Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cim Lab Manual 012110045623 1
Uploaded by
fhghsdfa7823645jkjOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cim Lab Manual 012110045623 1
Uploaded by
fhghsdfa7823645jkjCopyright:
Available Formats
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT LAB MANUAL Subject: Computer Integrated Manufacturing Semester-VII LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
13. CIM model for any industry. Manual part programming on CNC lathe, milling and Simula tion on CNC lathe and CNC mill. Study and demonstration on Robots. Study of comp uter aided process planning. Study of Group Technology & part families. Study of computer aided quality control. Introduction to CAD softwares. Introduction to CAM software. Study of computer controlled business functions. Study of interfac ing requirements in CIMS. Generation of any one simple solid model using any CAD software. Program for generation of any surface. drilling.
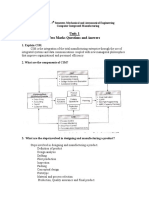
Experiment- 1 Aim - Study of CIM model for any Industry. Theory PART I 1) Definition of Automation. 2) Types of automation. a) Fixed auto mation. b) Programmable automation. c) Flexible automation. 3) Information proce ssing cycle. a) Business functions. b) Product Design c) Manufacturing Planning d) Manufacturing control e) Shop floor control f) Inventory control g) Quality c ontrol 4) Difference between Automation & CIM. 5) Evolution of CIM. 6) Various e lements of CIMS. 7) CIM Hardware & Software
PART II Case Study of any one local CIM based Industry. ObjectiveCompany pr Plant Layout Type of operation in industry Advancement in industrySuggestion if any Conclusion-
Experiment - 2 Aim - Manual Part Programming On CNC Lathe, Milling and Drilling . Theory 1) Introduction to Numerical Control (NC). 2) Basic Components of NC. 3) Co-ordinate system in NC 4) Machine Control Unit (MCU) & its positioning. 5) NC Programming method. 6) NC words. 7) Tape format 8) Programs. a) Program for lath e. b) Program for drilling. c) Program for milling. Conclusion-
Experiment - 3 Aim - Simulation o-n CNC Lathe and CNC Mill. Theory 1) G codes & M- codes for Lathe and Mill. a) Program for plain turning. b ) Program for step turning. c) Program for linear & circular interpolation. Conclusion.-
Experiment - 4 Aim Theory1) Introduction of Robot. 2) Robot anatomy. -- joints a nd links i) ii) iii) iv) v) Linear joint Orthogonal joint. Rotational joint. Twi sting joint. Revolving joint. - Study and Demonstration on Robots. 3) Robot configurations.i) ii) iii) iv) v) Polar configuration. Cylindrical conf iguration. Cartesian coordinate robot. Jointed arm robot. SCARA 4) Robot drive system. 5) Accuracy and repeatability. 6) Types of robot programm ing. 7) Safety monitoring. 8) End effectors and sensors in robots. 9) Applicatio n of robots. 10) Programming for some robotic application.
Conclusion -
Experiment - 5 Aim - Study Of Computer Aided Process Planning. Theory 1) Introduction. 2) Types of Computer aided process planning. i) ii) Retr ieval process planning. Generative process planning. 3) Advantages of computer aided process planning. Conclusion.
Experiment - 6 Aim - Study of Group Technology & Part Families. Theory 1. Introduction. 2. Part families. 3. Coding technology. 4. Obstacles to GT. 5. Methods of classification. i) ii) iii) Visual inspection. Classification and coding system. Production flow analysis. 6. Types of classification and coding system. 7 .Benefits of well designed class ification and coding stestem. 8. Machine cell design. 9. Types of cell design.. 10. Benefits of Group Technology. Conclusion-
Experiment - 7 Aim Theory - Study Of Computer Aided Quality Control. 1. Principl e of automated inspection. 2. QC Inspection. 3. QC testing. 4. Types of automate d inspection. i) ii) iii) 100 % automated inspection. Off-line and on-line inspe ction. Distributed inspection and final inspection. 5. Sensors technologies for automated inspection. 6. coordinates measuring machi nes. 7. CMM benefits. 8. Other contact inspection methods. 9. Machine vision. Conclusion.
Experiment - 8 Aim - Introduction To CAD Software. Theory 1. Fundamentals of CAD. 2. Traditional design process. 3. Computer Aided Design process. 4. Study of CAD softwares. Conclusion -
Experiment - 9 Aim - Introduction To CAM softwares. Theory 1. Fundamentals of CAM. 2. Study of any three CAM softwares. Conclusion-
Experiment - 10 Aim - Study of Computer Controlled Business functions Theory 1) Business Functions. a) Purchase order & receiving. b) Inventory manage ment c) Financial control 2) Job costing 3) Bill of Material. 4) Master producti on schedule 5) Material requirement planning. 6) Capacity planning. 7) Productio n planning. 8) Shop floor control. Conclusion-
Experiment - 11 Aim - Study of Interfacing Requirements in CIMS. Theory 1) Manufacturing system integration. 2) Manufacturing task to be integrat ed. a) Product design. b) Manufacturing planning. c) Manufacturing execution. 3) Requirements for integrated manufacturing system. a) System architecture. b) Pr oduct model. c) Data extraction. d) Manufacturing environment. e) Information ge neration & data collection. f) Database. 4) Benefits of integrated manufacturing systems. 5) Inspection 6) Co-ordinate measuring machine (CMM). Conclusion-
Experiment - 12 Aim - Generation Of Any One Simple Solid Model Using Any Cad Sof tware. Theory 1) Geometric Modeling. a) Wire frame model. b) Surface model. c) Solid mo del. 2) Generation of one simple solid model. Steps involved in model making pro cedure. Conclusion-
Experiment - 13 Aim - Program for Generation of any Surface. Theory 1) Program for generation of surface. Conclusion-
Lab- Manual Of Automation In Production Seven Semester Mechanical, Mechanical Engineering Department, G.H. Raisoni Colle ge Of Engg , Nagpur-16
You might also like
- Modeling Embedded Systems and SoC's: Concurrency and Time in Models of ComputationFrom EverandModeling Embedded Systems and SoC's: Concurrency and Time in Models of ComputationNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineers' Handbook, Volume 2: Design, Instrumentation, and ControlsFrom EverandMechanical Engineers' Handbook, Volume 2: Design, Instrumentation, and ControlsNo ratings yet
- PSD90-1C Operation ManualDocument41 pagesPSD90-1C Operation ManualmglemNo ratings yet
- The CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0From EverandThe CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Eclipse Tutorial3Document26 pagesEclipse Tutorial3Tariq AliNo ratings yet
- Product Design & CADDocument15 pagesProduct Design & CADHamizan MohdNo ratings yet
- Digital Circuit Testing: A Guide to DFT and Other TechniquesFrom EverandDigital Circuit Testing: A Guide to DFT and Other TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing One Mark Question & AnswersDocument14 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing One Mark Question & AnswersLovely ShalihNo ratings yet
- Engineering Applications: A Project Resource BookFrom EverandEngineering Applications: A Project Resource BookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (1)
- CNC LAB MANUAL AND RECORDDocument33 pagesCNC LAB MANUAL AND RECORDrajee10133% (3)
- Cim Lab Manual - 012110045623 - 1Document17 pagesCim Lab Manual - 012110045623 - 1Uday MavooriNo ratings yet
- AIP Lab Manual - 012110050524 - 1Document11 pagesAIP Lab Manual - 012110050524 - 1Martin De Boras PragashNo ratings yet
- Me6703 Cim - QBDocument22 pagesMe6703 Cim - QBMukesh SaravananNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing CourseDocument3 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing CoursesatheeshNo ratings yet
- Cim SyllabusDocument2 pagesCim SyllabusHarish HNo ratings yet
- CAD/CAM/CIM Course OverviewDocument126 pagesCAD/CAM/CIM Course OverviewA. I. RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cim Two MarksDocument23 pagesCim Two Marksrjesh194No ratings yet
- CIM Systems for Manufacturing Design, Planning & ControlDocument1 pageCIM Systems for Manufacturing Design, Planning & ControlJeganNo ratings yet
- ME2402 COMPUTER INTEGRATED MENUFACTURING (Questions & AnswersDocument9 pagesME2402 COMPUTER INTEGRATED MENUFACTURING (Questions & AnswersMartin De Boras Pragash100% (1)
- CADCAMDocument50 pagesCADCAMPrem Chander100% (5)
- Unit: 1 Two Marks Questions and Answers: ME2402 & Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument18 pagesUnit: 1 Two Marks Questions and Answers: ME2402 & Computer Integrated ManufacturingmanikandanNo ratings yet
- MP403 ComputerintegratedmanufacturingDocument3 pagesMP403 ComputerintegratedmanufacturingAbhay SajeevNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 - CAD CAM - CAE - Introduction of The CourseDocument21 pagesLecture01 - CAD CAM - CAE - Introduction of The CourseSameer shaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit: 1 Two Marks Questions and Answers: 1. Explain CIMDocument24 pagesUnit: 1 Two Marks Questions and Answers: 1. Explain CIMsathyanarayananNo ratings yet
- MT308 Ia Fe 2019Document7 pagesMT308 Ia Fe 2019khalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- Me8691 Cad&m UpdatedDocument70 pagesMe8691 Cad&m UpdatedkipseyNo ratings yet
- ME 1403 Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument20 pagesME 1403 Computer Integrated ManufacturingDhileepan Kumarasamy100% (1)
- Cim QBDocument23 pagesCim QBSenthilsuja Kumar67% (3)
- Design For Manufacture: CAD CAM CAE Transportability CIM Need of CIMDocument50 pagesDesign For Manufacture: CAD CAM CAE Transportability CIM Need of CIMعبدالرحمن سليمانNo ratings yet
- Design For Manufacture: CAD CAM CAE Transportability CIM Need of CIMDocument50 pagesDesign For Manufacture: CAD CAM CAE Transportability CIM Need of CIMHmwDyNo ratings yet
- 1.cim Text BookDocument18 pages1.cim Text BookVinayakNo ratings yet
- CIMS Two MarksDocument19 pagesCIMS Two Marksgnanasekar100% (1)
- Lecture 01 - IntroductionDocument29 pagesLecture 01 - IntroductionazizNo ratings yet
- ME6703 SCAD MSM by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument88 pagesME6703 SCAD MSM by WWW - Learnengineering.inAnonymous VC2zZcPCivNo ratings yet
- IE362 Group Technology and Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocument2 pagesIE362 Group Technology and Flexible Manufacturing SystemloshidhNo ratings yet
- CIM Question BankDocument5 pagesCIM Question Bankselvi6496No ratings yet
- Computer Aided Design 2 Mark Questions With AnswersDocument18 pagesComputer Aided Design 2 Mark Questions With AnswersM.Thirunavukkarasu100% (4)
- CadCam Lab Report FileDocument30 pagesCadCam Lab Report FileAzher Uddin100% (1)
- ATRIA CIM LAB MANUALDocument79 pagesATRIA CIM LAB MANUALPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 Computer Aided Manufacturing ME-418Document21 pagesAssignment-1 Computer Aided Manufacturing ME-418Prateek Kharbanda 79No ratings yet
- Application of Computer in Manufacturing DPE426: Experiments OnDocument14 pagesApplication of Computer in Manufacturing DPE426: Experiments OnPrabha KaranNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation for B.E. Mechanical EngineeringDocument82 pagesUniversity of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation for B.E. Mechanical EngineeringJayesh NavareNo ratings yet
- CIM Subject Guide for Mechanical Engineering StudentsDocument7 pagesCIM Subject Guide for Mechanical Engineering StudentsKeerthe VaasanNo ratings yet
- CIM Wheel-Product Design To Manufacturing Management.Document13 pagesCIM Wheel-Product Design To Manufacturing Management.Kartheek Musalimadugu33% (3)
- Mechanical - VI. Sem Syllabus GtuDocument115 pagesMechanical - VI. Sem Syllabus GtukishormechNo ratings yet
- CAD/CAM exam questions and answersDocument4 pagesCAD/CAM exam questions and answerssanyasirao1No ratings yet
- CC 9222 - Integrated Manufacturing SystemsDocument2 pagesCC 9222 - Integrated Manufacturing SystemsGuga PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cim (English)Document320 pagesCim (English)DaRkSouLNo ratings yet
- ME 010 507 CAD CAM LabDocument2 pagesME 010 507 CAD CAM LabJenny John MattamNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 2019Document261 pagesUnit-1 2019Mr. S. Paul JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Ie433 Cad/Cam Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Part-1 Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument27 pagesIe433 Cad/Cam Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Part-1 Introduction To CAD/CAMMuhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- B.E. Automobile Engineering Course DocumentsDocument73 pagesB.E. Automobile Engineering Course Documentssss0987654321No ratings yet
- Lass Rientation Ession: by Anand Partheeban C.M Asst Professor Mechanical United Institute of TechnologyDocument18 pagesLass Rientation Ession: by Anand Partheeban C.M Asst Professor Mechanical United Institute of TechnologyotakoothanNo ratings yet
- Ie433 Cad/Cam Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Part-1 Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument27 pagesIe433 Cad/Cam Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Part-1 Introduction To CAD/CAMJackson ..No ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing: Course ObjectivesDocument3 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing: Course ObjectivesPrashanth JNo ratings yet
- Cad-Cam Manual PDFDocument34 pagesCad-Cam Manual PDFM.Saravana Kumar..M.E100% (2)
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing: A Total Company Competitive StrategyFrom EverandComputer Integrated Manufacturing: A Total Company Competitive StrategyRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Viper 100Document8 pagesViper 100SeanNo ratings yet
- Sprinter DataLoader Instruction Rev134Document21 pagesSprinter DataLoader Instruction Rev134Fernan Chavez NavarroNo ratings yet
- Cisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Ericsson MD-110 With T1 PRI SignalingDocument11 pagesCisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Ericsson MD-110 With T1 PRI Signalinginr0000zhaNo ratings yet
- MSI Motherboard & Video Card PricelistDocument1 pageMSI Motherboard & Video Card PricelistMarvin Mark AbamongaNo ratings yet
- Intro 2 CiscoDocument196 pagesIntro 2 CiscoJocylen100% (1)
- Pro I I 93 Silent Install GuideDocument5 pagesPro I I 93 Silent Install Guidemfruge7No ratings yet
- Pre Int Teachers Book Unit 9Document8 pagesPre Int Teachers Book Unit 9Maria Andreina Diaz SantanaNo ratings yet
- The Complexity of Theorem-Proving ProceduresDocument8 pagesThe Complexity of Theorem-Proving ProceduresSrijit SanyalNo ratings yet
- BOLT! Mobile WiFi MF90 Update Tool v1.1 Manual Instruction For WindowsDocument7 pagesBOLT! Mobile WiFi MF90 Update Tool v1.1 Manual Instruction For WindowsSonia LimousNo ratings yet
- MC68HC11F1Document158 pagesMC68HC11F1Oscar ArangoNo ratings yet
- Picoblaze ManualDocument75 pagesPicoblaze ManualmarcelinyNo ratings yet
- 74HC151Document11 pages74HC151jnax101No ratings yet
- Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach ,: 5 Edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2009Document80 pagesComputer Networking: A Top Down Approach ,: 5 Edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2009Hoang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Multi-Channel UART Controller for Variable Baud Rates Using FPGA FIFODocument5 pagesImplementation of Multi-Channel UART Controller for Variable Baud Rates Using FPGA FIFOJNRNo ratings yet
- Gforth-0 7 0 PDFDocument282 pagesGforth-0 7 0 PDFdehammoNo ratings yet
- 9 - BICSI - Bob CamerinoDocument40 pages9 - BICSI - Bob CamerinoecorbelliniNo ratings yet
- DB1800ADocument2 pagesDB1800AMario DeejayNo ratings yet
- OMK55 Smart Optical Test Kit DatasheetDocument4 pagesOMK55 Smart Optical Test Kit Datasheetshahramkarimi76No ratings yet
- 74LS47 PDFDocument6 pages74LS47 PDFJhill-Jhill Jimenez Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Sdad 232Document6 pagesSdad 232Claudiu Ionuț BaltariuNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearings PDFDocument24 pagesBall Bearings PDFSamiullah AtaNo ratings yet
- 02 Xtralis Security Sols S3000RDR A4 Lores-1Document2 pages02 Xtralis Security Sols S3000RDR A4 Lores-1cristolosNo ratings yet
- Micro Controllers ECE-310 FinalDocument10 pagesMicro Controllers ECE-310 Finalramjee26No ratings yet
- Distributed DatabaseDocument24 pagesDistributed DatabaseHimashree BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Finite Diff PDFDocument14 pagesFinite Diff PDFElshan AliyevNo ratings yet
- HP Vectra VL 5xxx Series 4 PCDocument20 pagesHP Vectra VL 5xxx Series 4 PCmancangkulNo ratings yet
- Reloading Your Siemens 810/820 NC ControlDocument7 pagesReloading Your Siemens 810/820 NC ControlkumbrovNo ratings yet
- Refman1 PDFDocument439 pagesRefman1 PDFdeo penaburNo ratings yet