Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
Krizia Tepoot0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views2 pagesRespiratory rate of 30 - dyspnea - alteration in depth of breathing - pursed lip breathing - restlessness - facial grimace Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective breathing pattern related to pain Planning Short term goal: After 12-24 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be free. After 7 days of nursing intervention patient maintained a patent airway.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRespiratory rate of 30 - dyspnea - alteration in depth of breathing - pursed lip breathing - restlessness - facial grimace Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective breathing pattern related to pain Planning Short term goal: After 12-24 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be free. After 7 days of nursing intervention patient maintained a patent airway.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views2 pagesNCP
Uploaded by
Krizia TepootRespiratory rate of 30 - dyspnea - alteration in depth of breathing - pursed lip breathing - restlessness - facial grimace Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective breathing pattern related to pain Planning Short term goal: After 12-24 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be free. After 7 days of nursing intervention patient maintained a patent airway.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
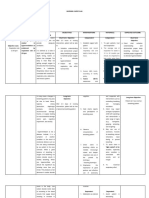
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: Ineffective breathing Short term goal: Independent: GOAL MET
pattern related to pain After 12-24 hours of
“Nahihirapan ako nursing intervention the 1. Identify etiology or Understanding the After 12-24 hours of
huminga kasi sumasakit patient will be free of precipitating factors. cause is necessary for nursing intervention the
sugat ko tuwing dyspnea choice of therapeutic patient was free of
humihinga ako” as measures. dyspnea
verbalized by the Long term goal:
patient. After 7 days of nursing 2. Monitor vital signs. After 7 days of nursing
intervention the patient Monitoring the vital intervention the patient
will maintain a patent signs is necessary to maintained a patent
Objective: airway evaluate the degree of airway
compromise.
- respiratory rate of 30 3. Assess lung sounds,
- dyspnea respiratory rate and
- alteration in depth of effort and the use of Respiratory rate less
breathing accessory muscles. than 12 or more than
- pursed lip breathing 24 or use of accessory
- restlessness muscles indicate
-facial grimace distress. Diminished
lung sounds indicate
possible poor air
movement and
4. Evaluate respiratory impaired gas exchange.
function, noting rapid or
shallow respirations,
dyspnea and changes in
vital signs. Respiratory distress and
changes in vital signs
occur as a result of
physiologic stress and
pain.
6. Encourage adequate
rest and limit activities
within client’s level of
tolerance. Promote a
calm and restful Helps limit oxygen
environment. needs and
consumption.
Dependent:
1. Administer
supplemental oxygen as
ordered by the
physician. Supplemental oxygen
decreases hypoxia.
2. Administer
medications as
prescribed by the
physician. To treat underlying
conditions.
You might also like
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMargaret ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRachelleNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Prioritization SignificanceDocument7 pagesVii. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Prioritization SignificanceMarichu Bajado0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Date Assessment Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Objectives Nursing Actions EvaluationDocument3 pagesDate Assessment Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Objectives Nursing Actions EvaluationJoyce Minerva Montero SamsonNo ratings yet
- Care of the Patient with Respiratory DisorderDocument1 pageCare of the Patient with Respiratory DisorderSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Task 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesTask 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTine SabaulanNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective ClearanceDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective ClearanceCynelle AguilonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangePrincess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- APOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)Document2 pagesAPOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)REYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pneumonia and HemorrhoidsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pneumonia and HemorrhoidsCharlene Grace ReginoNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Group 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalDocument59 pagesGroup 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalChristian Angelo LeonorNo ratings yet
- NCP (Case Pres)Document1 pageNCP (Case Pres)Flauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementwaadNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Patients with Uterine Fibroids and Acute Abdominal PainDocument10 pagesNursing Care for Patients with Uterine Fibroids and Acute Abdominal PainPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- Airway Clearance StrategiesDocument4 pagesAirway Clearance Strategiescammel ramos100% (1)
- CORPUZ QQQDocument3 pagesCORPUZ QQQRomm JacobNo ratings yet
- Lumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsDocument4 pagesLumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsPatricia Ortega100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- NCP MiniparDocument9 pagesNCP MiniparKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- "She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byDocument2 pages"She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaKerks Von Gladiel NapaoNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument6 pagesCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErica Denice CastilloNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing DiagnosisLovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- LORMA COLLEGES NURSING CARE PLAN FOR PEDIATRIC ASTHMADocument6 pagesLORMA COLLEGES NURSING CARE PLAN FOR PEDIATRIC ASTHMAPauline GarciaNo ratings yet
- Careplan 1Document11 pagesCareplan 1ligaba1559No ratings yet
- Gr.4 NCP Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesGr.4 NCP Health AssessmentAlessandro MadrigalNo ratings yet
- NCP For HemothoraxDocument12 pagesNCP For HemothoraxroseonabreezeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Record for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Process Record for Ineffective Breathing PatternTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- NCP Aryam HussienDocument1 pageNCP Aryam Hussienaarm22340No ratings yet
- NCP (Icu)Document2 pagesNCP (Icu)jessie_nuñez_263% (8)
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- DULNUANDocument2 pagesDULNUANJB tindonganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGeraldine SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermDocument7 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Performance Task # 9Document6 pagesPerformance Task # 9Aileen Reign MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis PneumoniaDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis PneumoniaPasa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluations Subjective Data: "I HaveDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluations Subjective Data: "I HaveRicha AcharyaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Decoding Meditation Backed By Science - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Understanding The Inner Workings Of Meditation For Lasting BenefitsFrom EverandDecoding Meditation Backed By Science - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Understanding The Inner Workings Of Meditation For Lasting BenefitsNo ratings yet
- Reflexology: The Definitive Practitioner's Manual: Recommended by the International Therapy Examination Council for Students and PractitonersFrom EverandReflexology: The Definitive Practitioner's Manual: Recommended by the International Therapy Examination Council for Students and PractitonersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Art and Practice of Hypnotic Induction: Favorite Methods of Master Clinicians: Voices of Experience, #1From EverandThe Art and Practice of Hypnotic Induction: Favorite Methods of Master Clinicians: Voices of Experience, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Drug ActDocument2 pagesDrug ActKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Endorsement SheetDocument1 pageEndorsement SheetKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument4 pagesLung CancerKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- DisorderDocument2 pagesDisorderKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Chicago Tribune-26AprDocument37 pagesChicago Tribune-26AprvnaliniNo ratings yet
- Ruhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDocument13 pagesRuhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Facebook Use Across GenerationsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Facebook Use Across GenerationsOscar Iván Negrete RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Crystal Meth AddictionDocument356 pagesOvercoming Crystal Meth AddictionSarah Menz100% (2)
- Case Study - Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesCase Study - Ectopic Pregnancykristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument23 pagesJob Analysispprashant7No ratings yet
- Gulfco 1049 MaxDocument5 pagesGulfco 1049 MaxOm Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry, Psychology and LawDocument28 pagesPsychiatry, Psychology and LawDaimon MichikoNo ratings yet
- ReDoc Sample SLP Reports PedsDocument16 pagesReDoc Sample SLP Reports PedsXlian Myzter YosaNo ratings yet
- B2 Reading TestDocument1 pageB2 Reading TestKrisztina KatyinaNo ratings yet
- VAED 1 Person-hood DevelopmentDocument4 pagesVAED 1 Person-hood DevelopmentAlbert Magno Caoile0% (1)
- Product Release Procedures: Batch Records andDocument3 pagesProduct Release Procedures: Batch Records andNafi Hasan ZahidNo ratings yet
- English in Nursing 1: Novi Noverawati, M.PDDocument11 pagesEnglish in Nursing 1: Novi Noverawati, M.PDRachellNo ratings yet
- Insights Regarding Personality Development Among 1st-Year Graduate Nursing Students - A Structured Education ProtocolDocument8 pagesInsights Regarding Personality Development Among 1st-Year Graduate Nursing Students - A Structured Education ProtocolIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- A History of The Early Days of Personality Testing in American Industry PDFDocument21 pagesA History of The Early Days of Personality Testing in American Industry PDFFernandoLacerdaNo ratings yet
- A4 Quantitative Study of Acceptability of Coconut CHPTR 1&2Document16 pagesA4 Quantitative Study of Acceptability of Coconut CHPTR 1&2Adiyan100% (2)
- Gensoc ReviewDocument6 pagesGensoc Reviewbernadeth magtibayNo ratings yet
- The Prehospital Management of Hypothermia - An Up-To-DateDocument16 pagesThe Prehospital Management of Hypothermia - An Up-To-DateGio VandaNo ratings yet
- DiagnosticsDocument38 pagesDiagnosticssweetyxocolatNo ratings yet
- Ijone Oct Dec 2019Document216 pagesIjone Oct Dec 2019chimmynyahNo ratings yet
- Banner HealthcareDocument6 pagesBanner HealthcareValNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS RESEARCH - PROBLEMS AND PRECAUTIONS TO THE RESEARCHER - Report by LEDocument16 pagesBUSINESS RESEARCH - PROBLEMS AND PRECAUTIONS TO THE RESEARCHER - Report by LEJovin Paul LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Research 1: Prof. Leilany Q. Ursua, RSWDocument47 pagesResearch 1: Prof. Leilany Q. Ursua, RSWJe CoNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 PetaDocument1 pagePe 1 PetaAinsley Martin VidadNo ratings yet
- MIT CSAIL Human Computer Interaction For User Experience Design Online Short CourseDocument10 pagesMIT CSAIL Human Computer Interaction For User Experience Design Online Short CoursePadma PGNo ratings yet
- 6 Surrogate MotherhoodDocument19 pages6 Surrogate Motherhoodreggie meolloNo ratings yet
- LGBTQ Students Inclusion and SafetyDocument11 pagesLGBTQ Students Inclusion and Safetyapi-610179160No ratings yet
- Meridian Educational Institution IncDocument33 pagesMeridian Educational Institution IncChristine Joyce MagoteNo ratings yet
- A Basic Breathing TechniqueDocument6 pagesA Basic Breathing TechniqueFebbe Nadia Okky LucianaNo ratings yet
- Change Readiness - Focusing Change Management Where It CountsDocument28 pagesChange Readiness - Focusing Change Management Where It CountsSergio RosaLopes DutraNo ratings yet