Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Matters Ch01 Textbk ANS
Uploaded by
ZeneonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Matters Ch01 Textbk ANS
Uploaded by
ZeneonCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Matters for G.C.E.
O Level
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Kinetic Particle Theory
Answers to Textbook Exercises
Test Yourself 1.1 (page 2) Solid, liquid and gas 1. Liquid Test Yourself 1.2 (page 6) 1. (a) Gas (b) Solid (c) Arrangement in (a):
gas
Arrangement in (b):
solid
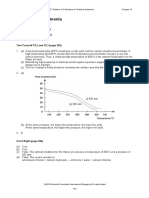
2. (a) The particles in a liquid are closely packed. However, the particles are not held in fixed position. The particles cannot be compressed but they can slide over one another. (b) Ice is a solid. The particles are closer together than in water vapour, giving it a higher density. In water vapour, the particles are much further away from each other, giving it a very low density. (1 g of ice has a volume of about 1.09 cm 3, 1 g of water has a volume of 1.0 cm3 and 1 g of water vapour has a volume of about 1333 cm3.) Test Yourself 1.3 (page 14) 1.
Temperature (C)
100 80 70
liquid solid and liquid
40
solid
Time (min)
Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Chemistry Matters for G.C.E. O Level
Chapter 1
2. (a) Sublimation occurred. The mothball must be made of substance that sublimes. (b) The volatile alcohol evaporated by absorbing heat from the skin. 3. Heat taken in sublimation, evaporation, boiling, melting Test Yourself 1.4 (page 19) 1. (a) (i) Nitrogen (ii) Chlorine (b) (slowest) Chlorine < sulphur dioxide < carbon dioxide < nitrogen (fastest) 2. Removal of unpleasant smells; removal of polluting gases; spreading of smell of flowers and perfumes 3. (i) Experiment III (ii) Experiment I Increase in temperature speeds up the rate of diffusion. Exercise 1 (page 20) Foundation 1. C 5. 2. C 3. A 4. D Heat given out condensation, freezing
(a) (i) E (ii) C and D (iii) A and B (b) As the temperature drops from 80 C, the gas particles lose kinetic energy and move more slowly. Eventually the movement of the particles is slow enough for the gas to change to a liquid at 58 C. On further cooling, the particles move slowly until the temperature reaches C and the liquid becomes a solid. The particles now can only vibrate in fixed positions. 7 As the temperature cools further to C, the particles vibrate more slowly in their fixed 10 positions.
6. The smell given out by perfumes is made up of tiny gas particles that move around freely. The particles diffuse from a region of higher concentration (the person) to a region of lower concentration (the other parts of the room). Challenge 1. D 2. (a) 50 C (b) 26 C. The temperature shown in the graph does not drop below 26 C. (c) The particles gain kinetic energy and move more rapidly until they reach their boiling point of 128 C. They now have sufficient energy to overcome the forces of attraction holding them together. The liquid X has changed to the gaseous state. (d) AB, BC and CD
Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Chemistry Matters for G.C.E. O Level
Chapter 1
(e)
Temperature (C) gas 128 liquid + gas
liquid 50 solid + liquid
solid 30 0
Time (s)
3. (a) When solid ammonium chloride is heated, it turns into a gas (ammonia and hydrogen chloride). Thus, it disappears. On the colder part of the test tube, the solid ammonium chloride vapour is reformed without going through liquid state. Thus, it reforms in the cooler part of the test tube. (b) Ammonia diffuses faster than hydrogen chloride gas. This is because the molecular mass of ammonia (i.e. 17) is less than the molecular mass of hydrogen chloride (i.e. 36.5). Hence, ammonia is detected first. 4. (a) Evaporates very readily at room temperature and pressure (b) As the ether evaporates, it absorbs heat, thus lowering the temperature. Ether evaporates faster than water, so the temperature of the gauze moistened with ether is lower. (c) Since ether catches fire very easily, keep the thermometers away from naked flames. 5. (a) Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. (b) Chlorine. It has the highest molecular mass. (c) Any gas with molecular mass greater than 71, e.g. bromine. (d) It is very soluble in water (e) Ethene has the same molecular mass as carbon monoxide.
6. Experiment 1: When the tap was opened, the bromine particles will collide with particles of
gases in bulb B and therefore diffuse more slowly to fill both bulbs. Experiment 2: There is no air and therefore no gas particles in bulb B. When the tap was opened, the particles of bromine can diffuse very rapidly to fill both bulbs due to less collision.
Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
You might also like
- CM TB Solutions C01Document3 pagesCM TB Solutions C01MahamIsmail86% (7)
- Chemistry Matters Ch16 Textbk ANSDocument2 pagesChemistry Matters Ch16 Textbk ANSZeneon63% (8)
- Chemistry Matters Ch04 Textbk ANSDocument2 pagesChemistry Matters Ch04 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (21)
- Chemistry Matters Ch06 Textbk ANSDocument2 pagesChemistry Matters Ch06 Textbk ANSZeneon79% (14)
- Chemistry Matters Ch07 Textbk ANSDocument4 pagesChemistry Matters Ch07 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (12)
- Chemistry Matters Ch05 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch05 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (12)
- CM TB Solutions C04Document2 pagesCM TB Solutions C04Robot Ninja67% (3)
- Speed of Reaction: Test Yourself 18.1 and 18.2 (Page 355)Document5 pagesSpeed of Reaction: Test Yourself 18.1 and 18.2 (Page 355)Jack Kowman25% (4)
- Chemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSZeneon82% (17)
- CM TB Solutions C06Document3 pagesCM TB Solutions C06Nisha75% (8)
- Metals: Test Yourself 14.1 (Page 250)Document4 pagesMetals: Test Yourself 14.1 (Page 250)Jack Kowman100% (2)
- Chemistry Matters Textbook Answers Chapter 3Document3 pagesChemistry Matters Textbook Answers Chapter 3MahamIsmail93% (15)
- Chemistry Matters Ch13 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch13 Textbk ANSZeneon50% (6)
- The Mole: Test Yourself 9.1 and 9.2 (Page 139)Document10 pagesThe Mole: Test Yourself 9.1 and 9.2 (Page 139)Ahmad Ahsan40% (5)
- Writing Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)Document1 pageWriting Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)khalil rehman100% (2)
- Chemistry Matters Ch17 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch17 Textbk ANSZeneon100% (3)
- Ammonia: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 381)Document4 pagesAmmonia: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 381)Jack Kowman100% (3)
- CM TB Answers C17Document3 pagesCM TB Answers C17khalil rehman100% (1)
- An Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 414)Document3 pagesAn Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 414)Jack Kowman75% (8)
- This Study Resource Was: WavesDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: WavesAhmad Ahsan100% (2)
- Alkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Document7 pagesAlkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Jack Kowman100% (1)
- The Mole: Test Yourself 9.1 and 9.2 (Page 139)Document8 pagesThe Mole: Test Yourself 9.1 and 9.2 (Page 139)Abdul moiz Waheed82% (11)
- Chemical Calculations: Mass of Cucl .2H O Molar Mass of Cucl .2H O 3.42 64 + (2 ! 35.5) + (2 ! 18)Document5 pagesChemical Calculations: Mass of Cucl .2H O Molar Mass of Cucl .2H O 3.42 64 + (2 ! 35.5) + (2 ! 18)khalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Test Yourself 23.1 and 23.2 (Page 453)Document2 pagesAlcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Test Yourself 23.1 and 23.2 (Page 453)khalil rehman40% (5)
- Writing Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)Document1 pageWriting Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)Zeeshan MunirNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C11Document6 pagesPM TB Solutions C11Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (8)
- Chemistry Matters Ch19 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch19 Textbk ANSZeneon100% (1)
- PM TB Solutions C06Document7 pagesPM TB Solutions C06Vishwajeet Ujhoodha88% (8)
- Alkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Document3 pagesAlkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)khalil rehman100% (2)
- Ionic Bonding: Test Yourself 6.1 and 6.2 (Page 95) Number of Protons Number of Neutrons Number of ElectronsDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding: Test Yourself 6.1 and 6.2 (Page 95) Number of Protons Number of Neutrons Number of Electronskhalil rehman0% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 pagesPure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFno one100% (3)
- PM TB Solutions C02Document10 pagesPM TB Solutions C02Vishwajeet Ujhoodha86% (14)
- PM TB Solutions C09Document3 pagesPM TB Solutions C09Vishwajeet Ujhoodha88% (8)
- Ecology: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 405)Document4 pagesEcology: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 405)leeNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C05Document6 pagesPM TB Solutions C05Vishwajeet Ujhoodha82% (11)
- Measurement: Test Yourself 1.2 (Page 5)Document5 pagesMeasurement: Test Yourself 1.2 (Page 5)Vishwajeet Ujhoodha92% (12)
- PM - TB Solutions - C09 PDFDocument3 pagesPM - TB Solutions - C09 PDFVishwajeet Ujhoodha59% (22)
- Excretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)Document2 pagesExcretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)leeNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C04Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C04Vishwajeet Ujhoodha75% (4)
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Document5 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Jack Kowman100% (8)
- This Study Resource Was: Current ElectricityDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Current ElectricityAbdul moiz Waheed100% (3)
- Transport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)Document3 pagesTransport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)lee100% (3)
- Electromagnetic Induction: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 430)Document7 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 430)Jack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 388)Document6 pagesMagnetism: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 388)Jack Kowman80% (5)
- The Periodic Table: Test Yourself 16.1 and 16.2 (Page 312)Document2 pagesThe Periodic Table: Test Yourself 16.1 and 16.2 (Page 312)khalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C08Document4 pagesPM TB Solutions C08Vishwajeet Ujhoodha80% (5)
- Chap 7 CMDocument4 pagesChap 7 CMhajraNo ratings yet
- Practical Electricity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 365)Document5 pagesPractical Electricity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 365)Jack Kowman67% (6)
- PM TB Solutions C03Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C03Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (5)
- Hormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)Document3 pagesHormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)leeNo ratings yet
- Heredity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 359)Document2 pagesHeredity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 359)lee0% (1)
- Nutrition in Humans: Test Yourself 6.1 (Page 96)Document3 pagesNutrition in Humans: Test Yourself 6.1 (Page 96)lee100% (1)
- PM TB Solutions C18 PDFDocument10 pagesPM TB Solutions C18 PDFAbdul moiz Waheed100% (5)
- Kinetic Particle Theory: Answers To Textbook ExercisesDocument3 pagesKinetic Particle Theory: Answers To Textbook ExercisesariiNo ratings yet
- CH - 1Document4 pagesCH - 1Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- HHW SC Class 9thDocument8 pagesHHW SC Class 9thSanjeeta SenNo ratings yet
- Matter Surrounding Level I NCERTDocument7 pagesMatter Surrounding Level I NCERTAmmar YasirNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Matter in Our Surroundings McqsDocument3 pagesClass 9 Matter in Our Surroundings McqsHariharan VIIA1No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions on States of Matter and Changes of StateDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on States of Matter and Changes of StateAgam VermaNo ratings yet
- ch1 1Document9 pagesch1 1vrndrnirmalkar11No ratings yet
- O Level Pure Physic Dynamics Revision ExerciseDocument3 pagesO Level Pure Physic Dynamics Revision ExerciseZeneon0% (1)
- O Level Pure Physic TYS Physics 1999 To 2008 AnswersDocument42 pagesO Level Pure Physic TYS Physics 1999 To 2008 AnswersZeneon47% (15)
- November 1997 Pure Chemistry PaperDocument11 pagesNovember 1997 Pure Chemistry PaperZeneon100% (1)
- Anderson Prelim Trend QN With AnswersDocument2 pagesAnderson Prelim Trend QN With AnswersZeneonNo ratings yet
- O Level Pure Physic - Physics Definition ListDocument5 pagesO Level Pure Physic - Physics Definition ListZeneon89% (9)
- Chemistry Matters Ch19 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch19 Textbk ANSZeneon100% (1)
- O Level Chem OCR Papers With AnswersDocument8 pagesO Level Chem OCR Papers With AnswersZeneonNo ratings yet
- O Level Pure Physic Static Electricity NotesDocument5 pagesO Level Pure Physic Static Electricity NotesZeneon100% (5)
- O Level Pure Physic Dynamics Revision ExerciseDocument3 pagesO Level Pure Physic Dynamics Revision ExerciseZeneon0% (1)
- O Level Chem June PapersDocument14 pagesO Level Chem June PapersZeneonNo ratings yet
- O Level Chem RevisionDocument9 pagesO Level Chem RevisionZeneon100% (1)
- Junyuan Prelim 2008 Section B Paper2 With AnswersDocument4 pagesJunyuan Prelim 2008 Section B Paper2 With AnswersZeneonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Ch17 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch17 Textbk ANSZeneon100% (3)
- Chemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSZeneon82% (17)
- Chemistry Matters Ch13 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch13 Textbk ANSZeneon50% (6)
- Chemistry Matters Ch05 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch05 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (12)
- O Level NOV 2004 1123 Examiner ReportDocument9 pagesO Level NOV 2004 1123 Examiner ReportZeneonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Ch02 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch02 Textbk ANSZeneon71% (14)
- GCE O Level Chem Qualitative AnalysisDocument4 pagesGCE O Level Chem Qualitative AnalysisZeneon86% (7)
- O Level NOV 2004 1123 QuestionDocument4 pagesO Level NOV 2004 1123 QuestionZeneonNo ratings yet
- O Level NOV 2004 1123 AnswersDocument14 pagesO Level NOV 2004 1123 AnswersZeneonNo ratings yet
- (Notes) ChannelisationDocument2 pages(Notes) ChannelisationZeneonNo ratings yet
- O Level NOV 2004 1123 InsertDocument4 pagesO Level NOV 2004 1123 InsertZeneonNo ratings yet
- Chapt 9-Reasons For Uneven Development in The WorldDocument11 pagesChapt 9-Reasons For Uneven Development in The WorldZeneon100% (1)
- Chapt 8-Variations in Development in The WorldDocument28 pagesChapt 8-Variations in Development in The WorldZeneon50% (2)
- ETABS Building Structure Analysis and Design ReportDocument84 pagesETABS Building Structure Analysis and Design ReportMd Awesshadab0% (1)
- Digital and Analog SignalsDocument10 pagesDigital and Analog SignalsSrishti GargNo ratings yet
- FT 539G Eng 01Document4 pagesFT 539G Eng 01lmw_arunNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue Chemical IndicatorsDocument28 pagesProduct Catalogue Chemical IndicatorsscribdddcNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Checklist: Macan/S/GTS/Turbo (2015-On)Document2 pagesMaintenance Checklist: Macan/S/GTS/Turbo (2015-On)edk34100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2LolmasterNo ratings yet
- 1-Newton Second Law-ForMATDocument5 pages1-Newton Second Law-ForMATVAIBHAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Debre Tabor University: Network and System AdministrationDocument33 pagesDebre Tabor University: Network and System AdministrationBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- TVL CSS11 Q4 M1Document12 pagesTVL CSS11 Q4 M1Richard SugboNo ratings yet
- Cross Taping - A Practical Guide 12Document2 pagesCross Taping - A Practical Guide 12jfjjfjfjjfjfNo ratings yet
- Post GreeDocument15 pagesPost GreeDwi PraptiNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Gases in LaboratoryDocument7 pagesPreparation of Gases in LaboratoryChu Wai Seng50% (2)
- Knight Boiler ManualDocument80 pagesKnight Boiler ManualAnonymous 7xHNgoKE6eNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Data Modeling and Database Design Volume 1 - The Shortest Advisable Path A Fully Algorithmic ApproachDocument662 pagesConceptual Data Modeling and Database Design Volume 1 - The Shortest Advisable Path A Fully Algorithmic ApproachErkan50% (2)
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDocument45 pagesAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamNo ratings yet
- Programming structures if, for and while loopsDocument16 pagesProgramming structures if, for and while loopsFrancisco AristizabalNo ratings yet
- Planetary AlignmentDocument7 pagesPlanetary AlignmentEbn MisrNo ratings yet
- PSD60-2R: Operation ManualDocument22 pagesPSD60-2R: Operation ManualOscar SantanaNo ratings yet
- MC0081Document385 pagesMC0081Purushottam KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Process ConditionsDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Process ConditionsIbrahim Al-HammadiNo ratings yet
- Final Project Regenerative BrakingDocument6 pagesFinal Project Regenerative Brakingdims irifiyinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Book AppliedAdvancedAnalyticsDocument236 pages2021 Book AppliedAdvancedAnalyticsKitykatmely LoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Basic Heat TransferDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Basic Heat TransferGabo MarquezNo ratings yet
- Información de Transmisión CVT ToyotaDocument151 pagesInformación de Transmisión CVT ToyotaMauricio Exequiel Chavez93% (15)
- Eca Lab Record PDFDocument71 pagesEca Lab Record PDFAlokNo ratings yet
- Self-Coached Climber - The Guide To Movem - Dan M (1) HagueDocument376 pagesSelf-Coached Climber - The Guide To Movem - Dan M (1) HagueBill Frisch100% (1)
- CHEM F111: General Chemistry II-Semester Lecture 35 (12-04-2019Document20 pagesCHEM F111: General Chemistry II-Semester Lecture 35 (12-04-2019Rachit ShahNo ratings yet
- Problem #1: Session #19: Homework SolutionsDocument4 pagesProblem #1: Session #19: Homework SolutionsMD Abu RaselNo ratings yet
- PID CONTROL SIMULATIONDocument6 pagesPID CONTROL SIMULATIONadrianordsNo ratings yet
- Richard A. Nyquist and Ronald O. Kagel (Auth.) - Handbook of Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic Compounds and Organic Salts. Infrared Spectra of Inorganic Compounds-Academic Press (1971)Document499 pagesRichard A. Nyquist and Ronald O. Kagel (Auth.) - Handbook of Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic Compounds and Organic Salts. Infrared Spectra of Inorganic Compounds-Academic Press (1971)Patrícia Bodanese PratesNo ratings yet