Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan - CAP-MR
Uploaded by
Carmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan - CAP-MR
Uploaded by
Carmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeCopyright:
Available Formats
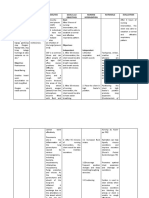
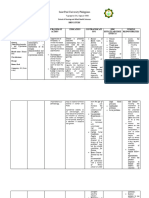
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Subjective: Impaired gas Inuubo ako at exchange nahihirapan related to akong inflammatory makahinga.
process in the lung parenchyma Mas and alveoli as nakakahinga ako ng maayos manifested by kapag ganitong restlessness. may Oxygen. Kapag wala, ang hirap talaga huminga at saka matanda na rin ako. Objective: Restlessness Nasal flaring Crackles heard upon auscultation on both lung filed Oxygen via nasal cannula
CUES
ANALYSIS
Communityacquired pneumo nia (CAP) is a disease in which individuals who have not recently been hospitalized develop an infection of the lungs (pneum Objectives: onia). Independent CAP is a common 1. After 30 minutes illness and can of intervention, the affect people of client would be able all ages. CAP to have normal often causes breath respiration problems like and breath sounds difficulty in within 20 minutes. breathing, fever, chest pains, and a cough. CAP occurs because the areas of the lung which 2. After 30 minutes absorb oxygen of nursing (alveoli) from the intervention, the client would be able atmosphere become filled to have easier with fluid and breathing. cannot work
GOALS and OBJECTIVES Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client will be able to establish a normal and effective respiratory pattern.
NURSING INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client was able to establish a normal and effective respiratory pattern.
Independent 1.Monitor respiration breath sounds
Tachypnea, stridor, and crackles or wheezes are indicative to repiratory distress and/or accumulation of fluid (Nurse's Pocket Guide by Doenges et al pp.78)
2. Place the client in Positioning the high fowler s client in high position. fowler's position promote lung expansion. (Fundamentals of Nursing by Kozier
effectively Pneumonia also is the inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by various microorganisms, including bacteria, mycobacteria, chlamydiae, mycoplasma, fungi, parasites and viruses. As the lung parenchyma and alveoli of the lungs are inflamed it impairs gas exchange due to the alterations in the alveoli which is the site for actual gas exchange.
pp.789)
3. After 45 minutes 3.1 Increased fluid Hydration can help of nursing intake. liquefy viscous intervention, the secretions and client would be able improve secretion to mobilize clearance. secretions. (Nurse's Pocket Guide Doenges.79)
3.2Encourage frequent position changes and deep breathing/coughing exercises.
Promotes optimal chest expansion and drainage of secretions.
3.3 Suctioning
Suction is used to clear airway when excessive or viscous secretions are blocking the airway or client is unable to cough effectively. (Nurse's Pocket Guide by Doenges et al pp.78)
3.4 Perform Chest Physiotherapy.
Chest Physiotherapy
is
used to mechanically dislodge tenacious secretions from the bronchial walls. (Nursing Care Management Skill Manual pp.60)
Dependent: 4. After 15 minutes of nursing intervention, the client would be able to take the medications and treatment prescribed by the physician within the order time and date of administration.
Dependent: 4.1 Administer bronchodilators as ordered by the physician.
Bronchodilators are antiinflammtory drugs, excpectorants and cough suppressants that may treat respiratory problems. (Fundamentals of Nursing by Kozier pp.1369)
4.2 Perform oxygen therapy or administer oxygen by nasal cannula.
Administration of oxygen to client to prevent or relieve hypoxia. (Nursing CareManagement Skill Manual pp.55)
Interdependent: 5. After 15 minutes 5.1 Instruct relatives of nursing to perform proper intervention, the nebulization client's relatives would be able to perform proper humidification and administer medication via nebulization.
Nebulization is performed to deliver finer mist at a faster rate to moisten membrane. (Nursing CareManagement Skill Manual pp.69)
You might also like
- Nursing Cheat LabValuesDocument4 pagesNursing Cheat LabValuessasukenoneko100% (5)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Oxygen TherapyDocument20 pagesOxygen TherapyPaul Gabriel CasquejoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Flow Rate CalculationDocument7 pagesIntravenous Flow Rate CalculationCarmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Mbdqor345235235 PDFDocument482 pagesMbdqor345235235 PDFM HaidarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilator CareDocument9 pagesMechanical Ventilator CareAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- NCP For Community Acquired PnuemoniaDocument7 pagesNCP For Community Acquired PnuemoniaAshley Gaton Alindogan100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- Gas GangreneDocument21 pagesGas GangreneSyaIra SamatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan:: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/18/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. IsananDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan:: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/18/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. IsananSofia LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Community Acquired PneumoniaEngely Mercader100% (1)
- NCP - Patient With Chest TubeDocument2 pagesNCP - Patient With Chest TubeSelwynVillamorPatente0% (1)
- NCP HemoDocument2 pagesNCP HemoJigs HechNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Nebulization Therapy Guide for Respiratory ConditionsDocument5 pagesNebulization Therapy Guide for Respiratory ConditionsTamil Villardo100% (2)
- Drug Study FluimucilDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluimucilJemina Rafanan Racadio0% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Introduction To Nursing PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 01 Introduction To Nursing PDFludwigs43100% (1)
- NCP PCAP CDocument4 pagesNCP PCAP CRio Bonifacio100% (2)
- Hemodialysis NCPDocument2 pagesHemodialysis NCPAfia Tawiah100% (1)
- Time Chart: Data Action ResponseDocument2 pagesTime Chart: Data Action ResponseAziil Liiza100% (2)
- NCP TBDocument6 pagesNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Asthma treatment steroid receptorDocument3 pagesAsthma treatment steroid receptorMuhammad Abubakar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceKenj Pereña100% (1)
- Effective airway clearance for pneumonia patientDocument5 pagesEffective airway clearance for pneumonia patientCamille Serrano100% (1)
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocument4 pagesGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Cap NCPDocument2 pagesCap NCPkyshb100% (2)
- St. Anthony's Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's Nursing Care PlanKristine Young100% (1)
- Risk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageRisk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_sane100% (1)
- History of SurgeryDocument35 pagesHistory of SurgeryImolaBakosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Community Acquired Pneumoniaderic92% (50)
- DuaventDocument2 pagesDuaventKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientDocument4 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Respiratory ConditionsDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for Respiratory ConditionsJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cap NCPDocument6 pagesCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- NCP For Ineffective Airway Clearance.Document2 pagesNCP For Ineffective Airway Clearance.Vanessa Joy Contreras100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For PcapDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For PcapMadsNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia_garonNo ratings yet
- NCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceJennelyn BayleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearancerozj0750% (2)
- NCP of MGH PatientDocument2 pagesNCP of MGH PatientMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans in 40 CharactersDocument1 pagePneumonia Nursing Care Plans in 40 Charactersjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceMary Joyce Limoico100% (1)
- Caring for an Elderly Patient with DepressionDocument2 pagesCaring for an Elderly Patient with DepressionSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearancepsengsonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Care: Ronald P. Mlcak, Oscar E. Suman, Linda E. Sousse, and David N. HerndonDocument12 pagesRespiratory Care: Ronald P. Mlcak, Oscar E. Suman, Linda E. Sousse, and David N. HerndonDavid ReyesNo ratings yet
- Abstrak 090014.id - enDocument1 pageAbstrak 090014.id - enIna OrengNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Chest Physiotherapy and Other Pulmonary Treatment ModalitiesDocument9 pagesChest Physiotherapy and Other Pulmonary Treatment ModalitiesJayferson SalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedDocument3 pagesNursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedNiña AngNo ratings yet
- 2 NCPDocument2 pages2 NCPJohn CenasNo ratings yet
- Demonstration On Chest Physiotherapy DefinitionDocument3 pagesDemonstration On Chest Physiotherapy Definitiondileep0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document1 pageNursing Care Plan 2JOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- 11 Mechanical Ventilation & Endotracheal Intubation Nursing Care Plans and Management - NurseslabsDocument55 pages11 Mechanical Ventilation & Endotracheal Intubation Nursing Care Plans and Management - NurseslabsCarissa EstradaNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea and NebulizationDocument42 pagesDyspnea and NebulizationHema AnkamreddyNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Effective Airway Clearance Nursing DiagnosisDocument30 pagesEffective Airway Clearance Nursing DiagnosisReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ValuesDocument2 pagesLaboratory ValuesCarmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ValuesDocument2 pagesLaboratory ValuesCarmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument1 pageEssential Newborn CareCarmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Normal VSDocument1 pageNormal VSCarmela Mabel Ansay PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Procedure Sick Bay 2017Document6 pagesProcedure Sick Bay 2017Syed FareedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument6 pagesChapter 39 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersMichael BoadoNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument9 pagesDaftar Pustakaaajeng ftnyNo ratings yet
- Essay Ingles 2Document3 pagesEssay Ingles 2Javi LiuNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article 2922Document4 pages2021 Article 2922AnirisulNo ratings yet
- Ambulance ServiceDocument9 pagesAmbulance ServicedennymxNo ratings yet
- Notice To Kettle Falls SDDocument2 pagesNotice To Kettle Falls SDErin RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Katie's story of recovery from anorexiaDocument8 pagesKatie's story of recovery from anorexiaAinjhel CalaraNo ratings yet
- CPD Book and Patient PictureDocument6 pagesCPD Book and Patient PicturePriyaNo ratings yet
- Burn WoundsDocument14 pagesBurn WoundsRuxandra BadiuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxants and Neuromuscular Blocking AgentsDocument7 pagesSkeletal Muscle Relaxants and Neuromuscular Blocking AgentsYanyan PanesNo ratings yet
- SOP For Ground Crossing On Covid-19Document6 pagesSOP For Ground Crossing On Covid-19Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Eric Thorhauer CVDocument7 pagesEric Thorhauer CVapi-251923314No ratings yet
- WSO Global Stroke Fact SheetDocument15 pagesWSO Global Stroke Fact SheetPentolNo ratings yet
- Diane Pills Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDiane Pills Drug StudyDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- 1 Laporan Pengeluaran Obat Dan Alkes Depyan 28 SEPTEMBER 2019Document18 pages1 Laporan Pengeluaran Obat Dan Alkes Depyan 28 SEPTEMBER 2019Indah SetyowatiNo ratings yet
- Manual Surgical Safety Checklist 1st EditionDocument28 pagesManual Surgical Safety Checklist 1st EditionJuandri Pia TorocozzickNo ratings yet
- HIV 12 Stat Pak Dipstick Product Packet EnglishDocument6 pagesHIV 12 Stat Pak Dipstick Product Packet EnglishSagkyNo ratings yet
- 香港脊醫 Hong Kong Chiropractors May 2018Document18 pages香港脊醫 Hong Kong Chiropractors May 2018CDAHKNo ratings yet
- Health HistoryDocument4 pagesHealth Historyapi-454903860No ratings yet
- BANSUANRDRECORDDocument4 pagesBANSUANRDRECORDclint xavier odangoNo ratings yet
- 214 Dominican Republic Fact SheetDocument2 pages214 Dominican Republic Fact Sheetfedemoncada89No ratings yet
- 22 PciDocument19 pages22 PciSoham MAITYNo ratings yet
- Nurse'S Notes: Date-Shift Focus Data - Action - ResponseDocument5 pagesNurse'S Notes: Date-Shift Focus Data - Action - ResponseRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet