Professional Documents
Culture Documents
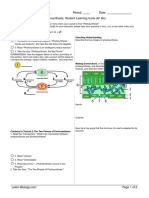
3.1.3 Cell and Transport
Uploaded by
Harshad GadhviOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
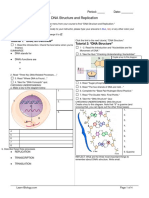
3.1.3 Cell and Transport
Uploaded by
Harshad GadhviCopyright:
Available Formats
1. The drawing shows part of a cell as seen under an electron microscope.
(a) Identify structures A to D.
A ................................................................................
B ................................................................................
C ................................................................................
D ................................................................................
(4)
(b) Describe how a sample of whole chloroplasts could be obtained from leaf tissue.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 7 marks)
Seven Kings High School 1
2. (a) \A Cell wall
B Cell membrane
C Ribosomes / rough endoplasmic reticulum
D Chloroplast 4
(b) Homogenise;
in ice cold;
isotomic solution;
then centrifuge any three 3
[7]
3. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic
cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect.
Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell
Contains ribosomes attached
to the endoplasmic reticulum
Genetic material consists
of linear chromosomes
Diameter of the cell is 1 µ m
(b) A student was asked to describe the structure of two organelles which were present on an
electron micrograph. From the descriptions below, identify the organelles and, in each
case, name the internal structures underlined.
(i) This organelle was disc shaped and had an outer envelope of two membranes.
Within it was a series of further membranes which crossed the organelle like
railway tracks. At intervals the membranes appeared to repeatedly double back on
themselves to form stack-like structures. In the spaces between the membranes was
a granular material.
Organelle............................................................................................................
Internal structures .............................................................................................
(2)
(ii) This organelle had a round shape and had an outer envelope of two membranes,
which was perforated in places. Within it were thin strands which did not appear to
have the width or organisation of membranes.
One large round structure was visible internally.
Organelle............................................................................................................
Internal structures .............................................................................................
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
Seven Kings High School 2
4. (a)
X
X
X
(All symbols in a column need to be correct for a mark) 2
(b) (i) chloroplast;
grana / thylakoids; 2
(ii) nucleus;
chromosomes / chromatin / chromatids; 2
[6]
5. (a) (i) Give two ways in which active transport differs from diffusion.
1..........................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
2.........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) Sodium ions move from the surrounding solution where they are at a low
concentration into the cytoplasm of a cell where they are at a higher concentration.
Cyanide ions stop the functioning of the electron carrier system in mitochondria.
Use these two pieces of information to explain how the addition of cyanide ions
would affect the uptake of sodium ions by a cell.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
Seven Kings High School 3
(b) Two major routes by which molecules are thought to cross membranes are:
1. by dissolving in the phospholipid layer.
2. by passing through channels in protein molecules.
These routes are illustrated in the diagram. The graphs show the rate of entry of molecules
into the cell by these two routes in relation to the external concentration of the molecules.
O u ts id e In s id e
A
R a te
of
e n tr y X
in to
c e ll
E x te rn a l c o n c e n tra tio n
M o le c u le s d is s o lv e in
p h o s p h o lip id la y e r
O u ts id e In s id e
B
R a te
of X
e n tr y
in to
c e ll
E x te rn a l c o n c e n tra tio n
M o le c u le s p a s s th ro u g h
p ro te in c h a n n e ls
(i) Explain why curves are similar up to point X
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
Seven Kings High School 4
(ii) Explain what causes the shapes of the curves to differ after point X.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
6. (a) (i) ATP used;
movement is against a concentration gradient; 2
(ii) stops / less movement of ions;
movement of ions needs ATP;
ATP / production linked to respiration /
electron carrier system; max. 2
(b) (i) greater concentration difference / increased gradient therefore more
molecules move in external concentration limiting factor /
increased concentration increases rate; 1
(ii) (limit imposed in situation B by)
limited number of molecules can move through the pores in unit time /
pores are full / number of pores is limiting factor; 1
[6]
7. Cell organelles can be separated by centrifuging a cell extract in a sucrose density gradient. The
organelles settle at the level in the sucrose solution which has the same density as their own.
Some animal cells were broken open and the cell extract centrifuged in a sucrose density
gradient. Three distinct fractions were obtained, A, B and C, as shown in the diagram.
In c re a s in g A
d e n s ity o f
su c ro se
s o lu tio n B
Seven Kings High School 5
One fraction contained nuclei, one contained ribosomes and a third contained mitochondria.
Complete the table by identifying the organelle in each fraction and describing one function of
each organelle.
Fraction Organelle Function
(Total 4 marks)
8.
A Ribosomes Making proteins/ assembling amino acid chain/ 1 mark
protein synthesis
B Mitochondria Respiration/ formation of ATP/ Krebs cycle/ 1 mark
Oxidative phosphorylation;
C Nuclei DNA/RNA synthesis/ controls protein 1 mark
production/ cell activity/ carries genetic
information;
1 mark
[4]
Seven Kings High School 6
9. The diagram shows an animal cell.
20µm
(a) The scale bar on the diagram represents a length of 20 pm. Use this to calculate the
magnification of this diagram. Show your working.
Magnification........................
(2)
(b) Use a guideline and the appropriate letter to show, on the diagram, a site in this cell where
(i) the enzymes controlling glycolysis are found (A);
(1)
(ii) molecules of enzymes are synthesised (B).
(1)
Seven Kings High School 7
(c) The number of cristae in the mitochondria of a cell with a high metabolic activity is
greater than the number in a cell with lower metabolic activity. Explain why.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
10. (a) Two marks for correct answer of 3000;
One mark if answer obtained by dividing actual length by 20 m; 2
(b) (i) Letter A indicating cytoplasm; 1
(ii) Letter B indicating ribosome; 1
(c) Cristae are site of ATP synthesis/oxidative phosphorylation;
by electron/hydrogen carriers;
Metabolism requires energy input/ATP; max 2
[6]
11. The diagram shows the structure of part of a cell as seen using an electron microscope.
E
A
(a) Name two features shown in the diagram which indicate that this is a eukaryotic, rather
than a prokaryotic cell.
1 ..................................................................................................................................
2 ..................................................................................................................................
(2)
Seven Kings High School 8
(b) At which of the lettered sites, A to E, would you expect each of the following to be
produced in the greatest amount?
(i) proteins _______________
(ii) carbon dioxide _______________
(iii) mRNA _______________
(3)
(c) This cell was supplied with a radioactive isotope which specifically labels thymine.
In which part of the cell would this label be most concentrated?
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
12. (a) presence of nucleus / nuclear membrane;
presence of named organelle (not ribosome)
(Features must be named - disallow letters) 2
(b) (i) C/ribosome;
(ii) D/mitochondnon;
(iii) A/nucleus; 3
(c) A/Nucleus; 1
[6]
13. The diagram shows a mitochondrion.
R ib o s o m e s
D N A lo o p
(a) (i) Name the part labelled X.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) A human liver cell contains several hundred mitochondria. A cell from a plant root
has only a small number.
Suggest an explanation for this difference.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
Seven Kings High School 9
(iii) Mitochondria contain some DNA and ribosomes.
Suggest the function of these.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Mitochondria may be separated from homogenised sells by differential centrifugation.
During this process the cells must be kept in an isotonic solution.
Explain why.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) Ribosomes in bacterial cells differ from those in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. When
centrifuged at high speed, the eukaryotic cell ribosomes sediment more rapidly than
bacterial ribosomes.
Explain what this tells you about the difference between bacterial and eukaryotic
ribosomes
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
14. (a) (i) Crista 1
(ii) (Mitochondria) provide energy / ATP;
liver cells have high energy requirement for metabolism- reactions
specific liver function, eg. glycogen synthesis or deamination (not just:
active transport/ growth) 2
(iii) Principle - protein synthesis;
Function of protein in mitochondria - e.g. synthesis of (respiratory)
enzymes / growth / repair / replication.
or:
DNA has genetic information;
ribosomes produce proteins / allows replication of mitochondria. 2
(b) Maintain concentrations/water potential same inside & outside (cells / mitochondria) /
prevent osmosis;
Prevent bursting / shrinkage of mitochondria/organelles (not cells) 2
Seven Kings High School 10
(c) Eukaryotic ribosomes denser/ heavier (not just ‘larger’). 1
[8]
15. The diagram shows a cross-section of a typical red blood cell. Red blood cells can carry both
oxygen and carbon dioxide. Each cell has a thinner central area as shown in the diagram.
(a) Explain one advantage of the shape of red blood cells.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Red blood cells do not have a nucleus or rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Give one function that red blood cells are therefore unable to carry out.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) In an experiment, the phospholipids were extracted from the surface membrane of a single
red blood cell. They were placed on the surface of water and allowed to spread out.
(i) Using ### to represent a single phospholipid molecule, draw on the diagram how
you would expect ten phospholipid molecules to be arranged on the water surface.
C o n ta in e r
W a te r
(2)
Seven Kings High School 11
(ii) The area of water covered by the phospholipid molecules was calculated. This area
was given an arbitrary value of 1. The surface area of an intact red blood cell was
measured on the same scale. What would you expect the arbitrary value of the red
blood cell surface area to be? Explain your answer.
Arbitrary value .............................................
Explanation ......................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(2)
16. (a) Faster gas exchange / diffusion;
Large / big / increased surface area / shorter pathway for
gas exchange / Hb not too far from membrane;
(NOT more / bigger / greater / easier / more efficient)
OR
Increases flexibility;
To pass through capillaries; 2
(b) Protein synthesis / Cell division / Mitosis; (NOT Meiosis) 1
(c) (i) Monolayer;
Tails up / heads in water;
(NOT completely submerged or floating in air) 2
(ii) 0.5 / ½;
Phospholipids are arranged in a bilayer; 2
[7]
Seven Kings High School 12
17. The diagram shows part of an animal cell as seen through an electron microscope.
(a) Name organelles A, B and C.
A ....................................................................
B ....................................................................
C ....................................................................
(3)
Seven Kings High School 13
(b) Describe the function of organelle X.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) The actual diameter of organelle Y is 0.5 pm.µ m.
Calculate the magnification of the diagram. Show your working.
Magnification .....................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
18. (a) A mitochondrion; 1
B nucleus; 1
C endoplasmic reticulum rough ER / ER;
(reject smooth ER, ribosomes neutral ) 1
(b) ref to proteins / glycoproteins / enzymes / lipids / hormones;
ref to fate of proteins / glycoproteins / enzymes / lipids / hormones; (linked to
previous mark e.g. vesicles / exocytosis / packaging / synthesis / processing
modifying)
If neither of these: reference to vesicles / exocytosis / packaging / synthesis
processing /modifying gains 1 mark
(Max 1 mark if incorrect function given) 2
(c) 30 000 - 34 000 gains 2 marks;; 2
If neither of these: evidence of sensible measured diameter ÷ actual (0.0005 mm)
gains 1 mark
[7]
Seven Kings High School 14
19. (a) Complete the table to give two ways in which active transport differs from
diffusion.
Active transport Diffusion
1 ................................................... ...................................................
................................................... ...................................................
2 ................................................... ...................................................
................................................... ...................................................
(2)
(b) The diagram represents a phospholipid.
A B
(i) Name the parts of the molecule A, B and C.
A ................................................................................
B ................................................................................
C ................................................................................
(3)
(ii) Describe the role of phospholipids in controlling the passage of molecules through
the cell membrane.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
Seven Kings High School 15
(c) (i) The diagrams show the water potentials (ψ ) of three cells in contact with one
another.
Use arrows to show the net direction of water movement between all three cells.
ψ = –230 kPa
ψ = –214 kPa ψ = –135 kPa
(1)
(ii) If solute were added to a cell, what effect would this have on the water potential
within the cell?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
20. (a) Max 2
Active transport Diffusion
may move substances against Substances moved down
concentration gradient; concentration gradient;
Requires ATP / energy; Does not require ATP / energy;
Requires membrane Does not (necessarily) require
proteins / carriers; membrane proteins / carriers;
(b) (i) A Phosphoric acid / phosphate
B Glycerol
C Fatty acid 3
(ii) Prevent passage of water-soluble molecules / ions / named molecules
OR allow passage of lipid-soluble molecules
OR retain water-soluble substances 1
(c) (i) All arrows in correct direction 1
(ii) More negative 1
[8]
21. The diagram shows the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure.
P ro te in
m o le c u le s
Seven Kings High School 16
(a) Suggest why this model is known as fluid mosaic.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Give two functions of the protein molecules in the cell membrane.
1. ................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
2. ................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) Explain how hydrophobic areas in the membrane are important to its function.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(d) (i) The diagram shows the water potentials ( ) of three cells in contact
with one another.
Use arrows to show the net direction of water movement between all three cells.
ψ = –230 kPa
ψ = –214 kPa ψ = –135 kPa
(1)
(ii) If solute were added to a cell what effect would this have on the water potential
within that cell ?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
22. (a) Molecules within the membrane able to move;
mixture of phospholipid and protein / arrangement of protein; 2
Seven Kings High School 17
(b) Carriers / reference to transport role;
receptors / antigens / reference to recognition;
enzyme; max. 2
(c) Selectivity;
stops the loss of water soluble / polar molecules from inside the cell;
e.g. enzyme;
OR converse
allows movement of lipid soluble / non polar molecules;
e.g. vitamins; max. 2
(d) (i) Arrows from high to low water potential; 1
(ii) Water potential is lower / more negative ; 1
[8]
23. The roots of two groups of pea plants were placed in solutions containing radioactive potassium
ions. For the experimental plants a respiratory inhibitor was added to the solution. The control
plants had no respiratory inhibitor added. At regular intervals the solutions surrounding the roots
were tested for radioactive potassium ions.
The table shows the results of this investigation.
Time from Concentration of radioactive potassium
placing ions in the solutions surrounding the roots /
roots in solution / arbitrary units
minutes
Experimental plants Control plants
0 7.5 7.5
15 6.6 3.3
30 6.4 2.9
60 6.3 2.4
120 6.3 1.2
240 6.3 0.6
(a) (i) The rate of uptake of potassium ions by the experimental plants in the
first 15 minutes was 0.06 units per minute.
Calculate the rate of uptake of potassium ions by the control plants over the same
time period.
Rate of uptake by control plants = ..................................................................
(1)
Seven Kings High School 18
(ii) Suggest an explanation for the difference between the rates of uptake by the
experimental and control plants in the first 15 minutes.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(iii) The rate of potassium ion uptake by the control plants in the first hour was faster
than in the second hour. Suggest why.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) At the end of the investigation sections were cut across the stems of the pea plants and the
amount of radioactivity in each tissue was measured.
The diagram shows a section across the stem of a pea plant.
(i) Give one feature by which this section can be recognised as a stem.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
Seven Kings High School 19
(ii) Using a guideline, label and name the tissue in which you would expect to find the
greatest amount of radioactivity.
(1)
(Total 7 marks)
24. (a) (i) 0.28; 1
(ii) uptake by active transport;
use energy / ATP from respiration;
amount absorbed by experimental plants is due to diffusion; max 2
(iii) concentration falls so rate of diffusion falls;
active transport involves carrier/membrane proteins;
more potassium ions so more chance of collisions with carriers max 2
(b) (i) cylindrical arrangement of vascular bundles/in vascular bundles 1
(ii) correct label to xylem; 1
[7]
25. Protein molecules in the cell surface membrane are involved in the active transport of glucose
molecules into the cell.
(a) The graph shows how the uptake of glucose by red blood cells varies with the glucose
concentration of the surrounding medium.
R a te o f
u p ta k e
g lu c o s e
C o n c e n tra tio n o f g lu c o s e
in s u rro u n d in g m e d iu m
Seven Kings High School 20
Explain the shape of the curve.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(b) The table shows the results of an investigation into differences in the rates of uptake of
different sugars by red blood cells.
Sugar Relative rate of uptake
Glucose 100
Galactose 13
Xylose 7
(i) Give one factor, other than the concentration of sugar in the surrounding medium,
which should have been standardised in this investigation. Describe and explain
how variation in this factor would affect the rate of uptake.
Factor...........................................................................................................................
Explanation..................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) Use your knowledge of protein molecules in cell surface membranes to suggest
why the rate of uptake of these sugars differs.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
26. (a) In first part of the curve concentration of glucose in surrounding
medium limiting/rate of uptake dependent on glucose;
More glucose molecules, more protein carriers occupied;
In second part number of proteins/carriers limiting/working at full capacity;
All carriers occupied; max 3
Seven Kings High School 21
(b) (i) Temperature;
Would increase the rate of movement/kinetic energy of molecules/
gives more chance of colliding with carrier;
or
Temperature/pH;
Denature protein carriers;
or
Number of red blood cells;
More uptake because greater surface area/more carriers;
or
Oxygen;
Linked to ATP/energy/respiration and active transport; 2
(ii) Concept of shape of different molecules/receptor site;
Concept of fit determining specificity;
More carriers for glucose; max 2
[7]
27. Read the following passage.
Most fruits are green when unripe because they contain a number of chlorophyll pigments. Some
varieties of apple remain green when fully ripe, some turn yellow and others go red. The
yellowing of apples is mainly due to the disappearance of the chlorophyll allowing other
pigments called carotenoids to show their colour. These carotenoids are located in the same
organelles as the chlorophyll molecules. The red colour, however, is due to the formation of a
new pigment called anthocyanin.
Unlike carotenoids and chlorophyll which are located in organelles in the cytoplasm,
anthocyanin is dissolved in the cell sap inside the vacuole of the cell. It can be extracted by
boiling a piece of apple skin. As the water boils, the red colour of the skin starts to disappear
because the pigment is being released from the cells into the water in which the skin is boiled.
This can be demonstrated by adding a few drops of acid to the water. It will immediately turn
red because anthocyanin turns red in the presence of an acid.
More information can be obtained by watching the process more closely. If another piece of skin
is dropped into boiling water, it will be seen to turn briefly from red to purple before the colour
fades away. Since alkalis turn anthocyanin purple, the anthocyanin must have momentarily
encountered alkaline cytoplasm during breakdown of the cell. This and similar observations
show that different parts of the cell have different characteristics. In a living cell there must be
some form of barrier between these different parts. This barrier will allow certain molecules to
pass through but not others.
Seven Kings High School 22
(a) Suggest how you could use chromatography to separate and identify chlorophyll pigments
present in the skin of different varieties of apple.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(4)
(b) Using the information in the passage, complete the diagram of the cell from the skin of an
apple to show
(i) the location of the chlorophylls, carotenoids and anthocyanins;
(ii) those parts of the cell that are acidic and those parts that are alkaline.
C e ll w a ll
V a c u o le
(2)
Seven Kings High School 23
(c) Suggest an explanation for each of the following observations.
(i) The volume of the vacuole increases if the cell is placed in distilled water.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(ii) Enzymes which are normally found in cell sap would be unable to function if they
were in the cytoplasm.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 12 marks)
28. (a) Make extract of pigments by grinding;
Load onto chromatography paper with reference to position;
Small droplets/number of drops to concentrate;
Run with paper dipped into solvent;
Mark solvent front;
Calculate Rf value/use standards; max 4
(b) Diagram showing
(i) carotenoids and chlorophyll in cytoplasm and anthocyanin in cell vacuole; 1
(ii) Vacuole acid and cytoplasm alkaline; 1
Seven Kings High School 24
(c) (i) Concentration of vacuole contents/solute greater than surrounding
medium;
Vacuole has lower/more negative water potential;
Vacuole surrounded by partially permeable membrane;
Water enters by osmosis; max 3
(ii) Difference in pH;
Affects tertiary structure of/denatures enzyme/charges around active site/
shape of active site;
Substrate will no longer fit/bind; 3
[12]
29. The diagram shows how an experiment was set up to investigate absorption by active transport
and diffusion in the small intestine. A piece of small intestine was turned inside out, so that the
surface with the villi was on the outside. The ends of the intestine were tied to form a sac. The
sac was placed in an oxygenated, buffered solution at 37°C. Substances which were transported
through the villi in the normal direction became concentrated within the sac.
m u c o s a l s u rfa c e o u tsid e
in te stin a l s a c
(a) Suggest why, in order to investigate active transport, the solution in which the sac was
placed was
(i) oxygenated;
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(ii) buffered.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(3)
Seven Kings High School 25
(b) Using this technique, the following data were obtained about the absorption of sugars
from small intestine which had been treated with a respiratory inhibitor and from
untreated small intestine.
R e la tiv e r a te s o f a b s o r p tio n f r o m s m a ll in te s tin e
S ugar tre a te d w ith
re s p ira to r y in h ib ito r u n tre a te d
G lu c o s e 30 100
F ru c to s e 31 30
Explain what the table suggests about the ways in which glucose and fructose are
absorbed from the small intestine.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 7 marks)
30. (a) (i) to allow aerobic respiration/respiration in mitochondria;
providing ATP;
(ii) to prevent denaturation of / provide optimum pH for enzymes/
protein carriers 3
(b) Glucose - active transport;
absorption much less in poisoned gut;
Fructose - diffusion;
absorption rates similar in normal and poisoned gut; 4
[7]
Seven Kings High School 26
31. The table shows the relative rate of diffusion of oxygen through three different media.
Medium Relative rate of
diffusion
Air 11.0
Water 3.4 × 10–5
Muscle tissue 1.4 × 10–5
(a) The measurements in the table were all made at the same temperature. Explain how an
increase in temperature affects the rate of diffusion.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) The lung alveoli have a moist surface.
(i) It is sometimes suggested that this moist surface makes gas exchange more
efficient. Use the information in the table to explain why this suggestion is
incorrect.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Explain how diffusion results in the alveoli having a moist surface.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(2)
Seven Kings High School 27
(c) The diagram shows the position of the tracheoles which supply oxygen to the muscles of
an insect.
T ra c h e o le s
M u s c le
This insect has more than 1.5 million tracheoles. The distance between the ends of the
tracheoles in the muscle is approximately 4 pm. Explain how these features allow efficient
oxygen supply.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 8 marks)
32. (a) Molecules will have more (kinetic) energy;
Move faster;
Reject references to vibrating in this context 2
(b) (i) Oxygen diffuses faster/has a higher rate of diffusion
in air than in water; 1
(ii) Alveolar epithelium/surface is permeable to small molecules;
Water is a small molecule;
Higher concentration of water in cell/blood than outside;
Water diffuses from blood/cells into alveoli; max 2
Seven Kings High School 28
(c) Large number gives large (total) surface area;
For diffusion;
Short distance between tracheoles gives short pathway;
Movement/diffusion through muscle is slow;
Reject references to muscle simply being close to tracheoles. Must convey
idea of short pathway to gain credit for third point. 3
[8]
33. (a) Give two differences between active transport and facilitated diffusion.
1 ..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
2 ..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Describe how ions are transported through a cell surface membrane by active transport.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) The table shows the concentration of three ions inside and outside a cell of an alga that
lives in pond water.
Concentration of ion in Concentration of ion in
Ion
cytoplasm / mmol dm–3 pond water / mmol dm–3
Chloride 58.0 1.3
Potassium 93.0 0.1
Sodium 51.0 1.0
(i) By how many times have the potassium ions been concentrated in the cytoplasm
compared with the pond water?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
Seven Kings High School 29
(ii) The ions enter the cell of the alga by active transport. What does the information in
the table suggest about the active transport of these three ions through the cell
surface membrane? Explain your answer.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
34. (a) Active transport requires energy / uses ATP;
moves substances against concentration gradient. 2
(b) Carrier protein (in membrane); (accept: channel/pore/intrinsic proteins;
reject: extrinsic protein, or just ‘protein’);
ion transported by change of shape / ‘flipping’ of carrier protein;
energy used to attach ion to carrier protein /.change shape.( not
just ‘ATP provides energy’) max 2
(c) (i) 930 1
(ii) Carrier proteins different or specific / ref to potassium (or other)
carrier / ions moved independently;
more potassium than other ions transported;
different degrees of concentration of ions.
(not just ‘moved against concentration gradient’) max 2
[7]
35. Peeled potatoes were cut into two sizes of cubes - 1cm3 (1cm x 1cm x 1cm) and 27cm3 (3cm x
3cm x 3cm). After weighing, twenty-seven of the 1cm3 cubes were placed in one beaker of
distilled water, and one 27cm3 cube was placed in another beaker. One hour later the cubes
were removed and their surfaces carefully dried. They were then reweighed. The results are
shown in the table.
Small cubes Large cube
Volume of cube / cm3 1 27
Surface area of cube / cm2 6 54
Number of cubes in beaker 27 1
Surface area : volume ratio of one cube
Total mass of cubes at start / g 52.75 52.97
Total mass after 1 hour in water / g 55.31 53.55
Increase in mass / g 2.56 0.58
Percentage increase in mass
Seven Kings High School 30
(a) Complete the table to show
(i) the surface area : volume ratio for each size of cube;
(ii) the percentage increase in mass after 1 hour in water.
(2)
(b) (i) Why did the experimenter use twenty-seven small cubes?
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Explain, in terms of water potential, why the potato cubes increased in mass when
placed in the distilled water.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(iii) The percentage increase in mass of the smaller cubes was greater than the
percentage increase in mass of the large cube. Explain the difference.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
36. (a) (i) 6 : 1 and 2 : 1
(Accept 54:27;reject 6 and 2) 1
(ii) 4.85 / 4.9 and 1.09 / 1.1 1
(b) (i) Same volume of potato / only surface area different 1
(ii) Potato (cubes) have lower/more negative water potential;
so water enters cubes (by osmosis). 2
(iii) Larger surface area (: volume ratio) of smaller cubes (for osmosis). 1
[6]
Seven Kings High School 31
37. (a) Describe the fluid-mosaic structure of a cell surface membrane.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(5)
(b) Explain each of the following processes by which substances pass through a cell surface
membrane.
(i) diffusion of oxygen
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(5)
(ii) facilitated diffusion of glucose
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(iii) active transport of sodium ions
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(9)
(Total 14 marks)
Seven Kings High School 32
38. (a) Phospholipids and proteins;
Phospholipid bilayer;
Arrangement of phospholipid molecules ‘Tails to tails’;
‘Floating’(protein) molecules / molecules can move in membrane;
Intrinsic proteins extend through bilayer;
Extrinsic proteins in outer layer only;
(Ref. to intrinsic and extrinsic, unqualified, gains 1 mark);
Detail of channel proteins / protein shapes / glycoproteins;
Presence of cholesterol. 5
(b) (i) Random movement of oxygen molecules;
(Net) movement from high to lower concentration;
Molecules can pass between phospholipid molecules / through bilayer;
Rate dependent on concentration gradient.
(ii) Movement from high to lower concentration;
Use of carrier / channel / intrinsic protein;
Proteins specific (to glucose);
Changes shape of protein and passes through channel / membrane;
No energy/ATP needed.
(iii) Movement against concentration gradient;
Use of carrier/channel/intrinsic/pump proteins;
Protein specific (to ion);
Energy / ATP required;
Energy used to change shape of proteins / attach ion to protein;
Ions moved through membrane as proteins change shape / position. max 9
[14]
QWC Award 1 or 0 according to criteria
39. (a) Give two ways in which osmosis differs from facilitated diffusion.
1 ..................................................................................................................................
2 ..................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Jam contains a high concentration of sugar. Explain why bacteria that cause decay do not
grow in jam.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 5 marks)
Seven Kings High School 33
40. (a) Osmosis transports water;
Proteins / carrier molecules not used / occurs through
phospholipid bilayer; 2
(b) Jam has a lower (more –ve) water potential than the
bacterial cytoplasm;
Water leaves the bacteria;
Effect (of water loss) on bacteria e.g. killed / chemical reactions
cannot occur; 3
[5]
41. (a) Explain the biological importance of water for living organisms.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(5)
(b) Cylinders of potato were cut using a cork borer. Each cylinder was placed into one of a
range of sucrose solutions of different concentrations. The cylinders were left for 6 hours
and then removed from the solutions. The mass of each cylinder was recorded before and
after immersion. The graph shows the results of this investigation.
+10
In c re a se
P e rc e n ta g e
C o n c e n tra tio n o f
c h a n g e in 0
su cro se / m o l d m –3
m ass 0 .1 0 .2 0 .3 0 .4 0 .5 0 .6 0 .7 0 .8 0 .9 1 .0
D e c re a se
–10
Seven Kings High School 34
(i) Explain why the change in mass was given as a percentage change.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) Explain the shape of the curve as the concentration of sucrose decreases from
0.3 mol dm–3 to 0.1 mol dm–3.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(4)
(iii) What concentration of sucrose solution is equivalent to the mean water potential of
the potato cells? Explain your answer.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) The diagram represents three plant cells and shows the water potential of two of these
cells. The arrows show the direction of water movement between these three cells.
A
–510 kPa
C
–550 kPa
Seven Kings High School 35
Suggest the range of possible values for the water potential of cell B. Explain your answer
fully.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 15 marks)
42. (a) Chemical reactions occur in solution;
Allows transport/secretion/excretion/dispersal of substances;
High specific heat capacity (e.w.) so minimises temperature fluctuations;
High latent heat of evaporation so cooling effect of sweat/transpiration;
Provides internal support e.g. hydrostatic skeleton/amniotic fluid/turgidity;
Provides external support e.g. aquatic organisms;
High surface tension e.g. pond skaters, cohesion-tension;
Transparent e.g. allows light penetration for aquatic organisms;
Less dense when frozen so ice floats and insulates;
Reactant e.g. hydrolysis/photosynthesis;
Lubricant e.g. synovial fluid/pleural fluid/mucus; 5
(b) (i) Initial mass of cylinders not identiical;
To be able to directly compare the results; 2
(ii) From 0.3 mol dm–3 to 0.1 mol dm–3 water moves into potato cells;
By osmosis;
So mass increases;
More water has entered potato cells 0.1 mol dm–3 / converse; 4
(iii) 0.35;
No mass change/no net osmosis/
volume of water in = volume of water out; 2
(c) Range from –511 to –549 kPa;
Reason e.g. Water moves from A to B, so must be lower than –510 and
Water moves from B to C, so must be higher than –550; 2
[15]
43. (a) Describe osmosis in terms of water potential.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
Seven Kings High School 36
(b) In an experiment, cylinders cut from a potato were placed in sucrose solutions of different
concentrations. The cylinders were measured before and after immersion in sucrose
solution.
The graph shows the effect of the sucrose solutions on the length of the potato cylinders.
1 .3
1 .2
R a tio o f in itia l
le n g th to fin a l 1 .1
le n g th o f p o ta to
c y lin d e r s
1 .0
0 .9
0 .8
0 .1 0 .2 0 .3 0 .4 0 .5
C o n c e n tra tio n o f s u c ro s e s o lu tio n / m o l d m –3
(i) The initial length of the potato cylinder in 0.1 mol dm–3 sucrose solution was
5.0 cm.
Calculate the final length of this cylinder. Show your working.
Final length ............................. cm
(2)
(ii) On the graph
1 mark with a T a point on the curve where the potato cells are turgid;
2 mark with a W a point on the curve where the potato cells have the same
water potential as the sucrose solution.
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
44. (a) diffusion / movement of water;
through a partially-permeable membrane;
(from less negative Ψ ) to more negative Ψ / (from higher Ψ ) to lower Ψ ; 3
(b) (i) 5.55 cm gains 2 marks; (allow 5.5 or 5.6 only if supported by correct
working)
else evidence of 5.0 ÷ 0.9 gains 1 mark 2
Seven Kings High School 37
(ii) T anywhere to left of 0.3 M; 1
W at 0.3 M; 1
[7]
45. The diagrams show part of the wall of the small intestine and part of an epithelial cell.
V illu s
E p ith e liu m
B lo o d
c a p illa r y
L a c te a l M ic r o v illu s
C ry p t o f
L ie b e rk ü h n
M ito c h o n d rio n
P a rt o f e p ith e lia l c e ll
M u s c le la y e r
(a) Describe one function of the muscle layer in the wall of the small intestine.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) Complete the table about enzyme action in the small intestine.
Enzyme Substrate Products
Amylase ........................................... Maltose
........................................... Peptides Dipeptides
Lipase ........................................... ...........................................
and ....................................
(4)
Seven Kings High School 38
(c) Describe the function in the small intestine of:
(i) the blood capillaries,
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) the lacteals.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(d) Explain how the following features of the epithelial cells increase the rate of absorption of
digested foods.
(i) Microvilli
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Large numbers of mitochondria
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 9 marks)
46. (a) e.g. moves along contents of gut / peristalsis 1
(b) Starch;
Exopeptidase;
Lipids / fats / triglycerides;
Fatty acids and glycerol; 4
(c) (i) Absorption of monosaccharides / named or amino acids 1
(ii) Absorption of lipid constituents 1
(d) (i) Increased surface area for absorption 1
(ii) Provide energy for active uptake 1
[9]
Seven Kings High School 39
You might also like
- Q1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeDocument56 pagesQ1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeZaksd100% (1)
- Unit f211 1.1 Questions Microscopes Part 2Document41 pagesUnit f211 1.1 Questions Microscopes Part 2Hazel100% (1)
- Cells-Microscopes-Cell-Cycle-and-Immunity-Questions GRADE 12 HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENTDocument36 pagesCells-Microscopes-Cell-Cycle-and-Immunity-Questions GRADE 12 HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENTAsha justin joseph100% (1)
- Bio Molecules Qs and MSDocument112 pagesBio Molecules Qs and MSAmaan Ahmed100% (1)
- Q1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument34 pagesQ1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisChee Beng Yeap100% (1)
- Stella YOON - 4.4 Climate Change Qs - 1Document2 pagesStella YOON - 4.4 Climate Change Qs - 1Seo Young YOON100% (1)
- AS Bio Chapter 1 QPDocument9 pagesAS Bio Chapter 1 QPAsif Ayaz100% (1)
- Edexcel A-LEVEL BIO4 June 2005 QPDocument20 pagesEdexcel A-LEVEL BIO4 June 2005 QPapi-3726022100% (1)
- TOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)Document6 pagesTOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)L Chan100% (1)
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutDocument16 pagesFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- Mixed Unit 1Document191 pagesMixed Unit 1sonali100% (1)
- 4 RespirationDocument80 pages4 RespirationTori Hop Along Clinch100% (1)
- Transport QuestionsDocument12 pagesTransport QuestionsForm 4B100% (1)
- Bio October 2107 QP Unit 3Document16 pagesBio October 2107 QP Unit 3clyde100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle & CANCERDocument17 pagesThe Cell Cycle & CANCERjesuslovers100% (1)
- 4.3 Classification and EvolutionDocument109 pages4.3 Classification and Evolutiontaaniya sadiq100% (1)
- Khan Academy DNA Technology QuestionsDocument4 pagesKhan Academy DNA Technology QuestionsLoraNo ratings yet
- CIE A-Level Biology Topic 13 Photosynthesis Exam Questions: Alevelbiology - Co.ukDocument15 pagesCIE A-Level Biology Topic 13 Photosynthesis Exam Questions: Alevelbiology - Co.ukMaisarah HalimNo ratings yet
- 23 How To Do Hardy Weinberg ProblemsDocument5 pages23 How To Do Hardy Weinberg ProblemstsrifNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6.1 - 6.2 - DNA Structure and Replication, Student Learning GuideDocument4 pagesTOPIC 6.1 - 6.2 - DNA Structure and Replication, Student Learning GuideL ChanNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3.4, 3.6 - Cellular Respiration Student Learning Guide (AP Bio)Document8 pagesTOPIC 3.4, 3.6 - Cellular Respiration Student Learning Guide (AP Bio)L Chan100% (1)
- Population QuestionsDocument81 pagesPopulation QuestionsRiyan Moussaoui100% (1)
- 11 Bio Yrly Exam 09 QuestionsDocument11 pages11 Bio Yrly Exam 09 QuestionsJay Li100% (1)
- MCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Document27 pagesMCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Leen Alodat100% (1)
- 6.6.Q BANK SLdocxDocument20 pages6.6.Q BANK SLdocxNaz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- Topic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNDocument11 pagesTopic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNliang yi choo100% (1)
- Unit1 l1Document48 pagesUnit1 l1hassaan aly100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Document6 pagesProtein Synthesis Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwk100% (1)
- Feeding Relationships 2 QPDocument12 pagesFeeding Relationships 2 QPfuensanta celdran100% (1)
- Organisation of The Organism PDFDocument79 pagesOrganisation of The Organism PDFrachit100% (2)
- Linked Gene Question To Practice: JQ JQDocument7 pagesLinked Gene Question To Practice: JQ JQAyaan Asim Khan100% (1)
- 10 - Genetics and Evolution (Worksheet)Document8 pages10 - Genetics and Evolution (Worksheet)Lim YH100% (1)
- Evolution ReviewDocument3 pagesEvolution ReviewJenna Vong100% (1)
- Lab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFDocument4 pagesLab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFBeth RobeliaNo ratings yet
- MT Sep 2021-22 XII Bio QP 004 FinalDocument10 pagesMT Sep 2021-22 XII Bio QP 004 FinalKalpna Rani100% (1)
- BIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewDocument45 pagesBIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewNigel Zhang100% (1)
- 2 Mem TransDocument6 pages2 Mem TransPhuong DoanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Cell Transport PDFDocument146 pages3.2 Cell Transport PDFtess_15100% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument60 pagesCell DivisionCharmaineNo ratings yet
- Sat II Real Evolution QuestionsDocument3 pagesSat II Real Evolution QuestionsMido MidoNo ratings yet
- H2 Evolution QuestionsDocument27 pagesH2 Evolution QuestionsWesley Tan100% (1)
- Cell Struc (Q)Document26 pagesCell Struc (Q)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and HydrolysisDocument10 pagesSynthesis and Hydrolysisapi-264011999100% (1)
- Cell Communication Packet 1Document20 pagesCell Communication Packet 1jade20090106100% (1)
- Enzyme ProtocolDocument6 pagesEnzyme Protocoltapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam ZsmuDocument84 pagesBio Exam ZsmuManthan Patil100% (1)
- Calculating Water Potential Worksheet-2012 2Document4 pagesCalculating Water Potential Worksheet-2012 2aemilianne100% (1)
- Solan Bab 3 StrukturDocument5 pagesSolan Bab 3 StrukturMuhammad Amir100% (1)
- Biocomp Exam 2013Document11 pagesBiocomp Exam 2013e100% (1)
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates NotesWutWut100% (1)
- Chapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Document6 pagesChapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Rafael G. Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- 2009 MidtermI Form1Document12 pages2009 MidtermI Form1svNo ratings yet
- Bio 171 Exam 1Document6 pagesBio 171 Exam 1api-283716901100% (1)
- Valence WorksheetDocument2 pagesValence WorksheetGelo Angeles100% (1)
- 3.2 Cell Transport PDFDocument146 pages3.2 Cell Transport PDFChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 CellsDocument4 pagesQuiz 3 Cells02quantum.beagleNo ratings yet
- 2001 June Module 1Document10 pages2001 June Module 1paolo maldiniNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Additional Questions (Cell Structure)Document25 pagesYear 12 Additional Questions (Cell Structure)dramitrajp9602No ratings yet
- Mock Cells TestDocument5 pagesMock Cells TestDavid LeechNo ratings yet
- Cells Microscopes Cell Cycle and Immunity QuestionsDocument36 pagesCells Microscopes Cell Cycle and Immunity QuestionsAzad AlizadaNo ratings yet
- NFPA 220 Seminar OutlineDocument2 pagesNFPA 220 Seminar Outlineveron_xiiiNo ratings yet
- Section-A: Terrace Ramp To Basement BalconiesDocument4 pagesSection-A: Terrace Ramp To Basement BalconiesRitikaNo ratings yet
- Material Specification: Mechanical Property RequirementsDocument2 pagesMaterial Specification: Mechanical Property RequirementsNguyễn Tấn HảiNo ratings yet
- Economics Half Yearly Question PaperDocument6 pagesEconomics Half Yearly Question PaperBhumika MiglaniNo ratings yet
- June 2019Document64 pagesJune 2019Eric SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Fora Active Plus P 30 ManualDocument32 pagesFora Active Plus P 30 ManualBvcNo ratings yet
- Continuous Microbiological Environmental Monitoring For Process Understanding and Reduced Interventions in Aseptic ManufacturingDocument44 pagesContinuous Microbiological Environmental Monitoring For Process Understanding and Reduced Interventions in Aseptic ManufacturingTorres Xia100% (1)
- Anatomy, Physiology & Health EducationDocument2 pagesAnatomy, Physiology & Health Educationsantosh vaishnaviNo ratings yet
- (Jill E. Thistlethwaite) Values-Based Interprofess (B-Ok - CC)Document192 pages(Jill E. Thistlethwaite) Values-Based Interprofess (B-Ok - CC)Ria Qadariah AriefNo ratings yet
- NHT Series High-Throughput Diffusion PumpsDocument12 pagesNHT Series High-Throughput Diffusion PumpsJosé Mauricio Bonilla TobónNo ratings yet
- Untitled Form - Google Forms00Document3 pagesUntitled Form - Google Forms00Ericka Rivera SantosNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On Water PollutionDocument1 pageReaction Paper On Water PollutionAztah KivycNo ratings yet
- Iso 2281 1990Document8 pagesIso 2281 1990jesus torresNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report KapilDocument66 pagesThesis Report Kapilkapilsharma2686100% (1)
- Death Obituary Cause of Death Ookht PDFDocument4 pagesDeath Obituary Cause of Death Ookht PDFMayerRhodes8No ratings yet
- NFPA 25 2011 Sprinkler Inspection TableDocument2 pagesNFPA 25 2011 Sprinkler Inspection TableHermes VacaNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDocument32 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDjebali MouradNo ratings yet
- Mil-Std-1949a NoticeDocument3 pagesMil-Std-1949a NoticeGökhan ÇiçekNo ratings yet
- Invertec 200 260 400tDocument16 pagesInvertec 200 260 400tJxyz QwNo ratings yet
- Dirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsDocument4 pagesDirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsMariuszNo ratings yet
- Hotel Transportation and Discount Information Chart - February 2013Document29 pagesHotel Transportation and Discount Information Chart - February 2013scfp4091No ratings yet
- Easy Rasam Recipe Made Without Rasam PowderDocument6 pagesEasy Rasam Recipe Made Without Rasam PowderPrantik Adhar SamantaNo ratings yet
- Prestress 3.0Document10 pagesPrestress 3.0Jonel CorbiNo ratings yet
- Red Winemaking in Cool Climates: Belinda Kemp Karine PedneaultDocument10 pagesRed Winemaking in Cool Climates: Belinda Kemp Karine Pedneaultgjm126No ratings yet
- 9 - 1 H Wood Cabinet Spec Options NelDocument8 pages9 - 1 H Wood Cabinet Spec Options NelinformalitybyusNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasNayre JunmarNo ratings yet
- Positioning Strategy - Mineral WaterDocument2 pagesPositioning Strategy - Mineral WaterRakesh SelvamNo ratings yet
- Tarot Cards: Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTarot Cards: Cheat SheetDipti100% (7)
- Data SheetDocument2 pagesData SheetsswahyudiNo ratings yet