Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Morphology
Uploaded by
Talha Zubair Masror NewtonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Morphology
Uploaded by
Talha Zubair Masror NewtonCopyright:
Available Formats
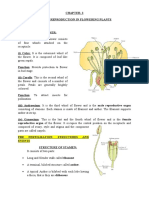
Morphology of Monocot seed (rice):
Generally seed contains three distinct parts
1. Seed coat
2. Endosperm
3. Embryo
Embryo consist three parts:
Cotyledons, radical, plumule
1. Seed coat:
It is the brownish membranous layer adherent to the grain. This layer is
made up of the seed coat and the wall of the fruit fused together. The seed coat
is marked by a hilum that represents the point of attachment of the seed to the
ovary wall. In addition a micropyle can be discerned just below the hilum.
2. Endosperm:
Develop from the fusion of polar nuclei and a pollen sperm .Endosperm
forms the main bulk of the grain and is the food storage tissue of it, being laden
with reserve food material, particularly starch .The outer most layer of the
endosperm is called aleurone layer which contain mainly protein
3. Embryo:
Embryo is very small and lies in grove at one end of the endosperm which
is developed from male and female
gametes. It consists of
i) One shield –shaped cotyledon
known as the scutellum
ii) A short axis with
a) The plumule
b) The radical protected by the root
cap.
The plumule is surrounded by minute
leaves or coleoptile and the radical is
surrounded by root sheath or
coleorhizae. Coleoptile and
coleorhizae is protective sheath of the
plumule and the radical.
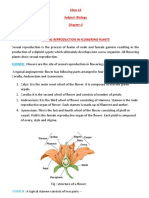
Morphology of Dicot seed :
1. Seed coat:
Seed coat of dicot seed is blackish or reddish and hard. The seed coat
consists of two layers fused together, the outer one being known as the testa and
the inner one is tegmen.
At one edge of the seed coat there is a whitish, elongated ridge, this ridge is
called the raphe.
At the basal portion of the raphe there is a distinct broad scar , this is
called hilum .Small opening immediately below the hilum ,which is minute but
distinct is called micropyle .
2. Embryo :
After removing the seed coat a freshly portion is seen known as embryo It
consists the following:
Radicle: The tip of the embryo axis towards the micropyler end is called
radicle.
Plumule: The other end of the embryo axis found deeper in between the
cotyledons is plumule.
Funiculus: A stalk of the ovule, containing vascular tissue.
Chalaza: The region a seed at the upper end of the raphe.
Pericarp: Ovary wall develops into pericarp.
Carnucle: A spongy structure, an outgrowth of the outer seed coat.
You might also like
- PRPM110L Module 5Document7 pagesPRPM110L Module 5CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction CHP 7Document19 pagesSexual Reproduction CHP 7Nabaratna BiswalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nerium Leaf, Ovule and Anatomy of Anther 26.10.2019Document2 pagesAnatomy of Nerium Leaf, Ovule and Anatomy of Anther 26.10.2019JAGGU BHAINo ratings yet
- The Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationDocument3 pagesThe Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationjaswanthNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomymomina tayyabNo ratings yet
- Flowers & Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesFlowers & Sexual Reproduction in PlantsRiza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Selaginella (Club Moss or Spike Moss) : LycopsidaDocument29 pagesSelaginella (Club Moss or Spike Moss) : LycopsidaAkshay KannanNo ratings yet
- CC CC: Cva A A AaaDocument5 pagesCC CC: Cva A A AaaPaul Alfred Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Lower and Higher PlantsDocument89 pagesReproduction in Lower and Higher Plantsmohdyasir6643No ratings yet
- Seed Structure and Germination: 38 Character TitleDocument14 pagesSeed Structure and Germination: 38 Character TitleShrishtika AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsRajnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document35 pagesChapter 24Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument82 pagesEmbryologypragyamaharjan2No ratings yet
- Anatomy of StemDocument15 pagesAnatomy of StemMonica LumbantobingNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction Super SheetDocument13 pagesPlant Reproduction Super SheetFarhan Azmain FahimNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Frog Embryology SlidesDocument10 pages5.1 Frog Embryology SlidesChandan kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsHarpreetNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument30 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerSufiyanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument18 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDianna josephNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Root and StemDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Root and StemLIONS GAMERSNo ratings yet
- 1 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pages1 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantssakeenasiddik22No ratings yet
- Note CH 1 Sexual Reproduction Flowering Plant 2Document25 pagesNote CH 1 Sexual Reproduction Flowering Plant 2Aditi ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument25 pagesClass 12 Biology Chapter 2 Revision NotesSrushti BhagitNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 1AbhishekDwivediNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKrittika DasNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - 09.03.2022Document4 pagesBiology Notes - 09.03.2022Bhargavi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Biology Preparation and Study of Transverse Section of Dicot and Monocot Roots and StemsDocument1 pageByjus Com Biology Preparation and Study of Transverse Section of Dicot and Monocot Roots and Stemssmm MamaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (Note 2020) Part IDocument11 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (Note 2020) Part IY S BAMMANAL y sNo ratings yet
- Primary Dicot Stem and Root in SunflowerDocument10 pagesPrimary Dicot Stem and Root in SunflowerPushkar kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 1Document34 pagesClass 12 Chapter 1Aditya MishraNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis in Mammals: Ova Production ProcessDocument4 pagesOogenesis in Mammals: Ova Production Processjohn benedickNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBħuvi ÀnthaRaNo ratings yet
- Universal Embryology SummaryDocument6 pagesUniversal Embryology SummaryJason TonioloNo ratings yet
- Key Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument17 pagesKey Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsAngelina DaisyNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsshikaanara8686No ratings yet
- Microscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueDocument16 pagesMicroscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- The SeedDocument4 pagesThe SeedAnonymous fe9UIiNo ratings yet
- Ovule MegasporogenesisDocument7 pagesOvule MegasporogenesisVivi yenni aryantiNo ratings yet
- SeedsDocument6 pagesSeedsLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- MICROSPOROGENOSISDocument20 pagesMICROSPOROGENOSISMerlyn CuantiosoNo ratings yet
- 05 - BIO IX ICSE Seeds - Structure and Germination PDFDocument6 pages05 - BIO IX ICSE Seeds - Structure and Germination PDFthe lilly0% (1)
- Veterinary Embryology Ovary and OogenesisDocument3 pagesVeterinary Embryology Ovary and OogenesisbingchillingNo ratings yet
- Terms in Biology: Oleh Wirda Taufik 16031071Document25 pagesTerms in Biology: Oleh Wirda Taufik 16031071Bintang MatahariNo ratings yet
- KOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1Document11 pagesKOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1mahender106yoNo ratings yet
- What seeds, tomatoes, cucumbers and okra have in commonDocument18 pagesWhat seeds, tomatoes, cucumbers and okra have in commonClemente MontillaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Handout For Feb 19 23Document10 pagesReproduction Handout For Feb 19 23cykg4qkbtqNo ratings yet
- GymnospermaeDocument63 pagesGymnospermaeMief MifdaulNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Notes on Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesClass 12 Biology Notes on Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSasi LokeshNo ratings yet
- Botany Lecture - Chapter 7Document30 pagesBotany Lecture - Chapter 7cherokeeNo ratings yet
- Structure of Ovule and TypesDocument10 pagesStructure of Ovule and TypesJemson KhundongbamNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Chapter-8: Cell The Unit of Life: Cbse + 1 Botany CDF MaterialDocument8 pagesUnit-Iii: Chapter-8: Cell The Unit of Life: Cbse + 1 Botany CDF Materialsimhaenator7109No ratings yet
- Biology 2 PucDocument23 pagesBiology 2 PucTULASI BAINo ratings yet
- Presentation On Objectives1.1-1.8Document54 pagesPresentation On Objectives1.1-1.8Shadecia DinnallNo ratings yet
- 2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument39 pages2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsIshvaryaNo ratings yet
- Practical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectDocument6 pagesPractical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectAfridi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Anthoceros ANTHOCEROS (Hornwort) : Morphology of ThallusDocument3 pagesAnthoceros ANTHOCEROS (Hornwort) : Morphology of ThallusyeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Embyology UG Part II Note 2 - Development of Amphioxus Drprity Mam2Document8 pagesEmbyology UG Part II Note 2 - Development of Amphioxus Drprity Mam2Adwika DeoNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet