Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U140eand U241
Uploaded by
yosergeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
U140eand U241
Uploaded by
yosergeyCopyright:
Available Formats
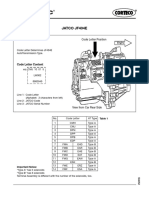
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-125
U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
JDESCRIPTION
D The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E D These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity 4-speed Super ECT (Electronically Controlled Transaxle). D The basic construction and operation of these automatic transaxles are the same. However, the gear ratio, disc, and spring number have been changed to accommodate the characteristic of the engine.
U140E " Specification A Model Transaxle Type Engine Type 1st 2nd 3rd Gear Ratio 4th Reverse Counter Gear Ratio Differential Gear Ratio Fluid Capacity Liters (US qts, Imp. qts) Fluid Type Dry Weight kg (lb)
161ES20
U241E
181CH09
02 Camry U140E 1MZ-FE 3.938*1 2.194*1 1.411*1 1.019*1 3.141*1 1.019 2.814 8.6 (9.1, 7.7)*2 ATF Type T-IV 91 (200.6) U241E 2AZ-FE 3.943*1 2.197*1 1.413*1 1.020*1 3.145*1 1.020 2.740 z z 82 (180.8) A140E 5S-FE 2.810 1.549 1.000 0.706 2.296 0.945
01 Camry A541E 1MZ-FE z z z 0.735 z z 3.933 6.8 (7.2, 5.9)*3 0.9 (0.9, 0.8)*4 z 83.3 (183.6)
3.944 5.6 (5.9, 4.9)*3 1.6 (1.7, 1.4)*4 ATF D-II or DEXRONIII (DEXRONII) 73 (160.9)
*1: Counter Gear Ratio Included *2: Differential Included
*3: Only for Transmission *4: Only for Differential
CH-126
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
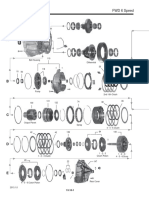
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear B1 C2 F1 Rear Planetary Gear B2
C1
Input Shaft
B3 Under Drive (U/D) Planetary Gear Differential Drive Pinion
F2
208CH01
C3 Counter Driven Gear
" Specification A Transaxle Type C1 C2 C3 B1 B2 B3 F1 F2 Forward Clutch Direct Clutch U/D Direct Clutch 2nd Brake 1st & Reverse Brake U/D Brake No. 1 One-Way Clutch U/D One-Way Clutch U140E 6 4 4 4 7 4 28 24 43 17 77 31 19 69 35 28 91 52 53 U241E 5 3 3 3 5 3 z 15 z z z z z z 32 26 83 50 51
The No. of Discs No
The No of Sprags No. The No. of Sun Gear Teeth The No. of Pinion Gear Teeth The No. of Ring Gear Teeth The No. of Sun Gear Teeth The No. of Pinion Gear Teeth The No. of Ring Gear Teeth The No. of Sun Gear Teeth The No. of Pinion Gear Teeth The No. of Ring Gear Teeth The No. of Drive Gear Teeth The No. of Driven Gear Teeth
Front Planetary Gear
Rear Planetary Gear
U/D Planetary Gear
Counter Gear
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-127
JTORQUE CONVERTER
D These torque converters have optimally designed fluid passages and impeller configuration resulting in substantially enhanced transmission efficiency to ensure better starting, acceleration and fuel economy. D Furthermore, a hydraulically operated lock-up mechanism which cuts power transmission losses due to slippage at medium and high speeds is used. D The basic construction and operation are the same as for the A541E for the previous models.
" Specification A Engine Type Transaxle Type Torque Converter Type Stall Torque Ratio 1MZ-FE U140E 2AZ-FE U241E
Turbine Runner Pump Impeller Lock-up Clutch Stator OD Input Shaft
3-Element, 1-Step, 2-Phase (with Lock-up Mechanism) 1.8 2.0
One-way Clutch
208CH02
JOIL PUMP
The oil pump is combined with torque converter, lubricates the planetary gear units and supplies operating pressure to the hydraulic control.
" Specification A Gear Drive Gear Driven Gear Gear Teeth 9 10 Pump Body Drive Gear
Stator Shaft Driven Gear
208CH03
CH-128
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
JPLANETARY GEAR UNIT 1. Construction
D The counter drive and driven gears are placed in front of the front planetary gear and the under drive (U/D) planetary gear unit is placed above the counter shaft. Furthermore, the force transmission method has been changed by eliminating the brake and the one-way clutch. As a result, a torque capacity that accommodates the high output engine has been attained, while realizing a compact gear unit. D A centrifugal fluid pressure canceling mechanism has been adopted in the C2 and C3 clutches that are applied when shifting from 2nd to 3rd and from 3rd to 4th.
Counter Drive Gear
B1 C2
F1
B2 Front Planetary Gear
C1
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear C3 Intermediate Shaft Differential Drive Pinion Sun Gear
F2
B3
(U/D) Planetary Gear Counter Driven Gear
Ring Gear
208CH04
2. Function of Component
C1 C2 C3 B1 B2 B3 F1 F2 Component Forward Clutch Direct Clutch U/D Direct Brake 2nd Brake 1st & Reverse Brake U/D Brake No. 1 One-Way Clutch U/D One-Way Clutch Function Connects input shaft and front planetary sun gear. Connects input shaft and rear planetary sun gear. Connects U/D sun gear and U/D planetary carrier. Prevents rear planetary carrier from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise. Prevents rear planetary carrier and front planetary ring gear from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise. Prevents U/D sun gear from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise. Prevents rear planetary carrier from turning counterclockwise. Prevents U/D planetary sun gear from turning clockwise. These gears change the route through which driving force is transmitted, in accordance with the operation of each clutch and brake, in order to increase or reduce the input and output speed.
Planetary Gears
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-129
3. Motive Power Transaxle
Shift Lever Position P R N Solenoid Valve Gear G Park Reverse Neutral 1st D 2nd 3rd 4th 2 L 1st 2nd 1st SL1 ON ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF ON SL2 ON OFF ON ON ON OFF OFF ON ON ON S4 OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF OFF DSL OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF/ON* OFF/ON* OFF OFF ON f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f C1 C2 C3 B1 B2 B3 f f f f f f f f f f F1 F2
*: Lock-up ON
1st Gear (D or 2 Position)
Counter Drive Gear
B1 C2
F1
B2
Front Planetary Gear
C1
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear
C3
Intermediate Shaft
Differential Drive Pinion Sun Gear
F2
B3 U/D Planetary Gear
Ring Gear
161ES09
Counter Driven Gear
CH-130
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
2nd Gear (D or 2 Position) Counter Drive Gear C1 B2 Front Planetary Gear Input Shaft
B1 C2
F1
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear
C3
Intermediate Shaft Differential Drive Pinion
F2
B3
Sun Gear U/D Planetary Gear Counter Driven Gear
Ring Gear
161ES10
3rd Gear (D Position) Counter Drive Gear
B1 C2
F1
B2 Front Planetary Gear
C1
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear
C3
Intermediate Shaft Differential Drive Pinion
F2
B3
Sun Gear U/D Planetary Gear Counter Driven Gear
Ring Gear
161ES11
4th Gear (D Position)
F1
B1 C2
Counter Drive Gear B2 Front Planetary Gear C1 Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear
C3
Intermediate Shaft Differential Drive Pinion
F2
B3
Sun Gear U/D Planetary Gear Counter Driven Gear
Ring Gear
161ES12
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1st Gear (L Position) Counter Drive Gear B2 Front Planetary Gear C1 Input Shaft
CH-131
B1 C2
F1
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear
C3
Intermediate Shaft Differential Drive Pinion
F2
B3
Sun Gear U/D Planetary Gear Counter Driven Gear
Ring Gear
161ES13
Reverse Gear (R Position) Counter Drive Gear C1 B2 Front Planetary Gear Input Shaft
B1 C2
F1
Rear Planetary Gear Sun Gear
C3
Intermediate Shaft Differential Drive Pinion
F2
B3
Sun Gear U/D Planetary Gear Counter Driven Gear
Ring Gear
181ES66
CH-132
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
4. Centrifugal Fluid Pressure Canceling Mechanism
There are two reasons for improving the conventional clutch mechanism: D To prevent the generation of pressure by the centrifugal force that applied to the fluid in piston fluid pressure chamber (hereafter referred to as chamber A) when the clutch is released, a check ball is provided to discharge the fluid. Therefore, before the clutch can be subsequently applied, it took time for the fluid to fill the chamber A. D During shifting, in addition to the original clutch pressure that is controlled by the valve body, the pressure that acts on the fluid in the chamber A also exerts influence, which is dependent upon revolution fluctuations. To address these two needs for improvement, a canceling fluid pressure chamber (hereafter referred to as chamber B) has been provided opposite chamber A. C2 Clutch C2 Clutch
Piston
Chamber A
Chamber B
C3 Clutch
208CH05
By utilizing the lubrication fluid such as that of the shaft, the same amount of centrifugal force is applied, thus canceling the centrifugal force that is applied to the piston itself. Accordingly, it is not necessary to discharge the fluid through the use of a check ball, and a highly responsive and smooth shifting characteristic has been achieved. Centrifugal Fluid Pressure Clutch Applied to the Chamber A Target Fluid Pressure
Centrifugal Fluid Pressure Applied to Chamber B Piston Fluid Pressure Chamber Chamber B (Lubrication Fluid)
Fluid Pressure Applied to Piston
Shaft Side
157CH17
Fluid pressure Centrifugal fluid pressure Target fluid pressure = (original clutch pressure) applied to piston - applied to chamber B
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-133
JVALVE BODY UNIT 1. General
The valve body consists of the upper and lower valve bodies and 5 solenoid valves. Apply orifice control, which controls the flow volume to the B3 brake, has been adopted in this unit. Solenoid Valve SL1 Solenoid Valve SLT
Upper Valve Body
Solenoid Valve DSL
Plate
Solenoid Valve SL2 Fluid Temperature Sensor
181CH11
Lower Valve Body Solenoid Valve S4 " Upper Valve Body A
2nd Regulator Valve Lock-up Relay Valve C2 Lock Valve Lock-up Control Valve
Solenoid Modulator Valve
B3 Orifice Control Valve B1 Lock Valve Clutch Apply Control Valve C2 Exhaust Check Valve
208CH06
CH-134
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
" Lower Valve Body A B2 Control Valve B1 Control Valve 3-4 Shift Valve Primary Regulator Valve C2 Control Valve
208CH07
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-135
2. Solenoid Valve
Solenoid Valves SL1, SL2, and SLT 1) General In order to provided a hydraulic pressure that is proportion to current that flows to the solenoid coil, the solenoid valve SL1, SL2, and SLT linearly controls the line pressure and clutch and brake engagement pressure based on the signals it receives from the ECM. The solenoid valves SL1, SL2, and SLT have the same basic structure.
Solenoid Coil Sleeve Hydraulic Pressure
Spool Valve Current
198CH31
2) Function of Solenoid Valve SL1, SL2, and SLT Solenoid Valve SL1 SL2 SLT Action For clutch and brake engagement pressure press re control For line pressure control Function B 1 brake pressure control Lock-up clutch pressure control C2 clutch pressure control Line pressure control Secondary pressure control
CH-136
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Solenoid Valves S4 and DSL 1) General The solenoid valves S4 and DSL use a three-way solenoid valve. Drain Control Pressure Line Pressure
Solenoid Valve ON
161ES65
Solenoid Valve OFF
181CH12
2) Function of Solenoid Valve S4 The solenoid valves S4 when set to ON controls the 3-4 shift valve to establish the 4th by changing over the fluid pressure applied to B3 brake and C3 clutch. Solenoid Valve S4 B3 Accumulator
Except 4th B3 Brake ON S4 OFF Line Pressure S4 ON C3 4th C3 Clutch ON B3
3-4 Shift Valve
161ES23
C3 Accumulator
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 3) Function of Solenoid Valve DSL
CH-137
The solenoid valve DSL controls the B2 control valve via the C2 lock valve when the transaxle is shifted in the R or L position. During lock-up, the lock-up relay valve is controlled via the C2 lock valve. Lock-up Relay Valve R Lock-up ON Chamber
Solenoid Valve DSL
Secondary Pressure
Lock-up OFF Chamber
Secondary Pressure C2 Lock Valve
R L B2
B2 Control Valve
208CH47
3. Apply Orifice Control
This control is effected by the B3 orifice control valve. The B3 orifice control valve has been provided for the B3 brake, which is applied when shifting from 4th to 3rd. The B3 orifice control valve is controlled by the amount of the line pressure in accordance with shifting conditions, and the flow volume of the fluid that is supplied to the B3 brake is controlled by varying the size of the control valves apply orifice. Line Pressure
Except 4th B3 Brake ON B3 B3 Orifice Control Valve
B3 Apply Fluid Pressure
B3 Accumulator
157CH19
CH-138
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
JELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General
The electronic control system of the U140E and U241E automatic transaxles consists of the control listed below. System Function Controls the pressure that is applied directly to B1 brake and C2 clutch by actuating the shift solenoid valve (SL1, SL2) in accordance with ECM signals. The solenoid valves SL1 and SL2 minutely controls the clutch pressure in accordance with the engine output and driving conditions. Actuates the solenoid valve SLT to control the line pressure in accordance with information from the ECM and the operating conditions of the transaxle. Retards the engine ignition timing temporarily to improve shift feeling during up or down shifting. Controls to restrict the 4th upshift or to provide appropriate engine braking by using the ECM to determine whether the vehicle is traveling uphill or downhill. The ECM sends current to the solenoid valve SL1 and/or SL2 based on signals from each sensor and shifts the gear. The ECM sends current to the shift solenoid valve (DSL) based on signals from each sensor and engages or disengages the lock-up clutch. The ECM sends signals to solenoid valve SLN when gear shift occurs to temporarily lower the accumulator back pressure so that the gear shift is completed smoothly. When the shift lever is shifted from N to D position, the gear is temporarily shifted to 2nd or O/D and then to 1st to reduce vehicle squat. When the shift lever is shifted from N to D position, the gear is temporarily shifted to 3rd and then to 1st to reduce vehicle squat. When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed section. To increase the speed for processing the signals, the 32-bit CPU of the ECM has been adopted. Even if a malfunction is detected in the sensors or solenoids, the ECM effects fail-safe control to prevent the vehicles drivability from being affected significantly. U140E, U241E A541E
Clutch Pressure Control
Line Pressure Optimal Control Engine Torque Control Shift Control in Uphill/Downhill Traveling Shift Timing Control Lock-up Timing Control Accumulator Back Pressure Control
f f f f f
f f f f f
f f f f
N to D Squat N D Control
f f
Diagnosis
Fail-safe
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-139
2. Construction
The configuration of the electronic control system in the U140E and U241E automatic transaxles are as shown in the following chart. SENSORS CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR NE SL1
ACTUATORS SOLENOID VALVE SL1
THW
SL2
SOLENOID VALVE SL2
VTA*1
VTA1*2
SLT
SOLENOID VALVE SLT
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR*1
NSW
R, D, 2, L
S4 SPD
SOLENOID VALVE S4
ABS SPEED SENSOR*2 ECM SKID CONTROL ECU*2 COMBINATION METER*2
SPD
DSL
SOLENOID VALVE DSL
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
COUNTER GEAR SPEED SENSOR
NC
INPUT TURBINE SPEED SENSOR
NT
ODLP
O/D OFF INDICATOR LIGHT
STOP LIGHT SWITCH
STP
THO FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR
ODMS
SIL TC
OVERDRIVE SWITCH *1: 2AZ-FE Engine Model *2: 1MZ-FE Engine Model
DATA LINK CONNECTOR 3
208CH08
CH-140
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
3. Layout of Components
Malfunction Indicator Light O/D OFF Indicator
ECM Overdrive Switch
Counter Gear Speed Sensor DLC3 Stop Light Switch Solenoid Valve SLT Solenoid Valve SL1 Vehicle Speed Sensor*
Input Turbine Speed Sensor Park/Neutral Position Switch
Solenoid Valve DSL Solenoid Valve SL2 *: 2AZ-FE Engine Model
Fluid Temperature Sensor
208CH09
Solenoid Valve S4
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-141
4. Construction and Operation of Main Component
Fluid Temperature Sensor A fluid temperature sensor is installed in the valve body for direct detection of the fluid temperature. Fluid temperature sensor is used for revision of clutches and brakes pressure to keep smooth shift quality every time.
Lower Valve Body
Fluid Temperature Sensor
181CH11
Speed Sensors The U140E and U241E automatic transaxles have adopted an input turbine speed sensor (for the NT signal) and a counter gear speed sensor (for the NC signal). Thus, the ECM can detect the timing of the shifting of the gears and appropriately control the engine torque and hydraulic pressure in response to the various conditions. D The input turbine speed sensor detects the input speed of the transaxle. The direct clutch (C2) drum is used as the timing rotor for this sensor. D The counter gear speed sensor detects the speed of the counter gear. The counter drive gear is used as the timing rotor for this sensor. Input Turbine Speed Sensor Counter Gear Speed Sensor
181CH14
CH-142
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
5. Clutch Pressure Control
Clutch to Clutch Pressure Control This control has been adopted for shifting from the 1st to 2nd gear, and from the 2nd to 3rd gear. Actuates solenoid valves SL1 and SL2 in accordance with the signals from the ECM, and guides this output pressure directly to the control valves B1 and C2 in order to regulate the line pressure that acts on the B1 brake and C2 clutch. As a result, compact B1 and C2 accumulators without a back pressure chamber have been realized. Signals from Individual Sensors
ECM
SL1 SL2
B1 Accumulator Solenoid Valve SL1 OFF # B1 Brake ON B1
C2 Accumulator Solenoid Valve SL2 OFF # C2 Clutch ON C2
B1 Control Valve
C2 Control Valve
161ES15
Clutch Pressure Optimal Control The ECM monitors the signals from various types of sensor such as the input turbine speed sensor, allowing shift solenoid valves SL1 and SL2 to minutely control the clutch pressure in accordance with engine output and driving conditions. As a result, smooth shift characteristics have been realized.
Input Shaft rpm
Target rpm Change Ratio ECM
Signals from Various Sensors Engine rpm Engine Torque Information Fluid Temperature
Practical rpm Change Ratio
Time Engine
Input Turbine Speed Sensor
SL2
Clutch/Brake Pressure
SL1
Solenoid Drive Signal
Output Shaft Torque
Time
198CH32
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-143
6. Shifting Control in Uphill/Downhill Traveling
General With shifting control in uphill/downhill traveling, the ECM calculates the throttle opening angle and the acceleration rate to determine whether the vehicle is in the uphill or downhill state. While driving uphill on a winding road with ups and downs, the 4th upshift is restricted to ensure a smooth drive. Also, if a brake application is detected while the ECM judges a downhill travel in 4th, the transmission automatically downshifts to 3rd in order to provide an appropriate engine brake. In addition, while the ECM judges a downhill travel, it restricts the travel in 3rd without keeping the brake application.
Uphill Corner
Without Control With Control
3rd 3rd
4th
3rd
4th 4th Brake Operation 3rd 4th
Shifting up to the 4th speed after down shifting to the 3rd speed is prohibited while uphill traveling is judged.
Down-shift to the 3rd speed occurs upon braking while downhill traveling is judged.
162CH09
Uphill/Downhill Judgment The actual acceleration calculated from the speed sensor signal is compared with the reference acceleration stored in the ECM to judge uphill or downhill traveling. The ECM judges an uphill travel if the actual acceleration is smaller than the reference acceleration, and restricts the 3rd to 4th upshift after a 4th to 3rd downshift has occurred. Also, the ECM judges a downhill travel if the actual acceleration is greater than the reference acceleration, and restricts the 4th upshift while traveling in 3rd. If a brake application is detected while traveling in 4th, it downshifts to 3rd. Actual Acceleration < Reference Acceleration Reference acceleration Actual acceleration Smaller Greater Uphill Downhill
162CH10
Actual Acceleration > Reference Acceleration
CH-144
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
7. Line Pressure Optimal Control
Through the use of the solenoid valve SLT, the line pressure is optimally controlled in accordance with the engine toque information, as well as with the internal operating conditions of the toque converter and the transaxle. Accordingly, the line pressure can be controlled minutely in accordance with the engine output, traveling condition, and the ATF temperature, thus realizing smooth shift characteristics and optimizing the workload in the oil pump.
Line Pressure
Primary Regulator
Solenoid Valve SLT
Solenoid Drive Signal
Input Turbine Speed Sensor Fluid Temperature Shift Position
Fluid Pressure
Current
Transaxle
Pump
Throttle Pressure
Engine
Throttle Valve Opening
Intake Air Volume Engine Coolant Temperature Engine rpm
ECM
161ES26
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-145
8. Diagnosis
D When the ECM detected a malfunction, the ECM makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed section. Furthermore, the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) in the combination meter illuminates or blinks toinform the driver. D At the same time, the DTCs (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) are stored in memory. The DTCs can be read by connecting a hand-held tester.
208CH36
Changes (from A541E) The DTCs (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) listed below have been added or discontinued. DTC No. P0710 P0711 P0765 Added DTC P0768 P1725 P1730 P1760 P1705 Discontinued Di ti d DTC P1765 Detection Item Transmission Fluid Temp. Sensor Malfunction (Fluid Temp. Sensor) Transmission Fluid Temp. Sensor Range/Performance Problem (Fluid Temp. Sensor) Shift Solenoid D Malfunction (Solenoid Valve S4) Shift Solenoid D Electrical Malfunction (Solenoid Valve S4) NT Revolution Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Input Turbine Speed Sensor) NC Revolution Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Counter Gear Speed Sensor) Linear Solenoid for Line Pressure Control Circuit Malfunction (Solenoid Valve SLT) NC2 Revolution Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Direct Clutch Speed Sensor) Linear Solenoid for Accumulator Pressure Control Circuit Malfunction (Solenoid Valve SLN)
Service Tip The length of time to clear the DTC by the battery terminal disconnection has been changed from the previous 10 seconds to 1 minute.
CH-146
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
9. Fail Safe
General This function minimizes the loss of operability when any abnormality occurs in each sensor or solenoid. " Fail-Safe Control List A Malfunction Part Speed Sensor Fluid Temp. Sensor Counter Gear Speed Sensor Function During a speed sensor malfunction, the vehicle speed is detected through the signals from the counter gear speed sensor to effect normal control. During a fluid temp. sensor malfunction, 4th upshift is prohibited. During a counter gear speed sensor malfunction, 4th upshift is prohibited. The current to the failed solenoid valve is cut off and control is effected by operating the other solenoid valves with normal operation. Shift control is effected as described in the table below, depending on the failed solenoid.
When shift solenoid SL1 is abnormal Traveling 3rd or 4th Solenoid Gear SL1 SL2 S4 ON OFF 3rd # OFF ON OFF 3rd # OFF OFF OFF 3rd Traveling 1st or 2nd Solenoid Gear SL1 SL2 S4 * ON OFF 2nd When SL2 is abnormal Solenoid SL2 S4 OFF Gear 3rd
Solenoid Valve SL1, SL2, and S4
When all solenoids are normal SL1 ON Solenoid SL2 S4 ON OFF Gear 1st
SL1 ON # OFF OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
2nd
ON OFF # ON OFF # ON
OFF OFF # ON ON
2nd
OFF OFF # ON ON
3rd
OFF
OFF
OFF
3rd
3rd
OFF
3rd
OFF
OFF
ON
4th
OFF
ON
4th
3rd
OFF
4th
*: B1 is constantly operating.
When S4 is abnormal Solenoid SL1 SL2 S4 ON ON Gear 1st When SL1 and SL2 are abnormal Solenoid SL1 SL2 S4 OFF Gear 3rd When SL1 and S4 are abnormal Traveling 3rd or 4th Traveling 1st or 2nd Solenoid Solenoid Gear Gear SL1 SL2 S4 SL1 SL2 S4 ON 3rd ON 2nd # OFF ON 3rd ON 2nd # OFF OFF OFF 3rd 2nd # # ON ON OFF # ON 3rd OFF # ON 2nd
OFF
ON
2nd
OFF
3rd
OFF
OFF
3rd
OFF
3rd
OFF
OFF
4th
ON
4th
(Continued)
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
When SL2 and S4 are abnormal Solenoid Gear SL1 SL2 S4 ON # 3rd OFF OFF 3rd OFF 3rd OFF 3rd When SL1, SL2 and S4 are abnormal Solenoid Gear SL1 SL2 S4 3rd 3rd 3rd 3rd
CH-147
JSHIFT CONTROL MECHANISM 1. General
D As in the past, the shift control mechanism of the 02 Camry consists of a straight shift lever that uses a shift control cable. D The O/D (overdrive) switch has been adopted on the momentary type. D A shift lock system consists of the key interlock device and shift lock mechanism, has been adopted.
2. Overdrive Switch
a) Turn the ignition switch from OFF to ON turns the overdrive ON. b) Pressing the O/D switch close (turn ON) the contact points, and releasing the switch opens (turn OFF) the contact points. c) Accordingly, pressing the switch cause the signal to be input into the ECM. d) The ECM turns OFF the overdrive (O/D OFF indicator light turn ON). e) Pressing the O/D switch again turns the overdrive back ON (O/D OFF indicator light turns OFF).
(d) O/D OFF Indicator Light O/D OFF ON Indicator Light OFF O/D Switch O/D Switch (Momentary Type) Ignition Switch ON OFF ON OFF (a) (a) (b) (e)
(d) ECM ODLP ODMS (c)
172GN01
CH-148
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
3. Shift Lock System
General D A shift lock system consists of the key interlock device and shift lock mechanism, that prevents the unintended operation of the shift lever has been provided. D A mechanical key interlock device that uses the key lock cable has been adopted. D An electrical shift lock mechanism, in which a shift lock solenoid and a shift lock ECU are integrated, has been adopted. Layout of Component
Key Cylinder
Shift Lock Override Button
Stop Light Cable Key Lock Cable Shift Lock Unit Shift Lock Solenoid Shift Lock ECU
208CH11
Key Interlock Device 1) General D This device will not allow the ignition key to be turned to the LOCK position or to pull out the ignition key unless the shift lever is moved to the P position. D This device, in which the shift lever and the key cylinder are connected via the key lock cable, mechanically limits the movement of the ignition key through the movement of the shift lever.
CHASSIS U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 2) Construction and Operation
CH-149
D The key cylinder contains a cam and a lock pin that move in unison with the ignition key. In addition, a key lock cable and a lock plate are placed above the lock pin. D When the driver moves the shift lever, the lock plate slides to restrict the movement of the lock pin, which in turn, restricts the movement of the ignition key. P Position Except P Position
LOCK ACC
Lock Plate Lock Pin Cam
IG Key
Key Lock Cable
208CH12
Shift Lock Mechanism D The shift lock mechanism prevents the shift lever from being shifted out of the P position to any other position unless the ignition switch is turned ON and the brake pedal is pressed. D A shift lock override button, which manually overrides the shift lock mechanism, is provided. " System Diagram A Shift Lock Unit Stop Light Switch Shift Lock ECU Ignition Switch
Shift Lock Solenoid
208CH13
You might also like
- U151e PDFDocument155 pagesU151e PDFAlejandro Roldan Valle88% (8)
- U341E GearDocument18 pagesU341E Gearpalaboy88875% (12)
- Guide to Toyota U240E and U341E Automatic TransaxlesDocument25 pagesGuide to Toyota U240E and U341E Automatic TransaxlesManuel Castillo77% (13)
- Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual Section TermsDocument132 pagesAutomatic Transaxle Repair Manual Section TermsRoman Filatov83% (6)
- A 340 e 343Document8 pagesA 340 e 343Mauricio Exequiel Chavez100% (1)
- Aw60 41sn Zip BookDocument8 pagesAw60 41sn Zip BookRiki Nurzaman100% (3)
- Toyota U151E-U250E Zip Kit: Electronic CautionsDocument8 pagesToyota U151E-U250E Zip Kit: Electronic CautionsMajdy Alsobhi100% (2)
- Location Valve Body U151EDocument5 pagesLocation Valve Body U151EgabotoyoNo ratings yet
- JF404EDocument8 pagesJF404EЙордан Василев50% (6)
- U140e U241e Zip PDFDocument8 pagesU140e U241e Zip PDFossoski100% (1)
- Auto Trans U241e PDFDocument396 pagesAuto Trans U241e PDFmasakp94% (16)
- Toyota U151ef U250eDocument1 pageToyota U151ef U250eMauricio Exequiel Chavez100% (1)
- MDMA Effects and IdentificationDocument16 pagesMDMA Effects and IdentificationJulio Chalbaud75% (4)
- Honda Accord, Acura RSX, TSX, CR-V Transmission SpecsDocument8 pagesHonda Accord, Acura RSX, TSX, CR-V Transmission Specshidraulic100% (5)
- Dokumen - Tips - Technical Service Information Atsg Toyotalexus U150u250 Preliminary Information PDFDocument5 pagesDokumen - Tips - Technical Service Information Atsg Toyotalexus U150u250 Preliminary Information PDFAleksandr Kuznichenko0% (1)
- U151E U250E VacTestDocument5 pagesU151E U250E VacTestbyungchul kimNo ratings yet
- JF016E-JF017E Vacuum Manual Valve BodyDocument4 pagesJF016E-JF017E Vacuum Manual Valve Bodyak_adamNo ratings yet
- A 240Document89 pagesA 240Mario Diaz Lopez100% (1)
- U140e U241e Zip inDocument10 pagesU140e U241e Zip inAnonymous DNM4ZI100% (4)
- U 151eDocument155 pagesU 151emauricio_ch_91100% (5)
- Overhaul A240eDocument140 pagesOverhaul A240eSamuel83% (6)
- U151E ComponentsDocument203 pagesU151E ComponentsAndres Chavez Barrios100% (3)
- Shop Manual U-341FDocument115 pagesShop Manual U-341FDavid100% (3)
- A340 VB ID PDFDocument5 pagesA340 VB ID PDFleeroy381No ratings yet
- Acura Honda Transmission Clutch Clearance SpecsDocument8 pagesAcura Honda Transmission Clutch Clearance Specspankituna5487100% (2)
- Baxa Resumen PDFDocument12 pagesBaxa Resumen PDFChepe Camacho100% (3)
- JR405EDocument8 pagesJR405ELalo Barajas Garcia100% (2)
- 83 Toyota 3A U140 U240 U241Document14 pages83 Toyota 3A U140 U240 U241Gabriel Hernandez Gaspar100% (1)
- JF015E VacTestGuide 1stCircRev 3-29-18 PDFDocument2 pagesJF015E VacTestGuide 1stCircRev 3-29-18 PDFhidraulic100% (2)
- Toyota U660E FWD 6-speed transmission rebuild kit guideDocument4 pagesToyota U660E FWD 6-speed transmission rebuild kit guidemickabd2002100% (1)
- A540e PDFDocument95 pagesA540e PDFAldair Víctor Huanca Santos100% (1)
- Nissan RE4F04AV Overhaul PDFDocument91 pagesNissan RE4F04AV Overhaul PDFpedro melendez100% (2)
- A541e Automatic TransaxleDocument132 pagesA541e Automatic TransaxleHuey_7480% (10)
- Valvebody Toyota U140.240Document5 pagesValvebody Toyota U140.240campollano14100% (4)
- Atra BulletinDocument2 pagesAtra Bulletinossoski100% (3)
- Re 4 Fo 4 ADocument116 pagesRe 4 Fo 4 AWissem RatelNo ratings yet
- Jactó 015eDocument2 pagesJactó 015ehidraulic100% (3)
- Valve Body Identification Guide Valve Body Identifi Cation GuideDocument11 pagesValve Body Identification Guide Valve Body Identifi Cation GuideUlloaEliasNo ratings yet
- Toyota U241 U140EDocument1 pageToyota U241 U140EPedroMecanico100% (2)
- Honda 5speedDocument11 pagesHonda 5speedLalo Barajas Garcia100% (2)
- Toyota Ab60e and Ab60f Automatic TransmissionDocument52 pagesToyota Ab60e and Ab60f Automatic Transmissioncfi2834657100% (10)
- U 140Document163 pagesU 140mauricio_ch_91100% (6)
- Hyundai A4AF1-2 - A4BF1-1Document4 pagesHyundai A4AF1-2 - A4BF1-1Tal Benyamin67% (6)
- Front Wheel Drive Automatic Transmission VT2Document6 pagesFront Wheel Drive Automatic Transmission VT2Erin Lam100% (2)
- Import Checkball Vol III 82-92 PDFDocument11 pagesImport Checkball Vol III 82-92 PDFJulio Chalbaud100% (1)
- F4A4x at Manual PDFDocument135 pagesF4A4x at Manual PDFDener Rogerio Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Jf016e Jf017e PDFDocument4 pagesJf016e Jf017e PDFSAMAD88% (8)
- 3040LE Cable-CompleteDocument13 pages3040LE Cable-CompleteZafer IlhanNo ratings yet
- AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE COMPONENTSDocument19 pagesAUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE COMPONENTSWissem RatelNo ratings yet
- U340 441E DescriptionDocument25 pagesU340 441E Descriptionruslan1580No ratings yet
- A340E and A343E automatic transmission specifications and operationDocument8 pagesA340E and A343E automatic transmission specifications and operationcalixtoruas75% (4)
- Automatic Transaxle GuideDocument194 pagesAutomatic Transaxle Guidebravo6d78% (9)
- Automatic A245E, A246EDocument17 pagesAutomatic A245E, A246EAntonio Carlos Santos77% (13)
- Auto 4HP16 (0 30)Document31 pagesAuto 4HP16 (0 30)Jose David Huanca Taype67% (3)
- 4f27e 2006 Workshop ManualDocument23 pages4f27e 2006 Workshop ManualTransmisiones Automáticas Chepe100% (5)
- Azera Automatic Transaxle SystemDocument170 pagesAzera Automatic Transaxle SystemPaulo Correa100% (1)
- Aa80e Intergration pt1 PDFDocument9 pagesAa80e Intergration pt1 PDFMothana Husban100% (4)
- At PDFDocument200 pagesAt PDFchory_1100% (1)
- Ishift and Powertronioc TrainingDocument265 pagesIshift and Powertronioc TrainingSherzad Chem100% (26)
- Qualifying Personnel To Visually Inspect Cleaned EquipmentDocument5 pagesQualifying Personnel To Visually Inspect Cleaned EquipmentLê Nho ĐánNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Technician Job OpeningDocument1 pageMaintenance Technician Job OpeningRizky NafandyNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 3196 MT-i - 3X4-13 - 130 m3h X 47 M GBQ - 49.991 - 14Document10 pagesData Sheet 3196 MT-i - 3X4-13 - 130 m3h X 47 M GBQ - 49.991 - 14Vinícius Toni MartinsNo ratings yet
- The Envelopes of The Arts Centre in SingaporeDocument12 pagesThe Envelopes of The Arts Centre in SingaporeAndriNo ratings yet
- Question 6Document4 pagesQuestion 6Ann SerratoNo ratings yet
- Cam350 810Document4 pagesCam350 810Frank ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Lookbook 2019 High ResolutionDocument74 pagesLookbook 2019 High ResolutionAis Mktg100% (1)
- INTERFACE LOADINGDocument31 pagesINTERFACE LOADINGNagraj Goud100% (1)
- ALGINATE ProductionDocument14 pagesALGINATE ProductionMarnel Roy MayorNo ratings yet
- Richa Industries Wins First Rail Over Bridge Project For Railways (Company Update)Document2 pagesRicha Industries Wins First Rail Over Bridge Project For Railways (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: Product Update: Drive Belt Auto-Tensioner Pivot Bolt ReplacementDocument4 pagesService Bulletin: Product Update: Drive Belt Auto-Tensioner Pivot Bolt ReplacementJeffrey TuasonNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning With GisDocument9 pagesUrban Planning With GisMostaque AhmedNo ratings yet
- TARA Framework explained with practical examplesDocument6 pagesTARA Framework explained with practical examplespoo12122No ratings yet
- Cross Laminated Timber MHMDocument17 pagesCross Laminated Timber MHMnaresworoNo ratings yet
- Catalog E EslonValve ManualOperationDocument72 pagesCatalog E EslonValve ManualOperationAnonymous ItzBhUGoiNo ratings yet
- KrisEnergy LTD - Appendix D - Volume2Document194 pagesKrisEnergy LTD - Appendix D - Volume2Invest StockNo ratings yet
- TFG A 020Document81 pagesTFG A 020Sergio FontechaNo ratings yet
- SOP Sample SubmissionDocument9 pagesSOP Sample SubmissionMUDASSAR AFZAL100% (1)
- IBIS Hotel Key Design and Construction CriteriaDocument2 pagesIBIS Hotel Key Design and Construction Criteriachien100% (1)
- Tesla v. Xpeng's Cao ComplaintDocument14 pagesTesla v. Xpeng's Cao ComplaintmashablescribdNo ratings yet
- Sharing The SkiesDocument357 pagesSharing The SkiesLava R5s2019No ratings yet
- Official Ied 1Document5 pagesOfficial Ied 1api-532866093No ratings yet
- Maruti SuzukiDocument33 pagesMaruti SuzukiNaman Arya100% (4)
- Bajaj PULSUR 220 DTS - OkokDocument75 pagesBajaj PULSUR 220 DTS - OkokSubramanya DgNo ratings yet
- CASE03-ABC-MfgDocument2 pagesCASE03-ABC-MfgLaura Catalina PerezNo ratings yet
- TcodeDocument5 pagesTcoderojeshpdNo ratings yet
- SCM CostsDocument9 pagesSCM CostsArnav VatsNo ratings yet
- Kiwiprop K4 Boss Assembly v2.4Document15 pagesKiwiprop K4 Boss Assembly v2.4adul sungkatinNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Vizag Steel Plant Distribution ChannelDocument91 pagesProject Report On Vizag Steel Plant Distribution ChannelPrisin Sudakaran0% (1)
- Module 7 (Maintenance Practices) Sub Module 7.1 (Safety Precautions-Aircraft and Workshop) PDFDocument42 pagesModule 7 (Maintenance Practices) Sub Module 7.1 (Safety Precautions-Aircraft and Workshop) PDFshareyhou100% (1)