Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP For Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
Uploaded by
Kim Celeste MatulacOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP For Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
Uploaded by
Kim Celeste MatulacCopyright:
Available Formats
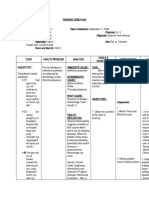
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES NURSING DIAGNOSIS OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: Natatakotakos asakitko as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Poor eye contact Restlessness Increased weariness Voice quivering Facial flushing Increased pulse rate Decreased blood pressure VS: T- 38 C P- 102 bpm R- 26 cpm
BP- 90/60 mmHg
Anxiety Related to Change in Health Status DEFINITION: Vague uneasy feeling of discomfort or dread accompanied by an autonomic response (the source often nonspecific or unknown to the individual); a feeling of apprehension cause by anticipation of danger. It is an altering signal that warns of impending danger and enables the individual to take measures.
At the end of my shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Appear relax and report anxiety is reduced to a manageable level. 2. Verbalize awareness of feeling of anxiety. 3. Identify healthy ways to deal with and express anxiety. 4. Demonstrate problem solving skills. 5. Use resources/ supportsystems effectively.
INDEPENDENT: Monitor vital signs To identify physical responses associated with both medical and emotional conditions To which can point the clients level of anxiety (mild, moderate, severe, panic) These medications can heighten feelings and sense of anxiety
1. Goal met as evidenced by appearance of relaxation and report of anxiety is reduced to a manageable level. 2. Goal met as evidenced by verbalized awareness of feelings of anxiety. 3. Goal partially met as evidenced by identified healthy ways to deal with an expressed anxiety. 4. Goal partially met as evidenced by demonstrated some problem solving skills.
Observe behavior
Determine current prescribed medications and recent drug history of current prescribed or over-the-counter medications Review coping skills used in the past Be aware of defense mechanism being used
To determine those that might be helpful in current circumstances To identify if there is interference that deals with the clients ability
REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
Provide accurate information about the situation Accept client as is
Helps client to identify what is based The client may need to be where she at this point in time, such as in denial after receiving the diagnosis of a terminal illness
5. Goal partially met. Used resources/sup port systems effectively.
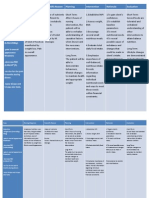
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
SUBJECTIVE: Hindi akomakatulog ngmaayos as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Restlessness Irritability VS: T- 39.2 C P- 97 bpm R- 23 cpm
BP- 90/60 mmHg
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Impaired Comfort related to be developed DEFINITION: Perceived lack of ease, relief and transcendence in physical, psychospiritual, environmental and social dimensions. REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Engage in behaviors or lifestyle changes to increase level of ease. 2. Verbalize sense of comfort or contentment. 3. Participate in desirable and realistic healthseeking behaviors.
INDEPENDENT: Determine locus of control Determine the type of discomfort client is experiencing such as physical pain, feeling of discontent, lack of ease in social settings or inability to rise ones problems or pain Discuss concerns with client and active listen to identify underlying issues Determine how client is managing pain and pain components Presence of external locus of control may hamper efforts to achieve sense of piece or contentment
1. Goal met as evidenced by engaged in behavior or lifestyle changes to increase level of ease. 2. Goal met as evidenced by verbalized sense of comfort or contentment. 3. Goal met as evidenced by participation in desirable and realistic healthseeking behaviors.
Helps to determine clients specific needs, ability to change own situation Lack of control may be related to issues, or emotions such as fear, loneliness, anxiety, noxious, stimuli, anger
Review knowledge base and note coping skills that had been used previously to change behavior/promote well-being Establish realistic activity goals with client Review medications or treatment regimen Provide age appropriate comfort measures
Brings these to clients awareness and promotes use in current situation Enhances commitment promoting optimal outcomes To determine possible changes or options to reduce side effects To provide nonpharmacologic pain management To promote physical stability
COLABORATIVE: Collaborate in treating or managing medical conditions involving oxygenation elimination, mobility, cognitive abilities, electrolyte balance, thermoregulation, hydration
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
SUBJECTIVE: Nilalagnatako as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Increase body temperature above normal range. Flushed skin; warm to touch Tachycardia Seizures T- 40.2 C P- 113 bpm R- 40 cpm
BP- 90/50 mmHg
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Hyperthermia related to illness DEFINITION: Body temperature elevated above normal range. REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. maintain core temperature within normal range 2. Identify underlying cause or contributing factors and importance of treatment, as well as sign and symptoms requiring further evaluative or intervention. 3. Demonstrate behaviors to monitor and promote normothermia 4. Be free of seizures activity
INTERVENTIONS
INDEPENDENT: Assess underlying cause Monitor vital signs Monitor respirations
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
1. Goal met as evidenced by maintained core temperature within normal range. 2. Goal met as evidenced byidentified underlying cause or contributing factors and importance of treatment, as well as sign and symptoms requiring further evaluative or intervention. 3. Goal met as evidenced by demonstrated behaviors to monitor and promote normothermia .
Monitor and record all sources of fluid loss such as urine vomiting and diarrhea; wounds, fistulas; and insensible losses Maintain bed rest
Monitor ventilation may initially be present, but ventilatoryeffo rt may eventually be impaired by seizures, hyper metabolic state. To reduce metabolic demands and consumption
To support circulating volume and tissue perfusion
Administer replacement fluids and electrolytes Discuss importance of adequate fluid intake.
To prevent dehydration To control shivering
4. Goal met as evidenced by free of seizure activity.
DEPENDENT: Administer medications as ordered
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
SUBJECTIVE: Bumabalik at nawawalaangla gnatko as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Fluctuate in body temperature above and below normal range Tachycardia Mild shivering Slow capillary refill VS: T- 39.2 C P- 97 bpm R- 23 cpm
BP- 90/60 mmHg
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Ineffective thermoregulation related to illness DEFINITION: Temperature fluctuation between hypothermia and hyperthermia REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Verbalize understanding of individual factors and appropriate interventions 2. Demonstrate techniques and behavior to correct underlying condition or situation 3. Maintain body temperature within normal range
INTERVENTIONS
INDEPENDENT: Identify individual factors or underlying condition Initiate emergent or immediate interventions prepare client and assist with procedures
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
1. Goal met as evidenced by: Verbalized understanding of individual factors and appropriate interventions 2. Goal met as evidenced by: Demonstrated techniques and behavior to correct underlying condition or situation 3. Goal met as evidenced by: Maintained body temperature within normal range.
It influences choice of intervention To restore or maintain body temperature within normal range To treat underlying cause of hypothermia and hyperthermia To restore or maintain body and organ function
DEPENDENT: Administer fluids, electrolytes and medications, as appropriate
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
SUBJECTIVE: nanghihinaako as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Poor skin turgor Decrease urine output Decrease blood pressure Elevated hematocrit VS: T- 39 C P- 100 bpm R- 30 cpm
BP- 90/50 mmHg
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Deficient fluid volume related to failure of regulatory mechanism DEFINITION: Decreased intravascular, interstitial, and or intracellular fluid. This refers to dehydration, water loss alone without change in sodium. REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced individually adequate urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor and prompt capillary refill, resolution of edema 2. Verbalize understanding of causative factors and purpose of individual therapeutic interventions and medications 3. Demonstrate behaviors to monitor and correct deficit as indicated
INTERVENTIONS
INDEPENDENT: Assess vital signs, noting low BPsevere hypotension, rapid heartbeat, and thread peripheral pulses Establish 24hour fluid replacement needs and routs to be used Change position frequently Provide frequent oral and eye care Encourage increase OFI Recommend restriction of caffeine alcohol as indicated
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
1. Goal met, as evidenced by clients response to interventions, teaching, and actions, performed 2. Attainment or progress towards desired outcome 3. Modification to plan of care
These changes in vital signs are associated with fluid volume loss and or hypovolemia Prevents peaks and valleys in fluid level To reduce pressure on fragile skin and tissue To prevent from injury from dryness For fluid replacement To reduce effects of diuresis
DEPENDENT: Administer medications as ordered
For treatment regimen
POTENTIAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
NOTE: A risk diagnosis is not evidenced by signs and symptoms, as the problem has not occurred; rather, nursing interventions are directed at prevention
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Risk for Bleeding related to inherent coagulopathies DEFINITION: At risk for a decrease in blood volume that may compromise health. REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Be free of signs of active bleeding 2. Display laboratory results for clotting times and factors within normal range for individual risks and engage in appropriate behaviors of lifestyle changes to prevent or reduce frequency of bleeding episodes
INTERVENTIONS
INDEPENDENT: Monitor vital signs Evaluate clients medication regimen
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
1. Goal met as evidenced by being free of signs of active bleeding. 2. Goal met as evidenced by satisfactory laboratory results for clotting times and factors within normal range and engaging in appropriate behaviors of lifestyle changes.
Maintain patency of vascular access
Necessity of regular medical and laboratory follow-up when on anticoagulants, such as Coumadin
Use of medications such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs etc. predispose client to bleeding For fluid administration or blood replacement as indicated To determine needed dosage change, or client management issues requiring monitoring and/or modification
Dietary measures
DEPENDENT: Administer medications as ordered
To promote blood clotting, when indicated, such as food rich in vitamin K
POTENTIAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
NOTE: A risk diagnosis is not evidenced by signs and symptoms, as the problem has not occurred; rather, nursing interventions are directed at prevention
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Hypovolemia risk for shock DEFINITION: At risk for an inadequate blood flow to the bodys tissue which may lead to lifethreatening cellular dysfunction REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Display hemodynamic stability as evidence by vital signs within normal range for client; prompt capillary refill; adequate urinary output within normal specific gravity; usual level of mentation. 2. Be afebrile and free of other signs of infection, achieve timely wound healing. 3. Verbalize understanding of disease process, risk factors, and treatment plan.
INDEPENDENT: Monitor vital signs Monitor intake/output Assess for history or presence of conditions leading to hypovolemic shock
DEPENDENT: Administer fluids, electrolytes, colloids, blood or blood products as indicated
Teach client purpose, dosage, schedule, precautions, and potential sideeffects of medications given to treat underlying conditions.
These conditions deplete the bodys circulating blood volume and ability to maintain organ perfusion and function To rapidly restore or sustain circulating volume, electrolyte balance, and prevent shock Enhances compliance with drug regimen, reducing individual risk
1. Goal partially met as evidenced by hemodynamic stability. 2. Goal partially met as evidenced by achieved timely wound healing but has an elevated body temperature. 3. Goal met as evidenced by verbalized understanding of disease process, risk factors, and treatment plan.
Encourage consumption of healthy diet, participation in regular exercise, adequate rest
For healing and immune system support
POTENTIAL NURSING CARE PLAN Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
CUES AND EVIDENCES
NOTE: A risk diagnosis is not evidenced by signs and symptoms, as the problem has not occurred; rather, nursing interventions are directed at prevention
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Illness risk for powerlessness DEFINITION: At risk for perceived lack of control over a situation and/or ones ability to significantly affect an outcome REFERENCE: Nurses Pocket Guide 12th edition by Marilynn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr
OBJECTIVES
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
At the end of my five hour shift, the patient will be able to: 1. Express sense of control over the present situation and hopefulness about future outcomes. 2. Verbalize positive selfappraisal in current situation. 3. Make choices related to and be involved in care. 4. Identify areas over which individual has control. 5. Acknowledge reality that some areas are beyond individuals control.
INDEPENDENT: Assess clients self-esteem and degree of mastery client has exhibited in life situations Be alert for signs of manipulative behavior and note reactions of client and care givers Make time to listen to clients perception of the situation Encourage questions Provide accurate verbal and written instructions about what is happening and what realistically might happen.
Passive individual may have more difficulty being assertive and standing up for rights Manipulation may be used for management of powerlessness because of fear and distrust Shows concern for client as a person
1. Goal met as evidenced by expressed sense of control over the present situation and hopefulness about future outcomes. 2. Goal met as evidenced by verbalized positive selfappraisal in current situation. 3. Goal met as evidenced by choices made related to and be involved in care. 4. Goal met as evidenced by identified areas over which individual has control.
Reinforces learning and promotes selfplaced review
5. Goal met as evidenced by clients acknowledge ment of reality that some areas are beyond individuals control.
You might also like
- NCP DengueDocument4 pagesNCP DengueJanna Carrel Isabedra Rodio100% (2)
- Nursing Care for Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument7 pagesNursing Care for Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverjoycevillamorNo ratings yet
- NCP-Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument8 pagesNCP-Dengue Hemorrhagic Feverjunrey1990No ratings yet
- Planning (Nursing Care Plans)Document14 pagesPlanning (Nursing Care Plans)plumhie100% (1)
- Reducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresDocument10 pagesReducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresKier Jucar de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageDengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume Deficitemman_abz100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plans for Dengue PatientDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans for Dengue PatientCarren Wingwash100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Dengue Hemmorrhagic FeverDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Dengue Hemmorrhagic FeverMean Elepaño100% (1)
- NCP DengueDocument3 pagesNCP DengueYeana Alon50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume Deficitnj_pink08179456% (9)
- made.FEU Institute of Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitDocument8 pagesmade.FEU Institute of Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficitelaine_tengco50% (2)
- Risk For Fluid Volume Deficit For DengueDocument3 pagesRisk For Fluid Volume Deficit For DengueRose Cua33% (3)
- NCP DengueDocument3 pagesNCP DengueRichmund Earl Geron100% (1)
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Dengue Fever RashesDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Dengue Fever RashesAriaNo ratings yet
- NCP DengueDocument4 pagesNCP Denguesarzlasco0980% (5)
- Patient's Name: Date of Admission: Age: Physician: Religion: Diagnosis: Nationality: Diet: Room and Bed No.Document4 pagesPatient's Name: Date of Admission: Age: Physician: Religion: Diagnosis: Nationality: Diet: Room and Bed No.rammyestellaNo ratings yet
- Lisa Elibox Nursing Care Plan for HyperthermiaDocument1 pageLisa Elibox Nursing Care Plan for Hyperthermiasamanthabox50% (2)
- Maintaining Fluid Balance in Dengue PatientDocument3 pagesMaintaining Fluid Balance in Dengue PatientjhaninahNo ratings yet
- NCP For DengueDocument1 pageNCP For DengueyelbonifacioNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMarla NavarroNo ratings yet
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverSherwin B. CaytapNo ratings yet
- Managing a 12-year-old female patient's careDocument3 pagesManaging a 12-year-old female patient's carealfonselay63% (8)
- NCP For DengueDocument6 pagesNCP For DenguePamela Ann Perez79% (33)
- DENGUE CS NCP 1Document8 pagesDENGUE CS NCP 1Karyl SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PatientDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PatientSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument9 pagesNeonatal Sepsis NCPHollan Galicia100% (1)
- NCP GrandcaseDocument5 pagesNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPkaylejordan_29100% (2)
- Case Study 5 Dengue Fever CorrectedDocument13 pagesCase Study 5 Dengue Fever CorrectedyounggirldavidNo ratings yet
- NCP (Hyperthermia)Document3 pagesNCP (Hyperthermia)Flauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaKirby ContaoiNo ratings yet
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionDocument3 pagesBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Document4 pagesDischarge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Cecille Ursua0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Fever AssessmentDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Fever AssessmentLuis Romnic Vinuya100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Document8 pagesPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Firenze Fil0% (1)
- Nursing Interventions for Fever Management: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, and EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Interventions for Fever Management: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, and EvaluationChristine Esguerra OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesChickenpox Nursing Care PlanBruno MercuryNo ratings yet
- Monitor for signs of bleedingDocument5 pagesMonitor for signs of bleedingBernadette Malamug50% (6)
- Hypertonic SolutionsDocument4 pagesHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument6 pagesHyperthermiaBerlyn FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department Name: O.J.KDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department Name: O.J.KKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverThirdy Aquino82% (28)
- IVF Color CodingDocument2 pagesIVF Color CodingLabs Mendoza100% (2)
- Emmil M. Gonzales Technology and CareDocument4 pagesEmmil M. Gonzales Technology and CarePeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCP PediaDocument3 pagesDengue NCP Pediaraven riveraNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- 1) Nursing Careplan For FeverDocument9 pages1) Nursing Careplan For FeverY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanSittie Rohaina SabanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument17 pagesNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Skills LabDocument56 pagesHealth Assessment Skills LabSIR ONENo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Case in SleDocument34 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Case in SlePaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document6 pagesCase 2Maryam Shoukat AliNo ratings yet
- NCPPPPDocument6 pagesNCPPPPIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- PlateletDocument16 pagesPlateletArgene Rose MilletNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- GERONTOLOGY Focuses On The Care of Older Adults and Addresses The PhysilogicalDocument7 pagesGERONTOLOGY Focuses On The Care of Older Adults and Addresses The PhysilogicalMhee FaustinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPLeolene Grace BautistaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nursing Notes 1Document12 pagesEmergency Nursing Notes 1pauchanmnl100% (2)
- Drug Study No. 1 Nursing Responsibilities: ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study No. 1 Nursing Responsibilities: ClozapineKim Celeste MatulacNo ratings yet
- Abruption PlacentaDocument8 pagesAbruption PlacentaKim Celeste MatulacNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Postop Nsg. Mngt.Document127 pagesGroup 3 Postop Nsg. Mngt.Kim Celeste MatulacNo ratings yet
- Duties of A Scrub NurseDocument2 pagesDuties of A Scrub NurseKim Celeste MatulacNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia (PPPres. Made by Another Person)Document18 pagesAnesthesia (PPPres. Made by Another Person)Kim Celeste MatulacNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapJUN JUN PALISOCNo ratings yet
- Ha Retdem ProceduresDocument12 pagesHa Retdem Proceduresaceh lorttNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs BrochureDocument6 pagesVital Signs Brochureapi-527956594No ratings yet
- Nursing English BookDocument72 pagesNursing English BookWahyu Unggul WidodoNo ratings yet
- VITAL SIGNS ReviewDocument4 pagesVITAL SIGNS ReviewA CNo ratings yet
- NASKAH ROLE PLAY B.INGGRIS Fix InsyaAllahDocument4 pagesNASKAH ROLE PLAY B.INGGRIS Fix InsyaAllahBaiq Rista Ananta PratiwiNo ratings yet
- AHA PALS Core Case Test ChecklistsDocument12 pagesAHA PALS Core Case Test ChecklistsVitor Hugo G CorreiaNo ratings yet
- NPS ExamDocument21 pagesNPS ExamJasmine JarapNo ratings yet
- Materi Manajemen NyeriDocument47 pagesMateri Manajemen NyeriNur AslindaNo ratings yet
- 20110419001758Document48 pages20110419001758أبو محمدNo ratings yet
- Context: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationDocument4 pagesContext: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationAR ManNo ratings yet
- Nursing 215 Care Plan 2 FinalDocument7 pagesNursing 215 Care Plan 2 Finalapi-283303129No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Summary ReviewDocument48 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Summary ReviewDarren VargasNo ratings yet
- Administer Medications As IndicatedDocument4 pagesAdminister Medications As IndicatedYza WagayenNo ratings yet
- EFCCS7EDocument649 pagesEFCCS7ESara Mendes100% (3)
- WMSU Citizen's Charter Fil-EngDocument144 pagesWMSU Citizen's Charter Fil-EngericwmsuNo ratings yet
- When Are Focused Assessments ConductedDocument26 pagesWhen Are Focused Assessments ConductedNozomi YukiNo ratings yet
- Activity Instructions FdarDocument10 pagesActivity Instructions FdarJae HeeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Reviewclobregas100% (3)
- Drug Therapy Considerations for Pregnancy and LactationDocument120 pagesDrug Therapy Considerations for Pregnancy and LactationNehimyaNo ratings yet
- NLE ReviewerDocument247 pagesNLE ReviewerDiana Rose DC0% (1)
- Module 3a - Steps in Health Assessment - Subjective DataDocument7 pagesModule 3a - Steps in Health Assessment - Subjective DataGhian Bataller GonzalesNo ratings yet
- De Sagun, Leila Camille, A. NCMB312-RLE BSN3Y1-1B Course Task #1Document1 pageDe Sagun, Leila Camille, A. NCMB312-RLE BSN3Y1-1B Course Task #1Carl SantosNo ratings yet
- Bolanle Fadunmila Nursing ResumeDocument5 pagesBolanle Fadunmila Nursing ResumeBola FadunmilaNo ratings yet
- THERMOMETER TECHNIQUE - NCM104B - RLE by Juvy L. Lagcao, MN-RNDocument2 pagesTHERMOMETER TECHNIQUE - NCM104B - RLE by Juvy L. Lagcao, MN-RNJuvy LittmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre OpDocument4 pagesNCP Pre OpKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Newborn: Cavite State UniversityDocument2 pagesChecklist For Newborn: Cavite State UniversityChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Automating A Manual Sepsis Screening Tool in A Pediatric Emergency DepartemenDocument6 pagesAutomating A Manual Sepsis Screening Tool in A Pediatric Emergency DepartemenDian RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- UTS B.ingg (Indri Dwi Septika.h)Document10 pagesUTS B.ingg (Indri Dwi Septika.h)Indri Dwi SeptikaNo ratings yet
- Sample Family Care Study (N107)Document51 pagesSample Family Care Study (N107)Dan Dan Soi T97% (31)