Professional Documents
Culture Documents
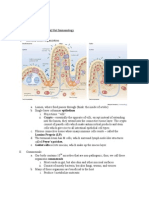
Compound Microscope Parts
Uploaded by
Andy AlvarezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compound Microscope Parts
Uploaded by
Andy AlvarezCopyright:
Available Formats
41
1.
2.
3.
4.
When using a compound microscope, objective lenses can be found to have a magnification of all of the following, EXCEPT? a. 4X b. 10X c. 40X d. 100X e. 1000X Answer: e A compound microscope has two lenses: an eyepiece lens and objective lens. The eyepiece lens usually has a magnification of 10X. There are objective lenses on the revolving nosepiece with varying magnifications. Most compound microscopes have objective lenses with magnification of 4X, 10X, and 40X. Some compound microscopes also have an oil immersion lens with a magnification of 100X. What is "compound microscope"? a. Microscope with the capability to view oil immersion b. Microscope with the capability to view compounds c. Microscope with a single lens d. Microscope with two lenses e. Microscope with three lenses Answer: d A compound microscope has two lenses: an eyepiece lens and objective lens. The eyepiece lens usually has a magnification of 10X. There are objective lenses on the revolving nosepiece with varying magnifications. Most compound microscopes have objective lenses with magnification of 4X, 10X, and 40X. Some compound microscopes also have an oil immersion lens with a magnification of 100X. What is the total magnification achieved with a compound microscope? a. Magnification of objective lens b. Magnification of ocular lens c. Magnification of ocular lens added to the magnification of the objective lens d. Magnification of ocular lens multiplied by the magnification of the objective lens e. Magnification of condenser lens multiplied by the magnification of the objective lens Answer: d To calculate the total magnification achieved with a compound microscope, the magnification of the ocular lens is multiplied by the magnification of the objective lens. For example, if viewing a sample with the 40x objective, the total magnification would be calculated as follows: a 10X ocular lens used with a 40X objective lens, the total magnification is 400X (10 x 40). What is the maximum resolving power seen with a compound microscope? a. 2 millimeters b. 2 millimeters c. 2 micrometers d. 2 micrometers e. 2 angstroms Answer: d Resolving power is the ability to see two things as discrete images. With normal vision, there is a resolving power of about of 100 micrometers. A compound microscope has a resolving power of approximately .2 micrometers. In other words, two marks .2 micrometers apart can be seen as two
ANDIE ALBINO
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
distinct entities. Any closer than this, they are perceived as one object. What is the turret? a. Base b. Nosepiece c. Stage d. Tube e. Diaphragm Answer: b The base is the bottom of the microscope. The revolving nosepiece is also called a turret. The objective lens are attached to the nosepiece (or turret). The slide rests on the stage. The tube is the structure which connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses (it is shaped like a tube; thus, its name). The diaphragm controls the diameter of the cone of light. On a microscope, what structure connects the eyepiece to the objective lens? a. Base b. Nosepiece c. Stage d. Tube e. Diaphragm Answer: d The base is the bottom of the microscope. The revolving nosepiece is also called a turret. The objective lens are attached to the nosepiece (or turret). The slide rests on the stage. The tube is the structure which connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses (it is shaped like a tube; thus, its name). The diaphragm controls the diameter of the cone of light. In a good compound microscope, the focus knob does not have to be readjusted when changing the magnification. What is this phenomenon called? a. Parfocal b. Unifocal c. Bifocal d. Focused e. Convergent Answer: a Parafocal is the term used for a microscope if the focus knob does not have to be readjusted when changing the magnifications. This phenomenon is seen with good compound microscopes. In other words, when the specimen is in focus at 4X and the objective is switched to 10X, the specimen remains in focus. What is another name for the light microscope? a. Simple microscope b. Compound microscope c. Phase contrast microscope d. Dissection microscope e. Transmission electron microscope Answer: b A simple microscope has only one lens. A compound microscope utilizes two lenses: an ocular lens and an objective lens. The compound microscope is also referred to as a "light microscope" or "bright field microscope". A phase contrast microscope is useful for examining living cells, because the specimen does not need to be stained. A dissection microscope uses low power magnification. Things appear three dimensional with a dissection microscope. A transmission electron microscope does not use light, but rather a beam of electrons. Which microscope does not rely on visible light? a. Simple microscope b. Compound microscope
42
10.
11.
12.
13.
c. Phase contrast microscope d. Dissection microscope e. Transmission electron microscope Answer: e A simple microscope has only one lens. A compound microscope utilizes two lenses: an ocular lens and an objective lens. The compound microscope is also referred to as a "light microscope" or "bright field microscope". A phase contrast microscope is useful for examining living cells, because the specimen does not need to be stained. A dissection microscope uses low power magnification. Things appear three dimensional with a dissection microscope. A transmission electron microscope does not use light, but rather a beam of electrons. Which microscope makes things appear three dimensional? a. Simple microscope b. Compound microscope c. Phase contrast microscope d. Dissection microscope e. Transmission electron microscope Answer: d A simple microscope has only one lens. A compound microscope utilizes two lenses: an ocular lens and an objective lens. The compound microscope is also referred to as a "light microscope" or "bright field microscope". A phase contrast microscope is useful for examining living cells, because the specimen does not need to be stained. A dissection microscope uses low power magnification. Things appear three dimensional with a dissection microscope. A transmission electron microscope does not use light, but rather a beam of electrons. When using a compound microscope, what is the magnification of the oil immersion lens? a. 4X b. 10X c. 40X d. 100X e. 1000X Answer: d A compound microscope has two lenses: an eyepiece lens and objective lens. The eyepiece lens usually has a magnification of 10X. There are objective lenses on the revolving nosepiece with varying magnifications. Most compound microscopes have objective lenses with magnification of 4X, 10X, and 40X. Some compound microscopes also have an oil immersion lens with a magnification of 100X. What is the usual magnification of the ocular lens on a compound microscope? a. 1X b. 10X c. 100X d. 1000X e. 10,000 X Answer: b The usual magnification of an ocular lens on a compound microscope is 10X. Some microscopes have a 15X eyepiece lens. The ocular lens is the lens at the top of the tube, the one that you first look through when using a microscope. It is also called the eyepiece lens. When using oil immersion to view a tissue, what is the refractive index of the oil? a. Zero b. Same as air c. Same as glass
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
d. Same as water e. None of the above Answer: c With light microscopy, there normally is a space of air between the slide and the lens. Oil immersion replaces that space of air with oil. The refractive index of the oil is the same as glass. What is the role of the condenser lens? a. Control the aperture of light b. Increase the magnification c. Focus the light on the specimen d. Initial magnification of 10X e. Provide light Answer: c The role of the condenser lens is to focus light on the specimen. It is used with higher magnifications. On a microscope, what structure varies the diameter of the cone of light? a. Base b. Nosepiece c. Stage d. Tube e. Diaphragm Answer: e The base is the bottom of the microscope. The revolving nosepiece is also called a turret. The objective lens are attached to the nosepiece (or turret). The slide rests on the stage. The tube is the structure which connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses (it is shaped like a tube; thus, its name). The diaphragm controls the diameter of the cone of light. Where do you place the slide when using a microscope? a. Base b. Nosepiece c. Stage d. Tube e. Diaphragm Answer: c The base is the bottom of the microscope. The revolving nosepiece is also called a turret. The objective lens are attached to the nosepiece (or turret). The slide rests on the stage. The tube is the structure which connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses (it is shaped like a tube; thus, its name). The diaphragm controls the diameter of the cone of light. What is the bottom of a microscope called? a. Base b. Nosepiece c. Stage d. Tube e. Diaphragm Answer: a The base is the bottom of the microscope. The revolving nosepiece is also called a turret. The objective lens are attached to the nosepiece (or turret). The slide rests on the stage. The tube is the structure which connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses (it is shaped like a tube; thus, its name). The diaphragm controls the diameter of the cone of light. What is another name for the bright field microscope? a. Simple microscope b. Compound microscope c. Phase contrast microscope d. Dissection microscope e. Transmission electron microscope Answer: b A simple microscope has only one lens. A compound microscope utilizes two lenses: an ocular lens and an
ANDIE ALBINO
43
19.
20.
21.
22.
objective lens. The compound microscope is also referred to as a "light microscope" or "bright field microscope". A phase contrast microscope is useful for examining living cells, because the specimen does not need to be stained. A dissection microscope uses low power magnification. Things appear three dimensional with a dissection microscope. A transmission electron microscope does not use light, but rather a beam of electrons. Which microscope would be particularly useful for looking at living cells? a. Simple microscope b. Compound microscope c. Phase contrast microscope d. Dissection microscope e. Transmission electron microscope Answer: c A simple microscope has only one lens. A compound microscope utilizes two lenses: an ocular lens and an objective lens. The compound microscope is also referred to as a "light microscope" or "bright field microscope". A phase contrast microscope is useful for examining living cells, because the specimen does not need to be stained. A dissection microscope uses low power magnification. Things appear three dimensional with a dissection microscope. A transmission electron microscope does not use light, but rather a beam of electrons. Which type of microscope has only one lens? a. Simple microscope b. Compound microscope c. Phase contrast microscope d. Dissection microscope e. Transmission electron microscope Answer: a A simple microscope has only one lens. A compound microscope utilizes two lenses: an ocular lens and an objective lens. The compound microscope is also referred to as a "light microscope" or "bright field microscope". A phase contrast microscope is useful for examining living cells, because the specimen does not need to be stained. A dissection microscope uses low power magnification. Things appear three dimensional with a dissection microscope. A transmission electron microscope does not use light, but rather a beam of electrons. Which of the following stain blue with H&E stain? a. Cytoplasm b. Collagen fibers c. Nucleus d. Elastic fibers e. Decalcified bone matrix Answer: c "H&E" stands for hematoxylin and eosin. Hematoxylin can be thought of as a basic dye. It binds to acidic structures, staining them blue to purple. For example, it will bind and stain nucleic acids. Therefore, the nucleus stains blue. What are Sudan stains used primarily for? a. Blood b. Fat c. Nervous tissue d. Elastic fibers e. Decalcified bone matrix Answer: b Sudan stains are used for staining of lipids and phospholipids. Examples of such stains are sudan black and sudan IV. Oil red O is another stain used for demonstrating fat.
ANDIE ALBINO
23. What is Mucicarmine stain used primarily for? a. Blood b. Fat c. Nervous tissue d. Elastic fibers e. Epithelial mucin Answer: e Mucicarmine is used to see epithelial mucin. It stains it a deep red. 24. What is Wright's stain used primarily for? a. Blood b. Fat c. Nervous tissue d. Elastic fibers e. Decalcified bone matrix Answer: a Wright's stain is used for blood smears and bone marrow. Red blood cells will stain pink. 25. What color do elastic fibers stain with Verhoeff Elastic stain? a. Red/Orange b. Pink/red c. Purple/Red d. Blue/black e. Green/blue Answer: d Verhoeff Elastic stain stains elastic fibers blue/black. Collagen stains pink/red. 26. During the preparation of a routine H&E slide, what step occurs after the tissue is preserved? a. Fixation b. Embedding in paraffin c. Staining d. Slicing e. Dehydration Answer: e 27. During the preparation of a routine H&E slide, how is the tissue preserved? a. Fixation b. Embedding in paraffin c. Staining d. Slicing e. Dehydration Answer: a 28. During the preparation of a routine H&E slide, what allows the tissue to be visualized? a. Fixation b. Embedding in paraffin c. Staining d. Slicing e. Dehydration Answer: c There are several steps in the preparation of a slide for microscopic examination. First, the tissue is "fixed" with formalin. This preserves it. After the tissue is fixed, it is dehydrated (dehydration will occur twice during slide preparation). The tissue sample is then embedded in paraffin. This forms a solid block, so that it can be placed in a microtome. It is then thinly sliced using a microtome. A thin slice of the specimen is then placed on a slide. The paraffin is removed by dissolving it with a chemical. The tissue is then rehydrated. In order to view the tissue, it is stained. After it is stained, it is again dehydrated. A coverslip is the mounted on top of it. The specimen is then ready for viewing. 29. Which of the following would be best suited to visualize reticular fibers? a. Wright's stain
44
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: d Which of the following would be best suited to visualize lipid? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: c Which of the following is NOT a membranous organelle? a. Lysosomes b. Peroxisomes c. Mitochondria d. Ribosomes e. Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: d Lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum are all membranous organelles. During the preparation of a routine H&E slide, what allows the tissue to hold its form? a. Fixation b. Embedding in paraffin c. Staining d. Slicing e. Dehydration Answer: b During the preparation of a routine H&E slide, what step occurs after the tissue is embedded in paraffin? a. Fixation b. Rehydration c. Staining d. Slicing e. Dehydration Answer: d During the preparation of a routine H&E slide, what step occurs after the tissue is stained? a. Fixation b. Embedding in paraffin c. Staining d. Slicing e. Dehydration Answer: e There are several steps in the preparation of a slide for microscopic examination. First, the tissue is "fixed" with formalin. This preserves it. After the tissue is fixed, it is dehydrated (dehydration will occur twice during slide preparation). The tissue sample is then embedded in paraffin. This forms a solid block, so that it can be placed in a microtome. It is then thinly sliced using a microtome. A thin slice of the specimen is then placed on a slide. The paraffin is removed by dissolving it with a chemical. The tissue is then rehydrated. In order to view the tissue, it is stained. After it is stained, it is again dehydrated. A coverslip is then mounted on top of it. The specimen is then ready for viewing. Which of the following is an acid dye? a. Azure II b. Toluidine blue c. Methylene blue d. Eosin e. Thionine
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
Answer: d Eosin is an acid dye. It will bind to and stain basic structures (or negatively charged structures), such as cationic amino groups on proteins. It stains them pink. Cytoplasm, muscle, connective tissue, and decalcified bone matrix all stain pink with eosin. "H&E" stand for hematoxylin and eosin. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is used for routine tissue preparation frequently. Azure II, Toluidine blue, Methylene blue, Thionine are all basic dyes. Which of the following would be best suited for peripheral blood smears? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: a Which of the following stains is used for routine histological examination? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: b A peripheral blood smear would be best visualized with Wright's stain. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is the most commonly used tissue stain for routine histological examination. Lipids are best displayed with a sudan stain. Silver impregnation, such as with a reticular stain, can be used to visualize reticular fibers. Collagen fibers can be differentiated from other fibers by staining with Masson's trichrome stain. What is Prussian blue stain used for? a. Sodium b. Potassium c. Calcium d. Copper e. Iron Answer: e Prussian blue stain is used to stain iron. What color does hematoxylin stain structures? a. Orange b. Blue c. Pink d. Red e. Green Answer: b "H & E" stands for hematoxylin and eosin. Hematoxylin can be thought of as a basic dye. It binds to acidic structures, staining them blue to purple. For example, it will bind and stains nucleic acids. Therefore, the nucleus stains blue. Which of the following would be best suited to differentiate collagen fibers from other fibers ? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: e A peripheral blood smear would be best visualized with Wright's stain. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is the most commonly used tissue stain for routine histological examination. Lipids are best displayed with a sudan stain. Silver impregnation, such as with a reticular stain, can be used to visualize reticular fibers.
ANDIE ALBINO
45
Collagen fibers can be differentiated from other fibers by staining with Masson's trichrome stain. 41. Which organelle contains digestive enzymes? a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum c. Lysosome d. Golgi apparatus e. Mitochondria Answer: c Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of tubules. If there are ribosomes on the tubules, it is termed "rough endoplasmic reticulum". Ribosomes produce proteins. When the ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum, the proteins produced by the ribosomes are exported. If there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, it is called "smooth endoplasmic reticulum". The role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is lipid metabolism. Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes. They are nicknamed "suicide sacs". The Golgi apparatus are stacks of membranous sacs. Proteins are sorted and packaged in the Golgi apparatus. The mitochondria is the site of ATP production for the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are nicknamed, the "powerhouse". 42. Which organelle is considered the powerhouse of the cell? a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum c. Lysosome d. Golgi apparatus e. Mitochondria Answer: e Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of tubules. If there are ribosomes on the tubules, it is termed "rough endoplasmic reticulum". Ribosomes produce proteins. When the ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum, the proteins produced by the ribosomes are exported. If there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, it is called "smooth endoplasmic reticulum". The role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is lipid metabolism. Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes. They are nicknamed "suicide sacs". The Golgi apparatus are stacks of membranous sacs. Proteins are sorted and packaged in the Golgi apparatus. The mitochondria is the site of ATP production for the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are nicknamed, the "powerhouse". 43. What structure is at the base of cilia? a. Ribosomes b. Peroxisome c. Microfilaments d. Centrioles e. Nucleoli Answer: d The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Peroxisomes contain enzymes for detoxification. One of the enzymes within peroxisomes is catalase. Catalase is involved in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Microfilaments are made of actin. They form the cells cytoskeleton. Centrioles are composed of microtubules. Centrioles are at the base of cilia and flagella. They are also involved with cell division.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleoli. The nucleolus is a spherical area within the cell nucleus. Which of the following is NOT considered an inclusion? a. Pigment b. Glycogen c. Lipid d. Secretory granules e. Mitochondria Answer: e Mitochondria is an organelle. Pigment, glycogen, lipid, and secretory granules are all considered inclusions. Organelles perform an activity; they have a job; they require energy. Inclusions are for storage. Inclusions do not perform an energy requiring job. Collectively, what is the cytoplasm and nucleus called? a. Plasmalemma b. Glycocalyx c. Protoplasm d. Cristae e. Ground substance Answer: c The cell boundary is defined by the cell membrane or plasmalemma. Glycocalyx is a polysacchride that can be found on the outer surface of the cell membranes. Collectively, the cytoplasm and nucleus form the protoplasm of a cell. The folds on the inner mitochodrial membrane are called cristae. The cytoplasm that surrounds organelles is the cytoplasmic ground substance or cytosol. How thick is the plasma membrane? a. 8-10 angstroms b. 8-10 nanometers c. 8-10 micrometers d. 8-10 millimeters e. None of the above Answer: b The plasma membrane is 8-10 nanometers thick. What is the term for the general process that cells us to expunge material from the cell? a. Endocytosis b. Exocytosis c. Pinocytosis d. Phagocytosis e. Active transport Answer: b Endotyosis is the term for the process cells use to have substances enter them. Exoctyosis is the term for the process cells use to remove substances. Phagocytosis is "cell eating" and is used for the transport of particulate matter. Pinocytosis is "cell drinking". Active transport is a method which requires energy. Which organelle sorts and packages proteins within a cell? a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum c. Lysosome d. Golgi apparatus e. Mitochondria Answer: d Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of tubules. If there are ribosomes on the tubules, it is termed "rough endoplasmic reticulum". Ribosomes produce proteins. When the ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum, the proteins produced by the ribosomes are exported. If there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, it is called "smooth
ANDIE ALBINO
46
49.
50.
51.
52.
endoplasmic reticulum". The role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is lipid metabolism. Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes. They are nicknamed "suicide sacs". The Golgi apparatus are stacks of membranous sacs. Proteins are sorted and packaged in the Golgi apparatus. The mitochondria is the site of ATP production for the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are nicknamed, the "powerhouse". Which of the following is NOT a membranous organelle? a. Lysosomes b. Filaments c. Peroxisomes d. Mitochondria e. Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: b Lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum are all membranous organelles. What are the folds on the inner mitochodrial membrane called? a. Plasmalemma b. Glycocalyx c. Protoplasm d. Cristae e. Ground substance Answer: d The cell boundary is defined by the cell membrane or plasmalemma. Glycocalyx is a polysacchride that can be found on the outer surface of the cell membranes. Collectively, the cytoplasm and nucleus form the protoplasm of a cell. The folds on the inner mitochodrial membrane are called cristae. The cytoplasm that surrounds organelles is the cytoplasmic ground substance or cytosol. Which organelle is involved in lipid metabolism? a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum c. Lysosome d. Golgi apparatus e. Mitochondria Answer: b Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of tubules. If there are ribosomes on the tubules, it is termed "rough endoplasmic reticulum". Ribosomes produce proteins. When the ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum, the proteins produced by the ribosomes are exported. If there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, it is called "smooth endoplasmic reticulum". The role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is lipid metabolism. Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes. They are nicknamed "suicide sacs". The Golgi apparatus are stacks of membranous sacs. Proteins are sorted and packaged in the Golgi apparatus. The mitochondria is the site of ATP production for the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are nicknamed, the "powerhouse". Which organelle contains detoxifying enzymes? a. Ribosomes b. Peroxisome c. Microfilaments d. Centrioles e. Nucleoli Answer: b The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
Peroxisomes contain enzymes for detoxification. One of the enzymes within peroxisomes is catalase. Catalase is involved in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Microfilaments are made of actin. They form the cells cytoskeleton. Centrioles are composed of microtubules. Centrioles are at the base of cilia and flagella. They are also involved with cell division. Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleoli. The nucleolus is a spherical area within the cell nucleus. Which of the following is NOT a membranous organelle? a. Microtubules b. Lysosomes c. Peroxisomes d. Mitochondria e. Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: a Lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum are all membranous organelles. What is the limiting membrane of a cell? a. Plasmalemma b. Glycocalyx c. Protoplasm d. Cristae e. Ground substance Answer: a The cell boundary is defined by the cell membrane or plasmalemma. Glycocalyx is a polysacchride that can be found on the outer surface of the cell membranes. Collectively, the cytoplasm and nucleus form the protoplasm of a cell. The folds on the inner mitochodrial membrane are called cristae. The cytoplasm that surrounds organelles is the cytoplasmic ground substance or cytosol. What is also called a low resistance junction? a. Tight junction b. Gap junction c. Junctional epithelium d. Junctional complex e. None of the above Answer: b A gap junction is a low resistance junction. Which of the following is an organelle? a. Pigment b. Glycogen c. Lipid d. Secretory granules e. Mitochondria Answer: e Mitochondria is an organelle. Pigment, glycogen, lipid, and secretory granules are all considered inclusions. Organelles perform an activity; they have a job; they require energy. Inclusions are for storage. Inclusions do not perform an energy requiring job. What is the term for the general process that cells us to bring things into the cell? a. Endocytosis b. Exocytosis c. Pinocytosis d. Phagocytosis e. Active transport Answer: a Endotyosis is the term for the process cells use to have substances enter them. Exoctyosis is the term for the process cells use to remove substances. Phagocytosis is "cell eating" and is used for the
ANDIE ALBINO
47
58.
59.
60.
61.
transport of particulate matter. Pinocytosis is "cell drinking". Active transport is a method which requires energy. Which organelle produces protein for export? a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum c. Lysosome d. Golgi apparatus e. Mitochondria Answer: a Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of tubules. If there are ribosomes on the tubules, it is termed "rough endoplasmic reticulum". Ribosomes produce proteins. When the ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum, the proteins produced by the ribosomes are exported. If there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, it is called "smooth endoplasmic reticulum". The role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is lipid metabolism. Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes. They are nicknamed "suicide sacs". The Golgi apparatus are stacks of membranous sacs. Proteins are sorted and packaged in the Golgi apparatus. The mitochondria is the site of ATP production for the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are nicknamed, the "powerhouse". Where are ribosomes constructed? a. Cytoskeleton b. Peroxisome c. Microfilaments d. Centrioles e. Nucleoli Answer: e The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Peroxisomes contain enzymes for detoxification. One of the enzymes within peroxisomes is catalase. Catalase is involved in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Microfilaments are made of actin. They form the cells cytoskeleton. Centrioles are composed of microtubules. Centrioles are at the base of cilia and flagella. They are also involved with cell division. Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleoli. The nucleolus is a spherical area within the cell nucleus. What is the term for the process used by cells for the transport in of particulate matter? a. Endocytosis b. Exocytosis c. Pinocytosis d. Phagocytosis e. Active transport Answer: d Endotyosis is the term for the process cells use to have substances enter them. Exoctyosis is the term for the process cells use to remove substances. Phagocytosis is "cell eating" and is used for the transport of particulate matter. Pinocytosis is "cell drinking". Active transport is a method which requires energy. What is another term for the cytoplasm outside of organelles? a. Plasmalemma b. Glycocalyx c. Protoplasm d. Cristae e. Ground substance Answer: e
ANDIE ALBINO
62.
63.
64.
65.
The cell boundary is defined by the cell membrane or plasmalemma. Glycocalyx is a polysacchride that can be found on the outer surface of the cell membranes. Collectively, the cytoplasm and nucleus form the protoplasm of a cell. The folds on the inner mitochodrial membrane are called cristae. The cytoplasm that surrounds organelles is the cytoplasmic ground substance or cytosol. What is the a small clear space within a cell? a. Space of Disse b. Space of Mall c. Vacuole d. Lacuna e. Howship's lacuna Answer: c The space of Disse is in the liver. The space of Disse is also called the perisinusoidal space. It is the space between the liver sinusoids and the hepatocytes. The space of Mall is also in the liver. The space of Mall is located at the portal canal and is the region between the connective tissue and the liver parenchymal cells. It is the site where lymph is formed within the liver. A vacuole is a small clear space within an individual cell. A lacuna is a small space or depression. The space that the chondrocyte rests in is a lacuna. Howship's lacuna is seen in bone. Howship's lacuna is a space seen underneath an osteoclast. Which of the following is NOT a membranous organelle? a. Lysosomes b. Peroxisomes c. Centrioles d. Mitochondria e. Endoplasmic reticulum Answer: c Lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum are all membranous organelles. What is the polysaccharide coating that is sometimes found on the cell membrane? a. Plasmalemma b. Glycocalyx c. Protoplasm d. Cristae e. Ground substance Answer: b The cell boundary is defined by the cell membrane or plasmalemma. Glycocalyx is a polysacchride that can be found on the outer surface of the cell membranes. Collectively, the cytoplasm and nucleus form the protoplasm of a cell. The folds on the inner mitochodrial membrane are called cristae. The cytoplasm that surrounds organelles is the cytoplasmic ground substance or cytosol. What process is nicknamed "cell drinking"? a. Endocytosis b. Exocytosis c. Pinocytosis d. Phagocytosis e. Active transport Answer: c Endotyosis is the term for the process cells use to have substances enter them. Exoctyosis is the term for the process cells use to remove substances. Phagocytosis is "cell eating" and is used for the transport of particulate matter. Pinocytosis is "cell
48
66.
67.
68.
69.
drinking". Active transport is a method which requires energy. Which organelle is studded with ribosomes? a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum c. Lysosome d. Golgi apparatus e. Mitochondria Answer: a Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of tubules. If there are ribosomes on the tubules, it is termed "rough endoplasmic reticulum". Ribosomes produce proteins. When the ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum, the proteins produced by the ribosomes are exported. If there are no ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum, it is called "smooth endoplasmic reticulum". The role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is lipid metabolism. Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs of digestive enzymes. They are nicknamed "suicide sacs". The Golgi apparatus are stacks of membranous sacs. Proteins are sorted and packaged in the Golgi apparatus. The mitochondria is the site of ATP production for the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are nicknamed, the "powerhouse". Where is the site of protein synthesis? a. Ribosomes b. Peroxisome c. Microfilaments d. Centrioles e. Nucleoli Answer: a The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Peroxisomes contain enzymes for detoxification. One of the enzymes within peroxisomes is catalase. Catalase is involved in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Microfilaments are made of actin. They form the cells cytoskeleton. Centrioles are composed of microtubules. Centrioles are at the base of cilia and flagella. They are also involved with cell division. Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleoli. The nucleolus is a spherical area within the cell nucleus. What structure contributes to the cells cytoskeleton? a. Ribosomes b. Peroxisome c. Microfilaments d. Centrioles e. Nucleoli Answer: c The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Peroxisomes contain enzymes for detoxification. One of the enzymes within peroxisomes is catalase. Catalase is involved in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Microfilaments are made of actin. They form the cells cytoskeleton. Centrioles are composed of microtubules. Centrioles are at the base of cilia and flagella. They are also involved with cell division. Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleoli. The nucleolus is a spherical area within the cell nucleus. What type of tissue lines the bladder? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium
70.
71.
72.
73.
e. Transitional epithelium Answer: e The lining of the bladder is transitional epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. There are domed shaped cells on the apical surface. What type of tissue lines most ducts? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: b The lining of most ducts is simple cuboidal epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple cuboidal epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Cuboidal" refers to the shape of the cells. What type of epithelium is associated with goblet cells? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: c Goblet cells are associated with simple columnar epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple columnar epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Columnar" cells are taller than they are wide and have an oval nucleus. What type of epithelial cells are as tall as they are wide? a. Simple b. Stratified c. Squamous d. Cuboidal e. Columnar Answer: d Epithelium that is classified by the number of cell layers and the cell shape. Epithelium that is one cell thick is classified as simple. Epithelium that is more than one cell layer thick is classified as stratified. If the cells are flat, the epithelium is termed squamous. If the cells are as tall as they are wide, it is cuboidal. If the cells are taller than they are wide, the epithelium is classified as columnar. What do you call the simple squamous epithelium that lines the blood vessels? a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified Answer: c Epithelial tissue has cells that are very tightly packed together. There is always a free surface associated with epithelial tissue. If a tissue is composed of a conglomeration of cells in tightly packed together, but it does not have a free surface, the tissue is called epithelioid tissue. An example of epithelioid tissue is the parenchyma of the adrenal gland. Mesothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the thoracic cavity. Endothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the vascular system. Transitional epithelium is seen in the urinary tract. Transitional epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface.
ANDIE ALBINO
49
74.
75.
76.
77.
78.
Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The prefix "pseudo" means false, such as pseudonym or pseudo-science. What cell type makes up the mucosa of the gallbladder? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: c The mucosa of the gallbladder is made of simple columnar epithelium. Note from Sarah Bellham: The simple columnar epithelium of the gallbladder is very tall! Which of the following is lined by a serosa? a. Genitourinary tract b. Peritoneal cavity c. Respiratory tract d. Alimentary canal e. All of the above are lined by a mucosa Answer: b Serosa lines the peritoneal cavity, pericardial cavity and pleural cavity. Mucosa lines the alimentary canal, genitourinary tract and respiratory tract. What type of gland secretes its product through a duct or tube? a. Endocrine gland b. Multicellular gland c. Exocrine gland d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c An endocrine gland secretes its product directly into the bloodstream, without a duct or tube. An exocrine gland secretes its product through a duct or tube. What is a gland called if the secretory portion is flask shaped? a. Simple gland b. Compound gland c. Tubular d. Alveolar e. Tubuloalveolar Answer: d A simple gland has an unbranched duct. A compound gland has a branched duct. If the secretory portion of a gland is tube shaped, it is called "tubular". If the secretory portion of a gland is flask shaped, it is called "alveolar" or "acinar". If the secretory portion of a gland is a tube shaped but at the terminus is flask shaped, it is called "tubuloalveolar". What forms the brush border? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: a Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border. Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear.
79.
80.
81.
82.
Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. What type of epithelium lines the trachea? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: e The trachea is lined by pseudostratified squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Pseudostratified squamous epithelium is "pseudostratified" because it is only one cell layer thick, yet it appears to be stratified. In reality, every cell touches the basement membrane. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "pseudo" is of Greek origin and it means false or counterfeit. For example: pseudonym, pseudoscience or pseudostratified. What type of tissue lines blood vessels? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: a The lining of a blood vessel is simple squamous epithelium. This lining is called endothelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple squamous epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the cells are flat. What type of epithelium is more than one layer thick? a. Simple b. Stratified c. Squamous d. Cuboidal e. Columnar Answer: b Epithelium that is classified by the number of cell layers and the cell shape. Epithelium that is one cell thick is classified as simple. Epithelium that is more than one cell layer thick is classified as stratified. If the cells are flat, the epithelium is termed squamous. If the cells are as tall as they are wide, it is cuboidal. If the cells are taller than they are wide, the epithelium is classified as columnar. What do you call a tissue composed of a conglomeration of cells which are tightly packed together, yet which does not have a free surface? An example of such a tissue would be the parenchyma of the adrenal gland. a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified Answer: a Epithelial tissue has cells that are very tightly packed together. There is always a free surface associated with epithelial tissue. If a tissue is composed of a conglomeration of cells in tightly packed together, but it does not have a free surface, the tissue is called epithelioid tissue. An example of epithelioid tissue is the parenchyma of the adrenal gland.
ANDIE ALBINO
50
83.
84.
85.
86.
Mesothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the thoracic cavity. Endothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the vascular system. Transitional epithelium is seen in the urinary tract. Transitional epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface. Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The prefix "pseudo" means false, such as pseudonym or pseudo-science. What type of epithelium appears stratified, but is not? a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified Answer: e Epithelial tissue has cells that are very tightly packed together. There is always a free surface associated with epithelial tissue. If a tissue is composed of a conglomeration of cells in tightly packed together, but it does not have a free surface, the tissue is called epithelioid tissue. An example of epithelioid tissue is the parenchyma of the adrenal gland. Mesothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the thoracic cavity. Endothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the vascular system. Transitional epithelium is seen in the urinary tract. Transitional epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface. Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The prefix "pseudo" means false, such as pseudonym or pseudo-science. Which of the following is lined by a mucosa? a. Peritoneal cavity b. Pericardial cavity c. Pleural cavity d. Alimentary canal e. All of the above are lined by a mucosa Answer: d Serosa lines the peritoneal cavity, pericardial cavity and pleural cavity. Mucosa lines the alimentary canal, genitourinary tract and respiratory tract. What type of gland secretes its product directly into the bloodstream? a. Endocrine gland b. Multicellular gland c. Exocrine gland d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a An endocrine gland secretes its product directly into the bloodstream, without a duct or tube. An exocrine gland secretes its product through a duct or tube. What is a gland called if it has an unbranched duct? a. Simple gland b. Compound gland c. Tubular
87.
88.
89.
90.
d. Alveolar e. Tubuloalveolar Answer: a A simple gland has an unbranched duct. A compound gland has a branched duct. If the secretory portion of a gland is tube shaped, it is called "tubular". If the secretory portion of a gland is flask shaped, it is called "alveolar" or "acinar". If the secretory portion of a gland is a tube shaped but at the terminus is flask shaped, it is called "tubuloalveolar". What is a gland called if the secretory portion is tube shaped ending in a flask shaped area at the terminus? a. Simple gland b. Compound gland c. Tubular d. Alveolar e. Tubuloalveolar Answer: e A simple gland has an unbranched duct. A compound gland has a branched duct. If the secretory portion of a gland is tube shaped, it is called "tubular". If the secretory portion of a gland is flask shaped, it is called "alveolar" or "acinar". If the secretory portion of a gland is a tube shaped but at the terminus is flask shaped, it is called "tubuloalveolar". What is the surface modification seen on the cells of the epididymis? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: b Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border. Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. What type of epithelium forms the epidermis? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: d The epidermis is formed by stratified squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Stratified squamous epithelium is "stratified" because it is more than one cell layer thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the surface cells of the stratified squamous layer are flat. This is important to note as the cells at the basal layer are cuboidal or even columnar. It is still classified as "squamous" based on the cells of the surface layer. What type of tissue lines most of the gastrointestinal tract? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: c
ANDIE ALBINO
51
91.
92.
93.
94.
The lining of the gastrointestinal tract is simple columnar epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple columnar epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Columnar" cells are taller than they are wide and have an oval nucleus. What type of tissue forms the alveoli in the lung? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: a The alveoli are formed by simple squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple squamous epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the cells are flat. What type of epithelium is composed of flat cells? a. Simple b. Stratified c. Squamous d. Cuboidal e. Columnar Answer: c Epithelium that is classified by the number of cell layers and the cell shape. Epithelium that is one cell thick is classified as simple. Epithelium that is more than one cell layer thick is classified as stratified. If the cells are flat, the epithelium is termed squamous. If the cells are as tall as they are wide, it is cuboidal. If the cells are taller than they are wide, the epithelium is classified as columnar. What do you call the simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity? a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified Answer: b Epithelial tissue has cells that are very tightly packed together. There is always a free surface associated with epithelial tissue. If a tissue is composed of a conglomeration of cells in tightly packed together, but it does not have a free surface, the tissue is called epithelioid tissue. An example of epithelioid tissue is the parenchyma of the adrenal gland. Mesothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the thoracic cavity. Endothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the vascular system. Transitional epithelium is seen in the urinary tract. Transitional epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface. Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The prefix "pseudo" means false, such as pseudonym or pseudo-science. What type of epithelium is composed of cells which all touch the basement membrane and is only one cell layer thick? a. Stratified squamous epithelium b. Transitional epithelium c. Stratified cuboidal epithelium d. Pseudostratified epithelium
ANDIE ALBINO
95.
96.
97.
98.
e. None of the above Answer: d Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The other type of epithelium where all cells touch the basement membrane and are only one layer thick is the entire class of all of the simple epithelium. Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "pseudo" is derived from the Greek word and means false, counterfeit or untrue; examples of its usage include pseudonym or pseudo-science. Which of the following is NOT lined by a mucosa? a. Genitourinary tract b. Pericardial cavity c. Respiratory tract d. Alimentary canal e. All of the above are lined by a mucosa Answer: b Serosa lines the peritoneal cavity, pericardial cavity and pleural cavity. Mucosa lines the alimentary canal, genitourinary tract and respiratory tract. What is a gland called if it has an branched duct? a. Simple gland b. Compound gland c. Tubular d. Alveolar e. Tubuloalveolar Answer: b A simple gland has an unbranched duct. A compound gland has a branched duct. If the secretory portion of a gland is tube shaped, it is called "tubular". If the secretory portion of a gland is flask shaped, it is called "alveolar" or "acinar". If the secretory portion of a gland is a tube shaped but at the terminus is flask shaped, it is called "tubuloalveolar". What are finger like projections on the surface of some cells called? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: a Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border. Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. What cell surface modification is made of microtubules? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: c Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border.
52
Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. 99. What type of tissue composes the kidney tubules? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: b The kidney tubules are simple cuboidal epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple cuboidal epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Cuboidal" refers to the shape of the cells. 100. What type of tissue lines the esophagus? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: d The lining of the esophagus is stratified squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Stratified squamous epithelium is "stratified" because it is more than one cell layer thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the surface cells of the layer are flat. 101. What type of epithelium is one cell layer thick? a. Simple b. Stratified c. Squamous d. Cuboidal e. Columnar Answer: a Epithelium that is classified by the number of cell layers and the cell shape. Epithelium that is one cell thick is classified as simple. Epithelium that is more than one cell layer thick is classified as stratified. If the cells are flat, the epithelium is termed squamous. If the cells are as tall as they are wide, it is cuboidal. If the cells are taller than they are wide, the epithelium is classified as columnar. 102. What type of epithelial cells are taller than they are wide? a. Simple b. Stratified c. Squamous d. Cuboidal e. Columnar Answer: e Epithelium that is classified by the number of cell layers and the cell shape. Epithelium that is one cell thick is classified as simple. Epithelium that is more than one cell layer thick is classified as stratified. If the cells are flat, the epithelium is termed squamous. If the cells are as tall as they are wide, it is cuboidal. If the cells are taller than they are wide, the epithelium is classified as columnar. 103. What type of epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface? a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified Answer: d
Epithelial tissue has cells that are very tightly packed together. There is always a free surface associated with epithelial tissue. If a tissue is composed of a conglomeration of cells in tightly packed together, but it does not have a free surface, the tissue is called epithelioid tissue. An example of epithelioid tissue is the parenchyma of the adrenal gland. Mesothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the thoracic cavity. Endothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the vascular system. Transitional epithelium is seen in the urinary tract. Transitional epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface. Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The prefix "pseudo" means false, such as pseudonym or pseudo-science. 104. Which of the following is NOT lined by a serosa? a. Peritoneal cavity b. Pericardial cavity c. Pleural cavity d. Respiratory tract e. All of the above are lined by a serosa Answer: d Serosa lines the peritoneal cavity, pericardial cavity and pleural cavity. Mucosa lines the alimentary canal, genitourinary tract and respiratory tract. 105. Which of the following is a unicellular gland? a. Squamous cell b. Goblet cell c. Basal cell d. Basket cell e. Sertoli cell Answer: b A goblet cell is a unicellular gland. 106. What forms the striated border? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: a Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border. Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. 107. What is a characteristic of the cells in the epidermis of the skin? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: d Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border.
ANDIE ALBINO
53
Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. 108. What is another term for an acinar gland? a. Simple gland b. Compound gland c. Tubular d. Alveolar e. Tubuloalveolar Answer: d A simple gland has an unbranched duct. A compound gland has a branched duct. If the secretory portion of a gland is tube shaped, it is called "tubular". If the secretory portion of a gland is flask shaped, it is called "alveolar" or "acinar". If the secretory portion of a gland is a tube shaped but at the terminus is flask shaped, it is called "tubuloalveolar". 109. Which of the following is NOT primarily composed of connective tissue? a. Blood b. Bone c. Tendon d. Intervertebral disc e. Myometrium Answer: e Of the four basic tissue types (epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue), connective tissue is the most diverse. Blood, bone, tendon, and intervertebral discs are all composed of connective tissue. The myometrium is the muscular layer of the uterus. Thus, the myometrium is composed of muscle tissue. 110. Which of the following is NOT a fiber found in connective tissue? a. Collagen fiber b. Elastic fiber c. Reticular fiber d. Purkinje fiber e. All of the above are fibers found in connective tissue Answer: d There are three types of fibers found in connective tissue: collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers. Collagen fibers are the most abundant fiber type in connective tissue. Purkinje fibers are seen in the heart. Purkinje fibers are specialized muscle fibers. 111. Which connective tissue cell type contains properties of smooth muscle cells? a. Fibroblast b. Myofibroblast c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: b Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. The histiocyte is a connective tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A
ANDIE ALBINO
(slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 112. Which cell is a connective tissue macrophage? a. Kupffer cells b. Histiocyte c. Dust cell d. Langerhans cell e. Microglia Answer: b Macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Many tissues have resident (fixed) macrophages. Fixed macrophages are given a unique name, depending on the tissue that they are located in. Kupffer cells are the hepatic macrophages. Histiocytes are macrophages seen in connective tissue. Dust cells are alveolar macrophage found in the respiratory tract. Langerhans cells are macrophages seen in the skin. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. 113. Which of the following can be classified as "specialized connective tissue"? a. Mesenchyme b. Mucous connective tissue c. Dense connective tissue d. Blood e. Loose connective tissue Answer: d Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 114. Which of the following can be classified as "embryonic connective tissue"? a. Cartilage b. Mucous connective tissue c. Adipose tissue d. Bone e. Blood Answer: b Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 115. What type of tissue makes up the dermis of the skin? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: d Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular
54
connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 116. What type of adipose tissue tends to increase as humans age? a. Brown adipose tissue b. White adipose tissue c. Unilocular adipose tissue d. Multilocular adipose tissue e. Both b and c Answer: e Brown adipose tissue is multilocular adipose tissue. This is present during fetal development and then decreases after birth. White adipose tissue is unilocular adipose tissue. This type of tissue persists into adulthood. 117. Which of the following would be best suited to differentiate collagen fibers from other fibers? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: e A peripheral blood smear would be best visualized with Wright's stain. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is the most commonly used tissue stain for routine histological examination. Lipids are best displayed with a sudan stain. Silver impregnation, such as with a reticular stain, can be used to visualize reticular fibers. Collagen fibers can be differentiated from other fibers by staining with Masson's trichrome stain. 118. Which of the following is NOT primarily composed of connective tissue? a. Bone marrow b. Articular cartilage c. Heart d. Mesenchyme e. Fat Answer: c Of the four basic tissue types (epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue), connective tissue is the most diverse. Bone marrow, articular cartilage, mesenchyme and fat are all composed of connective tissue. The heart is a muscle. The main tissue type in the heart is cardiac muscle. Note from Sarah Bellham: Please be aware that there is connective tissue in the heart. The blood in the heart, for example, is composed of connective tissue. The pericardium is also composed of connective tissue. However, the primary tissue composing the heart is cardiac muscle. 119. Which one of these cells is not a cell type routinely found in loose connective tissue? a. Fibroblast b. Microglia c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: b Microglia are supporting cells in the nervous system. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. The histiocyte is a tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A
(slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 120. Which connective tissue cell is a tissue macrophage? a. Fibroblast b. Myofibroblast c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: c The histiocyte is a tissue macrophage. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. The histiocyte is a connective tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A (slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 121. Which of the following can be classified as "specialized connective tissue"? a. Cartilage b. Loose connective tissue c. Mesenchyme d. Dense connective tissue e. Mucous connective tissue Answer: a Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 122. Which of the following can be classified as "connective tissue proper"? a. Adipose tissue b. Dense irregular connective tissue c. Bone d. Blood e. Cartilage Answer: b Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 123. What type of tissue is Wharton's jelly? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: a Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective
ANDIE ALBINO
55
tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 124. What type of tissue is a tendon composed of? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: e Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 125. What does connective tissue develop from? a. Mesothelium b. Mesenchyme c. Mesangial cells d. Mesentery e. Wharton's jelly Answer: b Connective tissue develops from mesenchyme. 126. What color do elastic fibers stain with Verhoeff Elastic stain? a. Red/Orange b. Pink/red c. Purple/Red d. Blue/black e. Green/blue Answer: d Verhoeff Elastic stain stains elastic fibers blue/black. Collagen stains pink/red. 127. Which of the following is a component of the ground substance? a. Hyaluronic acid b. Proteoglycans c. Glycosaminoglycans d. Chondroitin sulfate e. All of the above Answer: e Within connective tissue, the cells and fibers are embedded in the ground substance. The ground substance is amorphous material. It is composed of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. Hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate are glycosaminoglycans. 128. Which of the following is NOT primarily composed of connective tissue? a. Spinal cord b. Pubic symphysis c. Ligament d. Areolar tissue e. Organ capsule Answer: a Of the four basic tissue types (epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue), connective tissue is the most diverse. The pubic symphysis, ligaments, areolar tissue, and organ capsules are all composed of connective tissue. The spinal cord is composed of nervous tissue. 129. Which connective tissue cell type produces the ground substance in connective tissue? a. Fibroblast b. Myofibroblast
ANDIE ALBINO
c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: a Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. The histiocyte is a tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A (slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 130. Which connective tissue cell is derived from B lymphocytes? a. Fibroblast b. Myofibroblast c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: d Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. The histiocyte is a connective tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A (slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 131. Which of the following can be classified as "specialized connective tissue"? a. Mesenchyme b. Bone c. Dense connective tissue d. Mucous connective tissue e. Loose connective tissue Answer: b Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 132. Which of the following can be classified as "connective tissue proper"? a. Bone b. Blood c. Adipose tissue d. Loose irregular connective tissue e. Cartilage Answer: d Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue.
56
Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 133. What type of connective tissue is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: b Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 134. What type of tissue is a ligament composed of? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: e Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 135. Which of the following is not associated with connective tissue? a. Tightly packed cells b. Extracellular fibers c. Tissue fluid d. Ground substance e. None of the above; all of the above are seen with connective tissue Answer: a Connective tissue consists of cells and extracellular fibers in a ground substance and tissue fluid. There is generally abundant extracellular space in connective tissue; the cells are not tightly packed. 136. Which of the following would be best suited to visualize lipid? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: c A peripheral blood smear would be best visualized with Wright's stain. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is the most commonly used tissue stain for routine histological examination. Lipids are best displayed with a sudan stain. Silver impregnation, such as with a reticular stain, can be used to visualize reticular fibers. Collagen fibers can be differentiated from other fibers by staining with Masson's trichrome stain.
137. A beauty treatment for the reduction of wrinkles is the injection of hyaluronic acid into the wrinkle. What is hyaluronic acid? a. Dermatan sulfate b. Proteoglycan c. Glycosaminoglycan d. Chondroitin sulfate e. Keratan sulfate Answer: c Within connective tissue, the cells and fibers are embedded in the ground substance. The ground substance is amorphous material. It is composed of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. Hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan. Dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, and keratan sulfate are also glycosaminoglycans. 138. Which is the most abundant fiber in connective tissue? a. Collagen fiber b. Elastic fiber c. Reticular fiber d. Purkinje fiber e. Muscle fibers Answer: a There are three types of fibers found in connective tissue: collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers. Collagen fibers are the most abundant fiber type in connective tissue. Purkinje fibers are seen in the heart. Purkinje fibers are specialized muscle fibers. 139. Which connective tissue cell type produces collagen? a. Fibroblast b. Connective tissue macrophage c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: a Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. The histiocyte is a connective tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A (slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 140. Which connective tissue cell type secretes histamine? a. Fibroblast b. Myofibroblast c. Histiocyte d. Plasma cell e. Mast cell Answer: e Mast cells secrete histamine. The also secrete heparin, SRS-A (slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Fibroblasts, histiocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells are routinely seen in loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen. The fibroblast also produces the ground substance in connective tissue. Myofibroblasts contain properties of both fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. The histiocyte is a connective tissue macrophage. Plasma cells are derived from B lymphocytes. Mast cells secrete
ANDIE ALBINO
57
histamine. Mast cells also secrete heparin, SRS-A (slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis, ECF-A (eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. 141. Which of the following can be classified as "specialized connective tissue"? a. Loose connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Adipose tissue d. Mucous connective tissue e. Dense connective tissue Answer: c Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 142. Which of the following can be classified as "embryonic connective tissue"? a. Adipose tissue b. Bone c. Blood d. Cartilage e. Mesenchyme Answer: e Connective tissue can be sub-classified into connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue and embryonic connective tissue. Connective tissue proper consists of loose irregular connective tissue and dense connective tissue (regular and irregular). Specialized connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Embryonic connective tissue includes mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue. 143. What is areolar tissue? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: c Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 144. What type of adipose tissue tends to decrease as humans age? a. Brown adipose tissue b. White adipose tissue c. Unilocular adipose tissue d. Multilocular adipose tissue e. Both a and d Answer: e Brown adipose tissue is multilocular adipose tissue. This is present during fetal development and then decreases after birth. White adipose tissue is unilocular adipose tissue. This type of tissue persists into adulthood.
ANDIE ALBINO
145. Which of the following would be best suited to visualize reticular fibers? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Masson's trichrome stain Answer: d A peripheral blood smear would be best visualized with Wright's stain. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is the most commonly used tissue stain for routine histological examination. Lipids are best displayed with a sudan stain. Silver impregnation, such as with a reticular stain, can be used to visualize reticular fibers. Collagen fibers can be differentiated from other fibers by staining with Masson's trichrome stain. 146. What type of basic tissue type is cartilage? a. Muscle b. Nervous c. Cartilage d. Epithelium e. Connective tissue Answer: e Of the four basic tissue types (epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue), connective tissue is the most diverse. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue. 147. How many types of cartilage are there? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 Answer: c There are three types of cartilage: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage. 148. What do you call the space where a chondrocyte sits in? a. Space of Disse b. Space of Mall c. Vacuole d. Lacuna e. Howship's Lacuna Answer: d The space of Disse is in the liver. The space of Disse is also called the perisinusoidal space. It is the space between the liver sinusoids and the hepatocytes. The space of Mall is also in the liver. The space of Mall is located at the portal canal and is the region between the connective tissue and the liver parenchymal cells. It is the site where lymph is formed within the liver. A vacuole is a small clear space within an individual cell. A lacuna is a small space or depression. The space that the chondrocyte rests in is a lacuna. Howship's lacuna is seen in bone. Howship's lacuna is a space seen underneath an osteoclast. 149. What stain would be best to demonstrate the elastic fibers in elastic cartilage? a. Wright's stain b. Hematoxylin and eosin stain c. Sudan stain d. Silver impregnation e. Resorcin fuchsin and orcein Answer: e A peripheral blood smear would be best visualized with Wright's stain. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is the most commonly used tissue stain for routine
58
histological examination. Lipids are best displayed with a sudan stain. Silver impregnation, such as with a reticular stain, can be used to visualize reticular fibers. Resorcin fuchsin and orcein would best show the elastic fibers in elastic cartilage. 150. Which type of cartilage is found in the walls of the eustachian tube? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Elastic cartilage is found in the walls of the eustachian tube. 151. Which type of cartilage forms the skeleton of the fetus? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Hyaline cartilage forms the skeleton of the fetus. The cartilage forms a template of the bones. Endochondral ossification will occur during the childhood, replacing the hyaline cartilage with bone. 152. What type of tissue makes up the "Adam's apple"? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Fibrocartilage c. Elastic cartilage d. Both a and b e. Both a and c Answer: a The "Adam's apple" is a nickname for part of the larynx formed by the thyroid cartilage. The thyroid cartilage is composed of hyaline cartilage. 153. Which type of cartilage forms the intervertebral disc? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c Fibrocartilage forms the intervertebral disc. 154. Which type of cartilage forms the hammer, anvil and stirrup? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: e The hammer, anvil and stirrup are the bones in the middle ear. They are made of bone, not cartilage. 155. Which type of cartilage is characterized by the presence of elastic fibers? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Hyaline cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix. Elastic cartilage has elastic fibers in the matrix. Fibrocartilage has thick bundles of collagen fibers in the matrix. All three types of cartilage are composed of chondrocytes residing in lacunae and a hydrous
extracellular matrix. All three types of cartilage are avascular. 156. Which type of cartilage is highly vascular? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: e Hyaline cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix. Elastic cartilage has elastic fibers in the matrix. Fibrocartilage has thick bundles of collagen fibers in the matrix. All three types of cartilage are composed of chondrocytes residing in lacunae and a hydrous extracellular matrix. All three types of cartilage are avascular. 157. What cell produces the cartilaginous matrix? a. Chondrocyte b. Chondroblast c. Osteocyte d. Osteoclast e. Bone lining cell Answer: b The mature cell in cartilage is a chondrocyte. It rests in a lacunae surrounded by matrix. A chondroblast is an immature cartilage cell which produces the cartilaginous matrix. An osteocyte is a mature bone cell. An osteoclast is a bone cell which is involved in resorption of bone. A bone lining cell is a resting osteoblast. 158. Which type of cartilage is found in the larynx? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: d The larynx is composed of several cartilages. The thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, arytenoid cartilages, corniculate cartilages and cuneiform cartilages are all composed of hyaline cartilage. The epiglottis is elastic cartilage. There is no fibrocartilage in the larynx. 159. Which of the following is NOT a glycosaminoglycan in cartilage? a. Chondroitin sulfate b. Proteoglycans c. Keratan sulfate d. Hyaluronic acid e. All of the above are glycosaminoglycans in cartilage Answer: b Proteoglycans are composed of a protein core and attached glycosaminoglycans. Chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, and hyaluronic acid are all glycosaminoglycans. 160. Which type of cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Hyaline cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix. Elastic cartilage has elastic fibers in the matrix. Fibrocartilage has thick bundles of collagen fibers in the matrix.
ANDIE ALBINO
59
All three types of cartilage are composed of chondrocytes residing in lacunae and a hydrous extracellular matrix. All three types of cartilage are avascular. 161. Which type of cartilage is characterized by the presence of chondrocytes sitting in lacunae? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: d Hyaline cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix. Elastic cartilage has elastic fibers in the matrix. Fibrocartilage has thick bundles of collagen fibers in the matrix. All three types of cartilage are composed of chondrocytes residing in lacunae and a hydrous extracellular matrix. All three types of cartilage are avascular. 162. Which type of cartilage is the most abundant? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. Hyaline cartilage and elastic cartilage equally e. Elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage equally Answer: a Hyaline cartilage is the most abundant type of cartilage. 163. Which type of cartilage forms the articular surface on bones? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Hyaline cartilage forms the articular surface on bones. 164. Which type of cartilage is found in the external ear? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear. Note from Sarah Bellham: If you bend your ear forward, it bounces back into its proper position. This is due to the elastic cartilage. 165. Costal cartilage is composed of what type of cartilage? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Costal cartilage is the cartilage at the end of the ribs. It is hyaline cartilage. 166. Which type of cartilage forms the symphysis pubis? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c Fibrocartilage forms the symphysis pubis. 167. What structure is called white cartilage? a. Hyaline cartilage
ANDIE ALBINO
b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. Compact bone e. Spongy bone Answer: c Elastic cartilage is sometimes referred to as yellow cartilage. Fibrocartilage is sometimes referred to as white cartilage. 168. What is the connective tissue covering which surrounds cartilage? a. Perimysium b. Periosteum c. Perichondrium d. Perineurium e. Endosteum Answer: c The perimysium is the connective tissue sheath around fascicles of muscle. The periosteum is the connective tissue covering of a bone. The perichondrium is the connective tissue which surrounds cartilage. The perineurium is the covering of nerve fascicles. The endosteum is the lining of the inner bone (the side which abuts the medullary cavity). Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "peri" means around, such as in the word "perimeter". The prefix "endo" means within or inner, such as in "endosteum", "endocrine", "endoscope". 169. Where does cartilage come from? a. Ectoderm b. Endoderm c. Mesenchyme d. Connective tissue e. None of the above Answer: c Cartilage arises from mesenchyme. 170. What is the mature cell in cartilage called? a. Chondrocyte b. Chondroblast c. Osteocyte d. Osteoclast e. Bone lining cell Answer: a The mature cell in cartilage is a chondrocyte. It rests in a lacunae surrounded by matrix. A chondroblast is an immature cartilage cell which produces the cartilaginous matrix. An osteocyte is a mature bone cell. An osteoclast is a bone cell which is involved in resorption of bone. A bone lining cell is a resting osteoblast. 171. Regarding the blood supply to cartilage: a. Cartilage has minimal circulation b. Cartilage has a duel circulation c. Cartilage is highly vascular d. Cartilage is avascular e. There is nothing unique about the blood supply to cartilage Answer: d Cartilage is avascular. Nutrients reach cartilage by diffusion from the adjacent tissues. 172. Which type of cartilage is characterized by the presence of thick bundles of collagen fibers? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c
60
Hyaline cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix. Elastic cartilage has elastic fibers in the matrix. Fibrocartilage has thick bundles of collagen fibers in the matrix. All three types of cartilage are composed of chondrocytes residing in lacunae and a hydrous extracellular matrix. All three types of cartilage are avascular. 173. What percent of the matrix of cartilage is water? a. 0 b. 10-40 c. 40-60 d. 60-80 e. 80-100 Answer: d The matrix of cartilage is 60-80% water. 174. Which type of cartilage forms the epiphyseal growth plate? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Hyaline cartilage forms the epiphyseal growth plate. 175. What type of tissue makes up the rings of the trachea? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Fibrocartilage c. Elastic cartilage d. Both a and b e. Both a and c Answer: a The rings of the trachea are composed of hyaline cartilage. 176. What type of tissue makes up the epiglottis? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Fibrocartilage c. Elastic cartilage d. Both a and b e. Both a and c Answer: c The epiglottis is part of the larynx. It is composed of elastic cartilage. 177. Which type of cartilage is present in the temporomandibular joint? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c Fibrocartilage is present in the temporomandibular joint. 178. What structure is called yellow cartilage? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. Compact bone e. Spongy bone Answer: b Elastic cartilage is sometimes referred to as yellow cartilage. Fibrocartilage is sometimes referred to as white cartilage. 179. What is compact bone? a. Dense bone b. Woven bone c. Immature bone d. Cancellous bone
e. Spongy bone Answer: a Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 180. What cell is involved in bone resorption? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: a An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 181. What type of basic tissue type is bone? a. Epithelium b. Connective tissue c. Muscle d. Nervous e. Bone Answer: b Of the four basic tissue types (epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue), connective tissue is the most diverse. Bone is a type of connective tissue. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Keep in mind that the word "bone" can refer to either a type of tissue or to the organ. As a tissue, bone tissue is a type of connective tissue. When referring to a bone (the organ), there will be several types of tissue present. 182. What is woven bone? a. Cancellous bone b. Compact bone c. Dense bone d. Immature bone e. Spongy bone Answer: d Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 183. What are the spicules on spongy bone called? a. Canaliculi b. Sharpey's fibers c. Trabeculae d. Tome's process e. Lacuna Answer: c Canaliculi are the little tunnels within bone. Sharpey's fibers are collagen fibers that extend into a bone at an angle. Trabeculae are the spicules seen with spongy bone. Tome's process is seen in teeth, this process is responsible for enamel production. An osteocyte rests in a space called a lacuna.
ANDIE ALBINO
61
184. Which cell type is responsible for bone breakdown? a. Chondrocyte b. Chondroblast c. Osteocyte d. Osteoclast e. Bone lining cell Answer: d The mature cell in cartilage is a chondrocyte. It rests in a lacunae surrounded by matrix. A chondroblast is an immature cartilage cell which produces the cartilaginous matrix. An osteocyte is a mature bone cell. An osteoclast is a bone cell which is involved in resorption of bone. A bone lining cell is a resting osteoblast. 185. What is bone formation called when the bone is formed directly, without using a cartilage template? a. Intraosseous b. En bloc c. Intramembranous d. Endochondral e. Endosteum Answer: c Intramembranous bone formation is the process of bone formation where the bone is formed without a cartilage template. Endochondral bone formation is the process of bone formation where the bone is formed using a cartilage template. 186. What forms the epiphyseal growth plate? a. Elastic cartilage b. Fibrocartilage c. Hyaline cartilage d. Compact bone e. Spongy bone Answer: c Hyaline cartilage forms the epiphyseal growth plate. 187. Which type of bone has spicules? a. Immature bone b. Dense bone c. Compact bone d. Cancellous bone e. Woven bone Answer: d Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 188. What sits in a lacuna? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: c An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 189. What is dense bone? a. Immature bone b. Cancellous bone c. Compact bone
ANDIE ALBINO
d. Woven bone e. Spongy bone Answer: c Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 190. Which cell is a resting osteoblast? a. Chondrocyte b. Chondroblast c. Osteocyte d. Osteoclast e. Bone lining cell Answer: e The mature cell in cartilage is a chondrocyte. It rests in a lacunae surrounded by matrix. A chondroblast is an immature cartilage cell which produces the cartilaginous matrix. An osteocyte is a mature bone cell. An osteoclast is a bone cell which is involved in resorption of bone. A bone lining cell is a resting osteoblast. 191. What are the mineral crystals in bone called? a. Hydroxyapatite b. Calcite c. Tourmaline d. Rubellite e. Indicolite Answer: a Calcium is in a mineral structure in bone and tooth enamel called hydroxyapatite. The chemical formula is [Ca10 (PO4)6(OH)2] Calcite crystals are calcium carbonate. The main component of limestone is calcite and seashells are made of calcite. However, calcite crystals are not found in man. Tourmaline is a crystal found in nature. Pink-red tourmaline is called rubellite. Blue tourmaline is known as indicolite. Tourmaline crystals are not found in man, although sometimes they are found on the necks and fingers of women in the form of jewelry. 192. What is the cylindrical structure in compact bone? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: b An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 193. What are Sharpey's fibers? a. Elastic fibers b. Collagen fibers c. Reticular fibers d. Trabeculae e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: b Sharpey's fibers are collagen fibers that extend into a bone at an angle. 194. What is the space that an osteocyte rests in?
62
a. Canaliculi b. Sharpey's fibers c. Trabeculae d. Tome's process e. Lacuna Answer: e Canaliculi are the little tunnels within bone. Sharpey's fibers are collagen fibers that extend into a bone at an angle. Trabeculae are the spicules seen with spongy bone. Tome's process is seen in teeth, this process is responsible for enamel production. An osteocyte rests in a space called a lacuna. 195. What is bone formation called when the bone is formed from a cartilage template? a. Intraosseous b. En bloc c. Intramembranous d. Endochondral e. Endosteum Answer: d Intramembranous bone formation is the process of bone formation where the bone is formed without a cartilage template. Endochondral bone formation is the process of bone formation where the bone is formed using a cartilage template. 196. What is the primary component of red marrow? a. Hematopoietic tissue b. Fat c. Cartilage d. Fibrous tissue e. Bone Answer: a Red marrow contains active hematopoietic tissue. Yellow marrow is primarily fat. 197. What cell is an immature bone cell? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: d An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 198. What is bundle bone? a. Cancellous bone b. Compact bone c. Dense bone d. Spongy bone e. Immature bone Answer: e Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 199. What is cancellous bone? a. Dense bone b. Woven bone c. Immature bone
d. Compact bone e. Spongy bone Answer: e Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 200. What cell is involved in laying down new bone? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: d An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 201. What is in the bone matrix? a. Elastic fibers b. Collagen fibers c. Reticular fibers d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: b The matrix of bone is mineralized. Within the matrix are collagen fibers and proteoglycans. Elastic fibers and reticular fibers are types of fibers seen in connective tissue. However, collagen fibers are the fibers found in bone. Although bone is classified as a connective tissue, it is not classified nor is it composed of dense irregular connective tissue. Dense irregular tissue is seen in the dermis. Bone is not classified nor is it composed of dense regular connective tissue. Dense regular connective tissue is seen in tendons and ligaments. 202. What are the small tunnels seen in bone? a. Canaliculi b. Sharpey's fibers c. Trabeculae d. Tome's process e. Lacuna Answer: a Canaliculi are the little tunnels within bone. Sharpey's fibers are collagen fibers that extend into a bone at an angle. Trabeculae are the spicules seen with spongy bone. Tome's process is seen in teeth, this process is responsible for enamel production. An osteocyte rests in a space called a lacuna. 203. What is the hollow area underneath an osteoclast called? a. Space of Disse b. Space of Mall c. Vacuole d. Lacuna e. Howship's lacuna Answer: e
ANDIE ALBINO
63
The space of Disse is in the liver. The space of Disse is also called the perisinusoidal space. It is the space between the liver sinusoids and the hepatocytes. The space of Mall is also in the liver. The space of Mall is located at the portal canal and is the region between the connective tissue and the liver parenchymal cells. It is the site where lymph is formed within the liver. A vacuole is a small clear space within an individual cell. A lacuna is a small space or depression. The space that the chondrocyte rests in is a lacuna. Howship's lacuna is seen in bone. Howship's lacuna is a space seen underneath an osteoclast. 204. What is the covering of a bone? a. Perimysium b. Periosteum c. Perichondrium d. Perineurium e. Endosteum Answer: b The perimysium is the connective tissue sheath which surrounds muscle fascicles. The periosteum is the connective tissue covering of a bone. The perichondrium is the connective tissue which surrounds cartilage. The perineurium is the covering of nerve fascicles. The endosteum is the lining of the inner bone (the side which abuts the medullary cavity). Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "peri" means around, such as in the word "perimeter". The prefix "endo" means within or inner, such as in "endosteum", "endocrine", "endoscope". 205. What forms the articular surface on bones? a. Spongy bone b. Compact bone c. Hyaline cartilage d. Elastic cartilage e. Fibrocartilage Answer: c Hyaline cartilage forms the articular surface on bones. 206. What is the primary component of yellow marrow? a. Hematopoietic tissue b. Fat c. Cartilage d. Fibrous tissue e. Bone Answer: b Red marrow contains active hematopoietic tissue. Yellow marrow is primarily fat. 207. What is another term for the Haversian system? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: b An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 208. What is nonlamellar bone? a. Woven bone
ANDIE ALBINO
b. Dense bone c. Cancellous bone d. Compact bone e. Spongy bone Answer: a Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 209. What is the mature bone cell called? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: c An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 210. What is immature bone? a. Dense bone b. Woven bone c. Cancellous bone d. Compact bone e. Spongy bone Answer: b Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 211. What is unmineralized bone matrix? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: e An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 212. What are the collagen fibers that extend into bone at an angle called? a. Canaliculi b. Sharpey's fibers c. Trabeculae d. Tome's process e. Lacuna Answer: b Canaliculi are the little tunnels within bone. Sharpey's fibers are collagen fibers that extend into a bone at an angle.
64
Trabeculae are the spicules seen with spongy bone. Tome's process is seen in teeth, this process is responsible for enamel production. An osteocyte rests in a space called a lacuna. 213. Which cell is the mature bone cell? a. Chondrocyte b. Chondroblast c. Osteocyte d. Osteoclast e. Bone lining cell Answer: c The mature cell in cartilage is a chondrocyte. It rests in a lacunae surrounded by matrix. A chondroblast is an immature cartilage cell which produces the cartilaginous matrix. An osteocyte is a mature bone cell. An osteoclast is a bone cell which is involved in resorption of bone. A bone lining cell is a resting osteoblast. 214. What is the lining of the inner bone on the side which abuts the medullary cavity? a. Perimysium b. Periosteum c. Perichondrium d. Perineurium e. Endosteum Answer: e The perimysium is the connective tissue sheath which surrounds muscle fascicles. The periosteum is the connective tissue covering of a bone. The perichondrium is the connective tissue which surrounds cartilage. The perineurium is the covering of nerve fascicles. The endosteum is the lining of the inner bone (the side which abuts the medullary cavity). Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "peri" means around, such as in the word "perimeter". The prefix "endo" means within or inner, such as in "endosteum", "endocrine", "endoscope". 215. What forms the skeleton of the fetus? a. Elastic cartilage b. Hyaline cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. Spongy bone e. Compact bone Answer: b Hyaline cartilage forms the skeleton of the fetus. The cartilage forms a template of the bones. Endochondral ossification will occur during the childhood, replacing the hyaline cartilage with bone. 216. Which of the following is a multinucleated cell? a. Osteoclast b. Osteon c. Osteocyte d. Osteoblast e. Osteoid Answer: a An osteoclast is a multinucleated cell involved in the degradation of bone. It is a bone resorbing cell. An osteon is the cylindrical structure with bone. An osteon is also called a Haversian system. The mature bone cell is called an osteocyte. It sits in a space, called a lacuna. An osteoblast is an immature bone cell. The osteoblast is the bone forming cell. Osteoid is unmineralized bone matrix. 217. What is spongy bone a. Immature bone b. Compact bone
c. Cancellous bone d. Dense bone e. Woven bone Answer: c Compact bone is also called dense bone. Compact bone has the Haversian system. Immature bone is woven bone. It is nonlamellar bone or bundle bone. Spongy bone is also referred to as cancellous bone. The mineralized tissue is seen as spicules. Marrow spaces are also present. 218. What is the connective tissue covering of a muscle fascicle? a. Sarcolemma b. Endomysium c. Epimysium d. Sarcoplasm e. Perimysium Answer: e The outer connective tissue covering of a muscle is the epimysium. Within the muscle, there are subdivisions called fascicles. The perimysium surrounds these muscle fascicles. The endomysium is the covering around an individual muscle fiber. The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle cell. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell. 219. What is actin? a. Myofilament b. Myosin c. Muscle fibers d. Myofibrils e. Myocardium Answer: a Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 220. Which of the following is composed of smooth muscle? a. Upper esophagus b. Heart c. Tongue d. Biceps muscle e. Walls of the visceral organs Answer: e There are two chief categories of muscle: striated and non striated muscle (smooth muscle). Striated muscle can be sub-categorized into cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle. The tongue, biceps muscle, and upper esophagus are made of striated muscle. The heart is composed of cardiac muscle. Non striated muscle is also called smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is involuntary muscle. It is found in viscera and blood vessels. 221. What is a receptor in muscle? a. Motor unit b. Motor neuron c. Motor end plate d. Neuromuscular spindle e. Neurotransmitter Answer: d A single motor neuron and the aggregation of muscle fibers innervated by that single neuron is called the
ANDIE ALBINO
65
motor unit. A motor neuron is a neuron which innervates a muscle cell. The point of contact where a neuron contacts a muscle is the motor end plate. A neuromuscular spindle is a receptor which is sensitive to stretching of the muscle. A neurotransmitter is the chemical released by a nerve at a synapse. 222. Which fiber type is larger in diameter? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 223. Which fiber type is make up fast-twitch muscle? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 224. Which fiber type has more myoglobin? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power.
ANDIE ALBINO
225. Which fiber type gets its energy primarily from glycogen? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 226. Which fiber type is seen in skeletal muscle? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: d Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 227. What is line that bisects the dark band in muscle? a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. H band e. M line Answer: d The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 228. What is the outer connective tissue covering of a muscle? a. Epimysium b. Sarcoplasm c. Perimysium d. Sarcolemma e. Endomysium Answer: a The outer connective tissue covering of a muscle is the epimysium. Within the muscle, there are subdivisions called fascicles. The perimysium surrounds these muscle fascicles. The endomysium is the covering around an individual muscle fiber. The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle
66
cell. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell. 229. What is myosin? a. Muscle fibers b. Myofibrils c. Myocardium d. Myofilament e. Muscle cell Answer: d Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 230. Where is cardiac muscle found? a. Myofilaments b. Myosin c. Muscle fibers d. Myofibrils e. Myocardium Answer: e Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 231. What type of muscle has visible cross striations? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: d Both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle have visible striations. Collectively, skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle are classified as "striated muscle". 232. What type of muscle is specialized for contraction? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: e The fundamental property of muscle tissue is that it is specialized for contraction. 233. What is released at a synapse? a. Motor unit b. Motor neuron c. Motor end plate d. Neuromuscular spindle e. Neurotransmitter Answer: e A single motor neuron and the aggregation of muscle fibers innervated by that single neuron is called the motor unit. A motor neuron is a neuron which innervates a muscle cell. The point of contact where a neuron contacts a muscle is the motor end plate. A neuromuscular spindle is a receptor which is sensitive to stretching of the muscle. A neurotransmitter is the chemical released by a nerve at a synapse. 234. Which fiber type is more resistant to fatigue?
a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 235. Lance Armstrong is the seven time winner of the Tour de France. The Tour de France is a bicycle race which covers between 3500 to 4000 kilometers. What type of muscle fiber probably predominates in his legs? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 236. What region is made of thin filaments? a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. H band e. M line Answer: b The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 237. On a cross section of a muscle, how many thin filaments surround each thick filament? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 6 e. 8 Answer: d On a cross section of a muscle, each thick filament is surrounded by 6 thin filaments. 238. What is the plasma membrane of a muscle cell called?
ANDIE ALBINO
67
a. Endomysium b. Sarcolemma c. Sarcoplasm d. Perimysium e. Epimysium Answer: b The outer connective tissue covering of a muscle is the epimysium. Within the muscle, there are subdivisions called fascicles. The perimysium surrounds these muscle fascicles. The endomysium is the covering around an individual muscle fiber. The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle cell. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell. 239. What are the thin filaments? a. Myocardium b. Myofibrils c. Myofilaments d. Muscle fibers e. Myosin Answer: c Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 240. Which of the following is composed of skeletal muscle? a. Tongue b. Blood vessel c. Walls of the visceral organs d. Lower esophagus e. Heart Answer: a There are two chief categories of muscle: striated and non striated muscle (smooth muscle). Striated muscle can be sub-categorized into cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle. The tongue, biceps muscle, and upper esophagus are made of striated muscle. The heart is composed of cardiac muscle. Non striated muscle is also called smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is involuntary muscle. It is found in viscera and blood vessels. 241. What type of muscle is composed of spindle shaped cells? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: c Smooth muscle is composed of spindle shaped cells. 242. What type of muscle is always multinucleated? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: a Skeletal muscle is multinucleated. The nuclei are seen on the periphery. Occasionally, cardiac muscle is bi-nucleated. 243. Which fiber type is smaller in diameter? a. Red fibers b. White fibers
ANDIE ALBINO
c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 244. Which fiber type fatigues more readily? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 245. What type of muscle probably predominates in Charles Atlas, the worlds most famous power weight lifter? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 246. What is line that bisects the light band in muscle? a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. H band e. M line Answer: c The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band
68
bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 247. What is the name of the tissue which surrounds muscle fascicles? a. Perimysium b. Periosteum c. Perichondrium d. Perineurium e. Endosteum Answer: a The perimysium is the connective tissue sheath which surrounds muscle fascicles. The periosteum is the connective tissue covering of a bone. The perichondrium is the connective tissue which surrounds cartilage. The perineurium is the covering of nerve fascicles. The endosteum is the lining of the inner bone (the side which abuts the medullary cavity). Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "peri" means around, such as in the word "perimeter". The prefix "endo" means within or inner, such as in "endosteum", "endocrine", "endoscope". 248. What is the covering of an individual muscle fiber? a. Sarcoplasm b. Perimysium c. Endomysium d. Epimysium e. Sarcolemma Answer: c The outer connective tissue covering of a muscle is the epimysium. Within the muscle, there are subdivisions called fascicles. The perimysium surrounds these muscle fascicles. The endomysium is the covering around an individual muscle fiber. The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle cell. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell. 249. What are the thick filaments composed of? a. Myofilaments b. Myosin c. Muscle fibers d. Myofibrils e. Myocardium Answer: b Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 250. Which of the following is composed of cardiac muscle? a. Biceps muscle b. Tongue c. Heart d. Upper esophagus e. Walls of the visceral organs Answer: c There are two chief categories of muscle: striated and non striated muscle (smooth muscle).
Striated muscle can be sub-categorized into cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle. The tongue, biceps muscle, and upper esophagus are made of striated muscle. The heart is composed of cardiac muscle. Non striated muscle is also called smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is involuntary muscle. It is found in viscera and blood vessels. 251. What type of muscle contains centrally placed nuclei? a. Smooth muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Skeletal muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: d Skeletal muscle fibers are multinucleated. The nuclei are located on the periphery of the cell. In cardiac muscle, the nucleus is located centrally. In smooth muscle, there is also a centrally placed nucleus. PEARL from Sarah Bellham: This is an important point, as both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle are striated. The centrally placed nucleus seen in cardiac muscle is one of the things that can be used to distinguish between the two. 252. What is the point that a neuron contacts a muscle called? a. Motor unit b. Motor neuron c. Motor end plate d. Neuromuscular spindle e. Neurotransmitter A single motor neuron and the aggregation of muscle fibers innervated by that single neuron is called the motor unit. A motor neuron is a neuron which innervates a muscle cell. The point of contact where a neuron contacts a muscle is the motor end plate. A neuromuscular spindle is a receptor which is sensitive to stretching of the muscle. A neurotransmitter is the chemical released by a nerve at a synapse. 253. Which fiber type makes up slow-twitch muscle? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 254. Which fiber type uses more anaerobic metabolism? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than
ANDIE ALBINO
69
white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 255. What is the dark band in muscle? a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. H band e. M line Answer: a The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 256. What bisects the H band a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. E band e. M line Answer: e The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 257. What type of muscle has intercalated discs? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: b Intercalated discs are seen in cardiac muscle. Intercalated discs are specialized junctions between cardiac cells. 258. What is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell? a. Epimysium b. Sarcolemma c. Endomysium d. Sarcoplasm e. Perimysium Answer: d The outer connective tissue covering of a muscle is the epimysium. Within the muscle, there are subdivisions called fascicles. The perimysium surrounds these muscle fascicles. The endomysium is the covering around an individual muscle fiber. The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle cell. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell. 259. What is another term for muscle cells? a. Myofilaments b. Myosin c. Muscle fibers d. Myofibrils e. Myocardium Answer: c
ANDIE ALBINO
Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 260. Which of the following contains a substantial amount of smooth muscle? a. Upper esophagus b. Blood vessels c. Heart d. Biceps muscle e. Tongue Answer: b There are two chief categories of muscle: striated and non striated muscle (smooth muscle). Striated muscle can be sub-categorized into cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle. The tongue, biceps muscle, and upper esophagus are made of striated muscle. The heart is composed of cardiac muscle. Non striated muscle is also called smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is involuntary muscle. It is found in viscera and blood vessels. 261. What type of muscle contains actin and myosin? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: e All types of muscle contain actin and myosin. 262. What is a single neuron and the aggregation of muscle fibers innervated by that single neuron called? a. Motor unit b. Motor neuron c. Motor end plate d. Neuromuscular spindle e. Neurotransmitter Answer: a A single motor neuron and the aggregation of muscle fibers innervated by that single neuron is called the motor unit. A motor neuron is a neuron which innervates a muscle cell. The point of contact where a neuron contacts a muscle is the motor end plate. A neuromuscular spindle is a receptor which is sensitive to stretching of the muscle. A neurotransmitter is the chemical released by a nerve at a synapse. 263. Which fiber type has a lot of mitochondria? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. 264. Which fiber type uses more aerobic metabolism? a. Red fibers
70
b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 265. What is the light band in muscle? a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. H band e. M line Answer: b The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 266. What type of muscle contains sarcomeres? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: d Both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle have sarcomeres. Smooth muscle has no sarcomeres. 267. What type of muscle has branching cells? a. Skeletal muscle b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle d. Both "a" and "b" e. "a" "b" and "c" Answer: b Branching cells are seen in cardiac muscle. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: This is an important point, as both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle are striated. The branching seen with cardiac muscle is one of the things that can be used to distinguish between the two. 268. Which fiber type is seen in smooth muscle? a. Red fibers b. White fibers c. Intermediate fibers d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: e Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as red fibers, white fibers or intermediate fibers. Red fibers are smaller in diameter; white fibers are larger in diameter. Red fibers have more mitochondria than white fibers. Red fibers make up slow-twitch muscle; white fibers make up fast-twitch muscle. Red fibers are more resistant to fatigue than are white fibers. Red fibers have more myoglobin (oxygen binding
pigment) than white fibers. White fibers store glycogen and use anaerobic metabolism. Red fiber and slow twitch muscle is for endurance. White fiber and fast twitch muscle is for a burst of power. 269. A sarcomere is defined as the segment from _____ to ____? a. A band b. I band c. Z line d. H band e. M line Answer: c The A band is the darker staining band. The I band is the light band. The I band is made of thin filaments. The Z line runs through the I band. The H band bisects the A band. The M line runs through the H band. A sarcomere is the segment that runs from Z line to Z line. 270. What are the bundle of longitudinal contractile elements within a muscle cell called? a. Myofilaments b. Myosin c. Muscle fibers d. Myofibrils e. Myocardium Answer: d Myofilaments are the contractile protein within a muscle cell. The myofilaments are actin and myosin. The thin filaments are actin and the thick filaments are myosin. The muscle cell is a muscle fiber. The term "muscle cell" and "muscle fiber" are synonymous. A myofibril is a longitudinal bundle of myofilaments within a muscle cell. Myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. Thus, the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle. 271. Which of the following is composed of loose connective tissue? a. Epidermis b. Reticular layer of dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: c The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 272. Where is thick skin found? a. Over the knee b. Sole of the feet c. Breast d. Lips e. All of the above Answer: b 273. Which layer of the epidermis has cells which have keratohyaline granules? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: c
ANDIE ALBINO
71
The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs" 274. Which cell is a macrophage found in the skin? a. Kupffer cells b. Histiocyte c. Dust cell d. Langerhans cell e. Microglia Answer: d Macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Many tissues have resident (fixed) macrophages. Fixed macrophages are given a unique name, depending on the tissue that they are located in. Kupffer cells are the hepatic macrophages. Histiocytes are macrophages seen in connective tissue. Dust cells are alveolar macrophage found in the respiratory tract. Langerhans cells are macrophages seen in the skin. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. 275. A new miracle skin cream recently hit the beauty counters which is suppose to stimulate collagen production. Which cell is it supposedly stimulating? a. Langerhans cell b. Keratinocyte c. Melanocyte d. Merkel cell e. Fibroblast Answer: e Langerhans cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Merkel cells are all found in the epidermis. The Langerhans cell is a phagocyte. The keratinocyte is the most abundant cell in the epidermis. The melanocyte produces melanin, which is responsible for skin pigmentation. The Merkel cell is a mechanoreceptor. Fibroblasts are found in the dermis. Fibroblasts produces collagen. 276. What is the half moon shaped white area on a nail called? a. Lunula b. Eponychium c. Matrix d. Nail bed e. Root Answer: a The lunula is the half moon shaped white area on a nail. The anatomical term for the cuticle is the eponychium. The matrix is the region of the nails where there are dividing cells and nail growth. The nail plate rests on the nail bed. The nail root is the proximal portion of the nail that is underneath skin. 277. What is the growing part of the nail? a. Lunula b. Eponychium c. Matrix
ANDIE ALBINO
d. Nail bed e. Root Answer: c The lunula is the half moon shaped white area on a nail. The anatomical term for the cuticle is the eponychium. The matrix is the region of the nails where there are dividing cells and nail growth. The nail plate rests on the nail bed. The nail root is the proximal portion of the nail that is underneath skin. 278. What type of glands are the ceruminous glands? a. Sebaceous glands b. Eccrine sweat gland c. Endocrine gland d. Apocrine sweat gland e. Oil gland Answer: d The ceruminous glands of the ear are apocrine sweat glands. 279. Which of the following is the most abundant sensory receptor of the skin? a. Free nerve endings b. Ruffini's corpuscles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Krause's end bulbs e. Meissner's corpuscle Answer: a There are several different sensory receptors in the skin. The most abundant sensory receptor are the free nerve endings. Free nerve endings respond to pain and temperature. Ruffini's corpuscles respond to continuous pressure. Pacinian corpuscles respond to vibration and rapidly changing pressure. Krause's end bulbs are a receptor for fine touch which are located in mucous membranes and the tongue. Meissner's corpuscles are also a receptor for fine touch but they are located in the dermis. 280. Where can hair be found? a. Palms of hand b. Soles of feet c. Urogenital openings d. Lips e. Eyelid Hair is present over most of the body. It is not found on the palms of the hand, soles of the feet, urogenital openings, and lips. 281. Which of the following is composed of connective tissue? a. Epidermis b. Dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: e The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 282. Which of the following is composed of dense irregular connective tissue? a. Epidermis b. Reticular layer of dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: b
72
The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 283. Where is thick skin found? a. Lips b. Over the knee c. Palms d. Breast e. All of the above Answer: c Thick skin is found on the palms of the hand and the sole of the feet. Thin skin is found everywhere else. 284. Which layer of the epidermis is present only in thick skin? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: d The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Note from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs" 285. Which cell is a mechanoreceptors? a. Langerhans cell b. Keratinocyte c. Melanocyte d. Merkel cell e. Fibroblast Answer: d Langerhans cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Merkel cells are all found in the epidermis. The Langerhans cell is a phagocyte. The keratinocyte is the most abundant cell in the epidermis. The melanocyte produces melanin, which is responsible for skin pigmentation. The Merkel cell is a mechanoreceptor. Fibroblasts are found in the dermis. Fibroblasts produces collagen. 286. Which cell is found in the dermis? a. Langerhans cell b. Keratinocyte c. Melanocyte d. Merkel cell e. Fibroblast Answer: e Langerhans cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Merkel cells are all found in the epidermis. The Langerhans cell is a phagocyte. The keratinocyte is the most abundant cell in the epidermis. The
melanocyte produces melanin, which is responsible for skin pigmentation. The Merkel cell is a mechanoreceptor. Fibroblasts are found in the dermis. Fibroblasts produces collagen. 287. What is underneath the nail plate? a. Lunula b. Eponychium c. Matrix d. Nail bed e. Root Answer: d The lunula is the half moon shaped white area on a nail. The anatomical term for the cuticle is the eponychium. The matrix is the region of the nails where there are dividing cells and nail growth. The nail plate rests on the nail bed. The nail root is the proximal portion of the nail that is underneath skin. 288. What is the innervation of an eccrine sweat gland? a. Cholinergic; parasympathetic b. Cholinergic; sympathetic c. Adrenergic; parasympathetic d. Adrenergic; sympathetic e. Cholinergic; motor Answer: b Eccrine sweat glands are innervated by the sympathetic nervous system. The neurotransmitter for the eccrine sweat glands is acetylcholine. Thus it is cholinergic. Note from Sarah Bellham: For most postganglionic sympathetic neurons, the neurotransmitter is norepinephrine. Eccrine sweat glands are an exception to this generalization, as the innervation for eccrine sweat glands is cholinergic sympathetic. 289. Which of the following responds to continuous pressure? a. Free nerve endings b. Ruffini's corpuscles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Krause's end bulbs e. Meissner's corpuscle Answer: b There are several different sensory receptors in the skin. The most abundant sensory receptor are the free nerve endings. Free nerve endings respond to pain and temperature. Ruffini's corpuscles respond to continuous pressure. Pacinian corpuscles respond to vibration and rapidly changing pressure. Krause's end bulbs are a receptor for fine touch which are located in mucous membranes and the tongue. Meissner's corpuscles are also a receptor for fine touch but they are located in the dermis. 290. Which of the following is found in the hair follicle? a. Pigment epithelium b. Muller's cells c. Huxley's layer d. Horizontal cells e. Cones Answer: c Pigment epithelium, Muller's cells, horizontal cells, and cones are all part of the retina. Huxley's layer is a layer in the hair follicle. 291. The reticular layer is part of which layer? a. Epidermis b. Dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. None of the above Answer: b
ANDIE ALBINO
73
The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 292. Which of the following is NOT considered an epidermal appendage? a. Sweat gland b. Hair c. Hypodermis d. Nails e. Sebaceous glands Answer: c Sweat glands, hair, nails and sebaceous glands are all considered epidermal appendages. The hypodermis is not considered an epidermal appendage. The hypodermis is the loose connective tissue layer underneath the dermis. 293. Which layer of the epidermis is also called the stratum germinativum? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: a The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Note from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs" 294. Which layer of the epidermis is on the surface of the skin? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: e The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Note from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs"
ANDIE ALBINO
295. Which cell is the most abundant cell in the epidermis? a. Langerhans cell b. Keratinocyte c. Melanocyte d. Merkel cell e. Fibroblast Answer: b Langerhans cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Merkel cells are all found in the epidermis. The Langerhans cell is a phagocyte. The keratinocyte is the most abundant cell in the epidermis. The melanocyte produces melanin, which is responsible for skin pigmentation. The Merkel cell is a mechanoreceptor. Fibroblasts are found in the dermis. Fibroblasts produces collagen. 296. What type of epithelium forms the epidermis? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: d The epidermis is formed by stratified squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Stratified squamous epithelium is "stratified" because it is more than one cell layer thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the surface cells of the stratified squamous layer are flat. This is important to note as the cells at the basal layer are cuboidal or even columnar. It is still classified as "squamous" based on the cells of the surface layer. 297. What is the portion of the nail which is underneath skin? a. Lunula b. Eponychium c. Matrix d. Nail bed e. Root Answer: e The lunula is the half moon shaped white area on a nail. The anatomical term for the cuticle is the eponychium. The matrix is the region of the nails where there are dividing cells and nail growth. The nail plate rests on the nail bed. The nail root is the proximal portion of the nail that is underneath skin. 298. What type of glands are the glands of Moll? a. Endocrine gland b. Apocrine sweat gland c. Oil gland d. Sebaceous glands e. Eccrine sweat gland Answer: b The glands of Moll in the eyelid are apocrine sweat glands. 299. Which of the following responds to vibration and rapidly changing pressure? a. Free nerve endings b. Ruffini's corpuscles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Krause's end bulbs e. Meissner's corpuscle Answer: c There are several different sensory receptors in the skin. The most abundant sensory receptor are the free nerve endings. Free nerve endings respond to pain and temperature. Ruffini's corpuscles respond to continuous pressure. Pacinian corpuscles respond to vibration and rapidly changing pressure. Krause's end
74
bulbs are a receptor for fine touch which are located in mucous membranes and the tongue. Meissner's corpuscles are also a receptor for fine touch but they are located in the dermis. 300. Which of the following is a receptor for fine touch which is located in mucous membranes? a. Free nerve endings b. Ruffini's corpuscles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Krause's end bulbs e. Meissner's corpuscle Answer: d There are several different sensory receptors in the skin. The most abundant sensory receptor are the free nerve endings. Free nerve endings respond to pain and temperature. Ruffini's corpuscles respond to continuous pressure. Pacinian corpuscles respond to vibration and rapidly changing pressure. Krause's end bulbs are a receptor for fine touch which are located in mucous membranes and the tongue. Meissner's corpuscles are also a receptor for fine touch but they are located in the dermis. 301. Which of the following is composed of stratified squamous epithelium? a. Epidermis b. Dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: a The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 302. Which of the following is NOT a function of skin a. Vitamin D production b. Protection from water loss c. Sensory reception d. Heat regulation e. All are functions of skin Answer: e The skin is involved in the production of vitamin D from precursors with the aid of the sun. It protects the body from water loss. There are many sensory receptors in the skin: pain, pressure, fine touch. The skin is also involved in heat regulation. In addition, the skin protects the body. 303. Which layer of the epidermis contains dividing cells? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: a The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin.
The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Note from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs" 304. Which layer of the epidermis contains cells with no nuclei or organelles? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: e The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Note from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs" 305. Which cell is a phagocyte? a. Langerhans cell b. Keratinocyte c. Melanocyte d. Merkel cell e. Fibroblast Answer: a Langerhans cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Merkel cells are all found in the epidermis. The Langerhans cell is a phagocyte. The keratinocyte is the most abundant cell in the epidermis. The melanocyte produces melanin, which is responsible for skin pigmentation. The Merkel cell is a mechanoreceptor. Fibroblasts are found in the dermis. Fibroblasts produces collagen. 306. What is a characteristic of the cells in the epidermis of the skin? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b Answer: d Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border. Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. 307. Where are apocrine sweat glands NOT found? a. Areola b. External genitalia c. Posterior neck d. Axilla
ANDIE ALBINO
75
e. Circumanal region Answer: c Sweat glands are divided into apocrine and eccrine. Apocrine sweat glands are found on the areola, external genitalia, axilla, and curcumanal region. Eccrine sweat glands are distributed over most of the body. 308. What is the innervation of an apocrine sweat gland? a. Cholinergic; parasympathetic b. Cholinergic; sympathetic c. Adrenergic; parasympathetic d. Adrenergic; sympathetic e. Cholinergic; motor Answer: d Apocrine sweat glands are innervated by the sympathetic nervous system. The neurotransmitter for the apocrine sweat glands is norepinephrine. Thus it is adrenergic. 309. Which of the following is a receptor for fine touch which is located in the dermis? a. Free nerve endings b. Ruffini's corpuscles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Krause's end bulbs e. Meissner's corpuscle Answer: e There are several different sensory receptors in the skin. The most abundant sensory receptor are the free nerve endings. Free nerve endings respond to pain and temperature. Ruffini's corpuscles respond to continuous pressure. Pacinian corpuscles respond to vibration and rapidly changing pressure. Krause's end bulbs are a receptor for fine touch which are located in mucous membranes and the tongue. Meissner's corpuscles are also a receptor for fine touch but they are located in the dermis. 310. Which of the following is found in the hair follicle? a. Henle's layer b. Bipolar cells c. Amacrine cells d. Rods e. Ganglion cells Answer: a Bipolar cells, amacrine cells, rods, and ganglion cells are all part of the retina. Henle's layer is a layer in the hair follicle. 311. The papillary layer is part of which layer? a. Epidermis b. Dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. None of the above Answer: b The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 312. Which layer of the epidermis contains star shaped cells? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: b
ANDIE ALBINO
The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Note from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs" 313. Which of the following layers comprise the skin? a. Epidermis b. Dermis c. Hypodermis d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: d The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis. Underneath these layers lies the hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium. The dermis is composed of a papillary layer and a reticular layer. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. The hypodermis is a layer of loose connective tissue. 314. Which cell is responsible for skin pigmentation? a. Langerhans cell b. Keratinocyte c. Melanocyte d. Merkel cell e. Fibroblast Answer: c Langerhans cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Merkel cells are all found in the epidermis. The Langerhans cell is a phagocyte. The keratinocyte is the most abundant cell in the epidermis. The melanocyte produces melanin, which is responsible for skin pigmentation. The Merkel cell is a mechanoreceptor. Fibroblasts are found in the dermis. Fibroblasts produces collagen. 315. Which of the following responds to pain? a. Free nerve endings b. Ruffini's corpuscles c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Krause's end bulbs e. Meissner's corpuscle Answer: a There are several different sensory receptors in the skin. The most abundant sensory receptor are the free nerve endings. Free nerve endings respond to pain and temperature. Ruffini's corpuscles respond to continuous pressure. Pacinian corpuscles respond to vibration and rapidly changing pressure. Krause's end bulbs are a receptor for fine touch which are located in mucous membranes and the tongue. Meissner's corpuscles are also a receptor for fine touch but they are located in the dermis. 316. What is the correct term for cuticle? a. Lunula b. Eponychium c. Matrix d. Nail bed
76
e. Root Answer: b The lunula is the half moon shaped white area on a nail. The anatomical term for the cuticle is the eponychium. The matrix is the region of the nails where there are dividing cells and nail growth. The nail plate rests on the nail bed. The nail root is the proximal portion of the nail that is underneath skin. 317. What color is keratin with Masson's trichrome stain? a. Red b. Pink c. Green d. Black e. Yellow Answer: a A trichrome stain is a mixture of three dyes. Collagen fibers stain green with Masson's trichrome stain. Muscle and keratin will be red with Masson's trichrome stain. Cytoplasm will be pink. Nuclei will be black. 318. What type of tissue makes up the dermis of the skin? a. Mucous connective tissue b. Mesenchyme c. Loose irregular connective tissue d. Dense irregular connective tissue e. Dense regular connective tissue Answer: d Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue. It is an undifferentiated tissue found in the embryo. Mucous connective tissue is a type of embryonic connective tissue; it is a subset of mesenchyme. Wharton's jelly is mucous connective tissue. Loose irregular connective tissue is areolar tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue is seen in the dermis. Dense regular connective tissue comprises tendons and ligaments. 319. What are the pressure receptors in skin called? a. Psammoma bodies b. Corpora arenacea c. Hassall's corpuscles d. Prostatic concretions e. Pacinian corpuscles Answer: e Psammoma bodies are collections of calcium. It is derived from the Greek word "psammos", which means sand. Corpora arenacea refers to the calcifications seen in the pineal gland. Corpora arenacea is nicknamed "brain sand". Hassall's corpuscles are the ring like structures found in the thymus. The spherical structures seen in some prostatic alveoli are called prostatic concretions. Pacinian corpuscles are pressure receptors in the skin. 320. Which sensory receptor in the skin is NOT encapsulated? a. Ruffini endings b. Free nerve endings c. Pacinian corpuscles d. Meissner's corpuscles e. Merkel cells Answer: b Ruffini endings, pacinian corpuscles, meissner's corpuscles, and merkel cells are all encapsulated sensory receptors. Free nerve endings are not encapsulated. 321. Where is the primary site for absorption of nutrients? a. Stomach b. Small intestine
c. Ascending colon d. Descending colon e. Both a and b equally Answer: b The small intestine is the primary site for absorption of nutrients. 322. What are the finger like projections of mucosa that are seen in the small intestine? a. Lacteal b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: e There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 323. What is the outer layer of the GI tract called when it is abutting another organ? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: e The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 324. Where is masticatory mucosa found a. Tongue underside b. Hard palate c. Soft palate d. Lips e. Cheek Answer: b The masticatory mucosa is located on the hard palate and gingiva. Lining mucosa is found on the underside of the tongue, lips, cheek, and soft palate. 325. What is the surface layer of masticatory mucosa composed of? a. Non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium b. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium c. Simple squamous epithelium d. Pseudostratified squamous epithelium e. Both a and b Answer: e The masticatory mucosa is located on the hard palate and gingiva. The surface layer of masticatory mucosa is stratified squamous epithelium. (Remember,
ANDIE ALBINO
77
epithelium lines body cavities and covers body surfaces). The stratified squamous epithelium is keratinized. However, some regions of the masticatory mucosa are covered with non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and parakeratinized epithelium. Parakeratinized epithelium is similar to keratinized epithelium, except that in parakeratinized epithelium cell nuclei are present in the stratum corneum. 326. Which layer is NOT present in masticatory epithelium? a. Stratum basale b. Stratum spinosum c. Stratum granulosum d. Stratum lucidum e. Stratum corneum Answer: d The layers of the masticatory epithelium are similar to the layers of the epidermis. The stratum lucidum is not present in the masticatory epithelium. The epidermis is divided into five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale contains the dividing cells. This layer is also called the stratum germinativum. The stratum spinosum consists of a layer several cells deep. The cells have pointy or spiny processes on them. The cells in the stratum granulosum contain keratohyaline granules. The stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer. The cells in this layer are essentially bags of keratin. They contain no nuclei or organelles. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: My favorite mnemonic for remembering the layers of the skin: "Californian Ladies Give Superb Backrubs". 327. Which type of papillae on the tongue is the most abundant? a. Filiform papillae b. Circumvallate papillae c. Fungiform papillae d. Foliate papillae e. All of the above Answer: a The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant. Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue. Taste buds are found on cicumvallate, fungiform, and foliate papillae. 328. What is the innermost layer of the GI tract called? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: a The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa.
The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 329. What is the lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine called? a. Lacteal b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: a There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 330. Which type of papillae on the tongue is not well developed in man? a. Filiform papillae b. Circumvallate papillae c. Fungiform papillae d. Foliate papillae e. All of the above Answer: d The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant. Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue. Taste buds are found on cicumvallate, fungiform, and foliate papillae. 331. Which cranial nerve is responsible for taste to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue? a. V b. VII c. IX d. X e. XII Answer: c 332. Which cranial nerve to the tongue is responsible for movement? a. V b. VII c. IX d. X e. XII Answer: e 333. Which cranial nerve is responsible for general sensation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue? a. V b. VII c. IX d. X
ANDIE ALBINO
78
e. XII Answer: a 334. Which cranial nerve is responsible for taste to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue? a. V b. VII c. IX d. X e. XII Answer: b 335. Which cranial nerve is responsible for general sensation to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue? a. V b. VII c. IX d. X e. XII Answer: c Cranial nerve V (trigeminal nerve) is responsible for general sensation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue. Cranial nerve VII (facial nerve) is responsible for taste sensation from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue. Cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal nerve) is responsible for taste sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. Cranial nerve IX is also responsible for general sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. Cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal nerve) innervates the muscles of the tongue thereby eliciting movement of the tongue. 336. What covers the tooth that is embedded within the jaw? a. Pulp cavity b. Dentin c. Dental pulp d. Cementum e. Enamel Answer: d The central portion of a tooth is the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is surrounded by dentin. Within the pulp cavity is a soft tissue, called dental pulp. Cementum covers the part of the tooth that is within the jaw. Enamel covers the part of the tooth within the oral cavity. 337. What is within the pulp cavity? a. Pulp cavity b. Dentin c. Dental pulp d. Cementum e. Enamel Answer: c The central portion of a tooth is the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is surrounded by dentin. Within the pulp cavity is a soft tissue, called dental pulp. Cementum covers the part of the tooth that is within the jaw. Enamel covers the part of the tooth within the oral cavity. 338. What is the central portion of a tooth called? a. Pulp cavity b. Dentin c. Dental pulp d. Cementum e. Enamel Answer: a The central portion of a tooth is the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is surrounded by dentin. Within the pulp cavity is a soft tissue, called dental pulp. Cementum covers the part of the tooth that is within the jaw.
Enamel covers the part of the tooth within the oral cavity. 339. What covers the visible portion of a tooth ? a. Pulp cavity b. Dentin c. Dental pulp d. Cementum e. Enamel Answer: e The central portion of a tooth is the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is surrounded by dentin. Within the pulp cavity is a soft tissue, called dental pulp. Cementum covers the part of the tooth that is within the jaw. Enamel covers the part of the tooth within the oral cavity. 340. What surrounds the pulp cavity? a. Pulp cavity b. Dentin c. Dental pulp d. Cementum e. Enamel Answer: b The central portion of a tooth is the pulp cavity. The pulp cavity is surrounded by dentin. Within the pulp cavity is a soft tissue, called dental pulp. Cementum covers the part of the tooth that is within the jaw. Enamel covers the part of the tooth within the oral cavity. 341. Which layer contains the lamina propria? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: a The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 342. What is another term for the valve of Kerckring? a. Lacteal b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: c There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 343. Which type of papillae on the tongue is the smallest? a. Filiform papillae
ANDIE ALBINO
79
b. Circumvallate papillae c. Fungiform papillae d. Foliate papillae e. All of the above Answer: a The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant. Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue. Taste buds are found on cicumvallate, fungiform, and foliate papillae. 344. Where are Peyer's patches located? a. Esophagus b. Stomach c. Small intestine d. Large intestine e. Rectum Answer: c Peyer's patches are large nodules of lymphatic tissue. They are seen in the small intestine. 345. What type of muscle makes up the muscularis externa in the esophagus? a. Smooth b. Striated c. Cardiac d. both a and b e. a, b, and c. Answer: d The muscularis externa in the upper third of the esophagus is composed of striated muscle and in the lower third it is smooth muscle. The middle third is a blend. 346. What are mucous surface cells? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: c The epithelium on the stomach is lined by mucous surface cells which are a simple columnar epithelium. 347. Which layer consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: d The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The
adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 348. What is another term for the brush border? a. Lacteal b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: d There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 349. Which type of papillae on the tongue is arranged in a "V" shape on the tongue? a. Filiform papillae b. Circumvallate papillae c. Fungiform papillae d. Foliate papillae e. All of the above Answer: b The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant. Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue. Taste buds are found on cicumvallate, fungiform, and foliate papillae. 350. Which cells secrete intrinsic factor? a. Parietal cells b. Oxyntic cells c. Chief cells d. Mucous neck cells e. Both a and b Answer: e Chief cells secrete pepsinogen. Pepsinogen is the precursor for pepsin. Parietal cells are also called oxyntic cells. They secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. Mucous neck cells contain mucinogen granules. 351. Which layer contains the lining epithelium? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: a The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus.
ANDIE ALBINO
80
The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 352. Which type of papillae on the tongue does NOT contain taste buds? a. Filiform papillae b. Circumvallate papillae c. Fungiform papillae d. Foliate papillae e. All of the above Answer: a The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant. Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue. Taste buds are found on cicumvallate, fungiform, and foliate papillae. 353. Which layer contains Auerbach's plexus? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: c The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 354. Which cells secrete hydrochloric acid? a. Parietal cells b. Oxyntic cells c. Chief cells d. Mucous neck cells e. Both a and b Answer: e Chief cells secrete pepsinogen. Pepsinogen is the precursor for pepsin. Parietal cells are also called oxyntic cells. They secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. Mucous neck cells contain mucinogen granules. 355. What is another term for the intestinal glands? a. Lacteal b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: b There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands.
The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 356. Which organ has a mucosa lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium? a. Esophagus b. Stomach c. Small intestine d. Large intestine e. Rectum The mucosa of the esophagus is mucosa lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. 357. What are the folds of the stomach called? a. Ruffled border b. Taeniae coli c. Gastric glands d. Rugae e. Gastric pits The folds of the empty stomach are called rugae. 358. Which type of papillae on the tongue is mushroom shaped? a. Filiform papillae b. Circumvallate papillae c. Fungiform papillae d. Foliate papillae e. All of the above Answer: c The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant. Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue. Taste buds are found on cicumvallate, fungiform, and foliate papillae. 359. Which layer contains the muscularis mucosa? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: a The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 360. What are microvilli called that are seen in the small intestine? a. Lacteal b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares
ANDIE ALBINO
81
d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: d There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 361. Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains the gut associated lymphatic tissue? a. Mucosa b. Submucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Muscularis mucosae e. Serosa Answer: a The layers of the GI tract are: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa or adventitia. The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. The mucosa consists of a lining epithelium, lamina propria and muscularis mucosae. Gut associated lymphatic tissue (GALT) is found in the mucosa and sometimes extends into the submucosa. The submucosa is comprised of dense irregular connective tissue. Within the submucosa are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. The myenteric plexus of Auerbach is located in the muscularis externa. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells (mesothelium) and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 362. Which cells secrete pepsinogen? a. Parietal cells b. Oxyntic cells c. Chief cells d. Mucous neck cells e. Both a and b Answer: c Chief cells secrete pepsinogen. Pepsinogen is the precursor for pepsin. Parietal cells are also called oxyntic cells. They secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. Mucous neck cells contain mucinogen granules. 363. Which layer contains Meissner's plexus? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: b The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa.
The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. It contains Auerbach's plexus. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 364. What type of tissue lines most of the gastrointestinal tract? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: c The lining of the gastrointestinal tract is simple columnar epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple columnar epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Columnar" cells are taller than they are wide and have an oval nucleus. 365. What type of tissue lines the upper esophagus? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: d The lining of the upper esophagus is stratified squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Stratified squamous epithelium is "stratified" because it is more than one cell layer thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the surface cells of the layer are flat. 366. What are the modifications of the muscularis externa that is seen on the large intestine? a. Teniae coli b. Crypts of Lieberkuhn c. Plicae circulares d. Striated border e. Villi Answer: a The modifications of the muscularis externa seen on the large intestine are called teniae coli. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plicae circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plicae circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring. Microvilli that are seen on the epithelial cells in the small intestine form the brush border or striated border. Villi are finger like projections of mucosa seen in the small intestine. 367. Where are Brunner's glands located? a. Esophagus b. Stomach c. Small intestine d. Large intestine e. Rectum Answer: c Brunner's glands are glands in the submucosa of the small intestine. 368. What is the primary cell of the intestinal epithelium of the large intestine? a. Columnar absorptive cell b. Goblet cell c. Parietal cells d. Paneth cells
ANDIE ALBINO
82
e. Chief cells Answer: a The major cell of the lining epithelium of the large intestine is the columnar absorptive cell. 369. Which region are goblet cells most numerous? a. Esophagus b. Stomach c. Small intestine d. Large intestine e. Anus Answer: d Goblet cells are most numerous in the large intestine 370. Where is mesothelium found? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: d The layers of the GI tract are: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa or adventitia. The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. The mucosa consists of a lining epithelium, lamina propria and muscularis mucosae. Gut associated lymphatic tissue (GALT) is found in the mucosa and sometimes extends into the submucosa. The submucosa is comprised of dense irregular connective tissue. Within the submucosa are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle. The myenteric plexus of Auerbach is located in the muscularis externa. The outer layer of the GI tract is either an adventitia or serosa. The serosa consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells (mesothelium) and underlying connective tissue. The adventitia is the outer layer of the GI tract when it is abutting another organ the posterior abdominal wall. 371. Which of the following is the exocrine portion of the pancreas? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: e The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 372. What are divertiuclae of the mucosa of the gallbladder called? a. Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses b. Ducts of Luschka c. Duct of Wirsung d. Ampulla of Vater e. Sphincter of Oddi Answer: a Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are divertiuclae of the mucosa of the gallbladder. The small bile ducts which connec between the cystic duct and liver are the ducts of Luschka The duct of Wirsung is the pancreatic duct. The opening of the pancreatic duct into the
duodenum is at the ampulla of Vater. The valves which regulates the flow of bile into the small intestine is the sphincter of Oddi. 373. What structure is in the middle of the hepatic lobule? a. Hepatic artery b. Portal triad c. Central vein d. Portal vein e. Sinusoids Answer: c Hepatocytes are the liver cells. They are arranged to form a liver lobule, which is the functional unit of the liver. The liver lobule is a hexagonal shaped structure. At the angles of the liver lobule are portal triads. The portal triad is composed of a branch of the hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct. In the middle of the liver lobule is a central vein. Hepatic sinusoids run between the hepatocytes. 374. What is the space between the liver sinusoids and the hepatocytes called? a. Space of Disse b. Space of Mall c. Vacuole d. Lacuna e. Howship's lacuna Answer: a The space of Disse is in the liver. The space of Disse is also called the perisinosoidal space. It is the space between the liver sinusoids and the hepatocytes. The space of Mall is also in the liver. The space of Mall is located at the portal canal and is the region between the connective tissue and the liver parenchymal cells. It is the site where lymph is formed within the liver. A vacuole is a small clear space within an individual cell. A lacuna is a small space or depression. The space that the chondrocyte rests in is a lacuna. Howship's lacuna is seen in bone. Howship's lacuna is a space seen underneath an osteoclast. 375. What is the name of the cellular mass for the endocrine portion of the pancreas? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: a The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 376. Which structures are part of the portal triad? a. Portal vein b. Hepatic artery c. Central vein d. Sinusoids e. Both a and b Answer: e Hepatocytes are the liver cells. They are arranged to form a liver lobule, which is the functional unit of the liver. The liver lobule is a hexagonal shaped structure. At the angles of the liver lobule are portal triads. The portal triad is composed of a branch of the hepatic
ANDIE ALBINO
83
artery, portal vein, and bile duct. In the middle of the liver lobule is a central vein. Hepatic sinusoids run between the hepatocytes. 377. Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver? a. Metabolism of bilirubin b. Deamination of amino acids c. Storage of iron d. Storage of copper e. Storage of calcium Answer: e The liver performs many, many functions. Estimates range at over 500 different functions for the liver. Bilirubin is metabolized in the liver. The conversion of amino acids to carbohydrates through the process of deamination occurs in the liver. Iron is stored in the liver as ferritin. Copper is stored in the liver. The storage site for calcium is in the bones. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: If ever asked where a process occurs, and you absolutely have no idea, make an educated guess of the liver. 378. What is the functional unit of the liver? a. Lobule b. Portal triad c. Central vein d. Hepatocyte e. Sinusoids Answer: a Hepatocytes are the liver cells. They are arranged to form a liver lobule, which is the functional unit of the liver. The liver lobule is a hexagonal shaped structure. At the angles of the liver lobule are portal triads. The portal triad is composed of a branch of the hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct. In the middle of the liver lobule is a central vein. Hepatic sinusoids run between the hepatocytes. 379. What are the valves which regulates the flow of bile into the intestine? a. Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses b. Ducts of Luschka c. Duct of Wirsung d. Ampulla of Vater e. Sphincter of Oddi Answer: e Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are divertiuclae of the mucosa of the gallbladder. The small bile ducts which connec between the cystic duct and liver are the ducts of Luschka The duct of Wirsung is the pancreatic duct. The opening of the pancreatic duct into the duodenum is at the ampulla of Vater. The valves which regulates the flow of bile into the small intestine is the sphincter of Oddi. 380. What cells of the pancreas secrete somatostatin? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Gamma cells Answer: d The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 381. What is the opening of the pancreatic duct into the duodenum?
ANDIE ALBINO
a. Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses b. Ducts of Luschka c. Duct of Wirsung d. Ampulla of Vater e. Sphincter of Oddi Answer: d Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are divertiuclae of the mucosa of the gallbladder. The small bile ducts which connect between the cystic duct and liver are the ducts of Luschka The duct of Wirsung is the pancreatic duct. The opening of the pancreatic duct into the duodenum is at the ampulla of Vater. The valves which regulates the flow of bile into the small intestine is the sphincter of Oddi. 382. Which of the following is the exocrine portion of the pancreas? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: e The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas 383. Which of the following clotting factors is NOT produced in the liver? a. Factor I b. Factor II c. Factor IV d. Factor IX e. Factor X Answer: c The liver performs many, many functions. Estimates range at over 500 different functions for the liver. The liver makes clotting Factors I, II, VII, IX, and X. Fibrinogen is Factor I. Prothrombin is Factor II. Factor IV is calcium, which is not produced in the liver. Histology hint: If ever asked where a process occurs, and you absolutely have no idea, make an educated guess of the liver.---Sarah Bellham 384. In what structure does blood run through between the hepatocytes? a. Hepatic artery b. Portal triad c. Central vein d. Portal vein e. Sinusoids Answer: e Hepatocytes are the liver cells. They are arranged to form a liver lobule, which is the functional unit of the liver. The liver lobule is a hexagonal shaped structure. At the angles of the liver lobule are portal triads. The portal triad is composed of a branch of the hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct. In the middle of the liver lobule is a central vein. Hepatic sinusoids run between the hepatocytes. 385. What is the space called that is located at the portal canal between the hepatocytes and connective tissue? a. Space of Disse b. Space of Mall c. Vacuole
84
d. Lacuna e. Howship's lacuna The space of Disse is in the liver. The space of Disse is also called the perisinosoidal space. It is the space between the liver sinusoids and the hepatocytes. The space of Mall is also in the liver. The space of Mall is located at the portal canal and is the region between the connective tissue and the liver parenchymal cells. It is the site where lymph is formed within the liver. A vacuole is a small clear space within an individual cell. A lacuna is a small space or depression. The space that the chondrocyte rests in is a lacuna. Howship's lacuna is seen in bone. Howship's lacuna is a space seen underneath an osteoclast. 386. What layer is NOT found in the gallbladder? a. Mucosa b. Muscularis mucosa c. Muscularis d. Adventita e. Serosa Answer: b The gallbladder is comprised of three layers: mucosa, muscularis, and adventita or serosa. Serosa is found on the free surface of the gallbladder. The mucosa is simple columnar epithelium and lamina propria. There is no muscularis in the mucosa of the gallbladder. 387. What cell type makes up the mucosa of the gallbladder? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: c The mucosa of the gallbladder is made of simple columnar epithelium. 388. What is the classification of the pancreas? a. Mixed b. Endocrine c. Exocrine d. Both endocrine and exocrine e. None of the above Answer: d The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 389. Which cell is a hepatic macrophage? a. Kupffer cells b. Histiocyte c. Dust cell d. Langerhans cell e. Microglia Answer: a Macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Many tissues have resident (fixed) macrophages. Fixed macrophages are given a unique name, depending on the tissue that they are located in. Kupffer cells are the hepatic macrophages. Histiocytes are macrophages seen in connective tissue. Dust cells are alveolar macrophage found in the respiratory tract. Langerhans cells are macrophages seen in the
skin. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. 390. Where in the pancreas are islets of Langerhans most numerous? a. Head b. Body c. Tail d. Evenly distributed e. Depends on the individual Answer: c Islets of Langerhans are most numerous in the tail of the pancreas. 391. What cells of the pancreas secrete insulin? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Gamma cells Answer: c The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 392. What is the pancreatic duct? a. Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses b. Ducts of Luschka c. Duct of Wirsung d. Ampulla of Vater e. Sphincter of Oddi Answer: c Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are divertiuclae of the mucosa of the gallbladder. The small bile ducts which connec between the cystic duct and liver are the ducts of Luschka The duct of Wirsung is the pancreatic duct. The opening of the pancreatic duct into the duodenum is at the ampulla of Vater. The valves which regulates the flow of bile into the small intestine is the sphincter of Oddi. 393. What structure is at the angle of the liver lobule? a. Lobule b. Portal triad c. Central vein d. Hepatocyte e. Sinusoids Answer: b Hepatocytes are the liver cells. They are arranged to form a liver lobule, which is the functional unit of the liver. The liver lobule is a hexagonal shaped structure. At the angles of the liver lobule are portal triads. The portal triad is composed of a branch of the hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct. In the middle of the liver lobule is a central vein. Hepatic sinusoids run between the hepatocytes. 394. Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver? a. Cholecystokinin production b. Bile production c. Detoxification d. Albumin production e. Synthesis of clotting factors Answer: a The liver performs many, many functions. Estimates range at over 500 different functions for the liver. Bile production occurs in the liver. The liver receives blood from the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein.
ANDIE ALBINO
85
The blood in the hepatic portal vein is the "first stop" directly from the intestines, giving the liver the prime opportunity to detoxify substances. The liver synthesizes proteins such as albumin, fibrinogen, and prothrombin. Fibrinogen (Factor I) and prothrombin (Factor II) are clotting factors involved in clotting. The liver also makes Factors VII, IX, and X. Cholecystokinin is produced by the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: If ever asked where a process occurs, and you absolutely have no idea, make an educated guess of the liver. 395. What cells of the pancreas secrete glucagon? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Gamma cells Answer: b The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 396. What are the connection between the cystic duct and liver? a. Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses b. Ducts of Luschka c. Duct of Wirsung d. Ampulla of Vater e. Sphincter of Oddi Answer: b Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are divertiuclae of the mucosa of the gallbladder. The small bile ducts which connec between the cystic duct and liver are the ducts of Luschka The duct of Wirsung is the pancreatic duct. The opening of the pancreatic duct into the duodenum is at the ampulla of Vater. The valves which regulates the flow of bile into the small intestine is the sphincter of Oddi. 397. Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver? a. Conversion of glucose into glycogen b. Storage of glycogen c. Storage of bile d. Storage of fat soluble vitamins e. Cholesterol synthesis Answer: c The liver performs many, many functions. Estimates range at over 500 different functions for the liver. Glucose is converted to glycogen in the liver. Glycogen is stored in the liver. The liver stores of fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver. Once bile is produced by the liver, it is stored in the gallbladder. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: If ever asked where a process occurs, and you absolutely have no idea, make an educated guess of the liver. 398. What cells of the pancreas secrete pancreatic polypeptide? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Gamma cells
ANDIE ALBINO
Answer: e The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostain. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 399. What are the supporting cells in the central nervous system called? a. Schwann cells b. Basket cells c. Ganglion d. Neuroglia e. Satellite cells Answer: d Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Basket cells are a type of neuron seen in the cerebellum. A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS. Neuroglia are the supporting cells in the central nervous system Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Satellite cells are found in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. 400. Which of the following is an element of the peripheral nervous system? a. Receptors b. Brachial plexus c. Ganglia d. Sciatic nerve e. All of the above Answer: e The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. All other nervous system elements are considered to be in the peripheral nervous system. Thus the peripheral nervous system includes receptors, the brachial plexus, the sciatic nerve, and ganglia. 401. What are most neurons in the body? a. Unipolar b. Pseudounipolar c. Bipolar d. Multipolar e. Both a and b Answer: d Most neurons in the body (over 99%) are multipolar. Neurons can be classified based on the number of axons and dendrites stemming off of the cell body. A unipolar neuron has one process which branches off of it This process then immediately divides into two. Thus, a unipolar neuron is sometimes also called a pseudounipolar neuron. Sensory neurons are unipolar. A bipolar neuron has two process that branch from it: an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are not very common and are found in some of the organs for special senses. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina, inner ear, and the region of the nose involved with smell. Multipolar neurons have one axon and many (at least two) dendrites that branch off of it. Most neurons are multipolar. Motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 402. What is the cell body of a neuron called? a. Ganglion b. Perikaryon c. Astrocyte
86
d. Nissl e. Terminal bouton Answer: b A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The cell body of a neuron is called a perikaryon or soma. An astrocyte is a supporting cell seen in the central nervous system. The basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic seen in neuron cell bodies is called Nissl, Nissl bodies or Nissl substance. The terminal bouton is the end portion of an axon. It is also called an axon terminal or end bulb. The terminal bouton will be associated with another neuron in a synapse. 403. Which cell is a macrophage found in the central nervous system? a. Kupffer cells b. Histiocyte c. Dust cell d. Langerhans cell e. Microglia Answer: e Macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Many tissues have resident (fixed) macrophages. Fixed macrophages are given a unique name, depending on the tissue that they are located in. Kupffer cells are the hepatic macrophages. Histiocytes are macrophages seen in connective tissue. Dust cells are alveolar macrophage found in the respiratory tract. Langerhans cells are macrophages seen in the skin. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. 404. Which type of neuron is multipolar? a. Motor neurons b. Interneurons c. Sensory neurons d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: d Both motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 405. What provides tensile strength to a neuron? a. Meninges b. Myelinated nerve fibers c. Cell bodies d. Nodes of Ranvier e. Neurofilaments Answer: e The meninges are composed of the three connective tissue covers which surround the brain and spinal cord. White matter is myelinated nerve fibers. Gray matter is essentially neuron cell bodies and associated dendrites or unmyelinated axons. Nodes of Ranvier are the gaps that occur in the myelin sheath. Neurofilaments are a type of intermediate filaments seen in neurons which provide rigidity and tensile strength. 406. Which meninx is made of a delicate web like connective tissue? a. Dura mater b. Arachnoid c. Pia mater d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: b The meninges cover the brain and spinal cord. There are three: dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater. The dura mater is the outer meninx. The dura mater is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. The arachnoid is made of a delicate spider web like connective tissue.
The pia mater is the innermost meninx. It covers the brain intimately. Note from Sarah Bellham: Arachnoid is derived from the Greek word for spider. It is used in the words arachnophobia, arachnids and arachnoid. 407. What are the conglomerations of gray matter deep within the cerebrum and cerebellum called? a. Tracts b. Islets c. Soma d. Cortex e. Nuclei Answer: e A group of fibers traveling together to a destination is a tract. Islets of Langerhans are seen in the pancreas. Soma is another term for a neuron cell body. The outer part of the brain is gray matter called the cortex. The conglomerations of gray matter deep within the cerebrum and cerebellum are called nuclei. 408. Which of the following is involved in the blood brain barrier? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: a Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 409. Which of the following forms myelin in the peripheral nervous system? a. Schwann cells b. Basket cells c. Ganglion d. Neuroglia e. Satellite cells Answer: a Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Basket cells are a type of neuron seen in the cerebellum. A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS. Neuroglia are the supporting cells in the central nervous system Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Satellite cells are found in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. 410. Which of the following is an element of the central nervous system? a. Receptors b. Brachial plexus c. Sciatic nerve d. Ganglia e. Spinal cord Answer: e
ANDIE ALBINO
87
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. All other nervous system elements are considered to be in the peripheral nervous system. Thus the peripheral nervous system includes receptors, the brachial plexus, the sciatic nerve, and ganglia. 411. What are motor neurons? a. Unipolar b. Pseudounipolar c. Bipolar d. Multipolar e. Both a and b Answer: d Motor neurons are multipolar. Neurons can be classified based on the number of axons and dendrites stemming off of the cell body. A unipolar neuron has one process which branches off of it This process then immediately divides into two. Thus, a unipolar neuron is sometimes also called a pseudounipolar neuron. Sensory neurons are unipolar. A bipolar neuron has two process that branch from it: an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are not very common and are found in some of the organs for special senses. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina, inner ear, and the region of the nose involved with smell. Multipolar neurons have one axon and many (at least two) dendrites that branch off of it. Most neurons are multipolar. Motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 412. What is a collection of cell bodies outside the CNS called? a. Ganglion b. Perikaryon c. Astrocyte d. Nissl e. Terminal bouton Answer: a A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The cell body of a neuron is called a perikaryon or soma. An astrocyte is a supporting cell seen in the central nervous system. The basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic seen in neuron cell bodies is called Nissl, Nissl bodies or Nissl substance. The terminal bouton is the end portion of an axon. It is also called an axon terminal or end bulb. The terminal bouton will be associated with another neuron in a synapse. 413. What is tissue which surrounds a nerve fascicle? a. Perimysium b. Periosteum c. Perichondrium d. Perineurium e. Endosteum Answer: d The perimysium is the connective tissue sheath around fascicles of muscle. The periosteum is the connective tissue covering of a bone. The perichondrium is the connective tissue which surrounds cartilage. The perineurium is the covering of nerve fascicles. The endosteum is the lining of the inner bone (the side which abuts the medullary cavity). Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "peri" means around, such as in the word "perimeter". The prefix "endo" means within or inner, such as in "endosteum", "endocrine", "endoscope".
ANDIE ALBINO
414. The colloquialism "gray matter" refers to somebody using his intellect or reasoning ability. In reality, what is gray matter? a. Meninges b. Myelinated nerve fibers c. Cell bodies d. Nodes of Ranvier e. Neurofilaments Answer: c A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. White matter is myelinated nerve fibers. Gray matter is essentially neuron cell bodies. Nodes of Ranvier are the gaps that occur in the myelin sheath. Neurofilaments are a type of intermediate filaments seen in neurons. 415. Where is the cerebrospinal fluid? a. Between the dura mater and bone b. Subdural space c. Subarachnoid space d. Between the pia mater and brain e. None of the above Answer: c The cerebrospinal fluid is found in the subarachnoid space. The subarachnoid space is the space between the arachnoid and the pia mater. 416. Which of the following are considered to be part of the meninges? a. Dura mater b. Arachnoid c. Pia mater d. Both a and c e. All of the above Answer: e The meninges cover the brain and spinal cord. There are three: dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater. The dura mater is the outer meninx. The dura mater is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. The arachnoid is made of a delicate spider web like connective tissue. The pia mater is the innermost meninx. It covers the brain intimately. Note from Sarah Bellham: Arachnoid is derived from the Greek word for spider. It is used in the words arachnophobia, arachnids and arachnoid. 417. What is the outer gray matter of the brain called? a. Tracts b. Islets c. Soma d. Cortex e. Nuclei Answer: d A group of fibers traveling together to a destination is a tract. Islets of Langerhans are seen in the pancreas. Soma is another term for a neuron cell body. The outer part of the brain is gray matter called the cortex. The conglomerations of gray matter deep within the cerebrum and cerebellum are called nuclei. 418. Which of the following is the most abundant neuroglia cell? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: a Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia.
88
Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 419. Which of the following is a supporting cell found in the ganglia? a. Schwann cells b. Basket cells c. Ganglion d. Neuroglia e. Satellite cells Answer: e Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Basket cells are a type of neuron seen in the cerebellum. A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS. Neuroglia are the supporting cells in the central nervous system Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Satellite cells are found in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. 420. Which of the following is an element of the central nervous system? a. Receptors b. Brachial plexus c. Brain d. Ganglia e. Sciatic nerve Answer: c The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. All other nervous system elements are considered to be in the peripheral nervous system. Thus the peripheral nervous system includes receptors, the brachial plexus, the sciatic nerve, and ganglia. 421. What are interneurons? a. Unipolar b. Pseudounipolar c. Bipolar d. Multipolar e. Both a and b Answer: d Interneurons are multipolar. Neurons can be classified based on the number of axons and dendrites stemming off of the cell body. A unipolar neuron has one process which branches off of it This process then immediately divides into two. Thus, a unipolar neuron is sometimes also called a pseudounipolar neuron. Sensory neurons are unipolar. A bipolar neuron has two process that branch from it: an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are not very common and are found in some of the organs for special senses. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina, inner ear, and the region of the nose involved with smell. Multipolar neurons have one axon and many (at least two) dendrites that branch off of it. Most neurons are multipolar. Motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 422. Which of the following is supporting cell of the central nervous system?
a. Ganglion b. Perikaryon c. Astrocyte d. Nissl e. Terminal bouton Answer: c A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The cell body of a neuron is called a perikaryon or soma. An astrocyte is a supporting cell seen in the central nervous system. The basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic seen in neuron cell bodies is called Nissl, Nissl bodies or Nissl substance. The terminal bouton is the end portion of an axon. It is also called an axon terminal or end bulb. The terminal bouton will be associated with another neuron in a synapse. 423. How many neurons are in the body of man? a. 10,000 (10 to the 4th) b. 10,000,000 (10 to the 7th) c. 10,000,000,000 (10 to the 10th) d. 10,000,000,000,000 (10 to the 13th) e. 10,000,000,000,000,000 (10 to the 16th Answer: c There are 10,000,000,000 (10 to the 10th) to 100,000,000,000 (10 to the 11th) neurons. 424. What are the gaps that occur within the myelin sheath? a. Meninges b. Myelinated nerve fibers c. Cell bodies d. Nodes of Ranvier e. Neurofilaments Answer: d A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. White matter is myelinated nerve fibers. Gray matter is essentially neuron cell bodies. Nodes of Ranvier are the gaps that occur in the myelin sheath. Neurofilaments are a type of intermediate filaments seen in neurons. 425. What is the dura mater composed of? a. Loose irregular connective tissue b. Dense irregular connective tissue c. Dense regular connective tissue d. Simple squamous epithelium e. Nervous tissue Answer: b The meninges cover the brain and spinal cord. The dura mater is the outer meninx. The dura mater is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. 426. Where is gray matter? a. Outer surface of the cerebrum and cerebellum b. Outer surface of the spinal cord c. Inner portion of the spinal cord d. Both a and b e. Both a and c Answer: e The outer part of the cerebrum and cerebellum is gray matter. It is called the cortex. Underneath the cortex, is white matter. Gray matter is also found in conglomerations within the cerebrum and cerebellum where it is called nuclei. Gray matter is found in the central portion of the spinal cord in a butterfly shape. White matter is on the outer portion of the spinal cord. Note from Sarah Bellham: Notice that the distribution of gray matter and white matter for the brain and spinal cord is the reverse of each other. On the cerebrum and cerebellum, gray matter is on the outer
ANDIE ALBINO
89
portion, white matter is deeper. For the spinal cord, white matter is on the outer portion, and gray matter is deeper. 427. What surrounds a nerve? a. Neurium b. Perineurium c. Epineurium d. Endoneurium e. None of the above Answer: c The endoneurium surrounds a nerve fiber. The perineurium surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers. The epineurium surrounds a nerve. 428. Which of the following lines the ventricles? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: b Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 429. What is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the central nervous system called? a. Schwann cells b. Basket cells c. Ganglion d. Neuroglia e. Satellite cells Answer: c Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Basket cells are a type of neuron seen in the cerebellum. A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS. Neuroglia are the supporting cells in the central nervous system Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Satellite cells are found in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. 430. What percentage of neurons are interneurons? a. 0.1% b. 1% c. 20% d. 80% e. 99.9% Answer: e Interneurons are the neurons between the sensory and motor neurons. 99.9% of all neurons are interneurons. 431. What are sensory neurons? a. Unipolar b. Pseudounipolar c. Bipolar d. Multipolar e. Both a and b Answer: e
ANDIE ALBINO
Sensory neurons are unipolar. Unipolar neurons are sometimes also called pseudounipolar. Neurons can be classified based on the number of axons and dendrites stemming off of the cell body. A unipolar neuron has one process which branches off of it This process then immediately divides into two. Thus, a unipolar neuron is sometimes also called a pseudounipolar neuron. Sensory neurons are unipolar. A bipolar neuron has two process that branch from it: an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are not very common and are found in some of the organs for special senses. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina, inner ear, and the region of the nose involved with smell. Multipolar neurons have one axon and many (at least two) dendrites that branch off of it. Most neurons are multipolar. Motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 432. What is the end of an axon called? a. Ganglion b. Perikaryon c. Astrocyte d. Nissl e. Terminal bouton Answer: e A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The cell body of a neuron is called a perikaryon or soma. An astrocyte is a supporting cell seen in the central nervous system. The basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic seen in neuron cell bodies is called Nissl, Nissl bodies or Nissl substance. The terminal bouton is the end portion of an axon. It is also called an axon terminal or end bulb. The terminal bouton will be associated with another neuron in a synapse. 433. What is the connective tissue covering around the brain and spinal cord? a. Meninges b. Myelinated nerve fibers c. Cell bodies d. Nodes of Ranvier e. Neurofilaments Answer: a A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. White matter is myelinated nerve fibers. Gray matter is essentially neuron cell bodies. Nodes of Ranvier are the gaps that occur in the myelin sheath. Neurofilaments are a type of intermediate filaments seen in neurons. 434. Which meninx is made of a dense irregular connective tissue? a. Dura mater b. Arachnoid c. Pia mater d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: a The meninges cover the brain and spinal cord. There are three: dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater. The dura mater is the outer meninx. The dura mater is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. The arachnoid is made of a delicate spider web like connective tissue. The pia mater is the innermost meninx. It covers the brain intimately. Note from Sarah Bellham: Arachnoid is derived from the Greek word for spider. It is used in the words arachnophobia, arachnids and arachnoid.
90
435. What is a group of fibers traveling together? a. Tracts b. Islets c. Soma d. Cortex e. Nuclei Answer: a A group of fibers traveling together to a destination is a tract. Islets of Langerhans are seen in the pancreas. Soma is another term for a neuron cell body. The outer part of the brain is gray matter called the cortex. The conglomerations of gray matter deep within the cerebrum and cerebellum are called nuclei. 436. Where is white matter? a. Outer surface of the cerebrum and cerebellum b. Outer surface of the spinal cord c. Inner portion of the brain d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: e The outer part of the cerebrum and cerebellum is gray matter. It is called the cortex. Underneath the cortex, is white matter. Gray matter is also found in conglomerations within the cerebrum and cerebellum where it is called nuclei. Gray matter is found in the central portion of the spinal cord in a butterfly shape. White matter is on the outer portion of the spinal cord. Note from Sarah Bellham: Notice that the distribution of gray matter and white matter for the brain and spinal cord is the reverse of each other. On the cerebrum and cerebellum, gray matter is on the outer portion, white matter is deeper. For the spinal cord, white matter is on the outer portion, and gray matter is deeper. 437. Which of the following forms myelin in the central nervous system? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: c Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 438. What is the primary component of myelin? a. Amino acids b. Protein c. Carbohydrate d. Lipid e. Both b and c Answer: d The primary component of myelin is lipid. It is formed by the cell wrapping itself around the axon. Thus, it is
primarily the plasma membrane of either the Schwann cells or the oligodendrocytes. 439. Which of the following is found in the cerebellum? a. Schwann cells b. Basket cells c. Ganglion d. Neuroglia e. Satellite cells Answer: b Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Basket cells are a type of neuron seen in the cerebellum. A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS. Neuroglia are the supporting cells in the central nervous system Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Satellite cells are found in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. 440. What are neurons in the retina? a. Unipolar b. Pseudounipolar c. Bipolar d. Multipolar e. Both a and b Answer: c The neurons in the retina are bipolar. Neurons can be classified based on the number of axons and dendrites stemming off of the cell body. A unipolar neuron has one process which branches off of it This process then immediately divides into two. Thus, a unipolar neuron is sometimes also called a pseudounipolar neuron. Sensory neurons are unipolar. A bipolar neuron has two process that branch from it: an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are not very common and are found in some of the organs for special senses. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina, inner ear, and the region of the nose involved with smell. Multipolar neurons have one axon and many (at least two) dendrites that branch off of it. Most neurons are multipolar. Motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 441. What are the basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum seen in neurons called? a. Ganglion b. Perikaryon c. Astrocyte d. Nissl e. Terminal bouton Answer: d A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The cell body of a neuron is called a perikaryon or soma. An astrocyte is a supporting cell seen in the central nervous system. The basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic seen in neuron cell bodies is called Nissl, Nissl bodies or Nissl substance. The terminal bouton is the end portion of an axon. It is also called an axon terminal or end bulb. The terminal bouton will be associated with another neuron in a synapse. 442. All of the following are properties of neurons, except: a. High metabolic rate b. Longevity c. Specialized for conduction d. High mitotic rate e. Limited ability for oxygen deprivation Answer: d Neurons do not divide; therefore they do not have a high mitotic rate.
ANDIE ALBINO
91
Neurons have a high metabolic rate. They are unable to survive long without oxygen. They have an extremely long longevity, lasting a lifetime. Neurons are specialize for conduction. They send signals via a nervous impulse. 443. Which type of neuron is also called an internuncial neuron? a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Interneurons d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: c Interneurons are also called internuncial neurons. 444. What is white matter? a. Meninges b. Myelinated nerve fibers c. Cell bodies d. Nodes of Ranvier e. Neurofilaments Answer: b A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. White matter is myelinated nerve fibers. Gray matter is essentially neuron cell bodies. Nodes of Ranvier are the gaps that occur in the myelin sheath. Neurofilaments are a type of intermediate filaments seen in neurons. 445. What is another term for the cell body of a neuron? a. Tracts b. Islets c. Soma d. Cortex e. Nuclei Answer: c A group of fibers traveling together to a destination is a tract. Islets of Langerhans are seen in the pancreas. Soma is another term for a neuron cell body. The outer part of the brain is gray matter called the cortex. The conglomerations of gray matter deep within the cerebrum and cerebellum are called nuclei. 446. What is the covering of a nerve fiber? a. Neurium b. Perineurium c. Epineurium d. Endoneurium e. None of the above Answer: d The endoneurium surrounds a nerve fiber. The perineurium surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers. The epineurium surrounds a nerve. 447. Which of the following is the CNS macrophage? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: d Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages.
ANDIE ALBINO
Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 448. Which of the following is found in the peripheral nervous system? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: e Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 449. What is the cell body of a neuron called? a. Ganglion b. Soma c. Astrocyte d. Nissl e. Terminal bouton Answer: b A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. The cell body of a neuron is called a perikaryon or soma. An astrocyte is a supporting cell seen in the central nervous system. The basophilic clusters of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic seen in neuron cell bodies is called Nissl, Nissl bodies or Nissl substance. The terminal bouton is the end portion of an axon. It is also called an axon terminal or end bulb. The terminal bouton will be > associated with another neuron in a synapse. 450. Where is the ependyma found? a. Lining ventricles b. Lining spinal canal c. Covering the brain d. Covering the spinal cord e. Both a and b Answer: e The ependyma lines the ventricles and spinal canal. 451. Which type of neuron is most abundant? a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Interneurons d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: c The vast majority of neurons are interneurons. 452. What surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers? a. Neurium b. Perineurium c. Epineurium d. Endoneurium e. None of the above Answer: b
92
The endoneurium surrounds a nerve fiber. The perineurium surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers. The epineurium surrounds a nerve. 453. Which meninx covers the brain intimately? a. Dura mater b. Arachnoid c. Pia mater d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: c The meninges cover the brain and spinal cord. There are three: dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater. The dura mater is the outer meninx. The dura mater is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. The arachnoid is made of a delicate spider web like connective tissue. The pia mater is the innermost meninx. It covers the brain intimately. Note from Sarah Bellham: Arachnoid is derived from the Greek word for spider. It is used in the words arachnophobia, arachnids and arachnoid. 454. Which of the following is the largest neuroglia cell? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: a Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 455. Which of the following is NOT considered neuroglia? a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal cells c. Oligodendrocytes d. Microglia e. Schwann cells Answer: e Neuroglia are the supporting cells of the central nervous system. Sometimes, neuroglia called glial cells or glia. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglia are all neuroglia. Of the neuroglia cells, astrocytes are the most abundant and the largest. These are star shaped cells involved in the blood brain barrier. Ependymal cells line the ventricles and spinal canal. Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the central nervous system. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. Schwann cells are seen in the peripheral nervous system and are not considered neuroglia. Schwann cells are responsible for the myelination of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. 456. What is the innervation of an eccrine sweat gland? a. Cholinergic; parasympathetic
b. Cholinergic; sympathetic c. Adrenergic; parasympathetic d. Adrenergic; sympathetic e. Cholinergic; motor Answer: b Eccrine sweat glands are innervated by the sympathetic nervous system. The neurotransmitter for the eccrine sweat glands is acetylcholine. Thus it is cholinergic. Note from Sarah Bellham: For most postganglionic sympathetic neurons, the neurotransmitter is norepinephrine. Eccrine sweat glands are an exception to this generalization, as the innervation for eccrine sweat glands is cholinergic sympathetic. 457. What is the innervation of an apocrine sweat gland? a. Cholinergic; parasympathetic b. Cholinergic; sympathetic c. Adrenergic; parasympathetic d. Adrenergic; sympathetic e. Cholinergic; motor Answer: d Apocrine sweat glands are innervated by the sympathetic nervous system. The neurotransmitter for the apocrine sweat glands is norepinephrine. Thus it is adrenergic. 458. What is Bruch's membrane? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa Answer: d The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle. The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 459. What are neurons in the retina? a. Unipolar b. Pseudounipolar c. Bipolar d. Multipolar e. Both a and b Answer: c The neurons in the retina are bipolar. Neurons can be classified based on the number of axons and dendrites stemming off of the cell body. A unipolar neuron has one process which branches off of it This process then immediately divides into two. Thus, a unipolar neuron is sometimes also called a pseudounipolar neuron. Sensory neurons are unipolar. A bipolar neuron has two process that branch from it: an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are not very common and are found in some of the organs for special senses. Bipolar neurons are found in the retina, inner ear, and the region of the nose involved with smell.
ANDIE ALBINO
93
Multipolar neurons have one axon and many (at least two) dendrites that branch off of it. Most neurons are multipolar. Motor neurons and interneurons are multipolar. 460. Which structure is transparent? a. Choroid b. Ciliary body c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Cornea Answer: e The cornea is transparent. 461. Which of the following is the receptor for color? a. Rods b. Cones c. Bipolar cells d. Ganglion cells e. Horizontal cells Answer: b The eyeball has three layers. The innermost layer is the retina. The middle layer is the uvea. The outer layer is the sclera and cornea. The retina consists of the rods, cones, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells. The receptors for vision are the rods and cones. The rods are located on the periphery, and are not color sensitive. The cones are the receptors for color. 462. What is responsible for adjusting the lens? a. Choroid b. Ciliary muscle c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Sclera Answer: b The vascular pigmented structure of the uvea is the choroid. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is responsible for adjusting the lens. The most anterior portion of the uvea is the iris. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. The sclera is the "white of the eye". 463. What is the region called where the optic nerve exits the eye? a. Os b. Optic chiasm c. Lamina cribrosa d. Optic disc e. Ora serrata Answer: d An os is an opening or mouth. The optic chiasm is the anatomical region shaped like an "X" where the two optic nerves join. The region where the optic nerve exits the eye is the optic disc. The openings within the sclera which allow nerve fibers to exit is the lamina cribrosa. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. 464. Which of the following is a type of neuron? a. Rods b. Ganglion cells c. Cones d. Pigmented epithelium e. Supporting cells Answer: b The retina contains receptor cells, neurons, pigmented epithelium and supporting cells. The nervous element in the retina consists of bipolar cells and ganglion cells. 465. What is the space anterior to the iris? a. Anterior chamber b. Posterior chamber
ANDIE ALBINO
c. Vitreal cavity d. Both a and b e. All of a, b, and c Answer: a The region behind the lens is the vitreal cavity. The chambers anterior to the lens are the anterior chamber and posterior chamber. The iris separates the anterior chamber from the posterior chamber. 466. Which layer forms the majority of the cornea? a. Epithelium b. Endothelium c. Descemet's membrane d. Substantia propria e. Bowman's membrane Answer: d There are five layers to the cornea: epithelium, Bowman's membrane, substantia propria, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The surface of the cornea is covered by a non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Bowman's membrane and Descemet's membrane are acellular. The majority of the cornea is from the substantia propria. The endothelium is a simple epithelium. 467. What is the region where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa Answer: b The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle. The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 468. What are the receptors for vision? a. Rods b. Cones c. Bipolar cells d. Ganglion cells e. Both a and b Answer: e The retina consists of the rods, cones, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells. The receptors for vision are the rods and cones. The rods are located on the periphery, and are not color sensitive. The cones are the receptors for color. 469. Where is the ciliary muscle located? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa Answer: a The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle. The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the
94
anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 470. Where is the ciliary muscle located? a. Choroid b. Ciliary body c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Sclera Answer: b The vascular pigmented structure of the uvea is the choroid. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is responsible for adjusting the lens. The most anterior portion of the uvea is the iris. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. The sclera is the "white of the eye". 471. What are the openings within the sclera which allow nerve fibers to exit? a. Os b. Optic chiasm c. Lamina cribrosa d. Optic disc e. Ora serrata Answer: c An os is an opening or mouth. The optic chiasm is the anatomical region shaped like an "X" where the two optic nerves join. The region where the optic nerve exits the eye is the optic disc. The openings within the sclera which allow nerve fibers to exit is the lamina cribrosa. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. 472. Which of the following is NOT part of the retina? a. Receptor cells b. Neurons c. Pigmented epithelium d. Ciliary body e. Supporting cells Answer: d The retina contains receptor cells, neurons, pigmented epithelium and supporting cells. The nervous element in the retina consists of bipolar cells and ganglion cells. 473. What structure adjusts the shape of the lens? a. Internal oblique muscle b. Orbicularis oculi c. Tarsus d. Ciliary muscle e. Levator muscle Answer: d The ciliary muscle is within the ciliary body. The ciliary muscle adjusts the shape of the lens. 474. What is the inner layer of the choroid? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa Answer: d The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle.
The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 475. Where does aqueous humor from anterior chamber collect into? a. Canaliculi b. Canal of Hering c. Canal of Muller d. Canal of Descemet e. Canal of Schlemm Answer: e Aqueous humor collected from the anterior chamber via the canal of Schlemm. 476. Which layer of the cornea is acellular? a. Epithelium b. Endothelium c. Descemet's membrane d. Substantia propria e. None of the above Answer: c There are five layers to the cornea: epithelium, Bowman's membrane, substantia propria, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The surface of the cornea is covered by a non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Bowman's membrane and Descemet's membrane are acellular. The majority of the cornea is from the substantia propria. The endothelium is a simple epithelium. 477. Which structure is avascular? a. Retina b. Cornea c. Choroid d. Sclera e. Uvea Answer: b The cornea is avascular. 478. During the American Revolution, in the battle of Bunker Hill, an officer instructed his troops: "Don't fire until you see the whites of their eyes". What anatomical structure was he referring to? a. Choroid b. Ciliary body c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Sclera Answer: e The vascular pigmented structure of the uvea is the choroid. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is responsible for adjusting the lens. The most anterior portion of the uvea is the iris. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. The sclera is the "white of the eye". 479. Where is the region associated with maximum visual acuity? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa
ANDIE ALBINO
95
Answer: c The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle. The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 480. What is the suspensory ligament of the lens? a. Zonlular fibers b. Purkinje fibers c. Elastic fibers d. Spiral ligament e. Oval ligament Answer: a The zonular fibers are the suspensory ligament of the lens. 481. Which layer of the cornea is acellular? a. Bowman's membrane b. Substantia propria c. Epithelium d. Endothelium e. All of the above Answer: a There are five layers to the cornea: epithelium, Bowman's membrane, substantia propria, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The surface of the cornea is covered by a non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Bowman's membrane and Descemet's membrane are acellular. The majority of the cornea is from the substantia propria. The endothelium is a simple epithelium. 482. How many layers of tissue compose the eyeball? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 Answer: c The eyeball has three layers. The innermost layer is the retina. The middle layer is the uvea. The outer layer is the sclera and cornea. 483. What type of glands are the glands of Moll? a. Endocrine gland b. Apocrine sweat gland c. Oil gland d. Sebaceous glands e. Eccrine sweat gland Answer: b The glands of Moll in the eyelid are apocrine sweat glands. 484. Which structure is part the uvea? a. Ora serrata b. Pigmented epithelium c. Cornea d. Sclera e. Ciliary body Answer: e The uvea is the middle layer of the eyeball. It consists of the iris, choroid and ciliary body. 485. What is the space anterior to the lens?
ANDIE ALBINO
a. Anterior chamber b. Posterior chamber c. Vitreal cavity d. Both a and b e. All of a, b, and c Answer: d The region behind the lens is the vitreal cavity. The chambers anterior to the lens are the anterior chamber and posterior chamber. The iris separates the anterior chamber from the posterior chamber. 486. What is the vascular pigmented structure? a. Choroid b. Ciliary body c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Lens Answer: a The vascular pigmented structure of the uvea is the choroid. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is responsible for adjusting the lens. The most anterior portion of the uvea is the iris. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. The sclera is the "white of the eye". 487. What type of epithelium is on the surface of the cornea? a. Simple squamous b. Stratified squamous c. Simple cuboidal d. Simple columnar e. Transitional epithelium Answer: b The surface of the cornea is covered by a non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. 488. What structure was Crystal Gayle referring to when she sang, "Don't it make my brown eyes blue"? a. Pupil b. Lens c. Cornea d. Iris e. Retina Answer: d The iris is the colored part of the eyes. 489. What makes up the bulk of the cornea? a. Purkinje fibers b. Myofibrils c. Elastic fibers d. Reticular fibers e. Collagen fibers Answer: e The cornea is composed primarily of collagen fibers. 490. What is the middle layer of the eyeball? a. Uvea b. Rods c. Cones d. Bipolar cells e. Ganglion cells Answer: a The eyeball has three layers. The innermost layer is the retina. The middle layer is the uvea. The outer layer is the sclera and cornea. The retina consists of the rods, cones, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells. The receptors for vision are the rods and cones. The rods are located on the periphery, and are not color sensitive. The cones are the receptors for color. 491. What is the anterior pigmented portion of the retina called? a. Choroid b. Ciliary body
96
c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Sclera Answer: d The vascular pigmented structure of the uvea is the choroid. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is responsible for adjusting the lens. The most anterior portion of the uvea is the iris. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. The sclera is the "white of the eye". 492. Which one of the following is not found in the retina? a. Henle's layer b. Bipolar cells c. Amacrine cells d. Rods e. Ganglion cells Answer: a Bipolar cells, amacrine cells, rods, and ganglion cells are all part of the retina. Henle's layer is a layer in the hair follicle. 493. Which structure is part the uvea? a. Ora serrata b. Pigmented epithelium c. Choroid d. Cornea e. Sclera Answer: c The uvea is the middle layer of the eyeball. It consists of the iris, choroid and ciliary body. 494. What is the space posterior to the lens? a. Anterior chamber b. Posterior chamber c. Vitreal cavity d. Both a and b e. All of a, b, and c Answer: c The region behind the lens is the vitreal cavity. The chambers anterior to the lens are the anterior chamber and posterior chamber. The iris separates the anterior chamber from the posterior chamber. 495. Where is the blind spot? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa Answer: b The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle. The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 496. How many layers does the retina have? a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 5 e. 10 Answer: e
There are ten layers to the retina. 497. Which of the following is NOT a layer of the cornea? a. Bowman's membrane b. Substantia propria c. Descemet's membrane d. Lamina vitrea e. Endothelium Answer: d There are five layers to the cornea: epithelium, Bowman's membrane, substantia propria, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The surface of the cornea is covered by a non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Bowman's membrane and Descemet's membrane are acellular. The majority of the cornea is from the substantia propria. The endothelium is a simple epithelium. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. 498. Where on the retina are there no photoreceptors? a. Ciliary body b. Optic disc c. Fovea centralis d. Lamina vitrea e. Lamina cribrosa Answer: b The ciliary body is a thickening in the uvea. It contains the ciliary muscle. The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball is the optic disc. This region is also called the anatomical blind spot. Since there are no photoreceptors at this spot, it causes a blind spot in the visual field. The fovea centralis is part of the retina. There are only cone cells in the fovea centralis. It is the site for maximal visual acuity. The inner layer of the choroid is the lamina vitrea. The lamina vitrea is also referred to as Bruch's membrane. The lamina cribrosa are small openings within the sclera where the fibers forming the optic nerve travel through. 499. What makes up the bulk of the sclera? a. Purkinje fibers b. Myofibrils c. Elastic fibers d. Reticular fibers e. Collagen fibers Answer: e The sclera is composed primarily of collagen fibers. 500. Which is NOT part of the retina? a. Rods b. Cones c. Bipolar cells d. Ganglion cells e. Uvea Answer: e The eyeball has three layers. The innermost layer is the retina. The middle layer is the uvea. The outer layer is the sclera and cornea. The retina consists of the rods, cones, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells. The receptors for vision are the rods and cones. The rods are located on the periphery, and are not color sensitive. The cones are the receptors for color. 501. What is the most anterior portion of the uvea? a. Choroid b. Ciliary body c. Iris d. Ora serrata e. Sclera
ANDIE ALBINO
97
Answer: c The vascular pigmented structure of the uvea is the choroid. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is responsible for adjusting the lens. The most anterior portion of the uvea is the iris. The anterior pigmented portion of the retina is called the ora serrata. The sclera is the "white of the eye". 502. Which one of the following is not found in the retina? a. Pigment epithelium b. Muller's cells c. Huxley's layer d. Horizontal cells e. Cones Answer: c Pigment epithelium, Muller's cells, horizontal cells, and cones cells are all part of the retina. Huxley's layer is a layer in the hair follicle. 503. Which structure is part the uvea? a. Sclera b. Iris c. Ora serrata d. Pigmented epithelium e. Cornea Answer: b The uvea is the middle layer of the eyeball. It consists of the iris, choroid and ciliary body. 504. What is the space posterior to the iris? a. Anterior chamber b. Posterior chamber c. Vitreal cavity d. Both a and b e. All of a, b, and c Answer: b The region behind the lens is the vitreal cavity. The chambers anterior to the lens are the anterior chamber and posterior chamber. The iris separates the anterior chamber from the posterior chamber. 505. What is within the membranous labyrinth? a. Lymph b. Blood c. Endolymph d. Perilymph e. Air Answer: c 506. What is within the bony labyrinth? a. Lymph b. Blood c. Endolymph d. Perilymph e. Air Answer: d The membranous labyrinth contains endolymph. The bony labyrinth contains perilymph. 507. Which contains endolymph? a. Scala vestibuli b. Scala tympani c. Cochlear duct d. Both a and b e. All a, b, and c Answer: c 508. Which contains perilymph? a. Scala vestibuli b. Scala tympani c. Cochlear duct d. Both a and b e. All a, b, and c Answer: d The scala vestibuli and scala tympani contain perilymph. The cochlear duct contains endolymph.
ANDIE ALBINO
509. Where are the sensory receptors for hearing? a. Saccule b. Utricle c. Organ of Corti d. Semicircular canals e. Both a and b Answer: c 510. Where are the sensory receptors for movement? a. Saccule b. Utricle c. Organ of Corti d. Semicircular canals e. Both a and b Answer: d 511. Where are the sensory receptors for position? a. Saccule b. Utricle c. Organ of Corti d. Semicircular canals e. Both a and b Answer: e The receptors for hearing are located within the organ of Corti. The receptors for movement are located within the semicircular canals. The receptors for position are located within the utricle and saccule. 512. What structure is shaped like a snail shell? a. Saccule b. Utricle c. Organ of Corti d. Semicircular canals e. Cochlea Answer: e 513. Where is the organ of Corti? a. Saccule b. Utricle c. Crista ampullaris d. Semicircular canals e. Cochlea Answer: e The cochlea is a spiral shaped structure. Within the cochlea is the organ of Corti. 514. What sensation does the crista ampullaris recognize? a. Sound b. Position c. Movement d. Vibration e. All of the above Answer: c The crista ampullaris is the receptor for movement. 515. Which cell type is the receptor cell within the organ of Corti? a. Cells of Hensen b. Hair cells c. Inner border cells d. Outer phalangeal cells e. Inner pillar cells Answer: b The hair cells are the receptor cells. The other cells are supporting cells. 516. What is the glomerulus? a. Afferent arteriole b. Efferent arteriole c. Capillary tuft d. Peritubular capillaries e. Vasa recta Answer: c The afferent arteriole branches off the interlobular artery. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft. The
98
glomerular capillaries converge to form the efferent arteriole. The peritubular capillaries is a second capillary network which arise after the efferent arteriole. They surround the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Vasa recta are the "straight vessels" which arise from some of the efferent arterioles. 517. What is a renal pyramid and its associated cortex referred to? a. Medulla b. Lobe c. Renal columns d. Nephron e. Medullary ray Answer: b The kidney can be divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. A kidney lobe consists of a medullary pyramid, its overlying cortex, and the associated renal column. The renal columns are the tissue in between the pyramids. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. A region where a portion of the medulla project into the renal cortex are referred to as medullary ray. 518. Approximately how many nephrons are there in each kidney? a. 1,000 b. 10,000 c. 100,000 d. 1,000,000 e. 10,000,000 Answer: d There are approximately one million (1,000,000) nephrons in each kidney. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. 519. What is the Malpighian corpuscle? a. Glomerulus b. Bowman's capsule c. Renal corpuscle d. Loop of Henle e. Distal convoluted tubule Answer: c The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. The nephron can be divided into the glomerulus and uriniferous tubule. The capillary tuft of the nephron is referred to as the glomerulus. Bowman's capsule is a double layered cap surrounding the glomerulus. This is the first portion of the uriniferous tubule. The glomerulus and Bowman's capsule make up the renal corpuscle. Another term for the renal corpuscle is Malpighian corpuscle. Bowman's capsule leads to the proximal convoluted tubule. The proximal convoluted tubule leads to the loop of Henle. This then leads to the distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubule then leads to the collecting duct. 520. What are the ducts of Bellini? a. Collecting tubules b. Distal convoluted tubule c. Proximal convoluted tubule d. Loop of Henle e. Medullary ray Answer: a Large collecting tubules near the apex of the pyramid are the ducts of Bellini. The ducts of Bellini are also called a papillary ducts. 521. What are the foot processes on podocytes? a. Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule b. Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule c. Pedicels
d. Juxtaglomerular cells e. Macula densa Answer: c The inner layer of Bowman's capsule is the visceral layer. It consists of cells called podocytes. The outer layer of Bowman's capsule is the parietal layer. Pedicels are the foot processes on the podocytes. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin. The macula densa are specialized cells in the distal convoluted tubule that are sensitive to sodium. The juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 522. What vessel is a branch of the interlobular artery? a. Afferent arteriole b. Efferent arteriole c. Capillary tuft d. Peritubular capillaries e. Vasa recta Answer: a The afferent arteriole branches off the interlobular artery. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft. The glomerular capillaries converge to form the efferent arteriole. The peritubular capillaries is a second capillary network which arise after the efferent arteriole. They surround the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Vasa recta are the "straight vessels" which arise from some of the efferent arterioles. 523. What type of tissue lines the bladder? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: e The lining of the bladder is transitional epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. There are domed shaped cells on the apical surface. 524. What is the projection of the medulla into the renal cortex called? a. Medulla b. Lobe c. Renal columns d. Nephron e. Medullary ray Answer: e The kidney can be divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. A kidney lobe consists of a medullary pyramid, its overlying cortex, and the associated renal column. The renal columns are the tissue in between the pyramids. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. A region where a portion of the medulla project into the renal cortex are referred to as medullary ray. 525. What makes up the Juxtaglomerular apparatus? a. Pedicels b. Juxtaglomerular cells c. Macula densa d. Both a and b e. Both b and c Answer: e The inner layer of Bowman's capsule is the visceral layer. It consists of cells called podocytes. Pedicels are the foot processes on the podocytes. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin. The macula densa are specialized cells in the distal convoluted tubule that are sensitive to sodium. The juxtaglomerular cells
ANDIE ALBINO
99
and macula densa make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 526. What vessels arise from the efferent arteriole? a. Afferent arteriole b. Efferent arteriole c. Capillary tuft d. Peritubular capillaries e. Vasa recta Answer: d The afferent arteriole branches off the interlobular artery. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft. The glomerular capillaries converge to form the efferent arteriole. The peritubular capillaries is a second capillary network which arise after the efferent arteriole. They surround the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Vasa recta are the "straight vessels" which arise from some of the efferent arterioles. 527. Which structure does the proximal convoluted lead to? a. Glomerulus b. Bowman's capsule c. Renal corpuscle d. Loop of Henle e. Distal convoluted tubule Answer: d The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. The nephron can be divided into the glomerulus and uriniferous tubule. The capillary tuft of the nephron is referred to as the glomerulus. Bowman's capsule is a double layered cap surrounding the glomerulus. This is the first portion of the uriniferous tubule. The glomerulus and Bowman's capsule make up the renal corpuscle. Another term for the renal corpuscle is Malpighian corpuscle. Bowman's capsule leads to the proximal convoluted tubule. The proximal convoluted tubule leads to the loop of Henle. This then leads to the distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubule then leads to the collecting duct. 528. What is the correct term for the foot processes on podocytes? a. Pedis b. Pedicels c. Pedalis d. Pes e. Pediocyte Answer: b The inner layer of Bowman's capsule is the visceral layer. It consists of cells called podocytes. Pedicels are the foot processes on the podocytes. Note from Sarah Bellham: The Latin prefix pedalis, pes and pedis refers to the foot. Such words include pedal, pedicure, pedestrian and of course, the one we are all familiar with, the foot process on podocytes, which are pedicels. 529. Which of the following is NOT a function of the kidney? a. Erythropoietin production b. Vitamin D modification c. Acid base balance d. Aldosterone production e. Renin production Answer: d The kidney is involved in several things, in addition to urine production. Erythropoietin is produced in the kidney. Vitamin D is modified in the kidney, specifically, there is the
ANDIE ALBINO
addition of hydroxyl groups. The kidney plays an important role in acid base balance. Renin is produced in the kidney. Aldosterone is produced in the adrenal gland. 530. What is the space between the renal pyramids called? a. Medulla b. Lobe c. Renal columns d. Nephron e. Medullary ray Answer: c The kidney can be divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. A kidney lobe consists of a medullary pyramid, its overlying cortex, and the associated renal column. The renal columns are the tissue in between the pyramids. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. A region where a portion of the medulla project into the renal cortex are referred to as medullary ray. 531. What is the capillary tuft of the nephron? a. Glomerulus b. Bowman's capsule c. Renal corpuscle d. Loop of Henle e. Distal convoluted tubule Answer: a The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. The nephron can be divided into the glomerulus and uriniferous tubule. The capillary tuft of the nephron is referred to as the glomerulus. Bowman's capsule is a double layered cap surrounding the glomerulus. This is the first portion of the uriniferous tubule. The glomerulus and Bowman's capsule make up the renal corpuscle. Another term for the renal corpuscle is Malpighian corpuscle. Bowman's capsule leads to the proximal convoluted tubule. The proximal convoluted tubule leads to the loop of Henle. This then leads to the distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubule then leads to the collecting duct. 532. What vessel supplies blood to the glomerulus? a. Afferent arteriole b. Efferent arteriole c. Capillary tuft d. Peritubular capillaries e. Vasa recta Answer: a The afferent arteriole branches off the interlobular artery. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft. The glomerular capillaries converge to form the efferent arteriole. The peritubular capillaries is a second capillary network which arise after the efferent arteriole. They surround the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Vasa recta are the "straight vessels" which arise from some of the efferent arterioles. 533. What type of tissue composes the kidney tubules? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: b The kidney tubules are simple cuboidal epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple cuboidal epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Cuboidal" refers to the shape of the cells. 534. Where is renin secreted from?
100
a. Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule b. Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule c. Pedicels d. Juxtaglomerular cells e. Macula densa Answer: d The inner layer of Bowman's capsule is the visceral layer. It consists of cells called podocytes. The outer layer of Bowman's capsule is the parietal layer. Pedicels are the foot processes on the podocytes. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin. The macula densa are specialized cells in the distal convoluted tubule that are sensitive to sodium. The juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 535. What are the "straight vessels"? a. Afferent arteriole b. Efferent arteriole c. Capillary tuft d. Peritubular capillaries e. Vasa recta Answer: e The afferent arteriole branches off the interlobular artery. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft. The glomerular capillaries converge to form the efferent arteriole. The peritubular capillaries is a second capillary network which arise after the efferent arteriole. They surround the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Vasa recta are the "straight vessels" which arise from some of the efferent arterioles. 536. What is the inner region of the kidney called? a. Medulla b. Lobe c. Renal columns d. Nephron e. Medullary ray Answer: a The kidney can be divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. A kidney lobe consists of a medullary pyramid, its overlying cortex, and the associated renal column. The renal columns are the tissue in between the pyramids. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. A region where a portion of the medulla project into the renal cortex are referred to as medullary ray. 537. What is the double layered cap on the glomerulus? a. Glomerulus b. Bowman's capsule c. Renal corpuscle d. Loop of Henle e. Distal convoluted tubule Answer: b The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. The nephron can be divided into the glomerulus and uriniferous tubule. The capillary tuft of the nephron is referred to as the glomerulus. Bowman's capsule is a double layered cap surrounding the glomerulus. This is the first portion of the uriniferous tubule. The glomerulus and Bowman's capsule make up the renal corpuscle. Another term for the renal corpuscle is Malpighian corpuscle. Bowman's capsule leads to the proximal convoluted tubule. The proximal convoluted tubule leads to the loop of Henle. This then leads to the distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubule then leads to the collecting duct. 538. Where are podocytes seen?
a. Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule b. Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule c. Pedicels d. Juxtaglomerular cells e. Macula densa Answer: a The inner layer of Bowman's capsule is the visceral layer. It consists of cells called podocytes. The outer layer of Bowman's capsule is the parietal layer. Pedicels are the foot processes on the podocytes. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin. The macula densa are specialized cells in the distal convoluted tubule that are sensitive to sodium. The juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 539. What vessel is formed from an aggregation of the glomerular capillaries? a. Afferent arteriole b. Efferent arteriole c. Capillary tuft d. Peritubular capillaries e. Vasa recta Answer: b The afferent arteriole branches off the interlobular artery. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft. The glomerular capillaries converge to form the efferent arteriole. The peritubular capillaries is a second capillary network which arise after the efferent arteriole. They surround the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Vasa recta are the "straight vessels" which arise from some of the efferent arterioles. 540. What is the functional unit of the kidney? a. Medulla b. Lobe c. Renal columns d. Nephron e. Medullary ray Answer: d The kidney can be divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. A kidney lobe consists of a medullary pyramid, its overlying cortex, and the associated renal column. The renal columns are the tissue in between the pyramids. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. A region where a portion of the medulla project into the renal cortex are referred to as medullary ray. 541. Which structure leads to the collecting duct? a. Glomerulus b. Bowman's capsule c. Renal corpuscle d. Loop of Henle e. Distal convoluted tubule Answer: e The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. The nephron can be divided into the glomerulus and uriniferous tubule. The capillary tuft of the nephron is referred to as the glomerulus. Bowman's capsule is a double layered cap surrounding the glomerulus. This is the first portion of the uriniferous tubule. The glomerulus and Bowman's capsule make up the renal corpuscle. Another term for the renal corpuscle is Malpighian corpuscle. Bowman's capsule leads to the proximal convoluted tubule. The proximal convoluted tubule leads to the loop of Henle. This then leads to the distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubule then leads to the collecting duct.
ANDIE ALBINO
101
542. What cells are sensitive to sodium concentration? a. Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule b. Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule c. Pedicels d. Juxtaglomerular cells e. Macula densa Answer: e The inner layer of Bowman's capsule is the visceral layer. It consists of cells called podocytes. The outer layer of Bowman's capsule is the parietal layer. Pedicels are the foot processes on the podocytes. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin. The macula densa are specialized cells in the distal convoluted tubule that are sensitive to sodium. The juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 543. Which of the four basic tissue types does blood belong to? a. Epithelium b. Connective tissue c. Muscle d. Nervous tissue e. Blood Answer: b There are four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue. Connective tissue is the most diverse. Blood is considered a type of connective tissue. 544. Which of the following formed elements do not contain a nucleus? a. Platelets b. Erythrocytes c. Leukocytes d. Monocytes e. Both a and b Answer: e Blood is composed of the formed elements and plasma. Plasma is the liquid portion of blood. The formed elements consist of the cells and cell fragments. The erythrocytes (red blood cells), platelets, and leukocytes (white blood cells) are all considered formed elements. Erythrocytes do not contain a nucleus. During their development within the bone marrow, they have a nucleus. However, prior to their entering into the blood stream, the nucleus is ejected. Platelets are cell fragments. Platelets also do not contain a nucleus. They are fragments from megakaryocytes within the bone marrow. Leukocytes, which include monocytes, are cells with a nucleus. 545. What comes from a megakaryocyte? a. Lymphocytes b. Basophils c. Erythrocytes d. Monocytes e. Platelets Answer: e Platelets are cell fragments. They are fragments from megakaryocytes within the bone marrow. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "mega" is from the Greek "megas" which means great or big. For example: megaphone, megalomaniac, megabyte, and megakaryocyte. 546. Which leukocyte is the most abundant in a peripheral smear of blood? a. Lymphocytes b. Basophils c. Neutrophil d. Monocytes
ANDIE ALBINO
e. Eosinophils Answer: c Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocyte. Leukocytes are the white blood cells. The order of frequency of the leukocytes is: neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, basophil. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The order of frequency of the leukocytes can be remembered by the mnemonic: "Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas". 547. Which of the following is not a granulocyte? a. Lymphocytes b. Neutrophil c. PMN d. Eosinophils e. Basophils Answer: a The granulocytes are named because of the presence of visible cytoplasmic granules. The granulocytes consist of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. "PMN" is an abbreviation for polymorphonuclear neutrophil. Thus, it is a neutrophil, which is a granulocyte. The non-granulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Poly is from the Greek "polys", which means many. "Poly" is also sometimes used as a nickname for polymorphonuclear leukocyte. 548. Which of the following is a granulocyte? a. Thrombocyte b. Lymphocyte c. Eosinophil d. Monocyte e. Erythrocyte Answer: c The granulocytes are named because of the presence of visible cytoplasmic granules. The granulocytes consist of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. The non-granulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes. Erythrocytes are red blood cells. A thrombocyte is a platelet. Note from Sarah Bellham: The suffix (or prefix) "phil" comes from the Greek word meaning love. It is used to specify an attraction or affinity towards something. It is seen in such words as philosophy, philanthropy and bibliophile. This suffix is used in naming the three granulocytes: eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils. Eosinophils "love" or are attracted to the eosin dye; thus the granules in an eosinophil are orange/pink. Basophils "love" or are attracted to the basophilic dye; thus the granules in a basophil are blue. Neutrophils "love" or are attracted to the neutral dye; thus the granules in a neutrophil are neutral colored. 549. Which of the following is NOT a term used for a neutrophil? a. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils b. Poly's c. PMN d. NP e. Polymorph Answer: d Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph". 550. Which leukocyte has a multi-lobed (3-5 lobes) nucleus? a. Neutrophil
102
b. Lymphocytes c. Monocytes d. Eosinophil e. Basophils Answer: a The leukocytes consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph. Lymphocytes are agranulocytes. Lymphocytes can be categorized by three sizes: small, medium, and large. The small lymphocytes are the smallest leukocyte, being only slightly larger than an erythrocyte. Monocytes are agranulocytes. They are the largest leukocyte. Eosinophils are granulocytes. Eosinophils have prominent orange pink granules. The nucleus of eosinophils is usually bi-lobed. Basophils are granulocytes. Basophils have large blue granules, which often obscure the nucleus. The granules are basophilic, therefore they are blue. 551. Which cell has large blue granules, often obscuring the nucleus? a. Neutrophil b. Lymphocytes c. Monocytes d. Eosinophil e. Basophils Answer: e The leukocytes consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph". Lymphocytes are agranulocytes. Lymphocytes can be categorized by three sizes: small, medium, and large. The small lymphocytes are the smallest leukocyte, being only slightly larger than an erythrocyte. Monocytes are agranulocytes. They are the largest leukocyte. Eosinophils are granulocytes. Eosinophils have prominent orange pink granules. The nucleus of eosinophils is usually bi-lobed. Basophils are granulocytes. Basophils have large blue granules, which often obscure the nucleus. The granules are basophilic, therefore they are blue. 552. Which of the following is not considered a "formed element"? a. Plasma b. Erythrocytes c. Platelets d. Leukocytes e. Red blood cells Answer: a Blood is composed of the formed elements and plasma. Plasma is the liquid portion of blood. The formed elements consist of the cells and cell fragments. The erythrocytes (red blood cells), platelets, and leukocytes (white blood cells) are all considered formed elements. 553. Approximately what percentage of the volume of blood do the formed elements comprise? a. 5 b. 25
c. 45 d. 75 e. 90 Answer: c Blood is composed of the formed elements and plasma. Plasma is the liquid portion of blood. The formed elements consist of the cells and cell fragments. The erythrocytes (red blood cells), platelets, and leukocytes (white blood cells) are all considered formed elements. When a sample of blood is centrifuged, the percentage occupied by the formed elements is the hematocrit. An average hematocrit is about 45%. 554. Which of the following is the most abundant in a peripheral smear of blood? a. Neutrophils b. Basophils c. Erythrocytes d. Leukocytes e. Platelets Answer: c Erythrocytes (red blood cells) are the most abundant formed element in a peripheral smear of blood. 555. Which leukocyte is the least abundant in a peripheral smear of blood? a. Lymphocytes b. Basophils c. Neutrophil d. Monocytes e. Eosinophils Answer: b Basophils are the least abundant leukocyte. Leukocytes are the white blood cells. The order of frequency of the leukocytes is: neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, basophil. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The order of frequency of the leukocytes can be remembered by the mnemonic: "Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas". 556. Which of the following is not a granulocyte? a. PMN b. Basophils c. Neutrophil d. Monocytes e. Eosinophils Answer: d The granulocytes are named because of the presence of visible cytoplasmic granules. The granulocytes consist of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. "PMN" is an abbreviation for polymorphonuclear neutrophil. Thus, it is a neutrophil, which is a granulocyte. The non-granulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Poly is from the Greek "polys", which means many. "Poly" is also sometimes used as a nickname for polymorphonuclear leukocyte. 557. Which of the following is a granulocyte? a. Thrombocyte b. Monocyte c. Lymphocyte d. Basophil e. Erythrocyte Answer: d The granulocytes are named because of the presence of visible cytoplasmic granules. The granulocytes consist of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. The non-granulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes. Erythrocytes are red blood cells. A thrombocyte is a platelet.
ANDIE ALBINO
103
Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The suffix (or prefix) "phil" comes from the Greek word meaning love. It is used to specify an attraction or affinity towards something. It is seen in such words as philosophy, philanthropy and bibliophile. This suffix is used in naming the three granulocytes: eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils. Eosinophils "love" or are attracted to the eosin dye; thus the granules in an eosinophil are orange/pink. Basophils "love" or are attracted to the basophilic dye; thus the granules in a basophil are blue. Neutrophils "love" or are attracted to the neutral dye; thus the granules in a neutrophil are neutral colored. 558. Which of the following is described as having a "central pallor"? a. Leukocytes b. Monocytes c. Eosinophils d. Platelets e. Erythrocytes Answer: e Erythrocytes (red blood cells) are described as biconcave discs. When stained, this phenomenon results in the central portion of the cell staining lighter, thus the "central pallor". Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A biconcave disc can be visualized by holding two Frisbees together so that the middle portion is thinner than the top or bottom. 559. Which is the smallest leukocyte? a. Neutrophil b. Lymphocytes c. Monocytes d. Eosinophil e. Basophils Answer: b The leukocytes consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph. Lymphocytes are agranulocytes. Lymphocytes can be categorized by three sizes: small, medium, and large. The small lymphocytes are the smallest leukocyte, being only slightly larger than an erythrocyte. Monocytes are agranulocytes. They are the largest leukocyte. Eosinophils are granulocytes. Eosinophils have prominent orange pink granules. The nucleus of eosinophils is usually bi-lobed. Basophils are granulocytes. Basophils have large blue granules, which often obscure the nucleus. The granules are basophilic, therefore they are blue. 560. Which leukocyte usually has a bi-lobed nucleus? a. Neutrophil b. Lymphocytes c. Monocytes d. Eosinophil e. Basophils Answer: d The leukocytes consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph".
ANDIE ALBINO
Lymphocytes are agranulocytes. Lymphocytes can be categorized by three sizes: small, medium, and large. The small lymphocytes are the smallest leukocyte, being only slightly larger than an erythrocyte. Monocytes are agranulocytes. They are the largest leukocyte. Eosinophils are granulocytes. Eosinophils have prominent orange pink granules. The nucleus of eosinophils is usually bi-lobed. Basophils are granulocytes. Basophils have large blue granules, which often obscure the nucleus. The granules are basophilic, therefore they are blue. 561. What is the buffy coat? a. Leukocytes b. Platelets c. Erythrocytes d. Plasma e. Both a and b Answer e: The buffy coat is seen in a sample of centrifuged blood. It is the thin layer above the red blood cells, but below the plasma. It consists of the leukocytes and platelets. 562. What is another term for a platelet? a. Thrombocyte b. Monocyte c. Lymphocyte d. Basophil e. Erythrocyte Answer: a A thrombocyte is another name for a platelet. 563. Which leukocyte is the second most abundant in a peripheral smear of blood? a. Lymphocytes b. Basophils c. Neutrophil d. Monocytes e. Eosinophils Answer: a Lymphocytes are the second most abundant leukocyte. Leukocytes are the white blood cells. The order of frequency of the leukocytes is: neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, basophil. Histology hint fom Sarah Bellham: The order of frequency of the leukocytes can be remembered by the mnemonic: "Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas". 564. Which of the following is a granulocyte? a. Lymphocyte b. Neutrophil c. Monocyte d. Erythrocyte e. Thrombocyte Answer: b The granulocytes are named because of the presence of visible cytoplasmic granules. The granulocytes consist of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. The non-granulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes. Erythrocytes are red blood cells. A thrombocyte is a platelet. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The suffix (or prefix) "phil" comes from the Greek word meaning love. It is used to specify an attraction or affinity towards something. It is seen in such words as philosophy, philanthropy and bibliophile. This suffix is used in naming the three granulocytes: eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils. Eosinophils "love" or are attracted to the eosin dye; thus the granules in an eosinophil are orange/pink. Basophils
104
"love" or are attracted to the basophilic dye; thus the granules in a basophil are blue. Neutrophils "love" or are attracted to the neutral dye; thus the granules in a neutrophil are neutral colored. 565. Which leukocyte has orange-pink granules? a. Neutrophil b. Lymphocytes c. Monocytes d. Eosinophil e. Basophils Answer: d The leukocytes consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph". Lymphocytes are agranulocytes. Lymphocytes can be categorized by three sizes: small, medium, and large. The small lymphocytes are the smallest leukocyte, being only slightly larger than an erythrocyte. Monocytes are agranulocytes. They are the largest leukocyte. Eosinophils are granulocytes. Eosinophils have prominent orange pink granules. The nucleus of eosinophils is usually bi-lobed. Basophils are granulocytes. Basophils have large blue granules, which often obscure the nucleus. The granules are basophilic, therefore they are blue. 566. What is another term for a red blood cell? a. Thrombocyte b. Monocyte c. Lymphocyte d. Basophil e. Erythrocyte Answer: e An erythrocyte is another name for a red blood cell. 567. Which of the following is described as a "biconcave disc"? a. Platelets b. Erythrocytes c. Leukocytes d. Monocytes e. Eosinophils Answer: b Erythrocytes (red blood cells) are described as biconcave discs. When stained, this phenomenon results in the central portion of the cell staining lighter, thus the "central pallor". Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A biconcave disc can be visualized by holding two Frisbees together so that the middle portion is thinner than the top or bottom. 568. Which is the largest leukocyte? a. Neutrophil b. Lymphocytes c. Monocytes d. Eosinophil e. Basophils Answer: c The leukocytes consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are granulocytes. Neutrophils have a multi-lobed nucleus. The lobes are separated by a thin strand. Because of the shape of the nucleus, neutrophils are also called "polymorphonuclear neutrophils", "poly's", "PMN", or "polymorph".
Lymphocytes are agranulocytes. Lymphocytes can be categorized by three sizes: small, medium, and large. The small lymphocytes are the smallest leukocyte, being only slightly larger than an erythrocyte. Monocytes are agranulocytes. They are the largest leukocyte. Eosinophils are granulocytes. Eosinophils have prominent orange pink granules. The nucleus of eosinophils is usually bi-lobed. Basophils are granulocytes. Basophils have large blue granules, which often obscure the nucleus. The granules are basophilic, therefore they are blue. 569. At what level of the vascular tree does gas exchange occur? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: a Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 570. Which layer in an artery is primarily skeletal muscle? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: e The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves). 571. Which of the following is NOT a distinguishing feature between larger veins and arteries? a. Veins have valves whereas arteries do not have valves b. The tunics in veins are not as clearly delimited as are the tunics in arteries c. The walls in veins are thinner than the walls in arteries d. The lumen of a vein is smaller than the lumen of an artery e. None. All of the above are true
ANDIE ALBINO
105
Answer: d Veins have valves whereas arteries do not have valves. The tunics in veins are not as clearly delimited as are the tunics in arteries. The walls in veins are thinner than the walls in arteries. The lumen of a vein is larger than the lumen of an artery. 572. In which structure are things moved across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles? a. Continuous capillaries b. Fenestrated capillaries c. Sinusoidal capillaries d. AV anastomoses e. Venous sinus Answer: a A characteristic of continuous capillaries is that things are transported across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles. A characteristic of fenestrated capillaries is the presence of pores or fenestrae. Sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) are wide leaky capillaries. They are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. An arteriovenous anastomoses (AV anastomoses or AV shunt) is a direct route between arteries and veins. It bypasses the capillary bed. A venous sinus is a venous space lined by endothelium. A venous sinus surrounding the brain exists which is called the dural sinus. 573. What is a thoroughfare which is a an intermediate between an arteriole and capillary? a. Metcapillary b. Metartery c. Metvenule d. Metarteriole e. None of the above A metarteriole is a thoroughfare that can be considered an intermediate between an arteriole and capillary is a metarteriole. 574. Which layer in an artery contains the endothelium? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: a The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves). 575. What do you call the simple squamous epithelium that lines the blood vessels? a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified Answer: c Epithelial tissue has cells that are very tightly packed together. There is always a free surface associated with epithelial tissue. If a tissue is composed of a conglomeration of cells in tightly packed together, but it does not have a free surface, the tissue is called epithelioid tissue. An example of epithelioid tissue is the parenchyma of the adrenal gland.
Mesothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the abdominal cavity, the pericardial cavity, and the thoracic cavity. Endothelium is simple squamous epithelium that lines the vascular system. Transitional epithelium is seen in the urinary tract. Transitional epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface. Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that has cells which all touch the basement membrane. Pseudostratified epithelium is only one cell layer thick. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified, but it is not really stratified. Thus the name. The prefix "pseudo" means false, such as pseudonym or pseudo-science. 576. In which of the following is a portal system NOT found? a. Kidney b. Liver c. Muscle d. Brain e. None of the above is correct; a portal system is found in all of the above Answer: c The normal flow of blood is as follows: artery arteriole - capillary - post capillary venule -vein. However, exceptions to this pattern of blood flow exist. The phenomenon when a vein is between two capillary beds is called a venous portal system. An example of this is the hepatic portal system. Another example of a venous portal system is seen in the brain between the hypothalamus and pituitary. The phenomenon when an arteriole is between two capillary beds is called an arterial portal system. This is seen in the kidney. 577. What is the brachial artery? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: e Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 578. Which of the following is a distinct structure found specifically in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow? a. Continuous capillaries
ANDIE ALBINO
106
b. Fenestrated capillaries c. Sinusoidal capillaries d. AV anastomoses e. Venous sinus Answer: c A characteristic of continuous capillaries is that things are transported across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles. A characteristic of fenestrated capillaries is the presence of pores or fenestrae. Sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) are wide leaky capillaries. They are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. An arteriovenous anastomoses (AV anastomoses or AV shunt) is a direct route between arteries and veins. It bypasses the capillary bed. A venous sinus is a venous space lined by endothelium. A venous sinus surrounding the brain exists which is called the dural sinus. 579. Which layer in an artery is primarily smooth muscle? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: b The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves). 580. A pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of which type of vessel? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: e Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 581. Which of the following constitutes the microvascular bed of a tissue? a. Capillaries
Capillaries and arterioles Capillaries, arterioles, and post capillary venules d. Capillaries, arterioles, post capillary venules, and veins e. Capillaries, arterioles, post capillary venules, veins, and arteries Answer: c Capillaries, arterioles, and post capillary venules make up the microvascular bed of a tissue. 582. What are wide, leaky capillaries called? a. Continuous capillaries b. Fenestrated capillaries c. Sinusoidal capillaries d. AV anastomoses e. Venous sinus Answer: c A characteristic of continuous capillaries is that things are transported across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles. A characteristic of fenestrated capillaries is the presence of pores or fenestrae. Sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) are wide leaky capillaries. They are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. An arteriovenous anastomoses (AV anastomoses or AV shunt) is a direct route between arteries and veins. It bypasses the capillary bed. A venous sinus is a venous space lined by endothelium. A venous sinus surrounding the brain exists which is called the dural sinus. 583. What is a direct route between arteries and veins called? a. Continuous capillaries b. Fenestrated capillaries c. Sinusoidal capillaries d. AV anastomoses e. Venous sinus Answer: d A characteristic of continuous capillaries is that things are transported across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles. A characteristic of fenestrated capillaries is the presence of pores or fenestrae. Sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) are wide leaky capillaries. They are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. An arteriovenous anastomoses (AV anastomoses or AV shunt) is a direct route between arteries and veins. It bypasses the capillary bed. A venous sinus is a venous space lined by endothelium. A venous sinus surrounding the brain exists which is called the dural sinus. 584. Which layer in an elastic artery is the largest thickest? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica albuginea c. Tunica externa d. Tunica vaculosa e. Tunica media Answer: e In an elastic artery, the tunica media is the thickest. 585. In which of the following is an arterial portal system found? a. Kidney b. Liver c. Muscle d. Brain e. Stomach Answer: a
ANDIE ALBINO
b. c.
107
The normal flow of blood is as follows: artery arteriole - capillary - post capillary venule -vein. However, exceptions to this pattern of blood flow exist. The phenomenon when a vein is between two capillary beds is called a venous portal system. An example of this is the hepatic portal system. Another example of a venous portal system is seen in the brain between the hypothalamus and pituitary. The phenomenon when an arteriole is between two capillary beds is called an arterial portal system. This is seen in the kidney. 586. What are vasa vasorum? a. Vasoactive material b. Valves c. Vasopressin secreting cells d. Nerves e. Blood vessels Answer: e Vasa vasorum are the blood vessels of the blood vessels. These are the vessels which supply the vessel wall. 587. Which structure has one or two layers of muscle in the tunica media? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: b Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 588. Which layer in a large vessel contains the nervi vascularis? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves).
ANDIE ALBINO
589. What vessel regulates the amount of blood going into a capillary bed? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: b Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 590. What is the aorta? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: d Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 591. What are most of the named arteries in the body? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: e
108
Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 592. Which structure contains pores? a. Continuous capillaries b. Fenestrated capillaries c. Sinusoidal capillaries d. AV anastomoses e. Venous sinus Answer: b A characteristic of continuous capillaries is that things are transported across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles. A characteristic of fenestrated capillaries is the presence of pores or fenestrae. Sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) are wide leaky capillaries. They are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. An arteriovenous anastomoses (AV anastomoses or AV shunt) is a direct route between arteries and veins. It bypasses the capillary bed. A venous sinus is a venous space lined by endothelium. A venous sinus surrounding the brain exists which is called the dural sinus. 593. Which one of the following is a pluripotential cell that is prevalent around post capillary venules? a. Fibroblast b. Endothelial cell c. Pericyte d. Histiocyte e. Macrophage A pericyte is a pluripotential cell that is prevalent around post capillary venules. 594. Which layer in an artery is also called the tunica adventitia? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves).
595. Which layer in an artery is primarily connective tissue? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves). 596. What type of tissue lines blood vessels? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: a The lining of a blood vessel is simple squamous epithelium. This lining is called endothelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple squamous epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the cells are flat. 597. In which of the following is a venous portal system found? a. Kidney b. Liver c. Muscle d. Skin e. Stomach Answer: b The normal flow of blood is as follows: artery arteriole - capillary - post capillary venule -vein. However, exceptions to this pattern of blood flow exist. The phenomenon when a vein is between two capillary beds is called a venous portal system. An example of this is the hepatic portal system. Another example of a venous portal system is seen in the brain between the hypothalamus and pituitary. The phenomenon when an arteriole is between two capillary beds is called an arterial portal system. This is seen in the kidney. 598. What are nervi vascularis? a. Neuropil b. Neuroglia c. Pigmented lesion of a vessel d. Nerves e. Blood vessels Answer: d Nervi vascularis are nerves of the blood vessels. These are the nerves which supply the vessel wall. 599. Which structure receives blood from the capillary bed? a. Capillary b. Arteriole c. Venule d. Elastic artery e. Muscular artery Answer: c Capillaries are very thin walled in order to easily allow the exchange of gases. Gaseous exchange between
ANDIE ALBINO
109
the blood and tissues occurs at the level of the capillaries. Arterioles are small branches of arteries with only one or two layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. Arterioles regulate the amount of blood going into the capillary bed. Venules are small branches of veins. Elastic arteries are the arteries leaving the heart and the major branches. The aorta is an elastic artery. Most of the named arteries are muscular arteries (with the exception of the aorta and the major branches off the aorta). The dividing line between elastic arteries and muscular arteries is not clear cut. However, a pronounced internal elastic membrane and external elastic membrane are distinguishing characteristics of muscular arteries. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane. However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible. 600. Which layer in a large artery or vein contains the vasa vasorum? a. Tunica intima b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa d. All of the above e. None of the above Answer: c The tunica intima is the innermost layer of a blood vessel. It is lined by endothelium The tunica media is the middle layer of a blood vessel. The tunica media is primarily smooth muscle. The tunica externa or tunica adventitia is the outer layer of a blood vessel. In large vessels, the tunica adventitia contains vasa vasorum (blood vessels) and nervi vascularis (nerves). 601. What is the venous channel which is around the brain? a. Continuous capillaries b. Fenestrated capillaries c. Sinusoidal capillaries d. AV Anastomoses e. Venous sinus Answer: e A characteristic of continuous capillaries is that things are transported across the epithelium via pinocytotic vesicles. A characteristic of fenestrated capillaries is the presence of pores or fenestrae. Sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) are wide leaky capillaries. They are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. An arteriovenous anastomoses (AV anastomoses or AV shunt) is a direct route between arteries and veins. It bypasses the capillary bed. A venous sinus is a venous space lined by endothelium. A venous sinus surrounding the brain exists which is called the dural sinus. 602. Which layer of the heart is composed of cardiac muscle? a. Epicardium b. Pericardium c. Myocardium d. Endocardium e. Endomysium Answer: c The heart consists of three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium.
ANDIE ALBINO
The epicardium is the outer layer of the heart, containing the blood vessels and nerves which supply the heart. The myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. The endocardium is the inner layer of the heart. The innermost portion of the endocardium is composed of endothelium, a simple squamous epithelium. The pericardium is the connective tissue sac that the heart sits in. Endomysium is the connective tissue covering of an individual muscle cell. 603. Where is the myocardium the thickest? a. Right atria b. Left atria c. Right ventricle d. Left ventricle e. Both right and left ventricle Answer: d The myocardium is the middle layer of the heart. It is thickest in the left ventricle, since the left ventricle is responsible for pumping blood throughout the systemic circulation. 604. What is the connective tissue sac surrounding the heart? a. Epicardium b. Pericardium c. Myocardium d. Endocardium e. Endomysium Answer: b The heart consists of three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. The epicardium is the outer layer of the heart, containing the blood vessels and nerves which supply the heart. The myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. The endocardium is the inner layer of the heart. The innermost portion of the endocardium is composed of endothelium, a simple squamous epithelium. The pericardium is the connective tissue sac that the heart sits in. Endomysium is the connective tissue covering of an individual muscle cell. 605. What is the connective tissue called which surrounds an individual cardiac muscle fiber? a. Epicardium b. Pericardium c. Myocardium d. Endocardium e. Endomysium Answer: e The heart consists of three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. The epicardium is the outer layer of the heart, containing the blood vessels and nerves which supply the heart. The myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. The endocardium is the inner layer of the heart. The innermost portion of the endocardium is composed of endothelium, a simple squamous epithelium. The pericardium is the connective tissue sac that the heart sits in. Endomysium is the connective tissue covering of an individual muscle cell. 606. What is the pacemaker of the heart? a. Sinoatrial node b. Atrioventricular node c. Bundle of His d. Right bundle branch
110
e. Purkinje fiber Answer: a A cardiac impulse is transmitted through a specific pathway of modified cardiac tissue within the heart. The pacemaker of the heart is the sinoatrial node (SA node). The impulse then goes to the AV node. It goes through the ventricles via the bundle of His. The bundle of His is also called the atrioventricular bundle. This divides into right and left bundle branches. From there the impulse is transmitted into Purkinje fibers. 607. Which of the following is not true regarding the endocardium? a. The endocardium contains abundant adipose tissue b. The endocardium is layered c. The endocardium contains blood vessels d. The endocardium contains smooth muscle e. The endocardium is lined by endothelium Answer: a The epicardium contains abundant adipose tissue, not the endocardium. The endocardium is the inner layer of the heart. The layers of the heart being: endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium. The endocardium itself is layered. The innermost layer of the endocardium is lined by endothelium. The middle layer of the endocardium is connective tissue and smooth muscle. The outer layer of the endocardium is the subendocardial layer. The endocardium contains blood vessels. 608. What is the atrioventricular bundle? a. Sinoatrial node b. Atrioventricular node c. Bundle of His d. Right bundle branch e. Purkinje fiber Answer: c A cardiac impulse is transmitted through a specific pathway of modified cardiac tissue within the heart. The pacemaker of the heart is the sinoatrial node (SA node). The impulse then goes to the AV node. It goes through the ventricles via the bundle of His. The bundle of His is also called the atrioventricular bundle. This divides into right and left bundle branches. From there the impulse is transmitted into Purkinje fibers. 609. Where is endothelium located? a. Epicardium b. Pericardium c. Myocardium d. Endocardium e. Endomysium Answer: d The heart consists of three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. The epicardium is the outer layer of the heart, containing the blood vessels and nerves which supply the heart. The myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. The endocardium is the inner layer of the heart. The innermost portion of the endocardium is composed of endothelium, a simple squamous epithelium. The pericardium is the connective tissue sac that the heart sits in. Endomysium is the connective tissue covering of an individual muscle cell. 610. "Pulling on heartstrings" refers to strong feelings of love or sympathy pulling one's conscience. What anatomical structure is it reference to? a. Sinoatrial node b. Bundle of His
c. Right bundle branch d. Purkinje fiber e. Chordae tendinae Answer: e The chordae tendinae are threadlike structures between the papillary muscles to the valves of the heart. A cardiac impulse is transmitted through a specific pathway of modified cardiac tissue within the heart. The pacemaker of the heart is the sinoatrial node (SA node). The impulse then goes to the AV node. It goes through the ventricles via the bundle of His. The bundle of His is also called the atrioventricular bundle. This divides into right and left bundle branches. From there the impulse is transmitted into Purkinje fibers. 611. Where are the blood vessels which supply the heart located? a. Epicardium b. Pericardium c. Myocardium d. Endocardium e. Endomysium Answer: a The heart consists of three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. The epicardium is the outer layer of the heart, containing the blood vessels and nerves which supply the heart. The myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart. The endocardium is the inner layer of the heart. The innermost portion of the endocardium is composed of endothelium, a simple squamous epithelium. The pericardium is the connective tissue sac that the heart sits in. Endomysium is the connective tissue covering of an individual muscle cell. 612. What is another term for lymphatic nodules? a. Lymph follicles b. White pulp c. Peyer's patches d. Lymph node e. Diffuse lymphatic tissue Answer: a The localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract are lymph follicles. They are also called lymphatic nodules. The lymphatic tissue in the spleen is called white pulp. The large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum are called Peyer's patches. A lymph node is an encapsulated lymphatic organ. The random distribution of lymphocytes seen in the lamina propria of the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract is called diffuse lymphatic tissue. Difuse lymphatic tissue in not encapsulated. 613. Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains the gut associated lymphatic tissue? a. Mucosa b. Sub mucosa c. Muscularis externa d. Serosa e. Adventitia Answer: a The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. The mucosa consists of a lining epithelium, lamina propria and muscularis mucosae. Gut associated lymphatic tissue (GALT) is found in the mucosa and sometimes extends into the submucosa.
ANDIE ALBINO
111
614. Which of the following is NOT made of a framework of reticular fibers? a. Bone marrow b. Lymph node c. Spleen d. Thymus e. None of the above--all are made of a framework of reticular fibers. Answer: d Bone marrow, lymph nodes, the spleen and the thymus are all part of the lymphatic system. Most lymphatic organs are made of a framework of reticular fibers and reticular cells. However, the thymus is made of epithelioreticular cells instead. 615. What is the acronym for the diffuse lymphatic tissue found in the intestinal tract? a. BALT b. DALT c. FALT d. GALT e. HALT Answer: d Diffuse lymphatic tissue is non-encapsulated lymphatic tissue. It is found in the gastrointestinal tract, the genito-urinary tract, and the respiratory tract. In the gastrointestinal tract it is referred to as GALT (gut associated lymphatic tissue). In the respiratory tract it is referred to as BALT (bronchi associated lymphatic tissue). 616. What is another name for a splenic nodule? a. Malpighian corpuscle b. Trabeculae c. White pulp d. Red pulp e. Cords of Billroth Answer: a The spleen has a connective tissue capsule. The invaginations of the capsule into the splenic parenchyma are trabeculae. The parenchyma of the spleen can be divided into the white pulp and the red pulp. The white pulp of the spleen is the lymphatic portion of the spleen. Within the white pulp, splenic nodules are found. Splenic nodules are also called Malpighian corpuscles. The red pulp is made up of the splenic sinuses and splenic cords. The splenic cords are also called the cords of Billroth. 617. What is the term for the entire lymphatic region of the spleen? a. Malpighian corpuscle b. Trabeculae c. White pulp d. Red pulp e. Cords of Billroth Answer: c The spleen has a connective tissue capsule. The invaginations of the capsule into the splenic parenchyma are trabeculae. The parenchyma of the spleen can be divided into the white pulp and the red pulp. The white pulp of the spleen is the lymphatic portion of the spleen. Within the white pulp, splenic nodules are found. Splenic nodules are also called Malpighian corpuscles. The red pulp is made up of the splenic sinuses and splenic cords. The splenic cords are also called the cords of Billroth. 618. Which of the following is NOT a function of the spleen? a. Destruction of red blood cells
ANDIE ALBINO
b. Lymphocyte production c. Storage of blood d. Fetal blood cell formation e. All of the above are functions of the spleen Answer: e The spleen is involved in destruction of old or damaged red blood cells. Storage of blood occurs in the spleen. In the fetus, the spleen is involved in blood cell formation. Lymphocyte and antibody production occurs in the spleen. 619. When looking at a lymph node, where are lymphatic nodules? a. Deep cortex b. Tertiary cortex c. Juxtamedullary cortex d. Paracortical zone e. Outer cortex Answer: e Deep cortex, tertiary cortex, juxtamedullary cortex and paracortical zone are all terms for the same region in a lymph node. The deep cortex is the inner region of the cortex, next to the medulla. Lymphatic nodules are not found in the deep cortex. Lymphatic nodules are found in the outer cortex. 620. Where do T lymphocytes gain their immunocompetence? a. Thymus b. Thyroid c. Bursa of Fabricus d. Bone marrow e. Lymph node Answer: a T cells gain their immunocompetence in the thymus. 621. What do you call the random distribution of lymphocytes that are found in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract? a. Lymph follicles b. White pulp c. Peyer's patches d. Lymph node e. Diffuse lymphatic tissue Answer: e The localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract are lymph follicles. They are also called lymphatic nodules. The lymphatic tissue in the spleen is called white pulp. The large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum are called Peyer's patches. A lymph node is an encapsulated lymphatic organ. The random distribution of lymphocytes seen in the lamina propria of the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract is called diffuse lymphatic tissue. Difuse lymphatic tissue in not encapsulated. 622. What is a characteristic of a secondary nodule? a. Germinal center b. Lymphocytes c. Capsule d. Trabeculae e. None of the above Answer: a A secondary lymphatic nodule is characterized by the presence of a germinal center. 623. Which of the following is composed of epithelioreticular cells? a. Spleen b. Thymus c. Bone marrow
112
d. Lymph node e. None of the above Answer: b Bone marrow, lymph nodes, the spleen and the thymus are all part of the lymphatic system. Most lymphatic organs are made of a framework of reticular fibers and reticular cells. However, the thymus is made of epithelioreticular cells instead. 624. What is the acronym for the diffuse lymphatic tissue in the respiratory tract? a. BALT b. DALT c. FALT d. GALT e. HALT Answer: a Diffuse lymphatic tissue is non-encapsulated lymphatic tissue. It is found in the gastrointestinal tract, the genito-urinary tract, and the respiratory tract. In the gastrointestinal tract it is referred to as GALT (gut associated lymphatic tissue). In the respiratory tract it is referred to as BALT (bronchi associated lymphatic tissue). 625. What are the localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract? a. Lymph follicles b. White pulp c. Peyer's patches d. Lymph node e. Diffuse lymphatic tissue Answer: a The localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract are lymph follicles. They are also called lymphatic nodules. The lymphatic tissue in the spleen is called white pulp. The large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum are called Peyer's patches. A lymph node is an encapsulated lymphatic organ. The random distribution of lymphocytes seen in the lamina propria of the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract is called diffuse lymphatic tissue. Difuse lymphatic tissue in not encapsulated. 626. What is the lymphatic tissue in the spleen called? a. Lymph follicles b. White pulp c. Peyer's patches d. Lymph node e. Diffuse lymphatic tissue Answer: b The localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract are lymph follicles. They are also called lymphatic nodules. The lymphatic tissue in the spleen is called white pulp. The large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum are called Peyer's patches. A lymph node is an encapsulated lymphatic organ. The random distribution of lymphocytes seen in the lamina propria of the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract is called diffuse lymphatic tissue. Difuse lymphatic tissue in not encapsulated. 627. What are the splenic cords? a. Cords of Billroth b. Cords of Paneth c. Cords of Bellini
d. Cords of Rothchild e. Cords of Hassall Answer: a The splenic cords are also called the cords of Billroth. 628. When looking at the spleen, what are the invaginations of the capsule into the splenic parenchyma called? a. Malpighian corpuscle b. Trabeculae c. White pulp d. Red pulp e. Cords of Billroth Answer: b The spleen has a connective tissue capsule. The invaginations of the capsule into the splenic parenchyma are trabeculae. The parenchyma of the spleen can be divided into the white pulp and the red pulp. The white pulp of the spleen is the lymphatic portion of the spleen. Within the white pulp, splenic nodules are found. Splenic nodules are also called Malpighian corpuscles. The red pulp is made up of the splenic sinuses and splenic cords. The splenic cords are also called the cords of Billroth. 629. When looking at a lymph node, which term does not refer to the same region as all the others listed? a. Deep cortex b. Tertiary cortex c. Outer cortex d. Juxtamedullary cortex e. Paracortical zone Answer: c Deep cortex, tertiary cortex, juxtamedullary cortex and paracortical zone are all terms for the same region in a lymph node. The deep cortex is the inner region of the cortex, next to the medulla. 630. What are the spherical structures seen in the medulla of the thymus called? a. Psammoma bodies b. Corpora arenacea c. Hassall's corpuscles d. Prostatic concretions e. Pacinian corpuscles Answer: c Psammoma bodies are collections of calcium. It is derived from the Greek word "psammos", which means sand. Corpora arenacea refers to the calcifications seen in the pineal gland. Corpora arenacea is nicknamed "brain sand". Hassall's corpuscles are the ring like structures found in the thymus. The spherical structures seen in some prostatic alveoli are called prostatic concretions. Pacinian corpuscles are pressure receptors in the skin. 631. Where are Peyer's patches located? a. Esophagus b. Stomach c. Small intestine d. Large intestine e. Rectum Answer: c Peyer's patches are large nodules of lymphatic tissue. They are seen in the small intestine. 632. What are the large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum? a. Lymph follicles b. White pulp
ANDIE ALBINO
113
c. Peyer's patches] d. ymph node e. Diffuse lymphatic tissue Answer: c The localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract are lymph follicles. They are also called lymphatic nodules. The lymphatic tissue in the spleen is called white pulp. The large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum are called Peyer's patches. A lymph node is an encapsulated lymphatic organ. The random distribution of lymphocytes seen in the lamina propria of the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract is called diffuse lymphatic tissue. Difuse lymphatic tissue in not encapsulated. 633. Where is diffuse lymphatic tissue NOT found? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Central nervous system c. Genito-urinary tract d. Respiratory tract e. None of the above-diffuse lymphatic tissue is found in all of these regions Answer: b Diffuse lymphatic tissue is non-encapsulated lymphatic tissue. It is found in the gastrointestinal tract, the genito-urinary tract, and the respiratory tract. In the gastrointestinal tract it is referred to as GALT (gut associated lymphatic tissue). In the respiratory tract it is referred to as BALT (bronchi associated lymphatic tissue). Diffuse lymphatic tissue is not found in the central nervous system. 634. Where are the splenic sinuses? a. Malpighian corpuscle b. Trabeculae c. White pulp d. Red pulp e. Cords of Billroth Answer: d The spleen has a connective tissue capsule. The invaginations of the capsule into the splenic parenchyma are trabeculae. The parenchyma of the spleen can be divided into the white pulp and the red pulp. The white pulp of the spleen is the lymphatic portion of the spleen. Within the white pulp, splenic nodules are found. Splenic nodules are also called Malpighian corpuscles. The red pulp is made up of the splenic sinuses and splenic cords. The splenic cords are also called the cords of Billroth. 635. What does the acronym PALS stand for? a. Papillary layer sinus b. Peyer's lymphatic sheath c. Periarterial lymphatic sheath d. Peripheral lymphatic sinus e. Parenchymal lymphatic sheath Answer: c PALS stands for periarterial lymphatic sheath. Periarterial lymphatic sheaths are the lymphocytes which surround the central artery in the spleen. 636. Which of the following is an encapsulated lymphatic organ? a. Lymph follicles b. White pulp c. Peyer's patches d. Lymph node e. Diffuse lymphatic tissue Answer: d
ANDIE ALBINO
The localized concentrations of lymphocytes that are seen in the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract are lymph follicles. They are also called lymphatic nodules. The lymphatic tissue in the spleen is called white pulp. The large aggregates of lymphatic tissue in the ileum are called Peyer's patches. A lymph node is an encapsulated lymphatic organ. The random distribution of lymphocytes seen in the lamina propria of the respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract is called diffuse lymphatic tissue. Difuse lymphatic tissue in not encapsulated. 637. Which cell is a also called a septal cell? a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell Answer: c The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the alveolar epithelium. 638. Which cell is a respiratory macrophage? a. Kupffer cells b. Histiocyte c. Dust cell d. Langerhans cell e. Microglia Answer: c Macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Many tissues have resident (fixed) macrophages. Fixed macrophages are given a unique name, depending on the tissue that they are located in. Kupffer cells are the hepatic macrophages. Histiocytes are macrophages seen in connective tissue. Dust cells are alveolar macrophages found in the respiratory tract. Langerhans cells are macrophages seen in the skin. Microglia are the central nervous system macrophages. 639. Which cell is a type of neuron? a. Basal cells b. Brush cells c. Olfactory cells d. Sustentacular cells e. All of the above Answer: c Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory cells and sustentacular cells. Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type in the olfactory epithelium. 640. What cell types are found in the respiratory mucosa? a. Ciliated cells b. Goblet cells c. Basal cells d. Brush cells e. All of the above Answer: e
114
In man, respiratory mucosa is composed of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells. Respiratory mucosa contains several cell types: ciliated cells, goblet cells, basal cells, and brush cells. Respiratory mucosa is located lining the respiratory segment of the nasal cavity. It lines the conchae and the paranasal sinuses. 641. What type of tissue makes up the epiglottis? a. Compact bone b. Spongy bone c. Hyaline cartilage d. Fibrocartilage e. Elastic cartilage Answer: e The epiglottis is part of the larynx. It is composed of elastic cartilage. 642. What is the smallest airspace of the respiratory tree? a. Alveolar duct b. Alveoli c. Alveolar sac d. Respiratory bronchiole e. Terminal bronchiole Answer: b The respiratory tract is made of branching structures, much like the branches of a tree. The trachea branches into two bronchi which branch into smaller bronchi. The bronchi ultimately branch into smaller bronchioles. Bronchioles are distinguished from bronchi in that they do not have cartilage and submucosal glands. The terminal bronchioles are the last part of the airway in which gas exchange does not occur. Terminal bronchioles lead to the respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles are the first section of the respiratory tree that gas exchange can occur. The alveoli duct is analogous to a thoroughfare with many cul-du-sacs branching off of it. At the end of the alveoli duct is an alveoli sac. An alveoli sac is a cluster of alveoli, much like a cluster of grapes. Alveoli are individual sacs where gas exchange occurs. 643. What type of epithelium lines the trachea? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: e The trachea is lined by pseudostratified squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Pseudostratified squamous epithelium is "pseudostratified" because it is only one cell layer thick, yet it appears to be stratified. In reality, every cell touches the basement membrane. Note from Sarah Bellham: The prefix "pseudo" is of Greek origin and it means false or counterfeit. For example: pseudonym, pseudo-science or pseudostratified. 644. Which structure is part of the conducting portion of the airway? a. Bronchi b. Alveolar ducts c. Alveoli d. Alveolar sacs e. Respiratory bronchioles Answer: a The conducting portion of the airway is where air is moved, warmed and moistened. The nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi are all part of the conducting portion of the airway.
The respiratory portion of the airway is where gas exchange occurs. The respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs and alveoli are all part of the respiratory portion. 645. What type of epithelium lines the vestibule? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple columnar epithelium c. Stratified squamous epithelium d. Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells e. Transitional epithelium Answer: c The vestibule is lined by stratified squamous epithelium. 646. Which cartilage of the larynx is made of hyaline cartilage? a. Thyroid cartilage b. Cricoid cartilage c. Arytenoid cartilage d. Corniculate cartilage e. All of the above Answer: e The larynx is composed of several cartilages. The thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, arytenoid cartilages, corniculate cartilages and cuneiform cartilages are all composed of hyaline cartilage. The epiglottis is elastic cartilage. There is no fibrocartilage in the larynx. 647. What part of the respiratory tree is the functional unit where gas exchange occurs? a. Alveolar duct b. Alveoli c. Alveolar sac d. Respiratory bronchiole e. Terminal bronchiole Answer: b The respiratory tract is made of branching structures, much like the branches of a tree. The trachea branches into two bronchi which branch into smaller bronchi. The bronchi ultimately branch into smaller bronchioles. Bronchioles are distinguished from bronchi in that they do not have cartilage and submucosal glands. The terminal bronchioles are the last part of the airway in which gas exchange does not occur. Terminal bronchioles lead to the respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles are the first section of the respiratory tree that gas exchange can occur. The alveoli duct is analogous to a thoroughfare with many cul-du-sacs branching off of it. At the end of the alveoli duct is an alveoli sac. An alveoli sac is a cluster of alveoli, much like a cluster of grapes. Alveoli are individual sacs where gas exchange occurs. 648. Which cell type is involved in general sensation of the olfactory mucosa? a. Basal cells b. Brush cells c. Olfactory cells d. Sustentacular cells e. All of the above Answer: b Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory cells and sustentacular cells. Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells
ANDIE ALBINO
115
are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type in the olfactory epithelium. 649. What type of cells are found in the olfactory mucosa? a. Basal cells b. Brush cells c. Olfactory cells d. Sustentacular cells e. All of the above Answer: e Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory cells and sustentacular cells. Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type in the olfactory epithelium. 650. What type of tissue makes up the rings of the trachea? a. Compact bone b. Spongy bone c. Hyaline cartilage d. Fibrocartilage e. Elastic cartilage Answer: c The rings of the trachea are composed of hyaline cartilage. 651. Which cell is a squamous pulmonary epithelial cell? a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell Answer: b The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the alveolar epithelium. 652. Which cell is also called an alveolar phagocyte? a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell Answer: d The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the alveolar epithelium. 653. Which is structure is NOT part of the conducting portion of the airway? a. Bronchi b. Larynx c. Trachea d. Larynx e. Respiratory bronchioles Answer: e The conducting portion of the airway is where air is moved, warmed and moistened. The nasal cavities,
ANDIE ALBINO
pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi are all part of the conducting portion of the airway. The respiratory portion of the airway is where gas exchange occurs. The respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs and alveoli are all part of the respiratory portion. 654. What type of tissue lines the pharynx? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple columnar epithelium c. Stratified squamous epithelium d. Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells e. Both c and d Answer: e The pharynx is lined by both stratified squamous epithelium and ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells. Different regions are lined by a different type of epithelium. Regions of the pharynx that are likely to be roughened up by food are lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Other regions of the pharynx are lined by ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells. 655. What is an olfactory cell? a. Unipolar neuron b. Bipolar neuron c. Multipolar neuron d. Supporting cell e. None of the above Answer: b An olfactory cell is a bipolar neuron. 656. Which type of cartilage is found in the larynx? a. Hyaline cartilage b. Elastic cartilage c. Fibrocartilage d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: d The larynx is composed of several cartilages. The thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, arytenoid cartilages, corniculate cartilages and cuneiform cartilages are all composed of hyaline cartilage. The epiglottis is elastic cartilage. There is no fibrocartilage in the larynx. 657. What structure is similar to a "bunch of grapes? a. Alveolar duct b. Alveoli c. Alveolar sac d. Respiratory bronchiole e. Terminal bronchiole Answer: c The respiratory tract is made of branching structures, much like the branches of a tree. The trachea branches into two bronchi which branch into smaller bronchi. The bronchi ultimately branch into smaller bronchioles. Bronchioles are distinguished from bronchi in that they do not have cartilage and submucosal glands. The terminal bronchioles are the last part of the airway in which gas exchange does not occur. Terminal bronchioles lead to the respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles are the first section of the respiratory tree that gas exchange can occur. The alveoli duct is analogous to a thoroughfare with many cul-du-sacs branching off of it. At the end of the alveoli duct is an alveoli sac. An alveoli sac is a cluster of alveoli, much like a cluster of grapes. Alveoli are individual sacs where gas exchange occurs. 658. Which cell is found in large numbers in the terminal bronchioles? a. Clara cell
116
b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell Answer: a The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the alveolar epithelium. 659. Which cell type is located at the basal lamina of the olfactory mucosa? a. Basal cells b. Brush cells c. Olfactory cells d. Sustentacular cells e. All of the above Answer: a Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory cells and sustentacular cells. Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type in the olfactory epithelium. 660. Which cell type is most numerous in olfactory mucosa? a. Basal cells b. Brush cells c. Olfactory cells d. Sustentacular cells e. None of the above Answer: d Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory cells and sustentacular cells. Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type in the olfactory epithelium. 661. What type of epithelium is found in the respiratory mucosa of man? a. Non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells b. Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Transitional epithelium Answer: b In man, respiratory mucosa is composed of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells. Respiratory mucosa contains several cell types: ciliated cells, goblet cells, basal cells, and brush cells. Respiratory mucosa is located lining the respiratory segment of the nasal cavity. It lines the conchae and the paranasal sinuses. 662. What type of tissue makes up the "Adam's apple"? a. Compact bone b. Spongy bone
c. Hyaline cartilage d. Fibrocartilage e. Elastic cartilage Answer: e The "Adam's apple" is a nickname for part of the larynx formed by the thyroid cartilage. The thyroid cartilage is composed of hyaline cartilage. 663. What type of tissue forms the alveoli in the lung? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium Answer: a The alveoli are formed by simple squamous epithelium. Epithelium lines body cavities and surfaces. Simple squamous epithelium is "simple" because it is one cell thick. "Squamous" refers to the fact that the cells are flat. 664. What type of tissue lines the paranasal sinuses? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple columnar epithelium c. Stratified squamous epithelium d. Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells e. Transitional epithelium Answer: d The paranasal sinuses are lined by ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells. 665. In which structure does gas exchange NOT occur? a. Alveolar duct b. Alveoli c. Alveolar sac d. Respiratory bronchiole e. Terminal bronchiole Answer: e The respiratory tract is made of branching structures, much like the branches of a tree. The trachea branches into two bronchi which branch into smaller bronchi. The bronchi ultimately branch into smaller bronchioles. Bronchioles are distinguished from bronchi in that they do not have cartilage and submucosal glands. The terminal bronchioles are the last part of the airway in which gas exchange does not occur. Terminal bronchioles lead to the respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles are the first section of the respiratory tree that gas exchange can occur. The alveoli duct is analogous to a thoroughfare with many cul-du-sacs branching off of it. At the end of the alveoli duct is an alveoli sac. An alveoli sac is a cluster of alveoli, much like a cluster of grapes. Alveoli are individual sacs where gas exchange occurs. 666. Which cell secretes surfactant? a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell Answer: c The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the alveolar epithelium. 667. Which cartilage of the larynx is made of elastic cartilage?
ANDIE ALBINO
117
a. Thyroid cartilage b. Cricoid cartilage c. Arytenoid cartilage d. Epiglottis e. Corniculate cartilage Answer: d The larynx is composed of several cartilages. The thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, arytenoid cartilages, corniculate cartilages and cuneiform cartilages are all composed of hyaline cartilage. The epiglottis is elastic cartilage. There is no fibrocartilage in the larynx. 668. Which cell is rarely found in the alveolus? a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell Answer: e The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the alveolar epithelium. 669. What are the alveolar pores called? a. Pores of Luschka b. Pores of Descemet c. Pores of Mall d. Pores of Kohn e. Pores of Disse Answer: d The alveolar pores are the pores of Kohn. These are openings between adjacent alveoli. 670. What is the first portion of the respiratory tree where gas exchange can occur? a. Alveolar duct b. Alveoli c. Alveolar sac d. Respiratory bronchiole e. Terminal bronchiole Answer: d The respiratory tract is made of branching structures, much like the branches of a tree. The trachea branches into two bronchi which branch into smaller bronchi. The bronchi ultimately branch into smaller bronchioles. Bronchioles are distinguished from bronchi in that they do not have cartilage and submucosal glands. The terminal bronchioles are the last part of the airway in which gas exchange does not occur. Terminal bronchioles lead to the respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles are the first section of the respiratory tree that gas exchange can occur. The alveoli duct is analogous to a thoroughfare with many cul-du-sacs branching off of it. At the end of the alveoli duct is an alveoli sac. An alveoli sac is a cluster of alveoli, much like a cluster of grapes. Alveoli are individual sacs where gas exchange occurs. 671. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the endocrine system? a. Products secreted into blood b. Glands with ducts c. Secretes hormones d. Non localized response e. All of the following are characteristics of the endocrine system Answer: b
ANDIE ALBINO
The endocrine system is a system of cellular communication. The means of communication is via hormones. The hormones are secreted by ductless glands directly into the bloodstream. Generally, the response to hormones is non localized. If a gland secretes its product through a duct, it is an exocrine gland. 672. What type of hormone is testosterone? a. Protein b. Amino acid chain c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: c Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 673. What organ is nicknamed the "master gland" a. Adrenal medulla b. Adrenal cortex c. Brain d. Pituitary e. Heart Answer: d The pituitary is nicknamed the master gland. 674. What cell type secretes ACTH? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: d There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin. Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 675. Where is corpora arenacea found? a. Pituitary b. Pineal gland c. Adrenal gland d. Pancreas e. Thyroid Answer: b Corpora arenacea is nicknamed "brain sand". Corpora arenacea is calcification seen in the pineal gland. 676. Which gland secretes melatonin? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: c The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and
118
sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 677. Which cell type are involved in the secretion thyroglobulin? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: d There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 678. Where is insulin secreted from? a. Alpha cells b. Beta cells c. Gamma cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: b The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostatin. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 679. Which of the following is part of the adrenal gland? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. All of the above Answer: e The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 680. Which part the adrenal gland secretes glucocorticoids? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: d
The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 681. What type of hormone is insulin? a. Protein b. Peptide c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: a Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 682. What connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus? a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Infundibulum d. Adenohypophysis e. Neurohypophysis Answer: c The pituitary is nicknamed the master gland. The infundibulum connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus. The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The adenohypophysis (more specifically, the pars distalis of the adenohypophysis) secretes tropic hormones. Tropic hormones affect cellular activity in their target organ. The neurohypophysis secretes two hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone. 683. Which of the following is not part of the adenohypophysis? a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Pars distalis d. Pars nervosa e. All of the above are part of the adenohypophysis Answer: d The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The pars distalis is the anterior lobe of the pituitary. The neurohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars nervosa, infundibular stalk, and median eminence. The pars nervosa is the posterior lobe. 684. What cell type secretes prolactin? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells
ANDIE ALBINO
119
d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: a There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin. Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 685. Which of the following cells can be classified as an acidophil? a. Gonadotropic cells b. Corticotropic cells c. Thyrotropic cells d. Lactotropic cells e. All of the above Answer: d The cells of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary) can be classified as acidophils or basophils depending on their affinity for acid or basic dyes, respectively. The acidophils are the somatotropic cells and the lactotropic cells. Thus, growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by acidophilic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. Thus, the basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: There are two mnemonics to use when thinking of acidophils and basophils of the anterior pituitary. "GPA" (growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by the acidophils). "B-FLAT" (basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH). 686. Which gland secretes calcitonin? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: b The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 687. Which cell type are also called C cells? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: c There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the
thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 688. Where is glucagon secreted from? a. Alpha cells b. Beta cells c. Gamma cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: a The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostatin. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 689. Which of the following is a component of the adrenal medulla? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. All of the above Answer: a The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 690. What are the cells of the pineal gland called? a. Follicular cells b. Parafollicular cells c. Pinealocytes d. P cells e. PP cells Answer: c The cells of the pineal gland called pinealocytes. There are also glial cells in the pineal gland. PP cells are cells in the pancreas which secrete pancreatic polypeptide. 691. What type of hormone is prolactin? a. Protein b. Peptide c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: a Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 692. Where are tropic hormones secreted from?
ANDIE ALBINO
120
a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Infundibulum d. Adenohypophysis e. Neurohypophysis Answer: d The pituitary is nicknamed the master gland. The infundibulum connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus. The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The adenohypophysis (more specifically, the pars distalis of the adenohypophysis) secretes tropic hormones. Tropic hormones affect cellular activity in their target organ. The neurohypophysis secretes two hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone. 693. Which of the following is not part of the neurohypophysis? a. Median eminence b. Pars distalis c. Pars nervosa d. Infundibular stalk e. All of the above are part of the neurohypophysis Answer: b The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The pars distalis is the anterior lobe of the pituitary. The neurohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars nervosa, infundibular stalk, and median eminence. The pars nervosa is the posterior lobe. 694. What cell type secretes MSH? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: d There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin. Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 695. Which of the following cells can be classified as an acidophil? a. Corticotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Gonadotropic cells d. None of the above e. All of the above Answer: d The cells of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary) can be classified as acidophils or basophils depending on their affinity for acid or basic dyes, respectively. The acidophils are the somatotropic cells and the lactotropic cells. Thus, growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by acidophilic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. Thus, the basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham:
There are two mnemonics to use when thinking of acidophils and basophils of the anterior pituitary. "GPA" (growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by the acidophils). "B-FLAT" (basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH). 696. Which gland secretes epinephrine? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: e The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 697. Which gland secretes cortisol? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: d The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 698. Which cell type is found in the adrenal medulla? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: e There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 699. Where is pancreatic polypeptide secreted from? a. Alpha cells b. Beta cells c. Gamma cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: c The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon.
ANDIE ALBINO
121
The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostatin. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 700. Which of the following is the middle layer of the adrenal cortex? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: d The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids) 701. What type of hormone is antidiuretic hormone? a. Protein b. Peptide c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: b Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 702. Where is oxytocin secreted from? a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Infundibulum d. Adenohypophysis e. Neurohypophysis Answer: e The pituitary is nicknamed the master gland. The infundibulum connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus. The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The adenohypophysis (more specifically, the pars distalis of the adenohypophysis) secretes tropic hormones. Tropic hormones affect cellular activity in their target organ. The neurohypophysis secretes two hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone. 703. What cell type secretes LH? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: e There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin.
ANDIE ALBINO
Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 704. Which of the following cells can be classified as a basophil? a. Thyrotropic cells b. Lactotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. None of the above e. All of the above Answer: a The cells of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary) can be classified as acidophils or basophils depending on their affinity for acid or basic dyes, respectively. The acidophils are the somatotropic cells and the lactotropic cells. Thus, growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by acidophilic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. Thus, the basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: There are two mnemonics to use when thinking of acidophils and basophils of the anterior pituitary. "GPA" (growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by the acidophils). "B-FLAT" (basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH). 705. Which gland secretes T3? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: b The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 706. Which gland secretes sex steroids? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: d The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 707. Which of the following is the exocrine portion of the pancreas? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells
122
c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: e The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostatin. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 708. Where is somatostatin secreted from? a. Alpha cells b. Beta cells c. Gamma cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: d The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostatin. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 709. Which of the following is seen the innermost portion the adrenal gland? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: a The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 710. What cell of the parathyroid gland is also called a "chief cell"? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: a There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the
thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 711. What type of hormone is oxytocin? a. Protein b. Peptide c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: b Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 712. Where is antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secreted from? a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Infundibulum d. Adenohypophysis e. Neurohypophysis Answer: e The pituitary is nicknamed the master gland. The infundibulum connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus. The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The adenohypophysis (more specifically, the pars distalis of the adenohypophysis) secretes tropic hormones. Tropic hormones affect cellular activity in their target organ. The neurohypophysis secretes two hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone. 713. What cell type secretes FSH? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: e There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin. Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 714. Which of the following cells can be classified as a basophil? a. Lactotropic cells b. Corticotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. None of the above e. All of the above Answer: b The cells of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary) can be classified as acidophils or basophils depending on their affinity for acid or basic dyes, respectively. The acidophils are the somatotropic cells and the lactotropic cells. Thus, growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by acidophilic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. Thus, the basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH.
ANDIE ALBINO
123
Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: There are two mnemonics to use when thinking of acidophils and basophils of the anterior pituitary. "GPA" (growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by the acidophils). "B-FLAT" (basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH). 715. Which gland secretes norepinephrine? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: e The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 716. What is corpora arenacea? a. Brain sand b. Basal body c. Nissl body d. White body e. Degenerating corpus luteum Answer: a Corpora arenacea is nicknamed "brain sand". Corpora arenacea is calcification seen in the pineal gland. 717. What gland secretes aldosterone? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: d The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 718. What is the most common cell in the parathyroid gland? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: a There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 719. Where are catecholamines secreted from?
ANDIE ALBINO
a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: a The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 720. Which of the following is the outer layer of the adrenal cortex? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: c The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 721. What type of hormone is estradiol? a. Protein b. Amino acid chain c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: c Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 722. What is another term for the anterior lobe of the pituitary? a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Pars distalis d. Pars nervosa e. Infundibular stalk Answer: c The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The
124
adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The pars distalis is the anterior lobe of the pituitary. The neurohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars nervosa, infundibular stalk, and median eminence. The pars nervosa is the posterior lobe. 723. What cell type secretes growth hormone? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: c There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin. Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 724. Which of the following cells can be classified as a basophil? a. Somatotropic cells b. Lactotropic cells c. Gonadotropic cells d. None of the above e. All of the above Answer: c The cells of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary) can be classified as acidophils or basophils depending on their affinity for acid or basic dyes, respectively. The acidophils are the somatotropic cells and the lactotropic cells. Thus, growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by acidophilic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. Thus, the basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: There are two mnemonics to use when thinking of acidophils and basophils of the anterior pituitary. "GPA" (growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by the acidophils). "B-FLAT" (basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH). 725. Where is the endocrine portion of the pancreas housed? a. Islets of Langerhans b. Alpha cells c. Beta cells d. Delta cells e. Acini Answer: a The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is housed in the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, there are several cell types. The alpha cells secrete glucagon. The beta cells secrete insulin. The delta cells secrete somatostatin. The gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. The acini is the exocrine portion of the pancreas. 726. Which gland secretes glucagon? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla)
Answer: a The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 727. Which cell type secretes calcitonin? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: c There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 728. Which cell type is found in the parathyroid, but is not the most abundant cell type? a. Principal cell b. Oxyphil cell c. Parafollicular cells d. Follicular cells e. Chromaffin cells Answer: b There are two cell types in the parathyroid gland: principal cells and oxyphil cells. Principal cells are also called chief cells. Principal cells are the more prevalent. Oxyphil cells are also found in the parathyroid gland; however they are not as prevalent as principal cells. There are two cell types in the thyroid: follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Follicular cells release and store thyroid hormone. Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland are also called C cells. They secrete calcitonin. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. 729. Which part the adrenal gland secretes mineralocorticoids? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: c The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their
ANDIE ALBINO
125
respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 730. Which of the following is the inner layer of the adrenal cortex? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: b The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 731. What type of hormone is epinephrine? a. Protein b. Amino acid chain c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: d Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 732. What is another term for the posterior lobe of the pituitary? a. Pars intermedia b. Pars tuberalis c. Pars distalis d. Pars nervosa e. Infundibular stalk Answer: d The pituitary can be subdivided into the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis. The pars distalis is the anterior lobe of the pituitary. The neurohypophysis can be further sub-divided into the pars nervosa, infundibular stalk, and median eminence. The pars nervosa is the posterior lobe. 733. What cell type secretes TSH? a. Lactotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Somatotropic cells d. Corticotropic cells e. Gonadotropic cells Answer: b There are several cell types in the pars distalis (anterior pituitary). Lactotropic cells secrete prolactin. Thyrotropic cells secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Somatotropic cells secrete growth hormone. Corticotropic cells secrete adrenocorticotropic
ANDIE ALBINO
hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Gonadotropic cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). 734. Which of the following cells can be classified as a basophil? a. Corticotropic cells b. Thyrotropic cells c. Gonadotropic cells d. None of the above e. All of the above Answer: e The cells of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary) can be classified as acidophils or basophils depending on their affinity for acid or basic dyes, respectively. The acidophils are the somatotropic cells and the lactotropic cells. Thus, growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by acidophilic cells. The basophils are the gonadotropic cells, corticotropic cells and thyrotropic cells. Thus, the basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: There are two mnemonics to use when thinking of acidophils and basophils of the anterior pituitary. "GPA" (growth hormone and prolactin are secreted by the acidophils). "B-FLAT" (basophils secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH). 735. Which gland secretes insulin? a. Pancreas b. Thyroid c. Pineal gland d. Adrenal gland (cortex) e. Adrenal gland (medulla) Answer: a The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. The thyroid gland secretes the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. The cortex of the adrenal gland secretes a variety of corticosteroids. It secretes mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone), glucocorticoids (such as cortisol) and sex steroids. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medulla. 736. Which part the adrenal gland secretes sex steroids? a. Chromaffin cells b. Zona reticularis c. Zona glomerulosa d. Zona fasciculate e. None of the above Answer: b The adrenal gland is composed of the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The layers of the adrenal cortex, from outermost to innermost are: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. The respective principle products are: mineralocorticods, glucocorticoids, and sex steroids. The cells of the adrenal medulla are chromaffin cells. They secrete the catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: A mnemonic to remember the layers of the adrenal cortex and their respective products is "Go Find Rex; Make Good Sex" (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) (mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, sex steroids). 737. What is the classification of the pancreas? a. Mixed b. Endocrine
126
c. Exocrine d. Both endocrine and exocrine e. None of the above Answer: d The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ. 738. Where in the pancreas are islets of Langerhans most numerous? a. Head b. Body c. Tail d. Evenly distributed e. Depends on the individual Answer: c Islets of Langerhans are most numerous in the tail of the pancreas. 739. Which cells produce testosterone? a. Interstitial cells b. Leydig cells c. Sertoli cells d. Sustentacular cells e. Both a and b Answer: e Leydig cells produce testosterone. These are also called "interstitial cells" or "interstitial cells of Leydig". Sertoli cells are directly involved in spermatogenesis. They are also called "sustentacular cells" or "nurse cells". 740. How many seminiferous tubules are found in each testis of an average man? a. 4-6 b. 40-60 c. 400-600 d. 4000-6000 e. 40,000-60,000 Answer: c The average testis in an adult man has between 400 and 600 seminiferous tubules. 741. Which of the following are produced by the Leydig cells? a. Inhibin b. Androgen binding protein c. Testosterone d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: c Sertoli cells produce inhibin and androgen-binding protein. The interstitial cells of Leydig produce testosterone. 742. Which of the following is NOT considered part of the male genital duct system? a. Rete testis b. Tubuli recti c. Seminal vesicles d. Ductus deferens e. Ductus epididymidis Answer: c The male genital duct system contains: rete testes, tubuli recti, ductuli efferentes, ductus epididymidis, and ductus deferens. The male accessory glands contain the bulbourethral glands, seminal vesicles, and prostate. 743. What is the surface modification seen on the cells of the epididymis? a. Microvilli b. Stereocilia c. Cilia d. Keratinization e. Both a and b
Answer: b Microvilli are the finger like projections seen on the surface of some cells. The appearance of microvilli form what is also called the brush border or striated border. Stereocilia are very long microvilli. Stereocilia are seen in the epididymis and the hair cells of the ear. Cilia is the hair like surface modification seen on some epithelia. Cilia are made of microtubules. Keratinization is seen in the epidermis. Cells in the stratum corneum are essentially just bags of keratin. 744. What type of hormone is testosterone? a. Protein b. Amino acid chain c. Steroid d. Catecholamine e. None of the above Answer: c Hormones can have a variety of structures. Hormones which are proteins include insulin and prolactin. Peptide chains are short chains of amino acids. Examples of hormones which are peptide chains are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives. Steroid hormones include testosterone and estradiol. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines. 745. Which of the following is true? a. There is one corpus cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum b. There is one corpus cavernosa and two corpora spongiosum c. There are two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum d. There are two corpora cavernosa and two corpora spongiosum e. There are four corpora cavernosa and two corpora spongiosum Answer: c The corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum are erectile tissue. There are two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum. 746. What gland in the male is homologous to the greater vestibular gland in the female? a. Bartholin's gland b. Prostate gland c. Skene's gland d. Cowper's gland e. Brunner's gland Answer: d The prostate gland is found in males. Skene's glands are also called the lesser vestibular glands and are found in females. The bulbourethral glands are also called Cowper's glands. The bulbourethral glands are found in males and are homologous to the Bartholin's glands in females. Brunner's glands are found in the duodenum. 747. What is the most commonly seen type of epithelium in the prostate? a. Transitional b. Simple columnar c. Stratified squamous d. Simple squamous e. Simple cuboidal Answer: b The glandular epithelium of the prostate is most often simple columnar, however a variety of types can be found. 748. What type of epithelium lines the epididymis?
ANDIE ALBINO
127
a. Pseudostratified b. Simple columnar c. Stratified squamous d. Simple squamous e. Simple cuboidal Answer: a Pseudostratified epithelium lines the epididymis. 749. Which cells are directly involved in spermatogenesis? a. Interstitial cells b. Leydig cells c. Sertoli cells d. Sustentacular cells e. Both c and d Answer: e Leydig cells produce testosterone. These are also called "interstitial cells" or "interstitial cells of Leydig". Sertoli cells are directly involved in spermatogenesis. They are also called "sustentacular cells" or "nurse cells". 750. Which of the following are produced by the Sertoli cells? a. Inhibin b. Androgen binding protein c. Testosterone d. Both a and b e. All of the above Answer: d Sertoli cells produce inhibin and androgen-binding protein. The interstitial cells of Leydig produce testosterone. 751. Which of the following is NOT considered an accessory gland? a. Prostate b. Bulbourethral gland c. Seminal vesicles d. Ductus deferens e. None of the above Answer: d The male genital duct system contains: rete testes, tubuli recti, ductuli efferentes, ductus epididymidis, and ductus deferens. The male accessory glands contain the bulbourethral glands, seminal vesicles, and prostate. 752. What is another term for a bulbourethral gland? a. Bartholin's gland b. Prostate gland c. Skene's gland d. Cowper's gland e. Brunner's gland Answer: d Bartholin's glands are also called the greater vestibular glands. Bartholin's glands are found in females and are homologous to the bulbourethral glands in males. The prostate gland is found in males. Skene's glands are also called the lesser vestibular glands and are found in females. The bulbourethral glands are also called Cowper's glands. The bulbourethral glands are found in males and are homologous to the Bartholin's glands in females. Brunner's glands are found in the duodenum. 753. What are the spherical structures seen in some prostatic alveoli called? a. Psammoma bodies b. Corpora arenacea c. Hassall's corpuscles d. Prostatic concretions e. Pacinian corpuscles
ANDIE ALBINO
Answer: d Psammoma bodies are collections of calcium. It is derived from the Greek word "psammos", which means sand. Corpora arenacea refers to the calcifications seen in the pineal gland. Corpora arenacea is nicknamed "brain sand". Hassall's corpuscles are the ring like structures found in the thymus. The spherical structures seen in some prostatic alveoli are called prostatic concretions. Pacinian corpuscles are pressure receptors in the skin. 754. What type of epithelium lines the seminal vesicles? a. Pseudostratified b. Simple columnar c. Stratified squamous d. Simple squamous e. Simple cuboidal Answer: a Pseudostratified epithelium lines the seminal vesicles. 755. What type of epithelium lines the vas deferens? a. Pseudostratified b. Simple columnar c. Stratified squamous d. Simple squamous e. Simple cuboidal Answer: a Pseudostratified epithelium lines the vas deferens. 756. What type of gland composes the prostate? a. Simple straight tubular gland b. Simple coiled tubular gland c. Simple alveolar gland d. Compound tubular gland e. Compound tubuloalveolar gland A gland that has a duct that does not branch is called a simple gland. If the duct branches, it is referred to as a compound gland. If the the part of the gland which secretes elements is shaped like a tube, it is referred to as a tubular gland. If the ending of the tube is flasklike, it is tubuloalveoler. If the part of the gland which secretes elements is shaped like a flask, it is referred to as acinar or alveolar. The prostate is made of compound tuboloalveolar glands. 757. What is the stroma of the prostate? a. Loose irregular connective tissue b. Smooth muscle c. Fibromuscular d. Adipose tissue e. Dense irregular connective tissue Answer: c The glands of the prostate lie in a fibromuscular stroma. It is also referred to as a fibroelastic stroma. There are bundles of smooth muscle within dense irregular connective tissue. 758. How many layers of smooth muscle are in the vas deferens? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 Answer: c There are three layers of smooth muscle in the vas deferens. There is an inner longitudinal, a middle circular, and an outer longitudinal. 759. How many corpora cavernosa are there?
128
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 Answer: b The corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum are erectile tissue. There are two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The word "corpora" is plural; "corpus" is singular. It is derived from the Latin word meaning "body". 760. Which one of the following are the earliest cells of spermatogenesis? a. Primary spermatocytes b. Secondary spermatocytes c. Spermatids d. Spermatozoa e. Spermatogonia Answer: e The earliest cells of spermatogenesis are spermatogonia; these are primitive cells. The primary spermatocyte is derived from spermatogonia. This then develops into secondary spermatocytes . The secondary spermatocyte is haploid. These develop into spermatids. The mature sperm cell is spermatozoa. 761. Which cells are also called "nurse cells"? a. Interstitial cells b. Leydig cells c. Sertoli cells d. Sustentacular cells e. Both c and d Answer: e Leydig cells produce testosterone. These are also called "interstitial cells" or "interstitial cells of Leydig". Sertoli cells are directly involved in spermatogenesis. They are also called "sustentacular cells" or "nurse cells". 762. When do the testes descend into the scrotum? a. Fetal development b. Infancy c. Puberty d. Adulthood e. During arousal Answer: a The testes develop in the abdominal cavity. During fetal development, they descend to the scrotum. 763. Which is the largest accessory structure of the male reproductive system a. Epididymis b. Prostate c. Seminal vesicle d. Bulbourethral gland e. Cowper's gland Answer: b The prostate is the largest accessory structure of the male reproductive system. 764. What is the capsule that surrounds the testes? a. Tunica adventitia b. Tunica externa c. Tunica media d. Tunica intima e. Tunica albuginea The tunica albuginea is the thick capsule around each testis. 765. What is the "cap"at the anterior portion of a spermatazoon?
a. Head b. Tail c. Acrosome d. End piece e. Middle piece The acrosome is the "cap" at the anterior portion of a spermatozoon. 766. What is another term for the corpus cavernosum urethrae? a. Corpora cavernosa b. Corpus spongiosum c. Urethra d. Corpus cavernosum clitoridis e. Erectile tissue The corpus spongiosum is also called the corpus cavernosum urethrae. The corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum are erectile tissue. The corpus cavernosum clitoridis is in the female. The urethra is a muscular tube that runs from the bladder. It transports both urine and semen. 767. How many corpus spongiosum are there? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 Answer: a The corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum are erectile tissue. There are two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum. Histology hint from Sarah Bellham: The word "corpora" is plural; "corpus" is singular. It is derived from the Latin word meaning "body". 768. What is the mature sperm cell? a. Primary spermatocytes b. Secondary spermatocytes c. Spermatids d. Spermatozoa e. Spermatogonia Answer: d The earliest cells of spermatogenesis are spermatogonia; these are primitive cells. The primary spermatocyte is derived from spermatogonia. This then develops into secondary spermatocytes . The secondary spermatocyte is haploid. These develop into spermatids. The mature sperm cell is spermatozoa. 769. What are developing gametes called? a. Oogenesis b. Ovary c. Ovulation d. Oocyte e. Ova Answer: d The term for the production of gametes is called gametogenesis. Gametogenesis in the female is referred to as oogenesis. The ovary is the organ where gametogenesis (oogenesis) occurs. Ovulation is the release of an oocyte and occurs every 28-30 days. The developing gametes are called oocytes. The mature gamete is an ova. 770. What is the inner part of the ovary? a. Follicle b. Germinal epithelium c. Medulla d. Tunica albuginea e. Cortex Answer: c
ANDIE ALBINO
129
The ovary is covered with germinal epithelium. Underneath the germinal epithelium is connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The outer region of the ovary is called the cortex. The inner region of the ovary is called the medulla. The ovarian follicle contains the oocyte. Note from Sarah Bellham: The outer region of some other organs is also sometimes called a cortex. The inner/middle region of some other organs is also sometimes called a medulla. 771. Which stage of the follicle is arrested in prophase? a. Primordial follicle b. Primary follicle c. Secondary follicle d. Mature follicle e. Graffian follicle Answer: a A primordial follicle is a primary oocyte in the outer region of the cortex. It is arrested in the first meiotic prophase. It is surrounded by flattened follicular epithelial cells. The primary follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal and the oocyte becomes bigger. The presence of the antrum is a characteristic of a secondary follicle. A follicle at this stage is also called an "antral follicle". The mature follicle is also called the Graffian follicle. 772. What is the cavity within a secondary follicle? a. Graffian follicle b. Theca folliculi c. Granulosa cells d. Zona pellucida e. Antrum Answer: e The follicle which is ovulated is the Graffian follicle. The connective tissue layer around the primary follicle is the theca folliculi. The follicular cells are granulosa cells. The acidophilic glycoprotein coat surrounding the oocyte is the zona pellucida. A cavity within the follicle is the antrum. 773. During the first week to 10 days, what is the main hormone which stimulates the growth of the follicles? a. FSH b. LH c. HCG d. Estrogen e. Progesterone Answer: a During the first week to 10 days, FSH is the main hormone which stimulates the growth of the follicles. Ovulation is triggered by a dramatic increase in LH. During a pregnancy, HCG is the hormone which maintains the corpus luteum. 774. What is the female organ called where gametogenesis occurs? a. Oogenesis b. Ovary c. Ovulation d. Oocyte e. Ova Answer: b The term for the production of gametes is called gametogenesis. Gametogenesis in the female is referred to as oogenesis. The ovary is the organ where gametogenesis (oogenesis) occurs. Ovulation is the release of an oocyte and occurs every 28-30 days. The developing gametes are called oocytes. The mature gamete is an ova.
ANDIE ALBINO
775. Which stage of the follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal? a. Primordial follicle b. Primary follicle c. Secondary follicle d. Mature follicle e. Graffian follicle Answer: b A primordial follicle is a primary oocyte in the outer region of the cortex. It is arrested in the first meiotic prophase. It is surrounded by flattened follicular epithelial cells. The primary follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal and the oocyte becomes bigger. The presence of the antrum is a characteristic of a secondary follicle. A follicle at this stage is also called an "antral follicle". The mature follicle is also called the Graffian follicle. 776. What is ovulated? a. Graffian follicle b. Theca folliculi c. Granulosa cells d. Zona pellucida e. Antrum Answer: a The follicle which is ovulated is the Graffian follicle. The connective tissue layer around the primary follicle is the theca folliculi. The follicular cells are granulosa cells. The acidophilic glycoprotein coat surrounding the oocyte is the zona pellucida. A cavity within the follicle is the antrum. 777. What is the outer part of the ovary? a. Follicle b. Germinal epithelium c. Medulla d. Tunica albuginea e. Cortex Answer: e The ovary is covered with germinal epithelium. Underneath the germinal epithelium is connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The outer region of the ovary is called the cortex. The inner region of the ovary is called the medulla. The ovarian follicle contains the oocyte. Note from Sarah Bellham: The outer region of some other organs is also sometimes called a cortex. The inner/middle region of some other organs is also sometimes called a medulla. 778. During a pregnancy, which hormone which maintains the corpus luteum? a. FSH b. LH c. HCG d. Estrogen e. Progesterone Answer: c During the first week to 10 days, FSH is the main hormone which stimulates the growth of the follicles. Ovulation is triggered by a dramatic increase in LH. During a pregnancy, HCG is the hormone which maintains the corpus luteum 779. Which structure contains the oocyte? a. Follicle b. Germinal epithelium c. Medulla d. Tunica albuginea e. Cortex
130
Answer: a The ovary is covered with germinal epithelium. Underneath the germinal epithelium is connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The outer region of the ovary is called the cortex. The inner region of the ovary is called the medulla. The ovarian follicle contains the oocyte. Note from Sarah Bellham: The outer region of some other organs is also sometimes called a cortex. The inner/middle region of some other organs is also sometimes called a medulla. 780. Which follicular stage is also called an antral follicle? a. Primordial follicle b. Primary follicle c. Secondary follicle d. Mature follicle e. Graffian follicle Answer: c A primordial follicle is a primary oocyte in the outer region of the cortex. It is arrested in the first meiotic prophase. It is surrounded by flattened follicular epithelial cells. The primary follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal and the oocyte becomes bigger. The presence of the antrum is a characteristic of a secondary follicle. A follicle at this stage is also called an "antral follicle". The mature follicle is also called the Graffian follicle. 781. The appearance of the antrum is a characteristic of which stage of follicular development? a. Primordial follicle b. Primary follicle c. Secondary follicle d. Mature follicle e. Graffian follicle Answer: c A primordial follicle is a primary oocyte in the outer region of the cortex. It is arrested in the first meiotic prophase. It is surrounded by flattened follicular epithelial cells. The primary follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal and the oocyte becomes bigger. The presence of the antrum is a characteristic of a secondary follicle. A follicle at this stage is also called an "antral follicle". The mature follicle is also called the Graffian follicle. 782. What is the acidophilic glycoprotein coat which surrounds the oocyte? a. Graffian follicle b. Theca folliculi c. Granulosa cells d. Zona pellucida e. Antrum Answer: d The follicle which is ovulated is the Graffian follicle. The connective tissue layer around the primary follicle is the theca folliculi. The follicular cells are granulosa cells. The acidophilic glycoprotein coat surrounding the oocyte is the zona pellucida. A cavity within the follicle is the antrum. 783. What tissue surrounds the ovary? a. Follicle b. Germinal epithelium c. Medulla d. Tunica albuginea e. Cortex Answer: b
The ovary is covered with germinal epithelium. Underneath the germinal epithelium is connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The outer region of the ovary is called the cortex. The inner region of the ovary is called the medulla. The ovarian follicle contains the oocyte. Note from Sarah Bellham: The outer region of some other organs is also sometimes called a cortex. The inner/middle region of some other organs is also sometimes called a medulla. 784. What is a mature gamete called? a. Oogenesis b. Ovary c. Ovulation d. Oocyte e. Ova Answer: e The term for the production of gametes is called gametogenesis. Gametogenesis in the female is referred to as oogenesis. The ovary is the organ where gametogenesis (oogenesis) occurs. Ovulation is the release of an oocyte and occurs every 28-30 days. The developing gametes are called oocytes. The mature gamete is an ova. 785. Which stage of the follicle is characterized by a surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells? a. Primordial follicle b. Primary follicle c. Secondary follicle d. Mature follicle e. Graffian follicle Answer: a A primordial follicle is a primary oocyte in the outer region of the cortex. It is arrested in the first meiotic prophase. It is surrounded by flattened follicular epithelial cells. The primary follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal and the oocyte becomes bigger. The presence of the antrum is a characteristic of a secondary follicle. A follicle at this stage is also called an "antral follicle". The mature follicle is also called the Graffian follicle. 786. What is another term for the mature follicle? a. Primordial follicle b. Primary follicle c. Secondary follicle d. Antral follicle e. Graffian follicle Answer: e A primordial follicle is a primary oocyte in the outer region of the cortex. It is arrested in the first meiotic prophase. It is surrounded by flattened follicular epithelial cells. The primary follicle is marked by the surrounding of flattened (squamous) follicular cells becoming cuboidal and the oocyte becomes bigger. The presence of the antrum is a characteristic of a secondary follicle. A follicle at this stage is also called an "antral follicle". The mature follicle is also called the Graffian follicle. 787. What occurs cyclically in a female? a. Oogenesis b. Ovary c. Ovulation d. Oocyte e. Ova Answer: c
ANDIE ALBINO
131
The term for the production of gametes is called gametogenesis. Gametogenesis in the female is referred to as oogenesis. The ovary is the organ where gametogenesis (oogenesis) occurs. Ovulation is the release of an oocyte and occurs every 28-30 days. The developing gametes are called oocytes. The mature gamete is an ova. 788. What is the connective tissue layer around the primary follicle? a. Graffian follicle b. Theca folliculi c. Granulosa cells d. Zona pellucida e. Antrum Answer: b The follicle which is ovulated is the Graffian follicle. The connective tissue layer around the primary follicle is the theca folliculi. The follicular cells are granulosa cells. The acidophilic glycoprotein coat surrounding the oocyte is the zona pellucida. A cavity within the follicle is the antrum. 789. Ovulation is triggered by a dramatic increase in which hormone? a. FSH b. LH c. HCG d. Estrogen e. Progesterone Answer: b During the first week to 10 days, FSH is the main hormone which stimulates the growth of the follicles. Ovulation is triggered by a dramatic increase in LH. During a pregnancy, HCG is the hormone which maintains the corpus luteum. 790. What is the connective tissue which surrounds the ovary? a. Follicle b. Germinal epithelium c. Medulla d. Tunica albuginea e. Cortex Answer: d The ovary is covered with germinal epithelium. Underneath the germinal epithelium is connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The outer region of the ovary is called the cortex. The inner region of the ovary is called the medulla. The ovarian follicle contains the oocyte. Note from Sarah Bellham: The outer region of some other organs is also sometimes called a cortex. The inner/middle region of some other organs is also sometimes called a medulla. 791. In the female, what is the correct term for the production of gametes called? a. Oogenesis b. Ovary c. Ovulation d. Oocyte e. Ova Answer: a The term for the production of gametes is called gametogenesis. Gametogenesis in the female is referred to as oogenesis. The ovary is the organ where gametogenesis (oogenesis) occurs. Ovulation is the release of an oocyte and occurs every 28-30 days. The developing gametes are called oocytes. The mature gamete is an ova. 792. What are the follicular cells? a. Graffian follicle
ANDIE ALBINO
b. Theca folliculi c. Granulosa cells d. Zona pellucida e. Antrum Answer: c The follicle which is ovulated is the Graffian follicle. The connective tissue layer around the primary follicle is the theca folliculi. The follicular cells are granulosa cells. The acidophilic glycoprotein coat surrounding the oocyte is the zona pellucida. A cavity within the follicle is the antrum.
You might also like
- Phase I Handbook - MBBS Programme - University of BotswanaDocument43 pagesPhase I Handbook - MBBS Programme - University of BotswanaNil NilNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonics Memory HacksDocument7 pagesMedical Mnemonics Memory HacksHaseebUl haqNo ratings yet
- Bates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th EditionDocument9 pagesBates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th Editionmanes0% (1)
- 7 RespirationDocument15 pages7 RespirationCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of MD General MedicineDocument5 pagesSyllabus of MD General Medicine2shubhoNo ratings yet
- TREATMENTS FOR ANAEMIADocument51 pagesTREATMENTS FOR ANAEMIADrShahid Sahito100% (1)
- Medicosis Perfectionalis Clinical Vignettes Bleeding (FREE SAMPLE)Document7 pagesMedicosis Perfectionalis Clinical Vignettes Bleeding (FREE SAMPLE)Rocky Bhai100% (1)
- Heme Quiz 1-3Document14 pagesHeme Quiz 1-3Søren KierkegaardNo ratings yet
- Haemolysis in G6PD Deficiency and Heinz BodiesDocument69 pagesHaemolysis in G6PD Deficiency and Heinz BodiesIdrissa ContehNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument17 pagesMCQBethelhem BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Thesis of Dr. AKM Maruf Raza PDFDocument95 pagesThesis of Dr. AKM Maruf Raza PDFMaruf Raza DarubagiNo ratings yet
- Professionalism in Surgery QuizDocument29 pagesProfessionalism in Surgery QuizRichard100% (1)
- Yu - Git - Emb 2Document56 pagesYu - Git - Emb 2gtaha80No ratings yet
- Exam-Oriented Review in Physiology Second EditionDocument1 pageExam-Oriented Review in Physiology Second EditionGowtham G Dinesh0% (1)
- Chapter 1. History and Physical Examination - Art and ScienceDocument3 pagesChapter 1. History and Physical Examination - Art and SciencecarolineNo ratings yet
- Medical QuestionsDocument13 pagesMedical QuestionsHannah Lei100% (1)
- Patho Test 3Document7 pagesPatho Test 3Stephanie 'Sveen' HansenNo ratings yet
- Physiology Acid QuizDocument5 pagesPhysiology Acid QuizRavi AminNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury Mcqs ExplainedDocument5 pagesCell Injury Mcqs ExplainedPrahulNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Study GuideDocument13 pagesRespiratory System Study GuidebisnumNo ratings yet
- M-1 MCQDocument88 pagesM-1 MCQFrt TrfNo ratings yet
- Modular CG NightDocument5 pagesModular CG NightGenie SorianoNo ratings yet
- MCQ on Antibiotics and their Mode of ActionDocument3 pagesMCQ on Antibiotics and their Mode of ActionMinh AnhNo ratings yet
- Review Questions For: Physiology II-1Document26 pagesReview Questions For: Physiology II-1ngphm70% (1)
- Web Path AllDocument116 pagesWeb Path AllFYM0% (1)
- Gross Anatomy Practice Test #1Document4 pagesGross Anatomy Practice Test #1Medicine4theMassesNo ratings yet
- Bio StatisticsDocument101 pagesBio StatisticshferdjalNo ratings yet
- GI PathoDocument20 pagesGI Pathojutah2013No ratings yet
- Medical History Questions ExplainedDocument10 pagesMedical History Questions ExplainedAlex LxNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics Quiz 14 - 20Document12 pagesPharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics Quiz 14 - 20Killer VNo ratings yet
- 2 K 23 Mbbs CurriculumDocument300 pages2 K 23 Mbbs CurriculumAbdullah Nayyar100% (1)
- 300 Mcqs Waqar YounisDocument47 pages300 Mcqs Waqar Younishusnain nadeem100% (1)
- Epistaxis Thesis Lekshmi DEVI - 045602Document27 pagesEpistaxis Thesis Lekshmi DEVI - 045602Bhavya R Krishnan100% (1)
- Hematology & Lymphoid System Study Guide - Y1 2025Document43 pagesHematology & Lymphoid System Study Guide - Y1 2025Wahaj Mujahid100% (1)
- Physical Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesPhysical Examination of The Respiratory SystemMark CatabijanNo ratings yet
- EYE PATHOLOGIES REVEALEDDocument11 pagesEYE PATHOLOGIES REVEALEDDranreb Berylle MasangkayNo ratings yet
- Final General Surgery (1) - 230122 - 192353Document49 pagesFinal General Surgery (1) - 230122 - 192353Lika BukhaidzeNo ratings yet
- MCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First ComDocument74 pagesMCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First Commaisara10No ratings yet
- PSM 2nd With AnswerDocument24 pagesPSM 2nd With AnswerAshiq Syedali PichiVilaakamNo ratings yet
- FEBNM 2012 Doc06 MCQ ExamplesDocument12 pagesFEBNM 2012 Doc06 MCQ ExamplesTahir Bhat100% (1)
- Oxford McqsDocument15 pagesOxford McqsaliaaNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument11 pagesMicroSuman MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Mcq,Quiz هستو الترم الاولDocument74 pagesMcq,Quiz هستو الترم الاولMahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Haematology LastDocument65 pagesHaematology LastficocNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument385 pagesFetal DevelopmentManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument4 pagesMCQEliza SparkNo ratings yet
- Class Notes On Questionnaires For Pharmacology in The Gastrointestinal TractDocument12 pagesClass Notes On Questionnaires For Pharmacology in The Gastrointestinal TractMarqxczNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology Matching Terms and ActivitiesDocument4 pagesEpidemiology Matching Terms and Activitiesazkha_knowles3279No ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Notes - Mucosal ImmunityDocument5 pagesLecture 19 Notes - Mucosal ImmunityAlbert Mao LiNo ratings yet
- 200 PSM Questions Solved by DR AshwaniDocument16 pages200 PSM Questions Solved by DR AshwaniShaaron Sky SonaNo ratings yet
- Mbbs Question BankDocument38 pagesMbbs Question BankHappy MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- My Loving Parents and Teachers Medical NotesDocument38 pagesMy Loving Parents and Teachers Medical NotesGoL Di100% (1)
- Gestroresectional SyndromesDocument18 pagesGestroresectional SyndromesAna CotomanNo ratings yet
- Pharm Resp Mcqs PDFDocument8 pagesPharm Resp Mcqs PDFVikashgtmNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck QuestionsDocument2 pagesHead and Neck QuestionsPulkitNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Musculoskeletal Module: 1 Professional MBBS (Session 2018-19)Document42 pagesStudy Guide Musculoskeletal Module: 1 Professional MBBS (Session 2018-19)Shariq KhattakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 DNA Fingerprinting and Forensic AnalysisDocument13 pagesChapter 8 DNA Fingerprinting and Forensic AnalysisQais Bani HaniNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesFrom EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practice of Pharmacology for AnaesthetistsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practice of Pharmacology for AnaesthetistsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CorneaDocument65 pagesCorneaAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Matina Crossing PRA 2010Document85 pagesMatina Crossing PRA 2010Andy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Handout in Health ManagementDocument24 pagesHandout in Health ManagementAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cornea JaimeDocument48 pagesCornea JaimeAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- AgeDocument26 pagesAgeAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- AnesDocument51 pagesAnesAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation OBDocument36 pagesCase Presentation OBAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Surgery PresDocument96 pagesSurgery PresAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Freq GenDocument5 pagesFreq GenAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- High Altitude PhysiologyDocument4 pagesHigh Altitude PhysiologyAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- As Per RequestDocument1 pageAs Per RequestAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope PartsDocument91 pagesCompound Microscope PartsAndy Alvarez100% (1)
- DigestionDocument1 pageDigestionAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- DKA Electrolyte AbnormalitiesDocument1 pageDKA Electrolyte AbnormalitiesAndy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CH10 133-146 PDFDocument14 pagesCH10 133-146 PDFNexi anessaNo ratings yet
- Most Important Topics of BiologyDocument5 pagesMost Important Topics of BiologyAshraf AliNo ratings yet
- Gizmo Cell Structure FormDocument3 pagesGizmo Cell Structure FormDeyanat AliNo ratings yet
- Answers: Biology 9744/03Document8 pagesAnswers: Biology 9744/03Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Biochemistry of MetabolismDocument47 pagesGlycolysis: Biochemistry of MetabolismDozdiNo ratings yet
- Blood LecturesDocument128 pagesBlood LecturessrhrenaissanceNo ratings yet
- Liver Fibrosis Causes and Methods of Assessment ADocument11 pagesLiver Fibrosis Causes and Methods of Assessment AmichaelNo ratings yet
- Anti-FTO Antibody (EPR6894) Ab126605: 6 ImagesDocument4 pagesAnti-FTO Antibody (EPR6894) Ab126605: 6 Imageshorace35No ratings yet
- 12 3 PWPT PDFDocument22 pages12 3 PWPT PDFapi-262378640No ratings yet
- Anatrace Detergents Booklet FINALDocument12 pagesAnatrace Detergents Booklet FINALjfeiwgNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Quarter - 3 - Cluster - o - G11 - Stem - Genbio1drrDocument15 pagesModule 2 - Quarter - 3 - Cluster - o - G11 - Stem - Genbio1drrmery rose ortizNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Document25 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Dewi SallehNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Is The Basis of Reproduction For Every OrganismDocument3 pagesCell Division Is The Basis of Reproduction For Every OrganismAlliah MendozaNo ratings yet
- Utility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04Document8 pagesUtility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04u77No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biochemistry and The Organization in CellsDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Biochemistry and The Organization in Cellsjimeneztrishanne75% (4)
- Lymphatic System and Immunity: Student Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesLymphatic System and Immunity: Student Learning Outcomeslily1liang-1No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Aqa 1Document71 pagesBiological Molecules Aqa 1aminabNo ratings yet
- SLK-Science-Grade-8-Q4W2Document24 pagesSLK-Science-Grade-8-Q4W2Ellen QuiseoNo ratings yet
- MOLECULAR BASIS OF CANCERDocument29 pagesMOLECULAR BASIS OF CANCERdian.esterinaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Antigen-Specific T Cell Enrichment (Rapid ARTE) - All Protocols - Applications - Miltenyi Biotec - DeutschlandDocument11 pagesRapid Antigen-Specific T Cell Enrichment (Rapid ARTE) - All Protocols - Applications - Miltenyi Biotec - Deutschlandzixu wangNo ratings yet
- Bais Manish DVM PHD Nov 23sDocument3 pagesBais Manish DVM PHD Nov 23smanish.bais114017No ratings yet
- Bio 4212examDocument5 pagesBio 4212examAsheNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Small Template Class FileDocument5 pagesCambridge Small Template Class FileFresh Prince Of NigeriaNo ratings yet
- Science Alive - Group 4 - Louisa Choi Ambrose Leung Karen Lee Patrick Gale Clancy SteainsDocument23 pagesScience Alive - Group 4 - Louisa Choi Ambrose Leung Karen Lee Patrick Gale Clancy Steainsapi-347649201No ratings yet
- Introduction To VirusesDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Virusesyudith novidaNo ratings yet
- Expression Pattern of S1R MRNA and Protein in Mammalian Retina - Ola2001Document16 pagesExpression Pattern of S1R MRNA and Protein in Mammalian Retina - Ola2001nienminhNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Saliva: DR: Abou Sree EllethyDocument16 pagesBiochemistry of Saliva: DR: Abou Sree Ellethylethy2000No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Test - CellsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Test - CellsAndrae GenusNo ratings yet
- Pre AssessmentDocument3 pagesPre Assessmentapi-261786434No ratings yet
- 1.02 General Pathology - Cellular Pathology Part 1 - Dr. Abelardo AleraDocument9 pages1.02 General Pathology - Cellular Pathology Part 1 - Dr. Abelardo AleraCherry RahimaNo ratings yet