Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FDDI
Uploaded by
dolon10Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FDDI
Uploaded by
dolon10Copyright:
Available Formats
FDDI.
Ans) The 802 LANs (IEEE 802.3, 802.4,802.5) are all based on copper wires. For low speeds and shorter distances, this will do just fine, but for higher speeds and longer distances, LANs must be based on fiber optics. Fiber has high bandwidth, is thin and lightweight, is not affected by electromagnetic interference and has excellent security because it is nearly impossible to wiretap without detection.
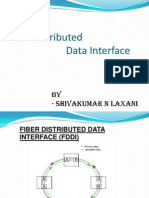
FDDI consists of two counter rotating rings
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) is a high performance fiber optic token ring LAN running at 100 Mbps over distances up to 200 km with up to 1000 stations connected. The FDDI cabling consists of two fiber rings, one transmitting clockwise and the other transmitting anti-clockwise. If either one breaks, the other can be used as backup. If both break at the same point, the two rings can be joined into a single ring approximately twice as long. Bytes >=8 Preamble 1 1 2 or 6 Destination Address 2 or 6 Source Address No limit 4 1 1
Data
Checksum
Frame Control Ending delimiter Frame Status Start delimiter FDDI frame format To transmit data, a station must first capture the token, then it transmits a frame . One difference between the FDDI and 802.5 is that, in 802.5 a station may not generate a new token until its frame has gone all the way around and come back. In FDDI, with 1000 stations and 200 km of fiber, the amount of time wasted waiting for the frame to travel the ring could be substantial. For this reason, it was decide to allow a station to put a new token back onto the ring as soon as it has finished transmitting its frames. In a large ring, several frames might be on the ring at the same time. The Start delimiter and the End delimiter field mark the frame boundaries. The Frame control field tells what kind of frame this is( data or control etc) and the Frame Status field holds the acknowledgement byte.
Dolon Mukherjee
You might also like
- Ccna Notes Ahmed SaeedDocument50 pagesCcna Notes Ahmed Saeedarif420_999No ratings yet
- System Design NotesDocument3 pagesSystem Design Notesdolon100% (1)
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- IEEE 803.2 / 802.2: Network TopologyDocument7 pagesIEEE 803.2 / 802.2: Network TopologySudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- FDDIDocument12 pagesFDDI2224 Momynul IslamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) &Document16 pagesPresentation On Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) &Shaurya KapoorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4jgarciablancoNo ratings yet
- FddiDocument10 pagesFddimmmaheshwariNo ratings yet
- What Is Fddi?: Counter-Rotating Fiber Optic Rings)Document21 pagesWhat Is Fddi?: Counter-Rotating Fiber Optic Rings)jibeshmNo ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface: By: Aziz Ur RehmanDocument26 pagesFiber Distributed Data Interface: By: Aziz Ur Rehmanapi-19795318No ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument23 pagesFiber Distributed Data Interfacelakshay187No ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument23 pagesFiber Distributed Data InterfaceKRISHAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- LAN (Local Area Network) : Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)Document6 pagesLAN (Local Area Network) : Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)Anand S PandeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment FDDI TokenRingDocument6 pagesAssignment FDDI TokenRingkavindagayaNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networks: Guest Instructor Elaine WongDocument29 pagesLocal Area Networks: Guest Instructor Elaine WongSahil AbbasNo ratings yet
- L-1 TXN Doc01Document25 pagesL-1 TXN Doc01Saqib ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Ids Unit 5Document15 pagesIds Unit 5aswinhacker28No ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface (Fddi) 2010-11Document20 pagesFiber Distributed Data Interface (Fddi) 2010-11manumang440No ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingummarimtiyazNo ratings yet
- Q. What Does FDDI Stand For?Document77 pagesQ. What Does FDDI Stand For?GauravNo ratings yet
- Network CablingDocument45 pagesNetwork CablingGokulCj GroveNo ratings yet
- Peer To Peer NetworksDocument18 pagesPeer To Peer NetworksDeepak AvNo ratings yet
- Network andDocument21 pagesNetwork andapi-3701823No ratings yet
- IEEE StandardsDocument3 pagesIEEE StandardsIshan ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Shining A Light On FDDI: FDDI and The OSI ModelDocument8 pagesShining A Light On FDDI: FDDI and The OSI ModeljibeshmNo ratings yet
- LAN Topologies and Media Access ControlDocument35 pagesLAN Topologies and Media Access ControlRudren Eswaran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Networks: Token Ring and FDDI 1Document25 pagesNetworks: Token Ring and FDDI 1Febi Audi RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Function and Frame Format of FDDI: Fiber Distributed-Data Interface (FDDI)Document12 pagesFunction and Frame Format of FDDI: Fiber Distributed-Data Interface (FDDI)dipamohantyNo ratings yet
- Tecnologias LANDocument31 pagesTecnologias LANAlexAnguloAbadNo ratings yet
- FDDIDocument25 pagesFDDIShivakumar LaxaniNo ratings yet
- Token Ring: Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument23 pagesToken Ring: Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceGirija VaniNo ratings yet
- Notes-Transmission MediaDocument22 pagesNotes-Transmission MediaRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 UpDocument18 pagesUnit 2 UpManju LaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Computer Networks: Ieee StandardsDocument5 pagesAssignment Computer Networks: Ieee StandardsketanNo ratings yet
- Adrian Mauly Rayi Tt4c Module8Document12 pagesAdrian Mauly Rayi Tt4c Module8Rayi Diah AriestaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Industrial Ethernet and Wireless CommunicationDocument15 pagesUnit 5 - Industrial Ethernet and Wireless Communicationjeevitha babuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4Kieren ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Recognize The Following Logical or Physical Network Topologies Given A Schematic Diagram or DescriptionDocument6 pages1.1 Recognize The Following Logical or Physical Network Topologies Given A Schematic Diagram or DescriptionChe MashepaNo ratings yet
- Fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)Document15 pagesFddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)ashok_it87No ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed - Data InterfaceDocument22 pagesFiber Distributed - Data Interfaceppareek16892No ratings yet
- Categories of UTP and STPDocument4 pagesCategories of UTP and STPIvan NagalNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Caramat, Exequiel Kirby EDocument20 pagesPrepared By: Caramat, Exequiel Kirby EPopoyNo ratings yet
- Token RingDocument23 pagesToken RingManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Lab FileDocument27 pagesComputer Network Lab FileVinayak KanherkarNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 3.1Document10 pagesInformation Sheet 3.1Danica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Transmission MediasDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Transmission Mediaschalie tarekegnNo ratings yet
- MAN TechnologiesDocument13 pagesMAN TechnologiesSunny acNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document4 pagesModule 8Knight KimNo ratings yet
- Fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)Document16 pagesFddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)jaigauthamNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 PDFDocument17 pagesExperiment No 1 PDFSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Module 4-7 No AnswerDocument22 pagesModule 4-7 No Answercharls.correa.143No ratings yet
- Introduction To Networking: The Business School University of KashmirDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Networking: The Business School University of Kashmirwasimshah011No ratings yet
- Transmitting Bits Across The Local MediaDocument19 pagesTransmitting Bits Across The Local MediaKawtar El ArifNo ratings yet
- Features of Star TopologyDocument14 pagesFeatures of Star TopologyKuldeep AttriNo ratings yet
- Medi-Caps University Indore: Computer Network Lab File Department of Computer Science Engineering Session: 2019-23Document46 pagesMedi-Caps University Indore: Computer Network Lab File Department of Computer Science Engineering Session: 2019-23Harsh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks (Version 7.00) - Modules 4 - 7: Ethernet Concepts ExamDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Networks (Version 7.00) - Modules 4 - 7: Ethernet Concepts ExamFatjonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Goals: Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument12 pagesChapter Goals: Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceXhy KatNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number: 01 Title:: Study of Existing LANDocument15 pagesExperiment Number: 01 Title:: Study of Existing LANAaizah WaniNo ratings yet
- Ieee802 StandardsDocument13 pagesIeee802 StandardsSaagar MinochaNo ratings yet
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksFrom EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo ratings yet
- TCP Ip CommandsDocument3 pagesTCP Ip Commandsdolon10No ratings yet
- Bca103 Sample Question BankDocument5 pagesBca103 Sample Question Bankdolon10No ratings yet
- Faq 1Document1 pageFaq 1dolon10No ratings yet
- Assignment Bca 193Document9 pagesAssignment Bca 193dolon10No ratings yet
- Software and Engineering (Questions and Answers-1)Document4 pagesSoftware and Engineering (Questions and Answers-1)dolon10100% (2)
- Data Communication FaqDocument4 pagesData Communication Faqdolon10No ratings yet