Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)
Uploaded by
julesubayubay542876%(25)76% found this document useful (25 votes)
39K views1 pageLoop diuretics increase the rate of delivery of tubular fluid and electrolytes to the distal sites of hydrogen and potassium ion secretion. Jaundice, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), sensitivity to light (photophobia), rash, pancreatitis, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and dizziness.
Original Description:
Original Title
DRUG STUDY_furosemide (Lasix)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLoop diuretics increase the rate of delivery of tubular fluid and electrolytes to the distal sites of hydrogen and potassium ion secretion. Jaundice, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), sensitivity to light (photophobia), rash, pancreatitis, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and dizziness.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
76%(25)76% found this document useful (25 votes)
39K views1 pageDRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)
Uploaded by
julesubayubay5428Loop diuretics increase the rate of delivery of tubular fluid and electrolytes to the distal sites of hydrogen and potassium ion secretion. Jaundice, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), sensitivity to light (photophobia), rash, pancreatitis, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and dizziness.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
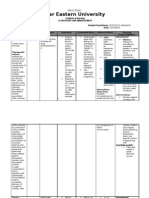
DRUG STUDY
Medical Diagnosis: hydrocephalus, status post- shunt insertion
Category:
Indication/ Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Nursing Considerations
Contraindication Adverse Effects
INDICATIONS: Inhibit reabsorption of low blood Assess patient’s nderlying
Generic Name: Edema due to cardiac, sodium and water in the pressure, condition before starting
furosemide hepatic & renal disease, ascending limb of the dehydration and theraphy.
burns; mild to moderate loop of Henle by electrolyte Monitor for renal
Brand Name: HTN, hypertensive interfering with the depletion (for cardiac,neurologic, GI
Lasix crisis, acute heart failure, chloride binding site of example, sodium, manifestations of
reduced urinary output the 1Na+, 1K+, 2Cl- potassium). hypokalemia.
Classification: due to gestoses, chronic cotransport system. jaundice, Monitor for CNS, GI,
Diuretics renal failure, nephrotic Loop diuretics increase ringing in the ears cardiovascular,
syndrome. the rate of delivery of (tinnitus), integumentarym
Dosage: tubular fluid and sensitivity to light neurologic manifestations
5mg(0.5ml) CONTRADICTIONS: electrolytes to the distal (photophobia), of jypocalcemia,
Anuria; hepatic coma & sites of hydrogen and rash, Monitor for CNS,
Frequency: precoma; severe potassium ion secretion, hyperactive reflexes,
pancreatitis,
Every 12 hours. Hold for hypokalemia &/or while plasma volume depressed cardiac
nausea,
BP less than 85 systolic hyponatremia; contraction increases output,nausea, vomiting,
aldosterone production. diarrhea,
hypovolemia w/ or w/o tachycardia
Route: The increased delivery abdominal pain,
hypotension. Assess fluid volume
IV Push and high aldosterone and dizziness.
Hypersensitivity to status(urine,color, quality
levels promote sodium Increased blood
sulfonamides. and specific gravity)
reabsorption at the distal sugar and uric
acid levels Assess patient tinnitus, or
tubules, thus increasing pain
the loss of potassium
and hydrogen ions.
You might also like
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LanoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LanoxinClariss Alota67% (3)
- Amiodarone (Cordarone)Document1 pageAmiodarone (Cordarone)jaybamanNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- Drug Study NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesDrug Study NorepinephrinePearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Furosemide Drug SyudyDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug SyudyallenininiNo ratings yet
- Diltiazem CardizemDocument2 pagesDiltiazem CardizemLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Dopamine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDopamine Drug StudyKwin Saludares100% (1)
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaronePauling Frez100% (5)
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar Izzo100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - Sodium BicarbonateDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - Sodium Bicarbonatejulesubayubay54280% (1)
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneMarianne Claire P. Bartolome50% (2)
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ClopidogrelDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Clopidogrelryan100% (1)
- Epoetin AlfaDocument2 pagesEpoetin AlfaKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin CalciumDocument1 pageAtorvastatin CalciumRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocument2 pagesDrug Study PantoprazoleFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyIsagani Socrates Loreto100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument3 pagesClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Drug Study Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study Calcium GluconateLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil DSDocument6 pagesPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument10 pagesWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- School Nursing Common DRUG STUDYDocument10 pagesSchool Nursing Common DRUG STUDYMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- K PotaDocument2 pagesK PotaJustine May GervacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Dexamethasoneamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- NebivololDocument2 pagesNebivololSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Sodium Bicarbonatejepong_paolo0283% (6)
- Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDopamine HCLianecunarNo ratings yet
- Furosemide (Diumide-K) Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide (Diumide-K) Drug StudyMariella Saavedra Aranda CercadoNo ratings yet
- Carvedilol Drug Name Classifications Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesCarvedilol Drug Name Classifications Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsClaudette Sanvictores0% (1)
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBenazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug Study - NitroglycerinDocument1 pageDrug Study - Nitroglycerinchriscustodio100% (1)
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument7 pagesInsulin Drug StudyKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDocument3 pagesArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- MetoprololDocument1 pageMetoprololjchowking100% (1)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug Studymilkv100% (12)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateRye AnchNo ratings yet
- DobutamineDocument2 pagesDobutamineJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNorepinephrine Drug StudyYou know who100% (9)
- Dobutamine Drug StudyDocument1 pageDobutamine Drug Studyzyr2189100% (2)
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium BicarbonateDocument5 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium BicarbonatehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- APIXABAN Drug Study FormatDocument1 pageAPIXABAN Drug Study FormatKristinelou Marie ReynaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (1)
- LactuloseDocument2 pagesLactuloseGrace Iloreta RN82% (11)
- DRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classifications: DoseDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classifications: DoseRAFNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document3 pagesDrug Study 1G4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- AV Fistula StudyDocument6 pagesAV Fistula Studyjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Summary of Nursing TheoriesDocument6 pagesSummary of Nursing Theoriesjulesubayubay5428100% (8)
- Summary of Key BLS Components For Adults Children and InfantDocument26 pagesSummary of Key BLS Components For Adults Children and Infantjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Autonomic Dysreflexia in Spinal Cord InjuryDocument5 pagesAutonomic Dysreflexia in Spinal Cord Injuryjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes PediaDocument10 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Pediajulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Cardiac Pump DisorderDocument9 pagesCardiac Pump Disorderjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Hematologic DisorderDocument16 pagesHematologic Disorderjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Japanese Occupation of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesJapanese Occupation of The Philippinesare_you_peopleNo ratings yet
- Job Descriptions of Nurse ManagersDocument8 pagesJob Descriptions of Nurse Managersjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Introduction and Precolonial Phil HistoryDocument17 pagesIntroduction and Precolonial Phil Historyjulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Timeline of Spanish Colonization of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesTimeline of Spanish Colonization of The Philippinesjulesubayubay542894% (36)
- American Period in PhilDocument23 pagesAmerican Period in Philjulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomyjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Injections WordDocument18 pagesInjections Wordjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Poison Control and Other Safety MeasuresDocument6 pagesPoison Control and Other Safety Measuresjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- NCM 105 Psych NursingDocument5 pagesNCM 105 Psych Nursingjulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Phil Health RevisedDocument16 pagesPhil Health Revisedjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Listening TechniquesDocument1 pageListening Techniquesjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Immediate Care of The Preterm InfantDocument6 pagesImmediate Care of The Preterm Infantjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument4 pagesNursing Informaticsjulesubayubay5428100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Amoxicillinjulesubayubay542886% (14)
- Development Stage of HumanDocument9 pagesDevelopment Stage of Humanjulesubayubay5428100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY PsycheDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Psychejulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Drug Study PediaDocument5 pagesDrug Study Pediajulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LidocaineDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Lidocainejulesubayubay542860% (5)
- Drug Study (Alnix)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Alnix)julesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument2 pagesDrug Study Nurseryjulesubayubay54280% (1)
- DRUG STUDY of Myo With Right Oopho 03Document44 pagesDRUG STUDY of Myo With Right Oopho 03julesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Drug Study 6th FloorDocument4 pagesDrug Study 6th Floorjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Las - Mapeh - Health Module 1Document5 pagesLas - Mapeh - Health Module 1Analiza SantosNo ratings yet
- Unicef: General InformationDocument2 pagesUnicef: General InformationjobNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Fatima University College of Nursing - Cabanatuan CityDocument3 pagesOur Lady of Fatima University College of Nursing - Cabanatuan CityDanica FrancoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Medication AdministrationDocument59 pagesPediatric Medication AdministrationHilary Alvarado100% (1)
- Rich Picture Blood BankDocument3 pagesRich Picture Blood Bankviannyzerlinda50% (2)
- Bone BiopsyDocument3 pagesBone BiopsySophia A. GoNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument7 pagesArgumentative EssayHuy BuiNo ratings yet
- Fulmer SPICES: An Overall Assessment Tool For Older AdultsDocument2 pagesFulmer SPICES: An Overall Assessment Tool For Older AdultsSteve GarrettNo ratings yet
- PARM LBP CPG 2nd Edition 2017 PDFDocument293 pagesPARM LBP CPG 2nd Edition 2017 PDFGumDropNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Renal CalculiDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans For Renal CalculiRaveen mayi77% (22)
- Refresher Course: Preboard Examination Nursing Practice III: Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations (Part A)Document9 pagesRefresher Course: Preboard Examination Nursing Practice III: Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial Alterations (Part A)Jastine Sabornido0% (1)
- Edwards Hemodynamic Monitoring For COVID Critically Ill PatientsDocument3 pagesEdwards Hemodynamic Monitoring For COVID Critically Ill PatientsblanquishemNo ratings yet
- HEPADNAVIRIDAEDocument14 pagesHEPADNAVIRIDAEnur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiNo ratings yet
- Notes On MRI - FinalDocument16 pagesNotes On MRI - FinalAnju GuptaNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroids 24613Document33 pagesCorticosteroids 24613NOorulain HyderNo ratings yet
- Astrazenica 2nd Dose 8-13-21 AlkieDocument109 pagesAstrazenica 2nd Dose 8-13-21 AlkieGanie Mar BiasonNo ratings yet
- LewisDocument12 pagesLewisLewis Nimsy Tunde100% (1)
- IleusDocument10 pagesIleusChyndi DamiNo ratings yet
- 3 NURSING-CARE-PLAN FinaaalDocument7 pages3 NURSING-CARE-PLAN FinaaalSam PothNo ratings yet
- University of The PhilppinesDocument22 pagesUniversity of The PhilppinesFibi Pho0% (1)
- Mock Congress Bill Research EssayDocument9 pagesMock Congress Bill Research Essayapi-302890064No ratings yet
- Revision Notes On FRCRDocument385 pagesRevision Notes On FRCRObaidy Albushaher100% (2)
- NHB Renewal Application 2022Document4 pagesNHB Renewal Application 2022Chandran OchathevarNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Living ThingsDocument23 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Living ThingsclarisseNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project On AnalgesicsDocument30 pagesInvestigatory Project On AnalgesicsAnurag Singh100% (1)
- Archaeus 4Document107 pagesArchaeus 4terrythecensorNo ratings yet
- Rachael Stanton Resume Rachael Stanton LVT 1 2Document2 pagesRachael Stanton Resume Rachael Stanton LVT 1 2api-686124613No ratings yet
- Generic Name: BudesonideDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeNo ratings yet
- Activity Journal Mobile Blood Donation Advocacy 1Document3 pagesActivity Journal Mobile Blood Donation Advocacy 1Cherrymae BenzonNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For ExamDocument4 pagesHow To Prepare For ExamJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet