Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract
Uploaded by
Arjun JayakumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
Uploaded by
Arjun JayakumarCopyright:
Available Formats
ABSTRACT MAGNETIC REFRIGERATION
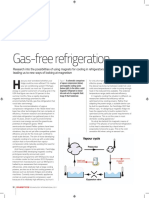
In recent years environmental aspects have been becoming an increasingly important issue in the design and development of refrigeration system. Especially in the vapour compression system, the banning of CFCs and HCFCs because of there environmental disadvantages has made way for other refrigeration technologies. One of these emerging technologies is magnetic refrigeration. Magnetic refrigeration, based on magnetocaloric effect (MCE), has received increased attention as an alternative to the well-established compression-evapouration cycle for room temperature application. The technique can be used to attain extremely low temperature (well below 1K), as well as the ranges used in common refrigerators depending on the design of the system. The common refrigent used in this type of refrigeration is gadolinium and its alloys. Gadoliniums temperature is observed to increase when it enters certain magnetic fields. When it leaves the magnetic field, the temperature drops. The effect is considerably stronger for the gadolinium alloy. This effect forms the basis of magnetic refrigeration. The magnetic refrigeration cycle can be performed quasi static which results in the possibility to operate close to Carnot efficiency. Magnetic refrigeration is an environmentally friendly cooling technique. It does not use ozone depleting chemicals, hazardous chemicals and greenhouse gases.
Submitted by Arjun Jayakumar S7, Me1 15
You might also like
- Ejectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid DynamicsFrom EverandEjectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar ON "Magnetic: Refrigeration"Document26 pagesTechnical Seminar ON "Magnetic: Refrigeration"ahmedNo ratings yet
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementFrom EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNo ratings yet
- "Magnetic Refrigeration": GuideDocument24 pages"Magnetic Refrigeration": GuideRishi MohanNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbines in Cold Climates: Icing Impacts and Mitigation SystemsFrom EverandWind Turbines in Cold Climates: Icing Impacts and Mitigation SystemsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration: The Oxford College of EngineeringDocument24 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: The Oxford College of EngineeringShehnaz FathimaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument17 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationswadishjNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration & Materials: RV Kalmekar Roll No-10MS60-D05Document26 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration & Materials: RV Kalmekar Roll No-10MS60-D05rajkalmekarNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON "Magnetic Refrigeration": Presented ByDocument26 pagesSeminar ON "Magnetic Refrigeration": Presented ByrakeshreddyNo ratings yet
- Aditya Silver Oak Institute of Technology: Magnetic RefrigerationDocument17 pagesAditya Silver Oak Institute of Technology: Magnetic RefrigerationNisarg PandyaNo ratings yet
- Magneti RefrigerationDocument25 pagesMagneti Refrigerationagastyadk100% (2)
- Magnetic Refrigeration SeminarDocument29 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration SeminarIdulla Birajdar100% (2)
- Magnetic Refrigeration: Presented By: Christy George Rajiv Gandhi Institute of TechnologyDocument9 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: Presented By: Christy George Rajiv Gandhi Institute of TechnologyChristy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument27 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationTochi Krishna Abhishek100% (1)
- Magneti RefrigerationDocument25 pagesMagneti RefrigerationlakshmyachuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument27 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationGanesh MurthiNo ratings yet
- Technical Proposal OnDocument12 pagesTechnical Proposal OnAshraf shaikhNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument5 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationNidheesh DasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration The Modern Refrigeration Technique A ReviewDocument9 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration The Modern Refrigeration Technique A ReviewkhathirzNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Magnetic RefrigeratorDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Magnetic Refrigeratorshvximwhf100% (1)
- Presentation of Magnetic RefrigerationDocument19 pagesPresentation of Magnetic Refrigerationjai singhNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration Research PaperDocument6 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration Research Papergz7gh8h0100% (1)
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument23 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationHarshith thanushNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Magn Refr 1233144769599259 1Document17 pagesSeminar On Magn Refr 1233144769599259 1Shourya ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2019Document40 pagesZhang 2019sanath santhoshNo ratings yet
- Agneto Caloric Effect and Magnetic Refrigeration: Submitted by Rohin Kaushik SIDDocument13 pagesAgneto Caloric Effect and Magnetic Refrigeration: Submitted by Rohin Kaushik SIDrohin kaushikNo ratings yet
- Gas Free RefrigerationDocument3 pagesGas Free RefrigerationYangyangNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration ReportDocument16 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration ReportAbhishekUpadhyay100% (1)
- Magnetic Refrigeration: A Promising Substitute For Vapour Compression SystemDocument7 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: A Promising Substitute For Vapour Compression SystemPallavi DigheNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration SeminarDocument19 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration SeminarSuraj KadamNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument21 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationVishnu RajuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument20 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationHARRYMAN008No ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration Research Paper PDFDocument6 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration Research Paper PDFngqcodbkf100% (1)
- Presentation On Magnetic RefrigerationDocument16 pagesPresentation On Magnetic RefrigerationAshish GauravNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration: BY Santhosh Kumar. R 1BJ07ME408 Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: BY Santhosh Kumar. R 1BJ07ME408 Department of Mechanical EngineeringSubash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument20 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationVineet DubeyNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Magnetic Ref.Document19 pagesSeminar Report On Magnetic Ref.Vishal JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Magnetic Refrigeration Sourabh SInghDocument9 pagesResearch Paper On Magnetic Refrigeration Sourabh SInghersourabh75% (4)
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument27 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationGanesh MurthiNo ratings yet
- Review (Suggest Name)Document14 pagesReview (Suggest Name)sreekesh mallyaNo ratings yet
- Overview On Magnetic Refrigeration: Introduction and Brief HistoryDocument12 pagesOverview On Magnetic Refrigeration: Introduction and Brief Historyguru smileNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument24 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationAnshul LallNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesSeminar ReportAashish AkatsukiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration V3Document3 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration V3Mirza MesanovicNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration-2017Document9 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration-2017ZerotheoryNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration: A Chilling AttractionDocument19 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: A Chilling AttractionVineetha KannepalliNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration: Presented By-Hardik Kothiya Guided by - J.R. MahajanDocument17 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: Presented By-Hardik Kothiya Guided by - J.R. MahajanvivekNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration SeminarDocument20 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration SeminarAshique cmNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration: Seminar OnDocument17 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: Seminar OnBharat CvNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument23 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationArjunPurandaranNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument19 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic DemagnetizationDocument10 pagesAdiabatic DemagnetizationBharath WajNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Enhancement in Heat Recovery Steam Generator Using Dry Ice Co Blasting Cleaning MethodDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Enhancement in Heat Recovery Steam Generator Using Dry Ice Co Blasting Cleaning MethodDimas PalgunadiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediavatsal07No ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument19 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationRavikanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Magnetocaloric Heat-Pump DevicesDocument6 pagesThe Evolution of Magnetocaloric Heat-Pump DevicesGiuseppe FioreNo ratings yet
- Mezaal 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 87 032024 PDFDocument8 pagesMezaal 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 87 032024 PDFTheen BadhushNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument19 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationMichael PerezNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigration My PresentationDocument24 pagesMagnetic Refrigration My Presentationmohammed kamrankaleemNo ratings yet
- Solid State Magnetocaloric Air Conditioning SystemDocument26 pagesSolid State Magnetocaloric Air Conditioning SystemM Muneeb VohraNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignFrom EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EFrom EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70ERating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Culture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsFrom EverandCulture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Workers' Inferno: The untold story of the Esso workers 20 years after the Longford explosionFrom EverandWorkers' Inferno: The untold story of the Esso workers 20 years after the Longford explosionNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesFrom EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityFrom EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)