Professional Documents
Culture Documents
American Federalism: Dividing Government Power
Uploaded by
trendwatcher140 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views8 pagesFederalism divides power between the national and state governments, allowing both to enact laws and govern within their own jurisdictions. The founding fathers believed this system would best protect liberty and disperse power to prevent the majority from dominating the minority. Over time, the balance of power between the national and state governments has shifted, with periods of more state-centered and centralized federalism. Today, both governments continue to share power while preemption and mandates influence their relationship.
Original Description:
Original Title
Federalism
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFederalism divides power between the national and state governments, allowing both to enact laws and govern within their own jurisdictions. The founding fathers believed this system would best protect liberty and disperse power to prevent the majority from dominating the minority. Over time, the balance of power between the national and state governments has shifted, with periods of more state-centered and centralized federalism. Today, both governments continue to share power while preemption and mandates influence their relationship.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views8 pagesAmerican Federalism: Dividing Government Power
Uploaded by
trendwatcher14Federalism divides power between the national and state governments, allowing both to enact laws and govern within their own jurisdictions. The founding fathers believed this system would best protect liberty and disperse power to prevent the majority from dominating the minority. Over time, the balance of power between the national and state governments has shifted, with periods of more state-centered and centralized federalism. Today, both governments continue to share power while preemption and mandates influence their relationship.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
American Federalism
Dividing Government Power
What is Federalism?
• Divides power between two separate
authorities: the national government and
the states.
– Both authorities enforce their own laws,
impose taxes, spend money, and maintain
their own courts.
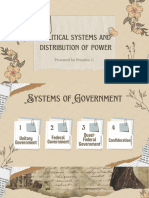
How is a Federal System Different?
• Unitary Systems
• Confederations
• Intergovernmental Relations
Why Federalism?
• The founding fathers wanted to protect the
minority from the majority.
• They believed that a federalist system
would better protect liberty, disperse
power, and manage factions.
• How does federalism protect liberty?
Features of Federalism
• Dispersal of Federal Power
• Increased Participation
• Policy Diversity
• Improved Efficiency
• Encourages Policy Responsiveness
• Encourages Policy Innovation
• Manages Conflict
The Original Design for Federalism
• Delegated Powers
• The National Supremacy Clause
• Concurrent and Reserved Powers
• Powers Denied to the States
• Powers Denied to both the states and the
national government
• The state’s obligation to each other
The Evolution of Federalism
• State-Centered Federalism: 1787-1868
• Dual Federalism: 1868-1913
• Cooperative Federalism: 1913-1964
• Centralized Federalism: 1964-1980
• New Federalism: 1980-1985
• Representational Federalism: 1985-1995
• Federalism Revived?
Federal Power Today
• Preemption
• Federal Mandates
You might also like
- CH 1 Principals of GovernmentDocument18 pagesCH 1 Principals of GovernmentJoseph WelockNo ratings yet
- Federalism 101Document13 pagesFederalism 101Murphy RedNo ratings yet
- In Search of A Federal Philippines - Dr. Clarita CarlosDocument61 pagesIn Search of A Federal Philippines - Dr. Clarita CarlosJennyfer Narciso MalobagoNo ratings yet
- Fedralism TarikuDocument41 pagesFedralism TarikuAmsalu BelayNo ratings yet
- Federalism Political SystemDocument17 pagesFederalism Political SystemArtiNo ratings yet
- Defining Federalism, ch03Document52 pagesDefining Federalism, ch03Murphy RedNo ratings yet
- Federalism: Federal, State and Local GovernmentDocument42 pagesFederalism: Federal, State and Local Governmentmaria sabirNo ratings yet
- Federalism: The Federal Government Did Not Create The States The States Created The Federal GovernmentDocument24 pagesFederalism: The Federal Government Did Not Create The States The States Created The Federal GovernmentRachel ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Defining Federalism, Ch03Document52 pagesDefining Federalism, Ch03lakanbastoneroNo ratings yet
- Constitution Notes Student 1Document14 pagesConstitution Notes Student 1iownu2beNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4api-262327064No ratings yet
- Federalism: Peter G. DoasDocument47 pagesFederalism: Peter G. DoasbmailNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Constitutional Underpinnings: FederalismDocument84 pagesUnit I - Constitutional Underpinnings: FederalismAA DR NNNo ratings yet
- Govch1notes 2Document4 pagesGovch1notes 2api-211765495No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 FederalisimDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Federalisimmohanshafi2000No ratings yet
- The Constitutional Framework of US GovernmentDocument24 pagesThe Constitutional Framework of US GovernmentWilliam Stark100% (1)
- Consti Law NotesDocument72 pagesConsti Law Notesmeranaamshankar786No ratings yet
- 524 Lecture 3 Forms of Federalism 2013 PDFDocument39 pages524 Lecture 3 Forms of Federalism 2013 PDFBrhane TeklayNo ratings yet
- United States Government and PoliticsDocument21 pagesUnited States Government and PoliticsTony BuiNo ratings yet
- AP NSL Study GuideDocument26 pagesAP NSL Study GuideThe Wh4TNo ratings yet
- Federalism AbrhamDocument275 pagesFederalism Abrhamyonas wonNo ratings yet
- Political Systems and Distribution of PowerDocument19 pagesPolitical Systems and Distribution of PowerCharmaine PenadosNo ratings yet
- Nature of ConstitutionDocument16 pagesNature of ConstitutionRoshan NazarethNo ratings yet
- MerajDocument16 pagesMerajmuzzumeraj490No ratings yet
- Reported By: Irah Mae E. CustodioDocument30 pagesReported By: Irah Mae E. CustodioIrah Mae Escaro CustodioNo ratings yet
- National DifferencesDocument49 pagesNational Differencesfarika aisya ningrumNo ratings yet
- PBL200 Notes (Chapter 2) 2Document11 pagesPBL200 Notes (Chapter 2) 2Ntyatyambozomzi YawaNo ratings yet
- Wepeopc14 LPPT ch03Document73 pagesWepeopc14 LPPT ch03johndavidgrangerNo ratings yet
- Federalist PapersDocument26 pagesFederalist Papersapi-261609166No ratings yet
- Understanding Federalism Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Federalism Advantages and DisadvantagesPhilip Jude AcidreNo ratings yet
- US ConstitutionDocument21 pagesUS ConstitutionAnasteishaNo ratings yet
- Iraq 0807 Federalism EngDocument11 pagesIraq 0807 Federalism EngAdreanah Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- AP US Gov - Chapter 3 NotesDocument9 pagesAP US Gov - Chapter 3 NotesphthysyllysmNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument19 pagesFederalismAditya BordoloiNo ratings yet
- Federalism: Federal, State and Local GovernmentDocument13 pagesFederalism: Federal, State and Local GovernmentAkil Adith A.MNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Federalism JcaDocument43 pagesPresentation On Federalism JcaJoselito AlisuagNo ratings yet
- Federalism and NationalismDocument5 pagesFederalism and NationalismHykouhi TergevorkianNo ratings yet
- Civic Chapter 4Document56 pagesCivic Chapter 4babyteshome1No ratings yet
- Government Eoc Test ReviewDocument53 pagesGovernment Eoc Test Reviewapi-326796190No ratings yet
- Mid-Term Exam Review PhilosophersDocument9 pagesMid-Term Exam Review Philosophersapi-130087742No ratings yet
- CH 2Document27 pagesCH 2hamidNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four State, Government & Citizenship Prepared by Befekadu DhabaDocument18 pagesChapter Four State, Government & Citizenship Prepared by Befekadu DhabaNigus SolomonNo ratings yet
- Introdcn To Political Science2009 (Compatibility Mode)Document53 pagesIntrodcn To Political Science2009 (Compatibility Mode)bsoc-gen-33-22No ratings yet
- Federalism Amsco Shari SchmidtDocument28 pagesFederalism Amsco Shari SchmidtRachel ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Legal Systems and Legal Methods 3Document25 pagesLegal Systems and Legal Methods 3onokaanne9No ratings yet
- .Document6 pages.Anup KumarNo ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument54 pagesEssential Questionsapi-328120679No ratings yet
- Federalism Part I (Ch1-6) General PartDocument143 pagesFederalism Part I (Ch1-6) General PartGammachiis QaddiimNo ratings yet
- Nation and State Note S 2021Document5 pagesNation and State Note S 2021mayank aryaNo ratings yet
- Federalism: Federal, State and Local GovernmentDocument32 pagesFederalism: Federal, State and Local GovernmentsouminidharNo ratings yet
- Anti FederalistsvsfederalistsDocument23 pagesAnti Federalistsvsfederalistsapi-262527276No ratings yet
- Political and Leadership StructuresDocument35 pagesPolitical and Leadership StructuresChain HabanaNo ratings yet
- Politics and The State: Pol 100: Session 4 by Rida AshfaqDocument16 pagesPolitics and The State: Pol 100: Session 4 by Rida AshfaqUshna hamidNo ratings yet
- Political EconomyDocument25 pagesPolitical EconomyMrigendra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Period 3 MidtermreviewDocument9 pagesPeriod 3 Midtermreviewapi-130087742No ratings yet
- Contempo Chapter 3 Political Dimension of GlobalizationDocument22 pagesContempo Chapter 3 Political Dimension of GlobalizationKate Crystel reyesNo ratings yet
- Federal State and Local GovernmentsDocument10 pagesFederal State and Local Governmentsapi-267310659No ratings yet
- Concepts and Problems of Comparative PoliticsDocument24 pagesConcepts and Problems of Comparative PoliticsPriya MathurNo ratings yet
- The Constitution Needs a Good Party: Good Government Comes from Good BoundariesFrom EverandThe Constitution Needs a Good Party: Good Government Comes from Good BoundariesNo ratings yet