Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP (Pulmonary Embolism)
Uploaded by
Nica RespondoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP (Pulmonary Embolism)
Uploaded by
Nica RespondoCopyright:
Available Formats
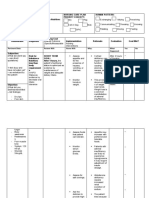
ASSESSMENT S - Dyspnea, Insipatory Chest pain, Cough and hemoptysis as complained by the patient.
O Dyspnea - Prolonged expiration phases - Decreased inspiratory pressure
DIAGNOSIS Ineffective Breathing Pattern r/t decreased lung expansion as evidenced by dyspnea and cough
PLANNING After 4 hours of nursing interventions the patient will be able to establish a normal/effective respiratory pattern as evidenced by absence of cyanosis and other signs/symptoms of hypoxia with ABGs within normal/acceptable range
INTERVENTION
Note emotional responses (e.g., gasping, crying, reports of tingling fingers) Have client breathe into a paper bag, if appropriate,
RATIONALE
Anxiety may be causing/exacerbating acute or chronic hyperventilation
EVALUATION After 4 hours of nursing interventions the patient was be able to establish a normal/effective respiratory pattern as evidenced by absence of cyanosis and other signs/symptoms of hypoxia with ABGs within clients normal/acceptable range
To correct hyperventilation (Research suggests this may not be effective and could actually stress the heart/respiratory system, potentially lowering O saturation, especially if the hyperventilation is not simply anxiety based) To assist client in taking control of the situation To limit level of anxiety
Encourage slower respirations, use of pursed-lip technique Maintain calm attitude while dealing with patient Avoid overeating/gas forming foods
May cause abdominal distention
ASSESSMENT S -Dyspnea and Visual Disturbances as complained by the patient O - Tachycardia - Hypoxia - Somnolence: Lethargy
DIAGNOSIS Impaired Gas Exchange r/t Ventilation perfusion imbalance (altered blood flow), alveolar-capillary membrane changes (atelectasis) as evidenced by profound dyspnea and somnolence
PLANNING After 4 hours of nursing interventions the patient will be able to Demonstrate improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation of tissues by ABGs within clients normal limits and absence of symptoms of respiratory distress
INTERVENTION
Assess nutritional status including serum albumin level and body mass index
RATIONALE
Resulting in a loss muscle mass in the respiratory muscles which can lead to respiratory failure
EVALUATION
After 4 hours of nursing interventions the patient was be able to Evaluate pulse To assess for Demonstrate oximetry to respiratory improved determine insufficiency ventilation and oxygenation; evaluate adequate lung volumes and oxygenation of forced vital capacity tissues by ABGs Elevate head of Promotes optimal within clients bed/position client chest expansion an normal limits and appropriately, drainage of secretions absence of provide airway symptoms of adjuncts and suction, respiratory as indicated distress
Help the client eat small frequent meals and use dietary supplements as necessary Encourage adequate rest and limit activities to within client tolerance. Promote calm/restful environment Having a BMI less than 21 has been associated with earlier mortality in patients with COPD Helps limit oxygen needs/consumption
ASSESSMENT S Chest Pain and Dyspnea as complained by the patient
DIAGNOSIS
PLANNING After 4 hours of nursing interventions the patient will be able to Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate (balanced I/O, absence of edema, free pain/discomfort)
INTERVENTION
Investigate reports of chest pain, note precipitating factors, changes in characteristics of pain episodes Note presence of/degree of dyspnea, cyanosis, hemoptysis Monitor vital signs, hemodynamics, heart sounds, and cardiac rhythm Caution client to avoid activities that increase cardiac work-load (e.g., straining at stool)
RATIONALE
To note degree of impairement/organ involvement
EVALUATION After 4 hours of nursing interventions the patient was be able to Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate (balanced I/O, absence of edema, free pain/discomfort)
Ineffective Cardiopulmonary Tissue Perfusion r/t exchange problems at alveolar level as O - Hemoptysis evidenced by - Presence of laboratory evidence edema in right of lower extremity ventilation/perfusion mismatch and dyspnea
To note degree of impairement/organ involvement To maximize tissue perfusion
To maximize tissue perfusion
Assist with treatment of To improve tissue underlying conditions perfusion/organ (e.g., stent replacement, functuion surgical reperfusion procedures, medications, fluid replacement/rehydration, nutrients, treatment of sepsis, etc.)
You might also like
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEsther RefuncionNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument46 pagesBreathingRamnaresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- NCP EmphysemaDocument9 pagesNCP Emphysemahermesdave188% (8)
- Class InsectaDocument30 pagesClass InsectaEdz SeletariaNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Pneumothorax'Harold Mark Borja100% (2)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNo ratings yet
- NCP Lung CancerDocument4 pagesNCP Lung CancerShizuen Mn83% (12)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE NCP For Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Angina Pectorisseanne_may100% (4)
- Respiratory Failure NCPDocument1 pageRespiratory Failure NCPkyaw100% (1)
- Optional (AEMT), Optional (Paramedic)Document76 pagesOptional (AEMT), Optional (Paramedic)Mark ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Septick Shock)Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan (Septick Shock)REMILYN ROSE ASUNCION67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Cardiac ComplicationDocument12 pagesCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Questions PulmDocument27 pagesNCLEX Questions PulmAnthony Hawley100% (2)
- Ards NCPDocument5 pagesArds NCPgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Joan Forsyth - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation-White Press Academic (2018)Document253 pagesJoan Forsyth - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation-White Press Academic (2018)Vlady78100% (1)
- NCP For Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNCP For Pleural EffusionLilian Linogao71% (7)
- Summative Test No. 2 Second Quarter Science 6Document5 pagesSummative Test No. 2 Second Quarter Science 6BALETENo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument10 pagesPulmonary HypertensionqingwenNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument7 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- NCP AnginaDocument3 pagesNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- 17Y Patient Pleural Effusion CareDocument4 pages17Y Patient Pleural Effusion CareTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- NCP For AnginaDocument5 pagesNCP For Anginacarizza_bernas100% (1)
- NCP Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesNCP Cardiogenic ShockTrixia Camporedondo100% (1)
- NCP - AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument6 pagesNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - EndocarditisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - EndocarditisJoanna Marie Datahan Estomo100% (12)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism: Risks, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument54 pagesPulmonary Embolism: Risks, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatmentعزيزي أحمد نوردين0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Tuberculosis (TBDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Tuberculosis (TBVen Belista86% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- 630 Occupational Profile AssignmentDocument13 pages630 Occupational Profile Assignmentapi-201999002No ratings yet
- NCP RHDDocument7 pagesNCP RHDHenry Roque Tagalag80% (5)
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 pagesCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismPui_Yee_Siow_6303100% (10)
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- NCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome AssessmentDocument3 pagesNCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome Assessmentsarahtot67% (3)
- Causes and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCauses and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionHania Polangi100% (1)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- Nursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainDocument3 pagesNursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Cardiac Case Study NDDocument11 pagesCardiac Case Study NDapi-313165458No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-252726911No ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCP 2 Addison's DiseaseDocument4 pagesNCP 2 Addison's DiseaseRenee RoSeNo ratings yet
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaDocument9 pagesLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- NCP - TBDocument2 pagesNCP - TBPahw BaluisNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesPneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentcrisolandNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Oxy Act 2Document5 pagesOxy Act 2Joshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToDocument8 pagesWhich It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangePaul VincentNo ratings yet
- History and Physical Examination in Pediatrics (1) - 1Document44 pagesHistory and Physical Examination in Pediatrics (1) - 1okwadha simion100% (1)
- Science Test: Chapter I Respiratory and Circulatory System Term I, Semester IDocument4 pagesScience Test: Chapter I Respiratory and Circulatory System Term I, Semester IimandaNo ratings yet
- Asma Dalam KehamilanDocument33 pagesAsma Dalam KehamilanAnonymous wztrzkVnNo ratings yet
- Broncho Ect As IsDocument28 pagesBroncho Ect As Ismeaza rorisaNo ratings yet
- Nazneen Science STD 3 Learning OutcomeDocument10 pagesNazneen Science STD 3 Learning Outcomenazneen OsmaniNo ratings yet
- HypoxiaDocument15 pagesHypoxiaاحمد حيدر يونس مهديNo ratings yet
- Management of Respiratory Failure Ventilator.17Document9 pagesManagement of Respiratory Failure Ventilator.17Margarida ReisNo ratings yet
- Summary of Learning-Pulmo Hour-Tantoco, Justin LareeDocument1 pageSummary of Learning-Pulmo Hour-Tantoco, Justin LareeJustin TantocoNo ratings yet
- BspedDocument12 pagesBspedDisaster GamingNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument13 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesTanmayee MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPDDocument2 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPDJoseph Angelo OcampoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology (SBI 3U1) Name: - Unit: Internal Systems Lab: Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection DateDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Biology (SBI 3U1) Name: - Unit: Internal Systems Lab: Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection DateSydney Drizis [Student]No ratings yet
- MCN KweenDocument4 pagesMCN KweenAngelo SigueNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2 The Human Body SystemsDocument36 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 2 The Human Body Systemsmaricar paracadNo ratings yet
- Chest RetractionDocument11 pagesChest RetractionJURY LEIGH SALUQUENNo ratings yet
- PFT interpretation: A basic approachDocument78 pagesPFT interpretation: A basic approachFelix ManyerukeNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Congestion Secondary To PneumoniaDocument104 pagesPulmonary Congestion Secondary To PneumoniaAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Patho Respiratory - KatherineDocument9 pagesPatho Respiratory - KatherineKayla MayerNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray AnnaDocument51 pagesChest X-Ray Annaapi-26159412100% (1)
- Material Engleza Medicina Anul 1 Sem 2 PDFDocument58 pagesMaterial Engleza Medicina Anul 1 Sem 2 PDFCiocarlan MihaiNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas Exchange - PresentationDocument62 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchange - PresentationAryan BhideNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Disturbance in a Man with Alcoholic Liver Disease and HypotensionDocument92 pagesAcid-Base Disturbance in a Man with Alcoholic Liver Disease and HypotensionManmeet SNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia NeonatorumDocument29 pagesAsphyxia Neonatorummamaalyssa100% (1)