocument15 pagesMap Symbolsgreyproperties88No ratings yet
- Color and Shade Matching in Operative DentistryDocument19 pagesColor and Shade Matching in Operative DentistryMarco Antonio García LunaNo ratings yet
- Colour CommunicationDocument28 pagesColour CommunicationCamilo SieteNo ratings yet
- Frank Stella, Harran II 1967Document25 pagesFrank Stella, Harran II 1967Hoang Ngan TRUONGNo ratings yet
- ColorDocument20 pagesColorokuwobiNo ratings yet
- Design Elements, Color Fundamentals by Aaris SherinDocument161 pagesDesign Elements, Color Fundamentals by Aaris SherinBranko Erakovic97% (71)
- Chapter 6 Color Image ProcessingDocument66 pagesChapter 6 Color Image ProcessingShiladitya GangulyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Digital Image Pixels & File FormatsDocument15 pagesIntroduction to Digital Image Pixels & File FormatsClaudea Pramesdila MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Colour Composition PDFDocument16 pagesColour Composition PDFCATIA V5 TutorialNo ratings yet
- DipDocument4 pagesDipLekshmi Devi RanjithNo ratings yet
- CG - Chapter 6 Color ModelsDocument19 pagesCG - Chapter 6 Color Modelstyv89783No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Color Image ProcessingDocument105 pagesLecture 3 - Color Image ProcessingAgnish SahuNo ratings yet
- Color Us CMYK: How Color Is ProducedDocument4 pagesColor Us CMYK: How Color Is ProducedPaulílio Castello BrancoNo ratings yet
- Icastech 2009 5409700Document6 pagesIcastech 2009 5409700Suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Image Color Feature CH 01Document28 pagesImage Color Feature CH 01Syed Hasib1971 AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Color and QualityDocument98 pagesColor and Qualityremote1 onlineNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 5 FINAL FOR CLASS Color Image ProcessingDocument63 pagesCHAPTER - 5 FINAL FOR CLASS Color Image ProcessingSomeoneNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Digital Image ProcessingDocument13 pagesIntroduction to Digital Image ProcessingKarol SolarteNo ratings yet
- 1) Architectural Color: Red - Green - Blue (RGB)Document7 pages1) Architectural Color: Red - Green - Blue (RGB)Reanne James Sicena QuibralNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Graphics: BY Muhammad Omer KhanDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Computer Graphics: BY Muhammad Omer KhancyrutNo ratings yet
- Digital ImagesDocument17 pagesDigital Imagessreejesh_rsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Color Image ProcessingDocument36 pagesChapter 4. Color Image ProcessingMạc ĐềNo ratings yet
- Color LessonDocument16 pagesColor LessonKristalyn BurnsNo ratings yet
- Primary ColorsDocument10 pagesPrimary ColorsSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Inch Disk Sander PlansDocument3 pagesInch Disk Sander PlansDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- Short Analysis of "Letter From A Birmingham Jail"Document2 pagesShort Analysis of "Letter From A Birmingham Jail"David (Dave) Melsness67% (3)
- Oedipus Rex - The Tyrant Is The Child of PrideDocument3 pagesOedipus Rex - The Tyrant Is The Child of PrideDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- Themes of Innocence and Experience in - Kite RunnerDocument5 pagesThemes of Innocence and Experience in - Kite RunnerDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- Exporting Democracy: The American Control FreakDocument3 pagesExporting Democracy: The American Control FreakDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- Fall of Saigon: Dave MelsnessDocument18 pagesFall of Saigon: Dave MelsnessDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ConfederacyDocument1 pageContemporary ConfederacyDavid (Dave) Melsness100% (1)
- The Confederacy Today: Organizational Interpretations of Confederate Symbols and Diffusion of Southern HeritageDocument9 pagesThe Confederacy Today: Organizational Interpretations of Confederate Symbols and Diffusion of Southern HeritageDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- Six Graphic Variables of CartographyDocument1 pageSix Graphic Variables of CartographyDavid (Dave) MelsnessNo ratings yet
- To Call A Function From BI PublisherDocument6 pagesTo Call A Function From BI PublisherbalasukNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plans for Empowerment TechnologiesDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plans for Empowerment TechnologiesCharlon Mamacos100% (9)
- RSRed DS RS200L Mod v5Document2 pagesRSRed DS RS200L Mod v5liebherrmanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Excel Formulas and FunctionsDocument80 pagesAdvanced Excel Formulas and FunctionsSanjay MoreNo ratings yet
- Cdte Thin Film Solar Module: Original SizeDocument2 pagesCdte Thin Film Solar Module: Original SizeKirsten HernandezNo ratings yet
- Image Classification With The MNIST Dataset: ObjectivesDocument21 pagesImage Classification With The MNIST Dataset: ObjectivesPraveen SinghNo ratings yet
- Big Data Simplified: Book DescriptionDocument14 pagesBig Data Simplified: Book DescriptionN C NAGESH PRASAD KOTINo ratings yet
- End of Chapter 8 (p.606) Questions 1,2,4,8,14.: Short AnswerDocument4 pagesEnd of Chapter 8 (p.606) Questions 1,2,4,8,14.: Short AnswerTung VanNo ratings yet
- IPC-6012B Table of Contents: About 261,000 Results (0.47 Seconds)Document2 pagesIPC-6012B Table of Contents: About 261,000 Results (0.47 Seconds)Moganraj MunusamyNo ratings yet
- GR00005200D 13a PDFDocument187 pagesGR00005200D 13a PDFbitadminaccNo ratings yet
- Low Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFDocument1 pageLow Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFJuber ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Brksec-3005 (2017)Document100 pagesBrksec-3005 (2017)Paul ZetoNo ratings yet
- Sunnxt AppDocument8 pagesSunnxt ApppsiphoniphoneNo ratings yet
- Soltek SL 65meDocument88 pagesSoltek SL 65meBernardo AntunesNo ratings yet
- Ibm Websphere Application Server Advanced Edition, v3.5 - Websphere Jms - Jta Support For Mqseries (370K) WasDocument49 pagesIbm Websphere Application Server Advanced Edition, v3.5 - Websphere Jms - Jta Support For Mqseries (370K) Wasimene IBNo ratings yet
- Modulo 4Document2 pagesModulo 4Monii TranquinoNo ratings yet
- Intel Inside.Document25 pagesIntel Inside.Rashed550% (1)
- KC130GT 1Document2 pagesKC130GT 1aleenizzyNo ratings yet
- Java Placement QuestionsDocument23 pagesJava Placement QuestionsVidhya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Accounting 12 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesAccounting 12 Course OutlineKenrose LaguyoNo ratings yet
- Billing Invoice Payment PlanDocument7 pagesBilling Invoice Payment PlanyogeshNo ratings yet
- Astrological Cycle Based Models in Timing Solution PDFDocument9 pagesAstrological Cycle Based Models in Timing Solution PDFanalystbank100% (2)
- A Technical Seminar ReportDocument28 pagesA Technical Seminar Reportnishitha pachimatlaNo ratings yet
- Android Voting System Synopsis Under 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesAndroid Voting System Synopsis Under 40 CharactersShivshankar GuptaNo ratings yet
- CGI in Movies vs Video GamesDocument21 pagesCGI in Movies vs Video GamesAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Parametric Design Language Guide 18.2Document110 pagesANSYS Parametric Design Language Guide 18.2Panda HeroNo ratings yet
- Automata and ComputabilityDocument240 pagesAutomata and ComputabilitySupiyanto HasanNo ratings yet
- 3 Process Fundamentals Chapter 2 and 3Document74 pages3 Process Fundamentals Chapter 2 and 3Terry Conrad KingNo ratings yet
- Una Buena Configuracion de CmiDocument72 pagesUna Buena Configuracion de Cmivicente rojasNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics B.Tech I Year, I-Semester, I-Mid ExamDocument3 pagesApplied Physics B.Tech I Year, I-Semester, I-Mid Examsumaiyah syedNo ratings yet